Description
You are given the head of a linked list. Delete the middle node, and return the head of the modified linked list.
The middle node of a linked list of size n is the ⌊n / 2⌋th node from the start using 0-based indexing, where ⌊x⌋ denotes the largest integer less than or equal to x.
For n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, the middle nodes are 0, 1, 1, 2, and 2, respectively.
Example 1:

Input: head = [1,3,4,7,1,2,6]
Output: [1,3,4,1,2,6]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list. The indices of the nodes are written below.
Since n = 7, node 3 with value 7 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
We return the new list after removing this node.
Example 2:
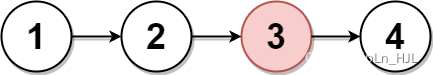
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,2,4]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list.
For n = 4, node 2 with value 3 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
Example 3:
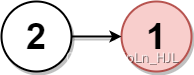
Input: head = [2,1]
Output: [2]
Explanation:
The above figure represents the given linked list.
For n = 2, node 1 with value 1 is the middle node, which is marked in red.
Node 0 with value 2 is the only node remaining after removing node 1.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 10^5].
1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution
Use fast, slow pointer. Every time, fast pointer moves 2 steps and slow pointer moves 1 step. When fast pointer reaches the end, the slow pointer points to the middle.
Time complexity:
o
(
n
)
o(n)
o(n)
Space complexity:
o
(
1
)
o(1)
o(1)
Code
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def deleteMiddle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
ret_head = ListNode(-1)
ret_head.next = head
slow, fast = ret_head, head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
# delete slow.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return ret_head.next