1.壁画

思路
1.求最坏情况下,画的墙总和是多少
2.画的墙在中间连续一段,画了的墙长度是 n / 2 向上取整
3.取最大的 n / 2 向上取整区间和
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e6 + 10;
char s[N];
int a[N];
int t, n;
int main(){
cin>>t;
for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++){
cin>>n;
// 从下标1开始读取
cin>>s + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x = s[i] - '0';
a[i] = a[i - 1] + x;
}
// n / 2 向上取整
int x = (n - 1) / 2 + 1;
int res = 0;
for(int i = x; i <= n; i++){
res = max(res, a[i] - a[i - x]);
}
// Case #1: 6
cout<<"Case #"<<i<<": "<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.前缀和

思路
模板题
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int n, m;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
a[i] += a[i - 1];
}
int l, r;
while(m--){
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
printf("%d\n", a[r] - a[l - 1]);
}
return 0;
}
3.子矩阵的和

思路
模板题
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
int a[N][N];
int n, m, q;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
a[i][j] += a[i - 1][j] + a[i][j - 1] - a[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
while(q--){
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
printf("%d\n", a[x2][y2] - a[x1 - 1][y2] - a[x2][y1 - 1] + a[x1 - 1][y1 - 1]);
}
return 0;
}
4.K倍区间

思路
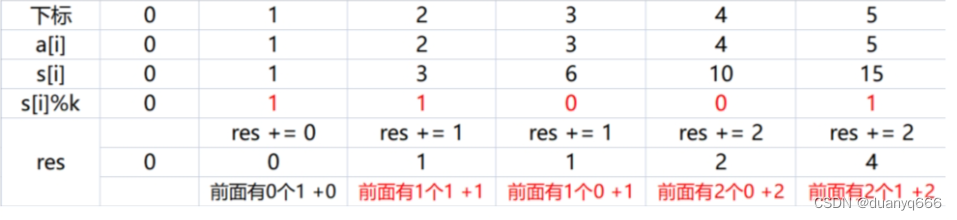
1.求有多少个 (a[r] - a[l - 1]) % k = 0,转化成 a[r] % k = a[l - 1] % k,即有多少个 l 和 r 匹配
2.用哈希表 cnt[x] 存储余数为 x 有多少个
3.右边界 a[r] 取 0 也是 k 的倍数,所以 cnt[0] 要初始化为 1,作为左边界
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
long long a[N];
int cnt[N];
int n, k;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
a[i] += a[i - 1];
}
long long res = 0;
cnt[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
// 第一次是找到左端点,下次找到余数相同的右端点再累加
res += cnt[a[i] % k];
cnt[a[i] % k]++;
}
printf("%lld", res);
return 0;
}
5.统计子矩阵

思路
1.由于每个数都是大于等于 0,保证了单调性,数越多总和越大
2.右边界往右走,左边界也一定往右走
3.暴力枚举上下边界,双指针枚举左右边界
4.方案数最多有 C(500, 2) * C(500, 2),要开 long long
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int a[N][N];
int n, m, k;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
a[i][j] += a[i - 1][j] + a[i][j - 1] - a[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
// i, l i, r
// j, l j, r
long long res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = i; j <= n; j++){
for(int l = 1, r = 1; r <= m; r++){
while(l <= r && a[j][r] - a[j][l - 1] - a[i - 1][r] + a[i - 1][l - 1] > k) l++;
if(l <= r) res += r - l + 1;
}
}
}
printf("%lld", res);
return 0;
}
6.递增三元组

思路
1.枚举 B,对于每个 bj 有多少个 ai 小于 bj,有多少个 ck 大于 bj
2.cnt[i] 为 i 在 a 中出现了多少次,s[i] 为 在 a 中 0 ~ i 一共出现了多少次
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int cnt1[N], cnt2[N], s1[N], s2[N];
int n;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
cnt1[a[i]]++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &b[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
cnt2[c[i]]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= 100000; i++){
s1[i] = s1[i - 1] + cnt1[i];
s2[i] = s2[i - 1] + cnt2[i];
}
long long res = 0;
// 枚举 B 数组
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
res += 1ll * s1[b[i] - 1] * (s2[100000] - s2[b[i]]);
}
printf("%lld", res);
return 0;
}
7.激光炸弹

思路
1.枚举每个 r * r 区域的前缀和,求最大值
2.题目下标从 0 开始,所以我们要加 1,防止出现 -1 下标
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3 + 10;
int a[N][N];
int n, r;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &r);
r = min(r, 5001);
int x, y, w;
while(n--){
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &w);
x++, y++;
a[x][y] += w;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 5001; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= 5001; j++){
a[i][j] += a[i - 1][j] + a[i][j - 1] - a[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
long long res = 0;
for(int i = r; i <= 5001; i++){
for(int j = r; j <= 5001; j++){
res = max(res, 1ll * a[i][j] - a[i - r][j] - a[i][j - r] + a[i - r][j - r]);
}
}
printf("%lld", res);
return 0;
}