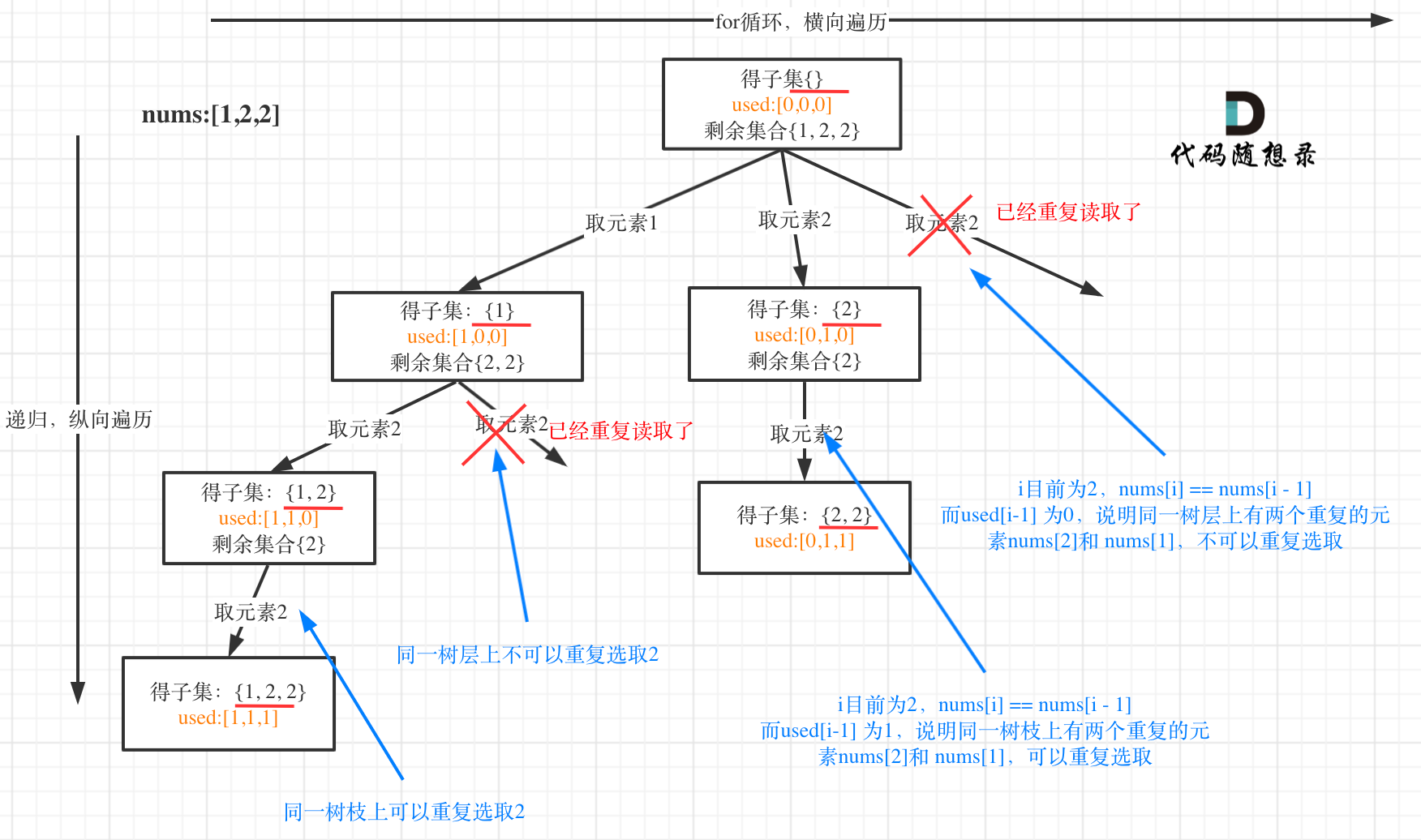
二叉搜索树
- 什么是二叉搜索树?
- 搜索二叉树的操作
- 查找
- 插入
- 删除
- 二叉搜索树的应用
- 二叉搜索树的代码实现
- K模型:
- KV模型
- 二叉搜索树的性能怎么样?
什么是二叉搜索树?
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
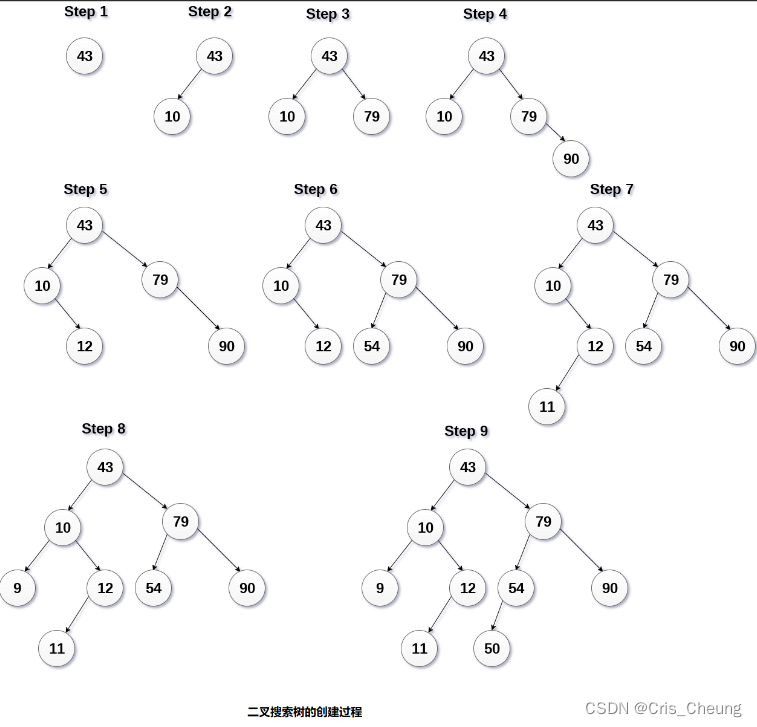
由上图可明显得知搜索二叉树的构建方式
搜索二叉树的操作
这里插入一个搜索二叉树为样例:
int a[] = {8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13};
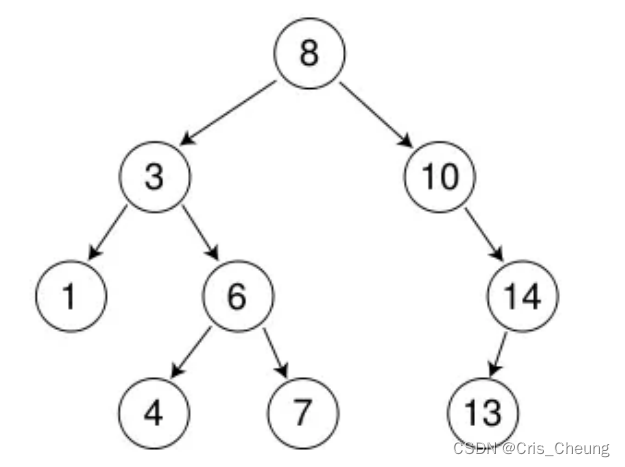
查找
- 从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找。
- 最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,则这个值不存在
插入
- 当这个树为空树时不用多说直接插入成根节点_root
- 当这个树不为空时,先找到所插入节点的位置,再进行插入
比如要在下面这棵搜索树中插入9
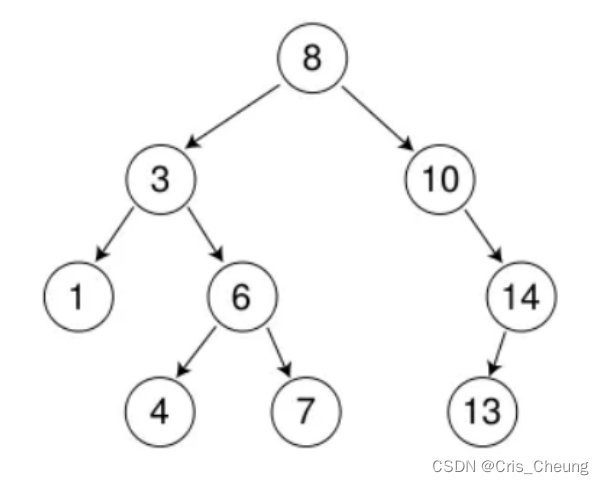
可以看出,9的位置应该在10的左子树位置:
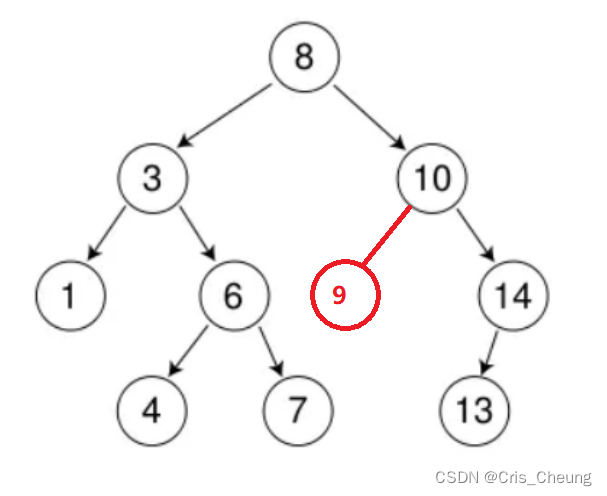
在数据结构上这样就算成功插入
删除
首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回false,否则要删除的结点可能分下面几种情况:
- 当这个节点是叶子节点或者只有左孩子时,先让父节点指向该节点的左孩子,再删除掉该节点–直接删除
- 当这个节点是叶子节点或者只有右孩子时,先让父节点指向该节点的右孩子,再删除掉该节点–直接删除
- 这个节点既有左子树又有右子树,则先将该节点的左子树链接到右子树的最左节点,再用右子树来替换该节点–替换法删除
前两种情况都好说,例如删除下列节点中的 7 和 14:
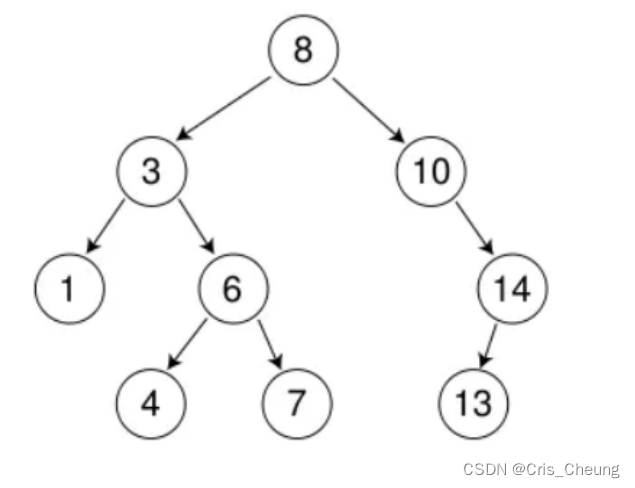
删7:直接删除
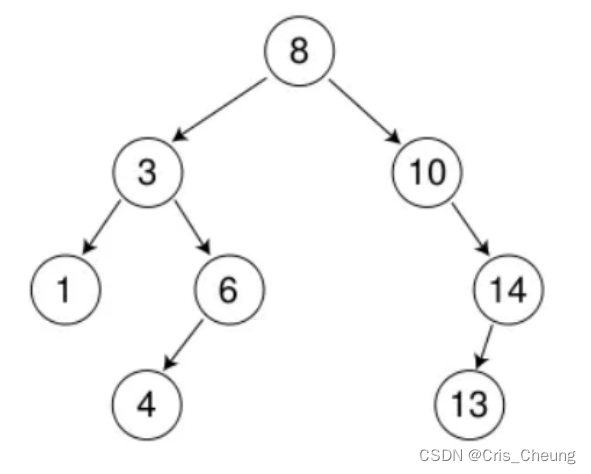
删14:删掉14并将14的左子树链接到10的右子树
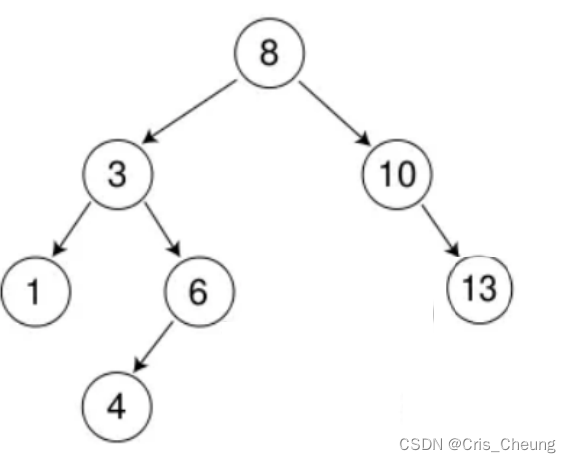
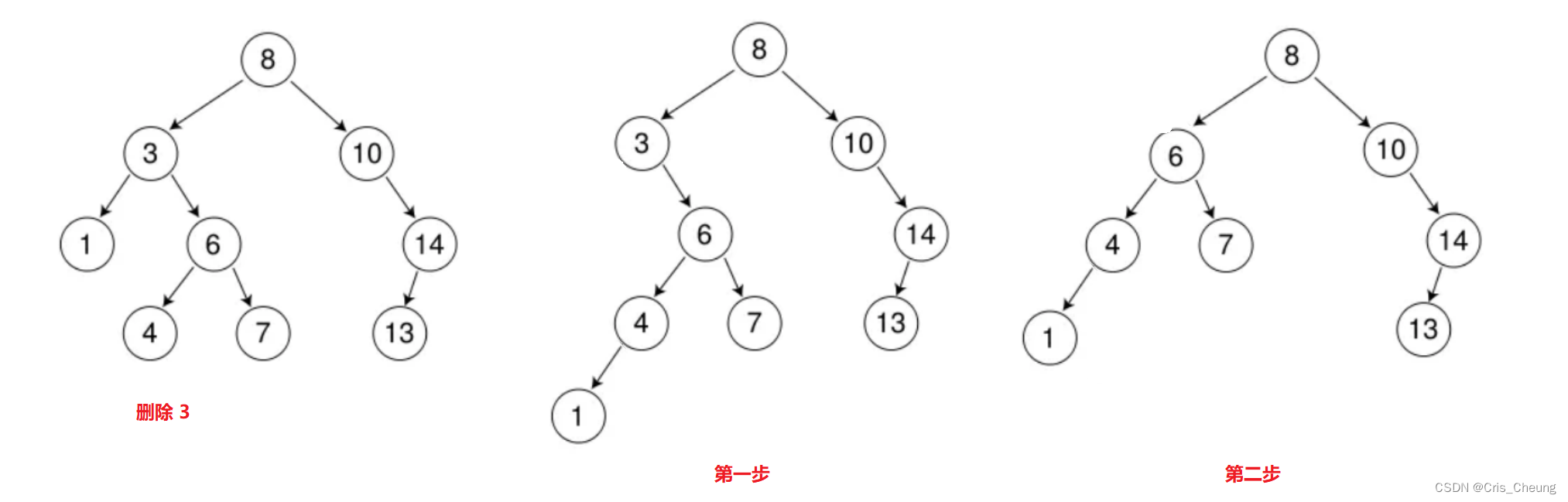
比较复杂的是最后一种情况:当要删除的节点既有左子树又有右子树的时候,则需要进行一些特殊调整,例如,删除下面这颗树中的3 和 8 时:
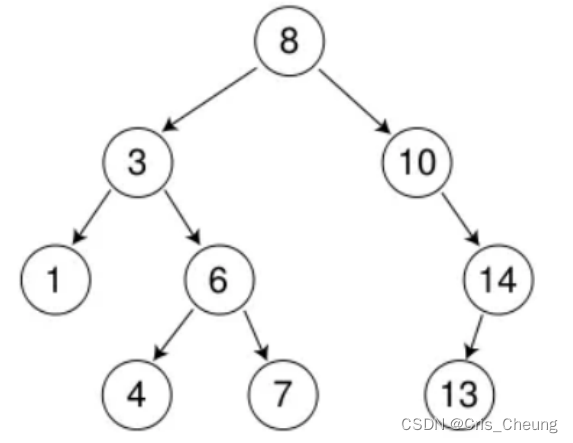
删除3,使用上述的第三种方法:
先将该节点的左子树链接到右子树的最左节点,再用右子树来替换该节点
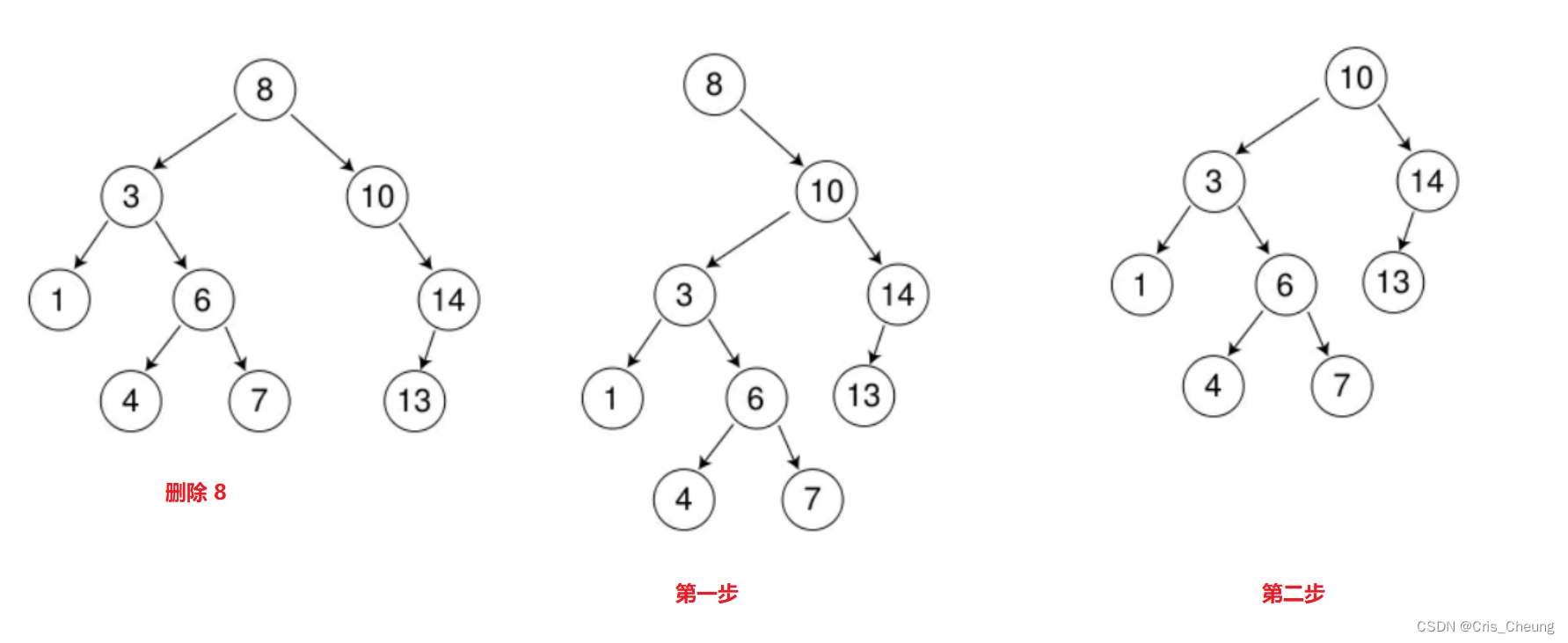
删除 8 ,使用上述的第三种方法:
先将该节点的左子树链接到右子树的最左节点,再用右子树来替换该节点
以上就是二叉搜索树的插入和删除的主要思想,接下来是具体实现
二叉搜索树的应用
二叉搜索树分为两种模型,一种是单键值的K模型,另一种是拥有键值对的KV模型,而后面需要学习的map,AVL树等都会涉及到KV模型.
- K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
- 以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树
- 在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
- KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。该种方式在现实生活中非常常见:
- 比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对;
- 再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是<word, count>就构成一种键值对
二叉搜索树的代码实现
K模型:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//单键值的搜索二叉树 K模型
template <class K>
struct BSTNode
{
BSTNode<K>* _left;
BSTNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
public:
typedef BSTNode<K> Node;
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return false;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
cout << " 存在" << endl;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//空树返回false
if (_root == nullptr)
return false;
//寻找key
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
//这里注意一下,一定要往下一步走的时候父节点才随着改变
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//找到了 分情况
//要删除的节点左孩子或右孩子为空
//左孩子为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//若删除的是根节点
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
//不是跟节点
else
{
//判断当前节点是父节点的左孩子还是右孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
//删除
delete cur;
}
//右孩子为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
//若删除的是根节点
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
//不是跟节点
else
{
//判断当前节点是父节点的左孩子还是右孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
//删除
delete cur;
}
//左右孩子都不为空
else
{
//找当前节点右树的最左节点来替换
Node* parent = cur;
Node* subright = cur->_right;
while (subright->_left)
{
parent = subright;
subright = subright->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, subright->_key);
//判断这个节点是parent的左孩子还是右孩子 若删除的是根节点就是右孩子,因此一定要判断
if (parent->_left == subright)
{
parent->_left = subright->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = subright->_right;
}
//删除
delete subright;
}
//找到返回true
return true;
}
}
//没找到
return false;
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root ,key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
//C++11 强制默认构造函数
BSTree() = default;
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
}
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t->_root);
return *this;
}
private:
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* NewRoot = new Node(root->_key);
NewRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
NewRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return NewRoot;
}
void Destroy(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
cout << "没找到" <<key<< endl;
return false;
}
//先找节点
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
//三种情况 左孩子空 右孩子空 左右都不空
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* tmp = root;
root = root->_right;
delete tmp;
return true;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* tmp = root;
root = root->_left;
delete tmp;
return true;
}
else
{
//左右孩子都不为空 用左孩子的最右节点 或 右孩子的最左节点
Node* subleft = root->_left;
while (subleft->_right)
{
subleft = subleft->_right;
}
swap(root->_key, subleft->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_left,key);
}
}
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left , key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
return true;
}
}
//注意 这里要用 *& 传值,以保证每次递归访问到每一个节点并能够对节点进行操作
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if(root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
KV模型
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace kv
{
template <class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key , const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
,_value(value)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
//parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while(cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//先找节点
if (_root == nullptr)
return false;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//左子树为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_right;
}
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
//右子树为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_left;
}
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}//左右都不为空
else
{
Node* parent = cur;
//左子树的最右节点和cur交换
Node* subleft = cur->_left;
while (subleft->_right)
{
subleft = subleft->_right;
}
swap(cur->_key, subleft->_key);
delete subleft;
}
}
}
//没找到
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << root->_value << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
二叉搜索树的性能怎么样?
在二叉搜索树中,插入和删除操作都必须先查找,查找效率代表了二叉搜索树中各个操作的性能.
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二叉搜索树的深度的函数,即结点越深,则比较次数越多。
但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树:
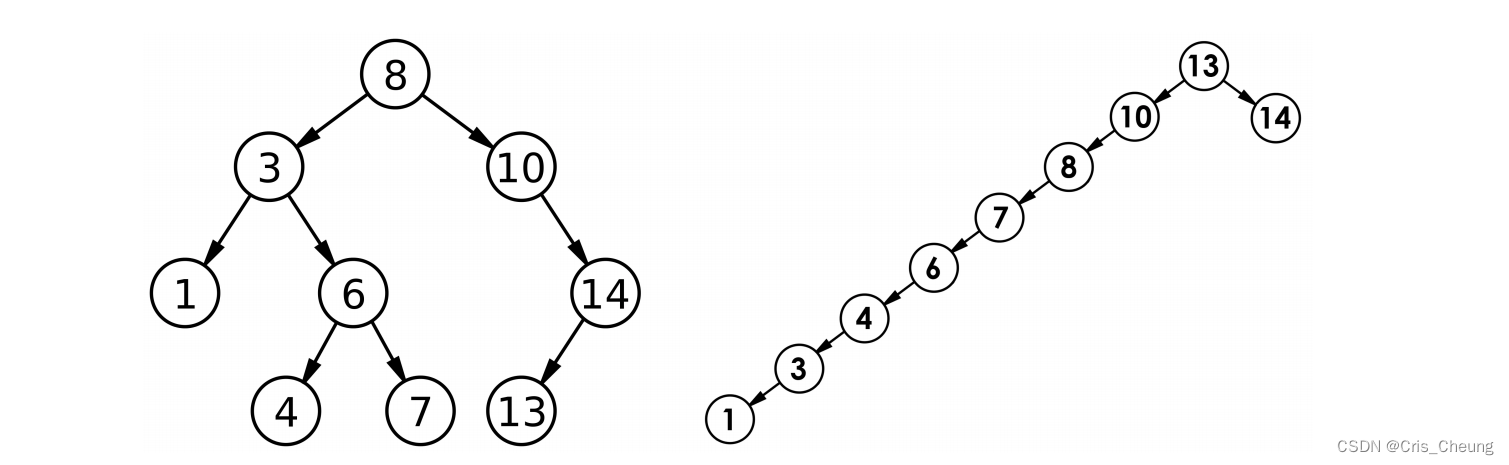
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树(或者接近完全二叉树),其平均比较次数为:
l
o
g
2
N
log_2 N
log2N
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树(或者类似单支),其平均比较次数为:
N
2
\frac{N}{2}
2N