目录
string对象的创建:
遍历+修改
const修饰的迭代器(只读):
反向迭代器:
reserve与resize:
find,rfind,substr:
insert:
erase:
getchar、getline:
string对象比较:
stoi、to_string:
srting的模拟实现:
简洁的string,不考虑增删查改(深浅拷贝):
考虑增删查改:
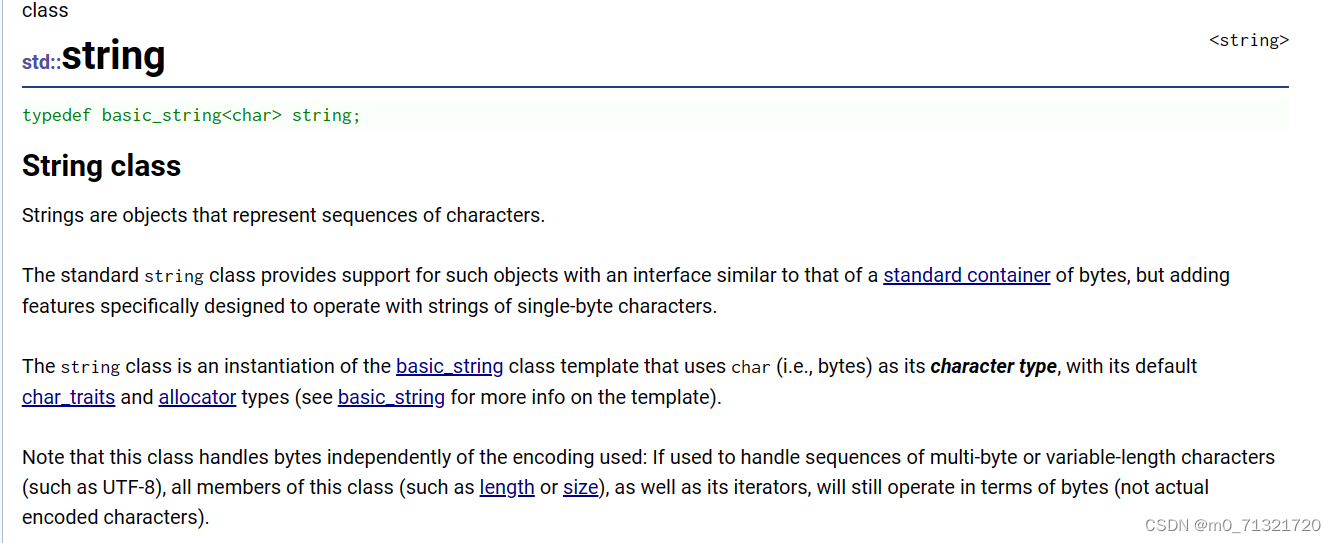
string是表示字符串的字符串类 ,该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,又添加了一些专门用来操作string的接口,如字符串的比较等等。 string在底层实现是:basic_string模板类的别名,
typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string; 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。在使用string类时,要包含头文件以及std;
下面是C++官网对string类的介绍:
string对象的创建:
我们首先来看怎么创建string对象。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
int main()
{
string s1; // 1 ...
string s2("hello world"); // 2 ...
string s3(s2); // 3 拷贝构造
//cin >> s1;
//cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4(s2, 2, 6); //从第二个向后拷6个
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5(s2, 2); //从第二个拷到最后
cout << s5 << endl;
string s6(s2, 2, 100); //不全的话拷到结束
cout << s6 << endl;
string s7("hello world", 3); //拷前3个
cout << s7 << endl;
string s8(10, '!'); //拷10个 !
cout << s8 << endl;
return 0;
}遍历+修改
接下来我们来看string对象的遍历,有三种方式实现:(迭代器是通用的遍历方式)
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
//遍历+修改
//方式1:下标+[]
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i] += 1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//方式2:迭代器
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
*it -= 1;
++it;
}
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//方式3:范围for,自动往后迭代,自动判断结束
for (auto& e : s1)
{
e -= 1;
}
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}const修饰的迭代器(只读):
void func(const string& s)
{
//string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
auto it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
//*it -= 1; //不可修改
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
//*rit = 'A';
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
}反向迭代器:
void test_string2()
{
//反向迭代器
string s1("hello world");
//string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
auto rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
//list<int> lt(10, 5);
//list<int>::iterator ltIt = lt.begin();
while (ltIt != lt.end())
{
cout << *ltIt << " ";
++ltIt;
}
cout << endl;
}查看vs下的增容情况:
void TestPushBack()
{
string s;
//s.reserve(1000); //申请至少能存储1000个字符的空间,不一定是1000个
size_t sz = s.capacity();
//cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
cout << "making s grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
//s.push_back('c');
s += 'c';
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
}
}
}reserve与resize:
void test_string3()
{
string s1;
s1.reserve(1000);
string s2;
s2.resize(100, 'x');
string s3("hello world");
s3.reserve(100);
string s4("hello world");
s4.resize(100, 'x');
string s5("hello world");
s5.resize(5);
}find,rfind,substr:
void test_string4()
{
string s("hello world");
cout << s << endl; //运算符重载
cout << s.c_str() << endl; //字符的那个
//string file("test.txt");
//FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "w");
要求取出文件后缀名
//size_t pos = file.find('.');
//if (pos != string::npos)
//{
// //string suffix = file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos);
// string suffix = file.substr(pos);
// cout << suffix << endl;
//}
string file("test.txt.zip");
FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "w");
size_t pos = file.rfind('.');
if (pos != string::npos)
{
//string suffix = file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos);
string suffix = file.substr(pos);
cout << suffix << endl;
}
string url("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/");
size_t pos1 = url.find(':');
string protocol = url.substr(0, pos1 - 1);
cout << protocol << endl;
size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3);
string domain =url.substr (pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));
cout << domain << endl;
string uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1);
cout << uri << endl;
}insert:
void test_string5()
{
string s("hello world");
s += ' ';
s += "!!!";
cout << s << endl;
//头插 效率O(N)
s.insert(0, 1, 'x');
s.insert(s.begin(), 'y');
s.insert(0, "test");
cout << s << endl;
//中间插
s.insert(4, "&&&");
cout << s << endl;
}erase:
void test_string6()
{
string s("hello world");
s.erase(0, 1);
s.erase(s.size() - 1, 1);
cout << s << endl; //ello worl
s.erase(3);
cout << s << endl; //ell
}getchar、getline:
int main()
{
string s1;
//char ch = getchar();
//while (ch != '\n')
//{
// s1 += ch;
// ch = getchar();
//}
getline(cin, s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}string对象比较:
void test_string7()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("string");
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << ("hehe" < s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 < "sport") << endl;
}stoi、to_string:
void test_string8()
{
int val = stoi("1234"); //i代表int,同理,double...
cout << val << endl;
string str = to_string(3.14);
cout << str << endl;
}srting的模拟实现:
简洁的string,不考虑增删查改(深浅拷贝):
//实现一个简洁的string,不考虑增删查改
namespace qwe
{
class string
{
public:
string(const char* str)
:_str(new char[strlen(str) + 1])
{
strcpy(_str, str);
}
传统写法
s2(s1)
//string(const string& s)
// :_str(new char[strlen(s._str)+1])
//{
// strcpy(_str, s._str);
//}
s1=s3
s3=s3
//string& operator+(const string& s)
//{
// if (this != &s)
// {
// char* tmp = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
// strcpy(tmp, s._str);
// delete[] _str;
// _str = tmp;
// }
// return *this;
//}
//现代写法
//s2(s1)
string(const string& s)
:_str(nullptr)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
}
//s1=s3
/*string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
string tmp(s);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
}
return *this;
}*/
string& operator=(string s)
{
swap(_str, s._str);
return *this;
}
~string()
{
if (_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2(s1);
string s3("sort");
s1 = s3;
s3 = s3;
}
}考虑增删查改:
namespace qwe
{
//增删查改
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
/*string()
:_str(new char[1])
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{
_str[0] = '\0';
}*/
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
, _capacity(_size)
{
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
s2(s1)
//string(const string& s)
// :_size(s._size)
// , _capacity(s._capacity)
//{
// _str = new char[_capacity + 1];
// strcpy(_str, s._str);
//}
s1=s3
s3=s3
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// if (this != &s)
// {
// char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
// strcpy(tmp, s._str);
// delete[] _str;
// _str = tmp;
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
// }
// return *this;
//}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
//s2(s1)
string(const string& s)
:_str(nullptr)
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
}
//s1=s3
string& operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n>_capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n <= _size)
{
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
memset(_str + _size, ch, n - _size);
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
/*if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';*/
insert(_size, ch);
}
void append(const char* str)
{
/*size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;*/
insert(_size, str);
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
size_t find(char ch)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (ch == _str[i])
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t fing(const char* s, size_t pos = 0)
{
const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return ptr - _str;
}
}
string& insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* s)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(s);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end >= pos+len)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
--end;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, s, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity; //能存储有效字符的空间数,不包含\0
static const size_t npos;
};
//"abcd" "abcd" false
//"abcd" "abcde" true
//"abcde" "abcd" false
bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
/*size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
while (i1 < s1.size() && i2 < s2.size())
{
if (s1[i1] < s2[i2])
{
return true;
}
else if (s1[i1] > s2[i2])
{
return false;
}
else
{
++i1;
++i2;
}
}
return i2 < s2.size() ? true : false;*/
return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) < 0;
}
bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) == 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2;
}
bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
//cout<<s1 operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
/*for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
out << s[i];
}
//out << s.c_str(); // 不能这么写
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' '&&ch != '\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
const size_t string::npos = -1;
void f(const string& s)
{
cout << s[0] << endl; //调用const修饰的[]
}
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s1[0] = 'x';
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string2()
{
string s1("hello world");
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
*it += 1;
++it;
}
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//编译时会替换成迭代器
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.push_back('#');
s1.push_back('&');
s1.append("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2;
s2 += 'x';
s2 += "me 1";
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.insert(0, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, "abcd");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.erase(5, 2);
s1.erase(5, 20);
}
void test_string6()
{
string s1("abcd");
string s2("abcd");
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
string s3("abcd");
string s4("abcde");
cout << (s3 < s4) << endl;
string s5("abcde");
string s6("abcd");
cout << (s5 < s6) << endl;
}
void test_string7()
{
string s1("hello");
cin >> s1;
cout << s1;
//string s1("hello");
//s1 += '\0';
//s1 += "world";
//cout << s1 << endl;
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
}

![[linux]vim编辑器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0511318ab1e94d548bed34a4335ece19.gif#pic_center)