C++第二阶段——数据结构和算法,之前学过一点点数据结构,当时是基于Python来学习的,现在基于C++查漏补缺,尤其是树的部分。这一部分计划一个月,主要利用代码随想录来学习,刷题使用力扣网站,不定时更新,欢迎关注!
文章目录
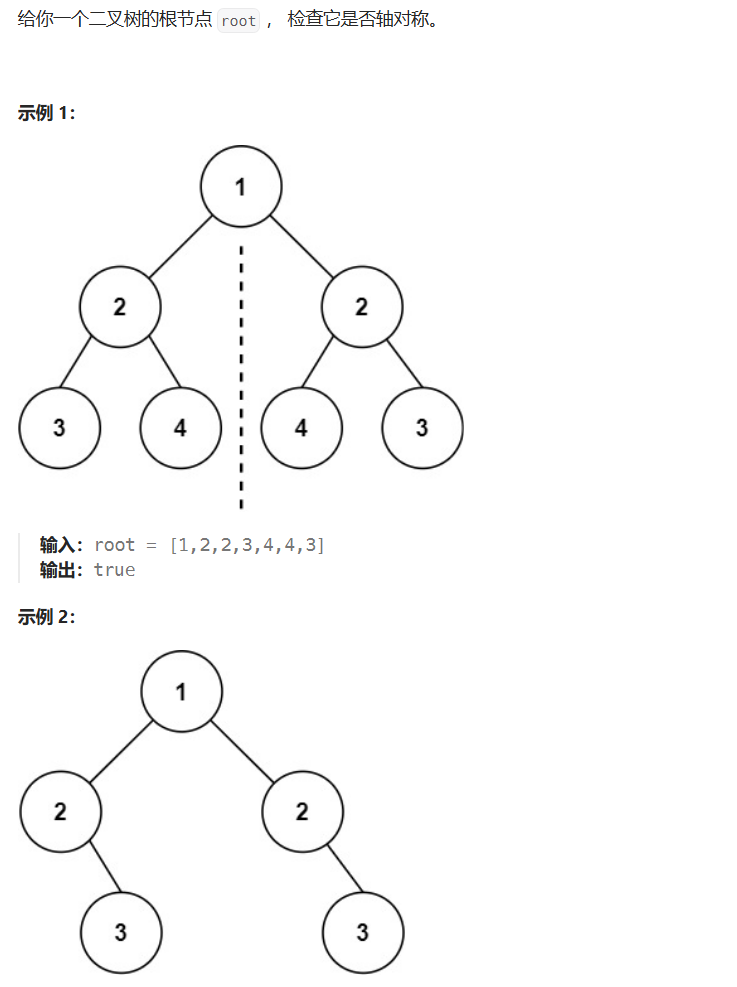
- 一、对称二叉树(力扣101)
- 二、二叉树的最大深度(力扣104)
- 三、二叉树的最小深度(力扣111)
- 四、完全二叉树的节点个数(力扣222)
- 五、平衡二叉树(力扣110)
- 六、二叉树的所有路径(力扣257)
- 七、左叶子之和(力扣404)
- 八、找树左下角的值(513)
- 九、路径总和(力扣112)
一、对称二叉树(力扣101)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return root;
return isSymmetricLeftRight(root->left,root->right);
}
bool isSymmetricLeftRight(TreeNode* left,TreeNode* right){
if(left==NULL&&right==NULL) return true;
else if(left==NULL&&right!=NULL) return false;
else if(left!=NULL&&right==NULL) return false;
else if(left->val!=right->val) return false;
else{
bool outside = isSymmetricLeftRight(left->left,right->right);
bool inside = isSymmetricLeftRight(left->right,right->left);
if(outside!=true||inside!=true){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
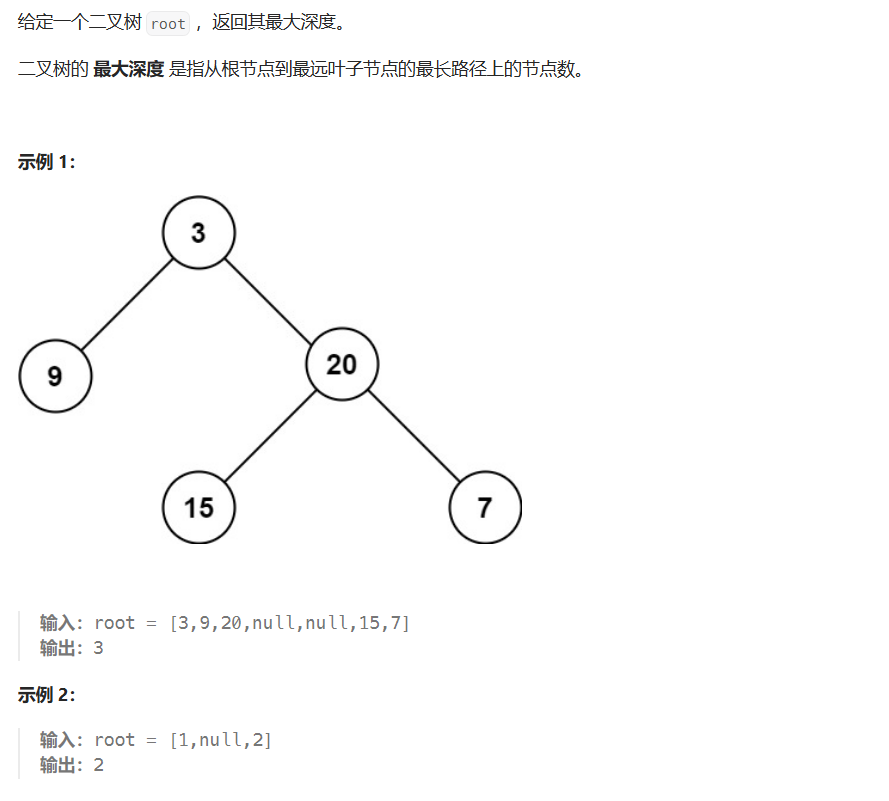
二、二叉树的最大深度(力扣104)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root->right);
int result = 1+max(leftDepth,rightDepth);
return result;
}
};
三、二叉树的最小深度(力扣111)

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = minDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root->right);
if (root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (root->left != NULL && root->right == NULL) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
return min(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}
};
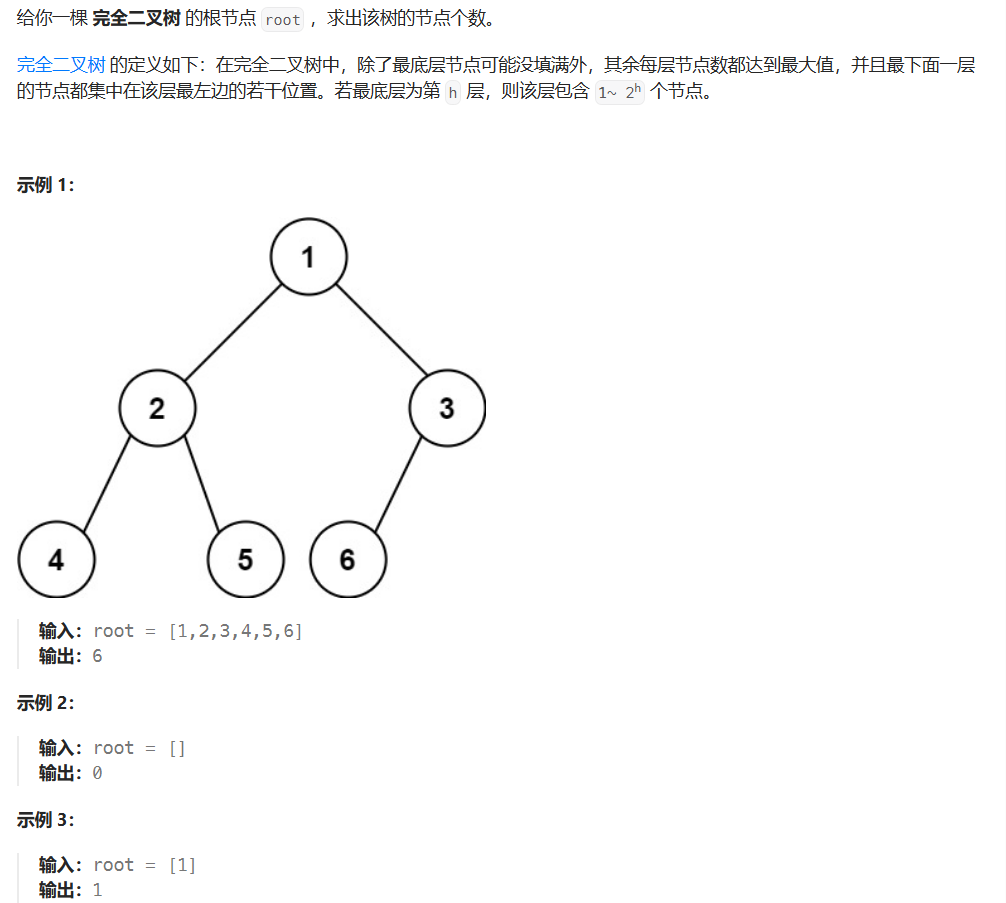
四、完全二叉树的节点个数(力扣222)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int count=0;
tr(root,count);
return count;
}
void tr(TreeNode* root,int &count){
if(root==NULL) return;
tr(root->left,count);
tr(root->right,count);
count++;
}
};
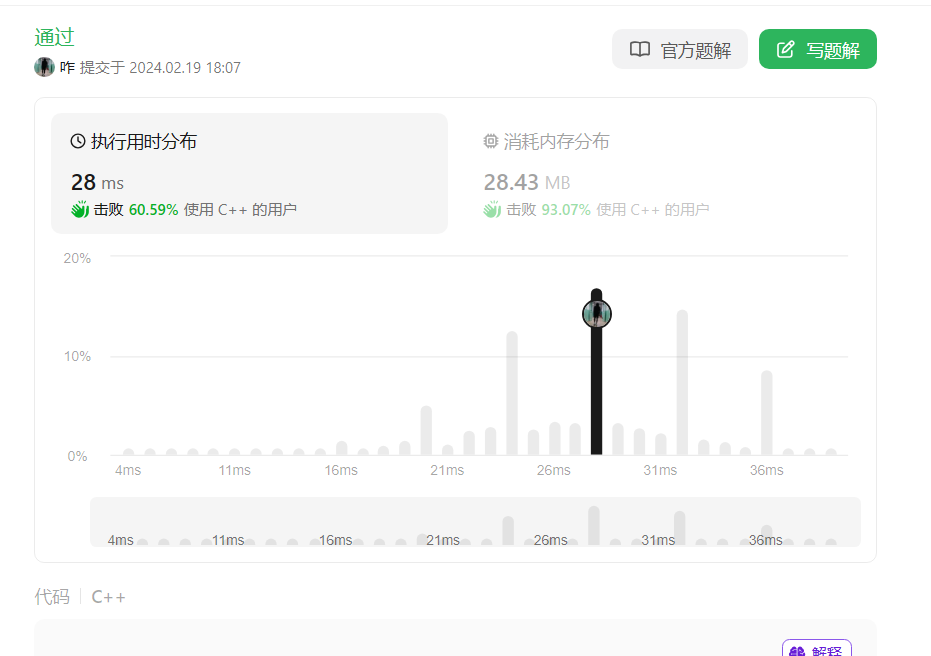
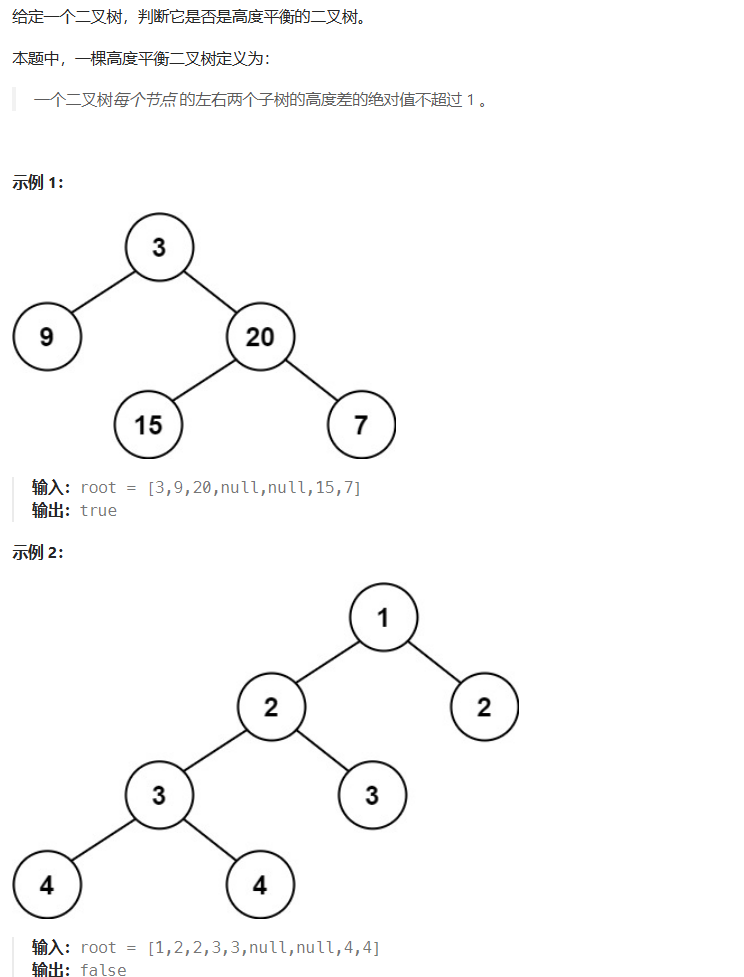
五、平衡二叉树(力扣110)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return true;
int result = getLength(root);
if(result==-1) return false;
return true;
}
int getLength(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int leftLength = getLength(root->left);
if(leftLength==-1) return -1;
int rightLength = getLength(root->right);
if(rightLength==-1) return -1;
int result;
if(abs(leftLength-rightLength)>1) return -1;
else{
result = max(rightLength,leftLength)+1;
}
return result;
}
};
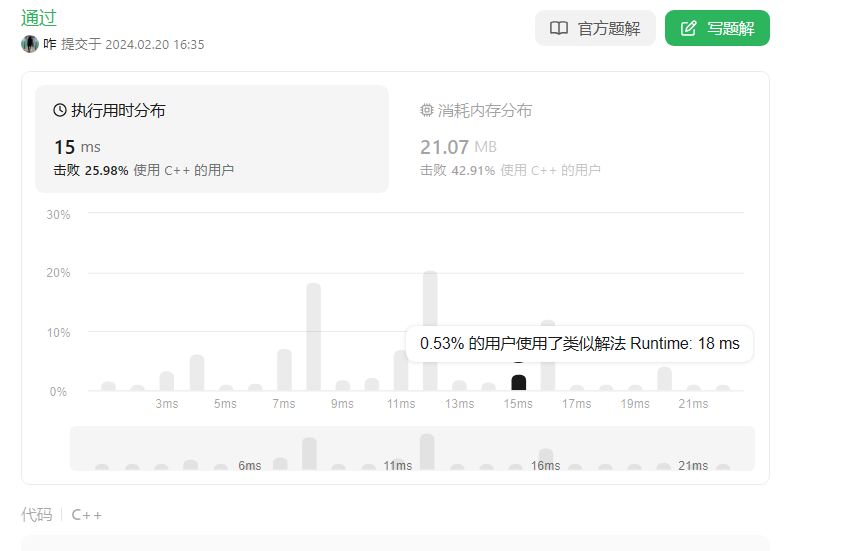
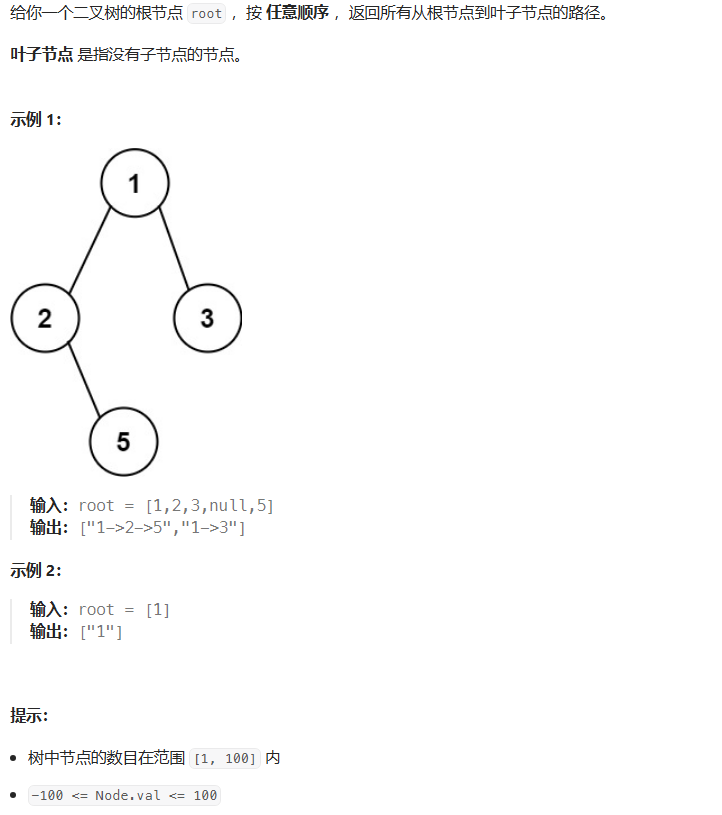
六、二叉树的所有路径(力扣257)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> result;
vector<int> path;
traversal(root,path,result);
return result;
}
void traversal(TreeNode * root,vector<int>& path,vector<string> &result){
path.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL) {
string temp;
for(int i=0;i<path.size();i++){
if(i==path.size()-1){
temp+= to_string(path[i]);
}
else{
temp+=to_string(path[i]);
temp+="->";
}
}
result.push_back(temp);
return;
}
if(root->left){
traversal(root->left,path,result);
path.pop_back();
}
if(root->right){
traversal(root->right,path,result);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
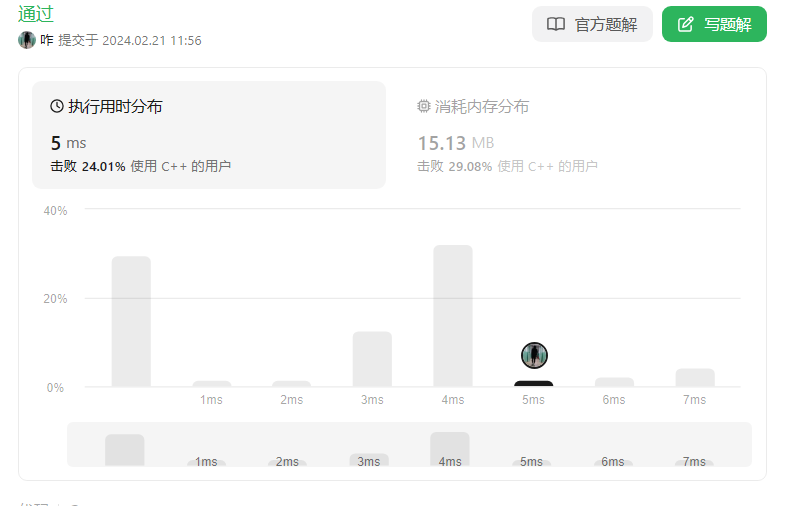
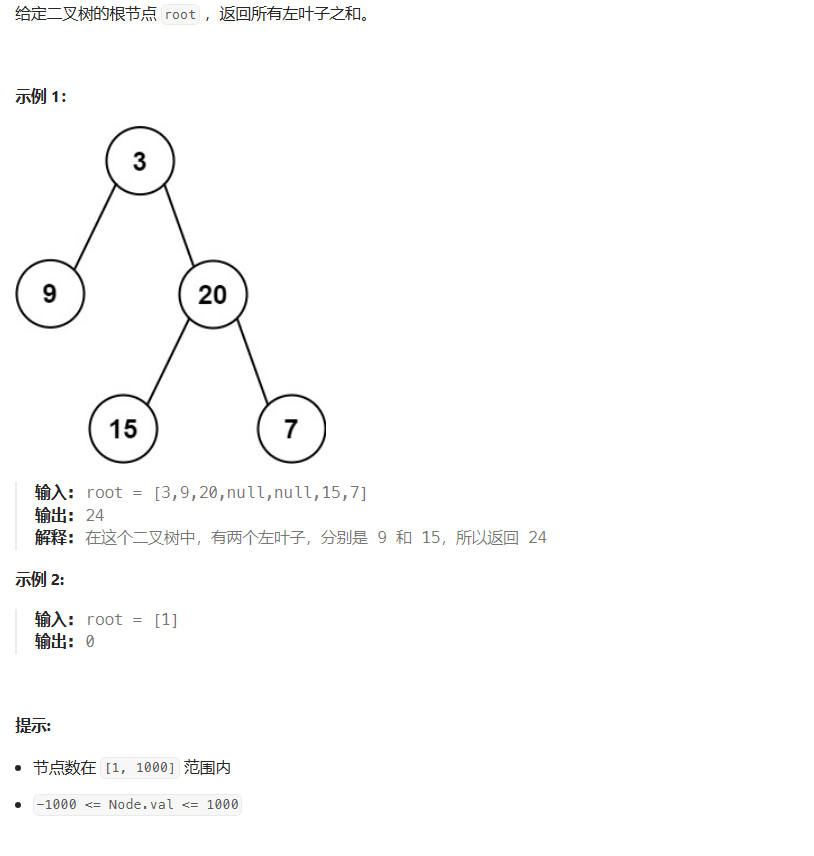
七、左叶子之和(力扣404)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
int sum=0;
return trv(root,sum);
}
// 后续遍历
int trv(TreeNode *root,int &sum){
if(root==NULL) return 0;
trv(root->left,sum);
trv(root->right,sum);
if(root->left!=NULL&&root->left->left==NULL&&root->left->right==NULL){
sum+= root->left->val;
}
return sum;
}
};
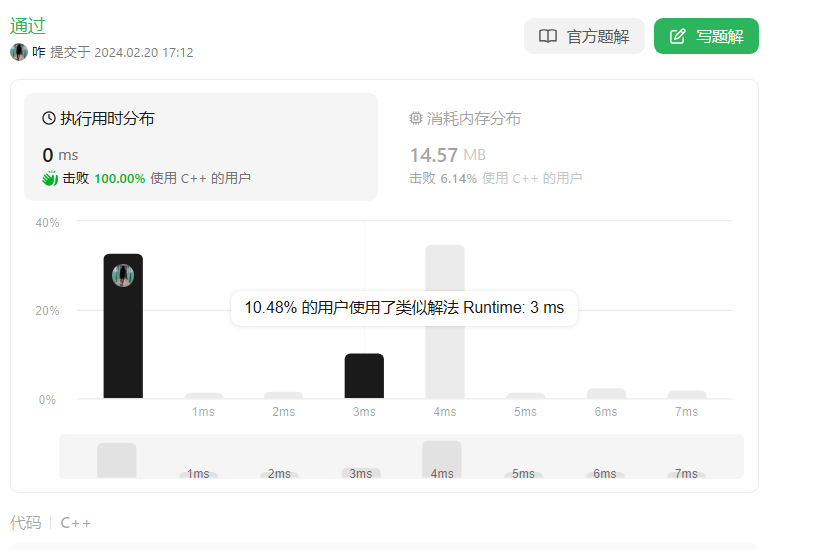
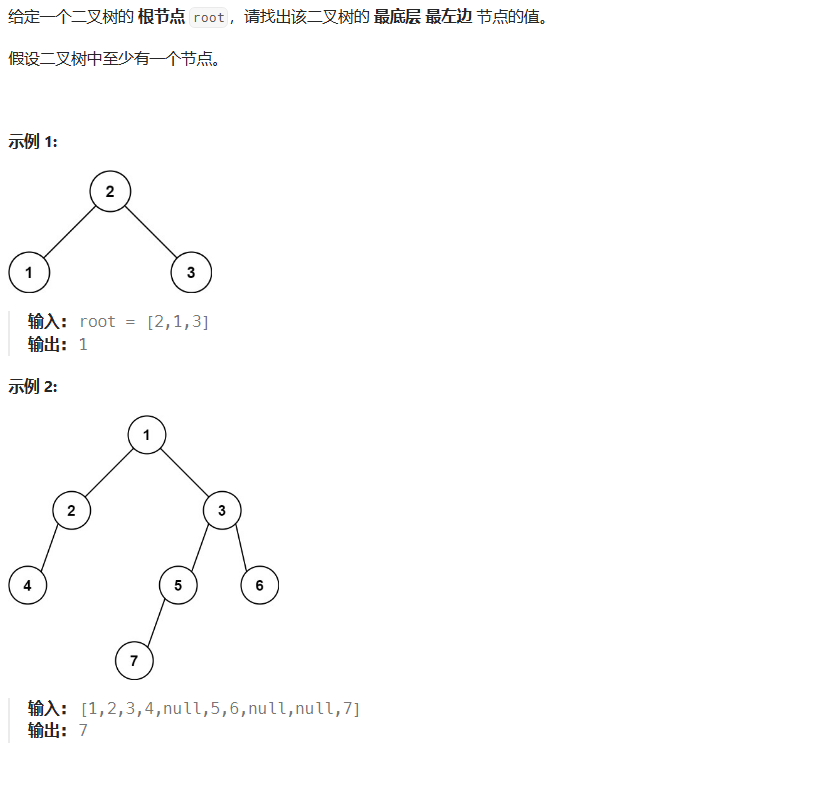
八、找树左下角的值(513)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result = func(root);
return result[result.size()-1][0];
}
// 层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> func(TreeNode* root){
vector<vector<int>> result;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root!=NULL) que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
vector<int> vec;
int Qsize=que.size();
while(Qsize--){
TreeNode * top = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(top->val);
if(top->left) que.push(top->left);
if(top->right) que.push(top->right);
}
result.push_back(vec);
}
return result;
}
};
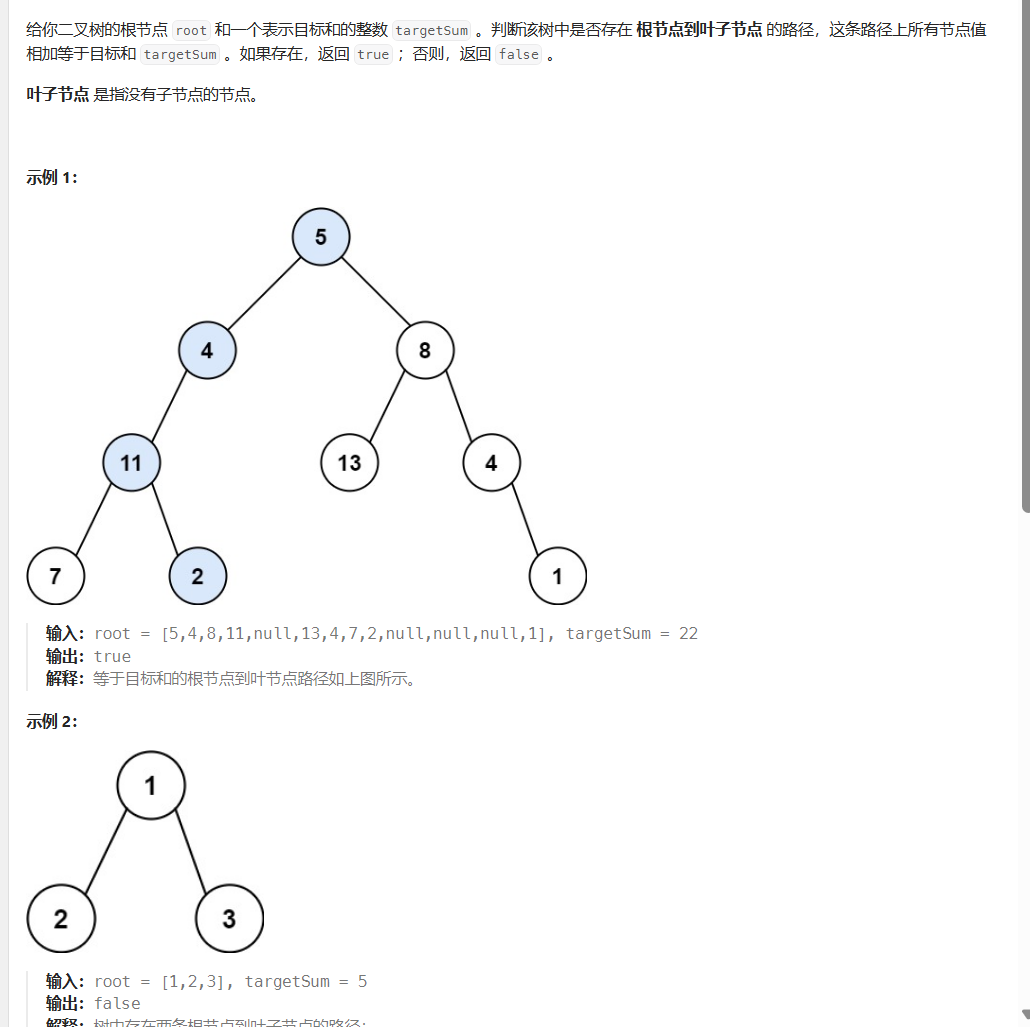
九、路径总和(力扣112)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<int> sumAll;
vector<int> path;
if(root==NULL) return false;
traversal(root,path,sumAll);
for(int i=0;i<sumAll.size();i++){
if(sumAll[i]==targetSum){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void traversal(TreeNode*root,vector<int> &path,vector<int> &result){
path.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<path.size();i++){
sum+= path[i];
}
result.push_back(sum);
}
if(root->left) {
traversal(root->left,path,result);
path.pop_back();
}
if(root->right){
traversal(root->right,path,result);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};