进程间的通信:
消息队列、共享内存、信号灯:
1. IPC对象:内存文件
1. ipcs:
查看系统中的消息队列,共享内存、信号灯的信息
2. ipcrm:
删除消息队列、共享内存、信号灯
ipcrm -Q/-M/-S key
ipcrm -q/-m/-s 消息对立ID/共享内存ID/信号灯ID1. 消息队列:
1. 操作流程:
创建消息队列 -> 发送消息 -> 接收消息
2. 函数接口:
1. ftok:
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);功能:根据pathname和proj_id生成一个key_t类型的key值,将来可以创建消息队列、共享内存、信号灯
参数:
pathename:文件路径
proj_id:8位非0值
返回值:
成功返回key_t类型的IPC对象的key值
失败返回-1
2. msgsnd:
int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg);功能:根据key值对象的IPC对象创建一个消息队列
参数:
key:IPC对象名字
msgflg:IPC_CREAT 对象不存在就创建
IPC_EXCL 对象存在报错
IPC_CREAT | 0664
返回值:
成功返回消息队列ID
失败返回-1
3. msgsnd:
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *msgp, size_t msgsz, int msgflg);功能:向消息队列中发送消息
参数:
msqid:消息队列的ID号
msgp:发送消息空间的首地址
struct msgbuf
{
int mtypes; /* message type, must be > 0 */
char mtext[1] /* message data */
};msgz:发送消息内容的大小(不包含发送消息类型)
msgflg:属性,默认位0
返回值:
成功返回0
失败返回-1
4. msgrcv:
ssize_t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_t msgsz, long msgtyp, int msgflg);功能:从消息队列中接收消息
参数:
msqid:消息队列的ID号
msgp:存放接收到消息空间的首地址
msgsz:最多接收消息的空间大小
msgtype:想要接收消息的类型
msgflg:属性,默认为0
返回值:
成功返回实际接收的字节数
失败返回-1
5. msgctl:
int msgctl(int msqid, int cmd, struct msqid_ds *buf);功能:向消息队列发送一条cmd命令
参数:
msqid:消息队列的ID号
cmd:IPC_RMID 删除消息队列
buf:默认传NULL
练习:
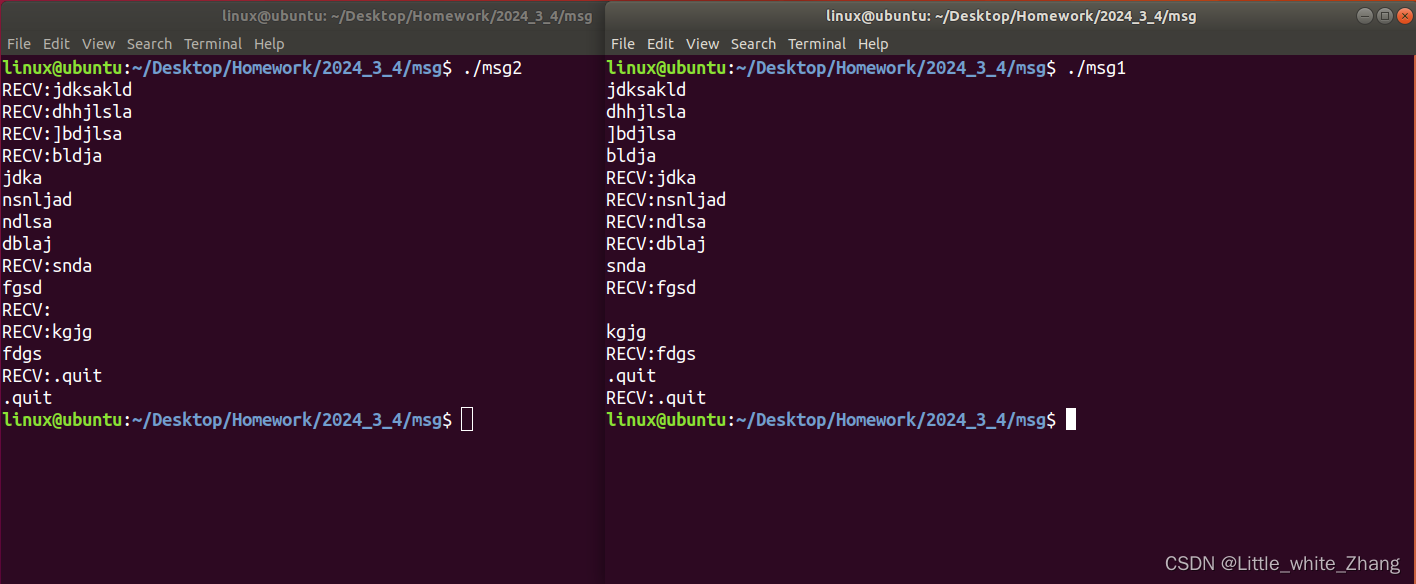
利用消息队列实现clientA和clientB两个进程任务的全双工聊天功能
clientA.c
#include "head.h"
key_t key;
int msgid = 0;
pthread_t atob;
pthread_t btoa;
struct msgbuf
{
long mtype;
char mtext[256];
};
void *thread_atob(void *arg)
{
struct msgbuf sndmsg;
while(1)
{
memset(&sndmsg, 0, sizeof(sndmsg));
sndmsg.mtype = 100;
gets(sndmsg.mtext);
msgsnd(msgid, &sndmsg, sizeof(struct msgbuf)-sizeof(long), 0);
if(strcmp(sndmsg.mtext, ".quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
pthread_cancel(atob);
return NULL;
}
void *thread_btoa(void *arg)
{
struct msgbuf recmsg;
while(1)
{
memset(&recmsg, 0, sizeof(recmsg));
msgrcv(msgid, &recmsg, sizeof(recmsg)-sizeof(long), 200, 0);
printf("RECV:%s\n", recmsg.mtext);
if(strcmp(recmsg.mtext, ".quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
pthread_cancel(btoa);
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_create(&atob, NULL, thread_atob, NULL);
pthread_create(&btoa, NULL, thread_btoa, NULL);
key = ftok(".", 'a');
if(key == -1)
{
perror("fail to ftok");
return -1;
}
msgid = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
if(msgid == -1)
{
perror("fail to msgget");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(atob, NULL);
pthread_join(btoa, NULL);
msgctl(msgid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
return 0;
}clientB.c
#include "head.h"
key_t key;
int msgid = 0;
pthread_t atob;
pthread_t btoa;
struct msgbuf
{
long mtype;
char mtext[256];
};
void *thread_btoa(void *arg)
{
struct msgbuf sndmsg;
while(1)
{
memset(&sndmsg, 0, sizeof(sndmsg));
sndmsg.mtype = 200;
gets(sndmsg.mtext);
msgsnd(msgid, &sndmsg, sizeof(struct msgbuf)-sizeof(long), 0);
if(strcmp(sndmsg.mtext, ".quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
pthread_cancel(btoa);
return NULL;
}
void *thread_atob(void *arg)
{
struct msgbuf recmsg;
while(1)
{
memset(&recmsg, 0, sizeof(recmsg));
msgrcv(msgid, &recmsg, sizeof(recmsg)-sizeof(long), 100, 0);
printf("RECV:%s\n", recmsg.mtext);
if(strcmp(recmsg.mtext, ".quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
pthread_cancel(atob);
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_create(&atob, NULL, thread_atob, NULL);
pthread_create(&btoa, NULL, thread_btoa, NULL);
key = ftok(".", 'a');
if(key == -1)
{
perror("fail to ftok");
return -1;
}
msgid = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
if(msgid == -1)
{
perror("fail to msgget");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(atob, NULL);
pthread_join(btoa, NULL);
msgctl(msgid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
return 0;
}
2. 共享内存:
进程间通信最高效的形式
1. 操作方式:
创建共享内存 -> 映射到共享内存中 -> 共享内存操作 -> 解除映射 -> 删除共享内存
2. 函数接口:
1. ftok:
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);功能:根据pathname和proj_id生成一个key_t类型的key值,将来可以创建消息队列、共享内存、信号灯
参数:
pathename:文件路径
proj_id:8位非0值
返回值:
成功返回key_t类型的IPC对象的key值
失败返回-1
2. shmget:
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);功能:创建一个共享内存
参数:
key:IPC对象名称
size:共享内存的大小
shmflg:
IPC_CREAT
IPC_EXCL
返回值:
成功返回共享内存ID
失败返回-1
3. shmat
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);功能:将一个地址映射到共享内存中
参数:
shmid:共享内存ID号
shmaddr:
NULL:让系统选择一个合适的地址映射
不为NULL:shmflg设定SHM_RND选择离给定地址最近的能够映射的地址进行映射,否则传递地址为4K的整数倍
4. shmdt:
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);功能:解除映射
参数:
shmaddr:映射的地址
返回值:
成功返回0
失败返回-1
5. shmctl:
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);功能:向共享内存发送命令
参数:
shmid:共享内存ID号
cmd:IPC_RMID 删除共享内存
buf:NULL
返回值:
成功返回0
失败返回-1
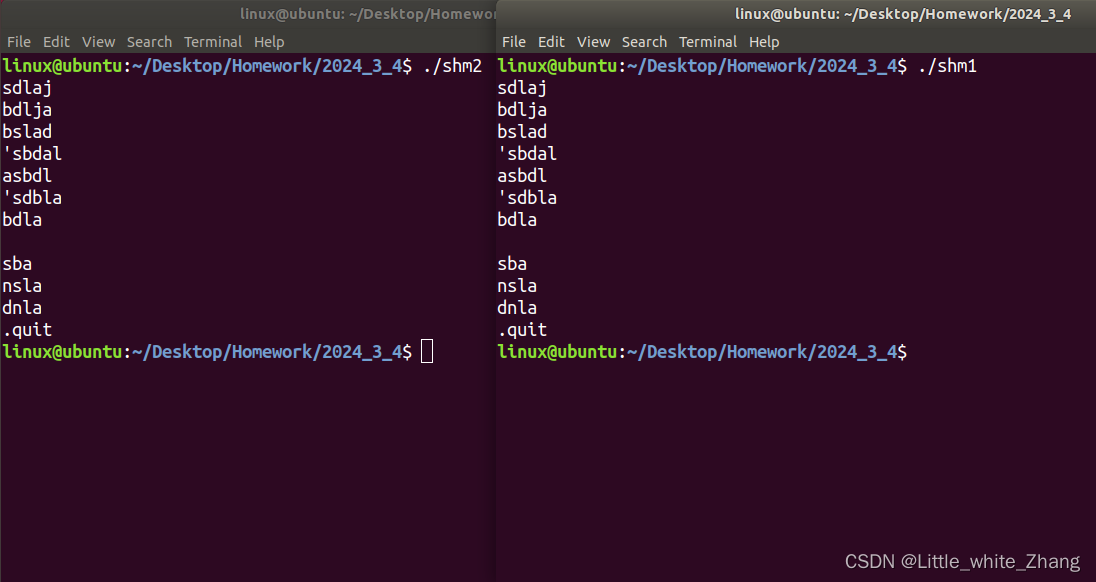
练习:
编写2个进程任务,write.c负责从终端接收字符串写入共享内存中,read.c负责将共享内存中的数据打印在终端
write.c
#include "head.h"
int main(void)
{
key_t key;
int shmid;
char *pshm = NULL;
key = ftok(".", 'a');
if(key == -1)
{
perror("fail to ftok");
return -1;
}
shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
if(shmid == -1)
{
perror("fail to shmget");
return -1;
}
pshm = (char *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if(pshm == NULL)
{
perror("fail to shmat");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
gets(pshm);
if(!strcmp(pshm, ".quit"))
{
shmdt(pshm);
break;
}
}
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
return 0;
}#include "head.h"
int main(void)
{
key_t key;
int shmid;
char *pshm = NULL;
char *ptmp = NULL;
key = ftok(".", 'a');
if(key == -1)
{
perror("fail to ftok");
return -1;
}
shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
if(shmid == -1)
{
perror("fail to shmget");
return -1;
}
pshm = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
ptmp = malloc(4096);
strcpy(ptmp, pshm);
while(1)
{
if (strcmp(pshm, ptmp) == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
printf("%s\n", pshm);
strcpy(ptmp, pshm);
}
if(!strcmp(pshm, ".quit"))
{
free(ptmp);
shmdt(pshm);
break;
}
}
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
return 0;
}
在这里使用了一个ptmp和原来的pshm比较,从而实现了一个从终端写一个,接收一个,其实应该使用信号灯实现,但是在这里还没有学,所以先暂时使用这个来实现。如果不加判断的话,终端输出的结果如下所示:
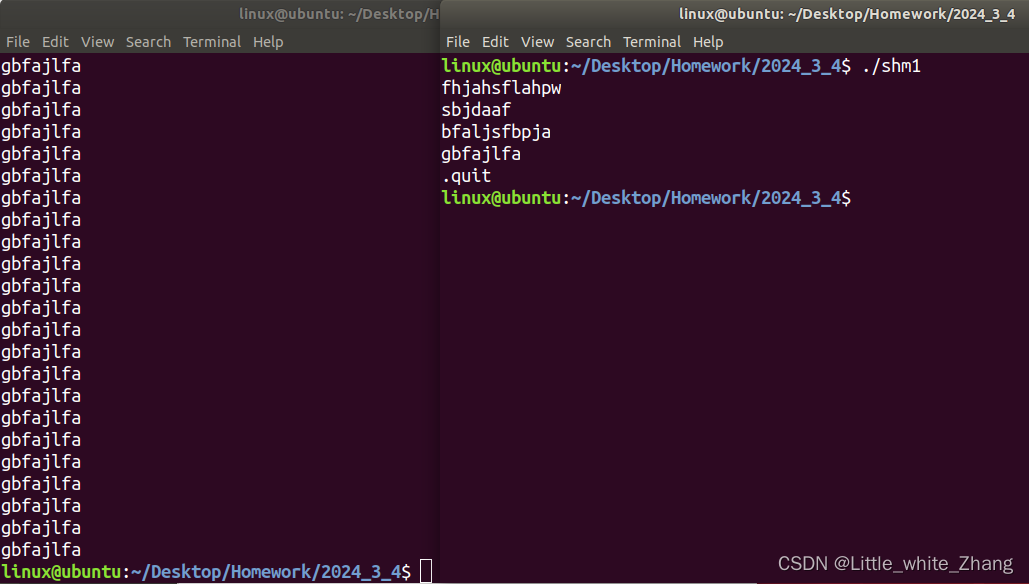
终端会一直持续打印共享内存中的数据,继而需要用到信号灯来实现,写一条,只接收一条