1 综述
1.1 目的
Bloom Filter Join,或者说Row-level Runtime Filtering(还额外有一条Semi-Join分支),是Spark 3.3对运行时过滤的一个最新补充
之前运行时过滤主要有两个:动态分区裁剪DPP(开源实现)、动态文件裁剪DFP(Databricks实现),两者都能有效减少数据源层面的Scan IO
Bloom Filter Join的主要优化点是在shuffle层,通过在join shuffle前对表进行过滤从而提高运行效率
1.2 场景
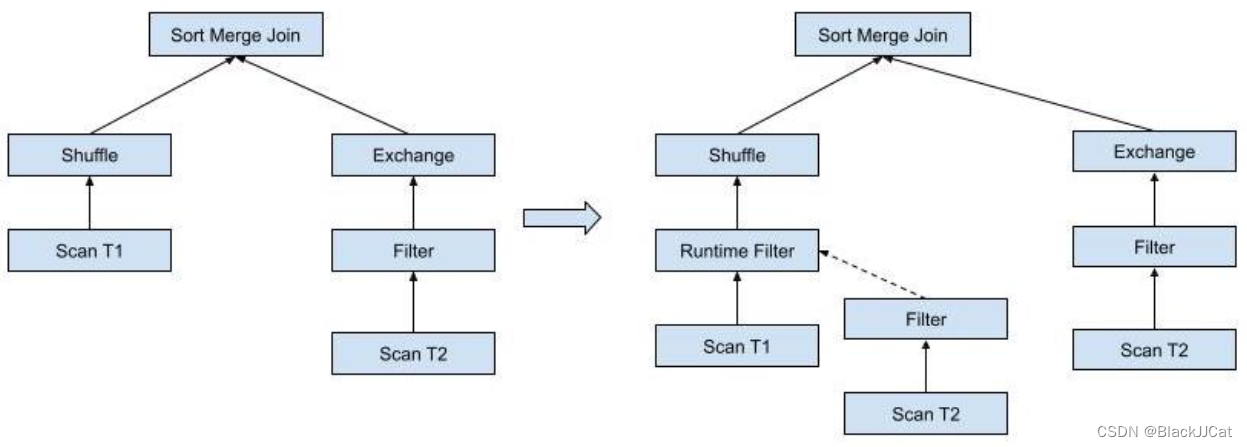
-
普通的shuffle join
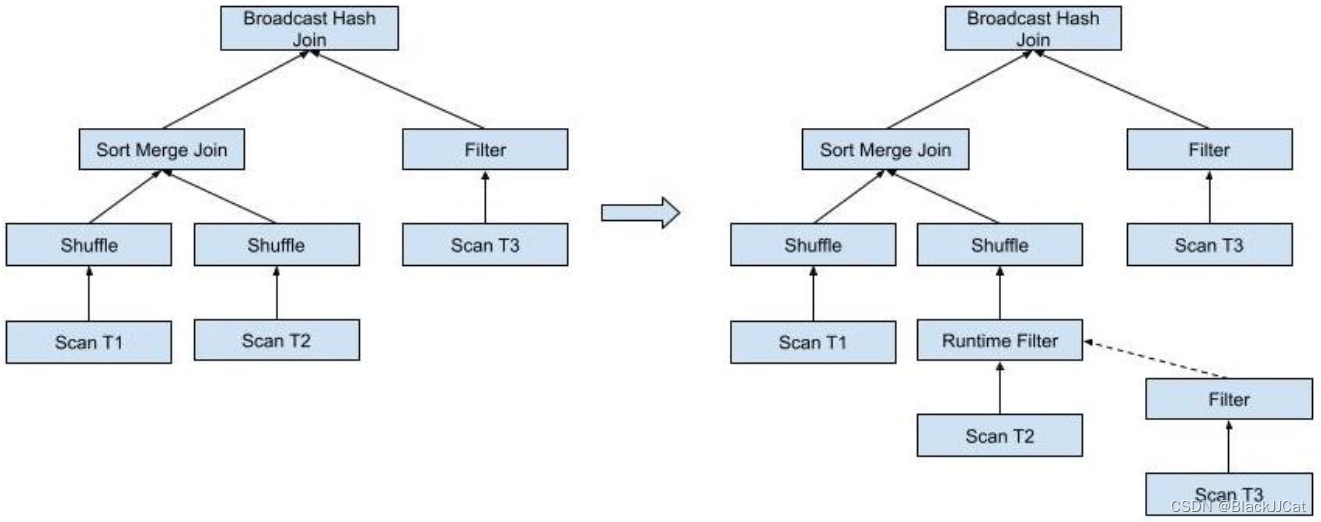
-
Broadcast join并且子结构中存在shuffle
1.3 基础过程
将存在过滤条件的小表端称为Filter Creation Side,另一层称为Filter Application Side
对于如下的SQL:SELECT * FROM R JOIN S ON R.r_sk = S.s_sk where S.x = 5
首先Creation端进行bloomFilter创建,简单来说就是对小表创建一个bloomFilter的过滤数据集合
SELECT BloomFilterAggregate(XxHash64(S.s_sk), n_items, n_bits)
FROM S where S.x = 5
之后Application端进行重写(实际是整个查询重写),就是把小表的bloomFilter数据集合拿来对大表的数据进行过滤
根据上面的场景图看,其实小表Creation端在整个SQL树上并没有变化,只改变了大表端的树结构
SELECT *
FROM R JOIN S ON R.r_sk = S.s_sk
WHERE S.x=5 AND BloomFilterMightContain(
(
SELECT BloomFilterAggregate(XxHash64(S.s_sk), n_items, n_bits) bloom_filter
FROM S where S.x = 5 ), -- Bloom filter creation
XxHash64(R.r_sk)) -- Bloom filter application
1.4 触发条件
设计文档中写的触发条件
- 小表在broadcast join当中(存疑)
- 小表有过滤器
- 小表是Scan (-> Project) -> Filter的建档形式,否则依赖流增加可能延长查询时间
- 小表是确定性的
- 大表端有shuffle,小表可以通过shuffl传送bloomFilter结果
- join的列上没有应用DPP
2 InjectRuntimeFilter
InjectRuntimeFilter是Spark源码中对应的优化器类,只执行一次(FixedPoint(1)和Once的差异是Once强制幂等)
Batch("InjectRuntimeFilter", FixedPoint(1),
InjectRuntimeFilter) :+
apply中定义了规则的整体流程,前面是两个条件判断
// 相关子查询不支持,相关子查询的子查询结果依赖于主查询,不能应用
case s: Subquery if s.correlated => plan
// 相关的配置开关是否开启
case _ if !conf.runtimeFilterSemiJoinReductionEnabled &&
!conf.runtimeFilterBloomFilterEnabled => plan
case _ =>
// 应用优化规则,尝试注入运行时过滤器
val newPlan = tryInjectRuntimeFilter(plan)
// semi join配置未开或者规则应用后无变化,不处理
if (conf.runtimeFilterSemiJoinReductionEnabled && !plan.fastEquals(newPlan)) {
// 子查询重写成semi/anti join
RewritePredicateSubquery(newPlan)
} else {
newPlan
}
相关的配置为,默认bloomFilter开启了,Semi join关闭的
val RUNTIME_FILTER_SEMI_JOIN_REDUCTION_ENABLED =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtimeFilter.semiJoinReduction.enabled")
.doc("When true and if one side of a shuffle join has a selective predicate, we attempt " +
"to insert a semi join in the other side to reduce the amount of shuffle data.")
.version("3.3.0")
.booleanConf
.createWithDefault(false)
val RUNTIME_BLOOM_FILTER_ENABLED =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtime.bloomFilter.enabled")
.doc("When true and if one side of a shuffle join has a selective predicate, we attempt " +
"to insert a bloom filter in the other side to reduce the amount of shuffle data.")
.version("3.3.0")
.booleanConf
.createWithDefault(true)
2.1 tryInjectRuntimeFilter
tryInjectRuntimeFilter使用核心的处理流程,尝试应用Runtime Filter,整体代码如下
private def tryInjectRuntimeFilter(plan: LogicalPlan): LogicalPlan = {
var filterCounter = 0
val numFilterThreshold = conf.getConf(SQLConf.RUNTIME_FILTER_NUMBER_THRESHOLD)
plan transformUp {
case join @ ExtractEquiJoinKeys(joinType, leftKeys, rightKeys, _, _, left, right, hint) =>
var newLeft = left
var newRight = right
(leftKeys, rightKeys).zipped.foreach((l, r) => {
// Check if:
// 1. There is already a DPP filter on the key
// 2. There is already a runtime filter (Bloom filter or IN subquery) on the key
// 3. The keys are simple cheap expressions
if (filterCounter < numFilterThreshold &&
!hasDynamicPruningSubquery(left, right, l, r) &&
!hasRuntimeFilter(newLeft, newRight, l, r) &&
isSimpleExpression(l) && isSimpleExpression(r)) {
val oldLeft = newLeft
val oldRight = newRight
if (canPruneLeft(joinType) && filteringHasBenefit(left, right, l, hint)) {
newLeft = injectFilter(l, newLeft, r, right)
}
// Did we actually inject on the left? If not, try on the right
if (newLeft.fastEquals(oldLeft) && canPruneRight(joinType) &&
filteringHasBenefit(right, left, r, hint)) {
newRight = injectFilter(r, newRight, l, left)
}
if (!newLeft.fastEquals(oldLeft) || !newRight.fastEquals(oldRight)) {
filterCounter = filterCounter + 1
}
}
})
join.withNewChildren(Seq(newLeft, newRight))
}
}
过程中有很多的条件判断,应用Runtime Filter的基本条件:
- 插入的Runtime Filter没超过阈值(默认10)
- 等值条件的Key上不能有DPP、Runtime Filter
- 等值条件的Key是一个简单表达式(即没有套上UDF等)
之后根据条件,选择将Runtime Filter应用到左子树还是右子树,条件为
- Join类型支持下推(比如RightOuter只能用于左子树)
- Application端支持通过joins、aggregates、windows下推过滤条件
- Creation端有过滤条件
- 当前join是shuffle join或者是一个子结构中包含shuffle的broadcast join
- Application端的扫描数据大于阈值(默认10G)
提到的两个阈值的配置项
val RUNTIME_FILTER_NUMBER_THRESHOLD =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtimeFilter.number.threshold")
.doc("The total number of injected runtime filters (non-DPP) for a single " +
"query. This is to prevent driver OOMs with too many Bloom filters.")
.version("3.3.0")
.intConf
.checkValue(threshold => threshold >= 0, "The threshold should be >= 0")
.createWithDefault(10)
val RUNTIME_BLOOM_FILTER_APPLICATION_SIDE_SCAN_SIZE_THRESHOLD =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtime.bloomFilter.applicationSideScanSizeThreshold")
.doc("Byte size threshold of the Bloom filter application side plan's aggregated scan " +
"size. Aggregated scan byte size of the Bloom filter application side needs to be over " +
"this value to inject a bloom filter.")
.version("3.3.0")
.bytesConf(ByteUnit.BYTE)
.createWithDefaultString("10GB")
2.2 injectFilter
injectFilter是核心进行Runtime Filter规则应用的地方,在此处,bloomFilter和Semi Join是互斥的,只能有一个执行
if (conf.runtimeFilterBloomFilterEnabled) {
injectBloomFilter(
filterApplicationSideExp,
filterApplicationSidePlan,
filterCreationSideExp,
filterCreationSidePlan
)
} else {
injectInSubqueryFilter(
filterApplicationSideExp,
filterApplicationSidePlan,
filterCreationSideExp,
filterCreationSidePlan
)
2.3 injectBloomFilter
2.3.1 执行条件
首先进行一个判断,在Creation端的数据不能大于阈值(Creation端数据量大会导致bloomFilter的误判率高,最终过滤效果差)
// Skip if the filter creation side is too big
if (filterCreationSidePlan.stats.sizeInBytes > conf.runtimeFilterCreationSideThreshold) {
return filterApplicationSidePlan
}
阈值配置默认10M
val RUNTIME_BLOOM_FILTER_CREATION_SIDE_THRESHOLD =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtime.bloomFilter.creationSideThreshold")
.doc("Size threshold of the bloom filter creation side plan. Estimated size needs to be " +
"under this value to try to inject bloom filter.")
.version("3.3.0")
.bytesConf(ByteUnit.BYTE)
.createWithDefaultString("10MB")
Creation端的数据是一个预估数据,是LogicalPlan中的属性LogicalPlanStats获取的,分是否开启CBO,具体获取方式待研究
def stats: Statistics = statsCache.getOrElse {
if (conf.cboEnabled) {
statsCache = Option(BasicStatsPlanVisitor.visit(self))
} else {
statsCache = Option(SizeInBytesOnlyStatsPlanVisitor.visit(self))
}
statsCache.get
}
2.3.2 创建Creation端的聚合
就是创建一个bloomFilter的聚合函数BloomFilterAggregate,是AggregateFunction的子类,属于Expression。根据统计信息中是否存在行数,会传入不同的参数
val rowCount = filterCreationSidePlan.stats.rowCount
val bloomFilterAgg =
if (rowCount.isDefined && rowCount.get.longValue > 0L) {
new BloomFilterAggregate(new XxHash64(Seq(filterCreationSideExp)), rowCount.get.longValue)
} else {
new BloomFilterAggregate(new XxHash64(Seq(filterCreationSideExp)))
}
2.3.3 创建Application端的过滤条件
根据1.3中的描述,此处就是把上节中Creation端创建的bloomFilter过滤条件构建成Application端的条件
Alias就是一个别名的效果;ColumnPruning就是进行列裁剪,后续不需要的列不读取;ConstantFolding就是进行常量折叠;ScalarSubquery是标量子查询,标量子查询的查询结果是一行一列的值(单一值)
BloomFilterMightContain就是一个内部标量函数,检查数据是否由bloomFilter包含,继承自Predicate,返回boolean值
val alias = Alias(bloomFilterAgg.toAggregateExpression(), "bloomFilter")()
val aggregate =
ConstantFolding(ColumnPruning(Aggregate(Nil, Seq(alias), filterCreationSidePlan)))
val bloomFilterSubquery = ScalarSubquery(aggregate, Nil)
val filter = BloomFilterMightContain(bloomFilterSubquery,
new XxHash64(Seq(filterApplicationSideExp)))
最终结果是在原Application端的计划树上加一个filter,如下就是最终的返回结果
Filter(filter, filterApplicationSidePlan)
2.4 injectInSubqueryFilter
injectInSubqueryFilter整体流程与injectBloomFilter差不多,差异应该是在Application端生成的过滤条件变成in
val actualFilterKeyExpr = mayWrapWithHash(filterCreationSideExp)
val alias = Alias(actualFilterKeyExpr, actualFilterKeyExpr.toString)()
val aggregate =
ColumnPruning(Aggregate(Seq(filterCreationSideExp), Seq(alias), filterCreationSidePlan))
if (!canBroadcastBySize(aggregate, conf)) {
// Skip the InSubquery filter if the size of `aggregate` is beyond broadcast join threshold,
// i.e., the semi-join will be a shuffled join, which is not worthwhile.
return filterApplicationSidePlan
}
val filter = InSubquery(Seq(mayWrapWithHash(filterApplicationSideExp)),
ListQuery(aggregate, childOutputs = aggregate.output))
Filter(filter, filterApplicationSidePlan)
这里有一个小优化就是mayWrapWithHash,当数据类型的大小超过int时,就是把数据转为hash
// Wraps `expr` with a hash function if its byte size is larger than an integer.
private def mayWrapWithHash(expr: Expression): Expression = {
if (expr.dataType.defaultSize > IntegerType.defaultSize) {
new Murmur3Hash(Seq(expr))
} else {
expr
}
}
3 BloomFilterAggregate
类有三个核心参数:
- child:子表达式,就是InjectRuntimeFilter里传的XxHash64,目前看起来数据先经过XxHash64处理成long再放入BloomFilter
- estimatedNumItemsExpression:估计的数据量,如果InjectRuntimeFilter没拿到统计信息,就用配置的默认值
- numBitsExpression:要使用的bit数
case class BloomFilterAggregate(
child: Expression,
estimatedNumItemsExpression: Expression,
numBitsExpression: Expression,
estimatedNumItemsExpression和numBitsExpression对应的配置如下
val RUNTIME_BLOOM_FILTER_EXPECTED_NUM_ITEMS =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtime.bloomFilter.expectedNumItems")
.doc("The default number of expected items for the runtime bloomfilter")
.version("3.3.0")
.longConf
.createWithDefault(1000000L)
val RUNTIME_BLOOM_FILTER_NUM_BITS =
buildConf("spark.sql.optimizer.runtime.bloomFilter.numBits")
.doc("The default number of bits to use for the runtime bloom filter")
.version("3.3.0")
.longConf
.createWithDefault(8388608L)
BloomFilter用的是Spark自己实现的一个类BloomFilterImpl,BloomFilterAggregate的createAggregationBuffer接口中创建
override def createAggregationBuffer(): BloomFilter = {
BloomFilter.create(estimatedNumItems, numBits)
}
参数就是前面的estimatedNumItemsExpression和numBitsExpression,是懒加载的参数(应该在处理过程会被改变,所以实际跟前面的值之间还加了一层与默认值的比较赋值)
// Mark as lazy so that `estimatedNumItems` is not evaluated during tree transformation.
private lazy val estimatedNumItems: Long =
Math.min(estimatedNumItemsExpression.eval().asInstanceOf[Number].longValue,
SQLConf.get.getConf(RUNTIME_BLOOM_FILTER_MAX_NUM_ITEMS))
处理数据的接口应该是update,把数据用XxHash64处理后加入BloomFilter
override def update(buffer: BloomFilter, inputRow: InternalRow): BloomFilter = {
val value = child.eval(inputRow)
// Ignore null values.
if (value == null) {
return buffer
}
buffer.putLong(value.asInstanceOf[Long])
buffer
}
对象BloomFilterAggregate有对应的序列化和反序列化接口
object BloomFilterAggregate {
final def serialize(obj: BloomFilter): Array[Byte] = {
// BloomFilterImpl.writeTo() writes 2 integers (version number and num hash functions), hence
// the +8
val size = (obj.bitSize() / 8) + 8
require(size <= Integer.MAX_VALUE, s"actual number of bits is too large $size")
val out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(size.intValue())
obj.writeTo(out)
out.close()
out.toByteArray
}
final def deserialize(bytes: Array[Byte]): BloomFilter = {
val in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes)
val bloomFilter = BloomFilter.readFrom(in)
in.close()
bloomFilter
}
}
4 BloomFilterMightContain
有两个参数
- bloomFilterExpression:是上节BloomFilter的二进制数据
- valueExpression:应该跟上节的child一致,对输入数据做处理的表达式,XxHash64
case class BloomFilterMightContain(
bloomFilterExpression: Expression,
valueExpression: Expression)
bloomFilter通过反序列化获取
// The bloom filter created from `bloomFilterExpression`.
@transient private lazy val bloomFilter = {
val bytes = bloomFilterExpression.eval().asInstanceOf[Array[Byte]]
if (bytes == null) null else deserialize(bytes)
}
做数据判断的应该是eval,就是调用的BloomFilter的接口进行判断。eval应该就是Spark中Expression表达式的执行接口
override def eval(input: InternalRow): Any = {
if (bloomFilter == null) {
null
} else {
val value = valueExpression.eval(input)
if (value == null) null else bloomFilter.mightContainLong(value.asInstanceOf[Long])
}
}
也有doGenCode接口用来生成代码
override def doGenCode(ctx: CodegenContext, ev: ExprCode): ExprCode = {
if (bloomFilter == null) {
ev.copy(isNull = TrueLiteral, value = JavaCode.defaultLiteral(dataType))
} else {
val bf = ctx.addReferenceObj("bloomFilter", bloomFilter, classOf[BloomFilter].getName)
val valueEval = valueExpression.genCode(ctx)
ev.copy(code = code"""
${valueEval.code}
boolean ${ev.isNull} = ${valueEval.isNull};
${CodeGenerator.javaType(dataType)} ${ev.value} = ${CodeGenerator.defaultValue(dataType)};
if (!${ev.isNull}) {
${ev.value} = $bf.mightContainLong((Long)${valueEval.value});
}""")
}
}
5 计划变更
取Spark单元测试的样例(InjectRuntimeFilterSuite):select * from bf1 join bf2 on bf1.c1 = bf2.c2 where bf2.a2 = 62
- 规则前的plan
GlobalLimit 21
+- LocalLimit 21
+- Project [cast(a1#38430 as string) AS a1#38468, cast(b1#38431 as string) AS b1#38469, cast(c1#38432 as string) AS c1#38470, cast(d1#38433 as string) AS d1#38471, cast(e1#38434 as string) AS e1#38472, cast(f1#38435 as string) AS f1#38473, cast(a2#38436 as string) AS a2#38474, cast(b2#38437 as string) AS b2#38475, cast(c2#38438 as string) AS c2#38476, cast(d2#38439 as string) AS d2#38477, cast(e2#38440 as string) AS e2#38478, cast(f2#38441 as string) AS f2#38479]
+- Join Inner, (c1#38432 = c2#38438)
:- Filter isnotnull(c1#38432)
: +- Relation spark_catalog.default.bf1[a1#38430,b1#38431,c1#38432,d1#38433,e1#38434,f1#38435] parquet
+- Filter ((isnotnull(a2#38436) AND (a2#38436 = 62)) AND isnotnull(c2#38438))
+- Relation spark_catalog.default.bf2[a2#38436,b2#38437,c2#38438,d2#38439,e2#38440,f2#38441] parquet
- 规则后的plan
GlobalLimit 21
+- LocalLimit 21
+- Project [cast(a1#38430 as string) AS a1#38468, cast(b1#38431 as string) AS b1#38469, cast(c1#38432 as string) AS c1#38470, cast(d1#38433 as string) AS d1#38471, cast(e1#38434 as string) AS e1#38472, cast(f1#38435 as string) AS f1#38473, cast(a2#38436 as string) AS a2#38474, cast(b2#38437 as string) AS b2#38475, cast(c2#38438 as string) AS c2#38476, cast(d2#38439 as string) AS d2#38477, cast(e2#38440 as string) AS e2#38478, cast(f2#38441 as string) AS f2#38479]
+- Join Inner, (c1#38432 = c2#38438)
:- Filter might_contain(scalar-subquery#38494 [], xxhash64(c1#38432, 42))
: : +- Aggregate [bloom_filter_agg(xxhash64(c2#38438, 42), 1000000, 8388608, 0, 0) AS bloomFilter#38493]
: : +- Project [c2#38438]
: : +- Filter ((isnotnull(a2#38436) AND (a2#38436 = 62)) AND isnotnull(c2#38438))
: : +- Relation spark_catalog.default.bf2[a2#38436,b2#38437,c2#38438,d2#38439,e2#38440,f2#38441] parquet
: +- Filter isnotnull(c1#38432)
: +- Relation spark_catalog.default.bf1[a1#38430,b1#38431,c1#38432,d1#38433,e1#38434,f1#38435] parquet
+- Filter ((isnotnull(a2#38436) AND (a2#38436 = 62)) AND isnotnull(c2#38438))
+- Relation spark_catalog.default.bf2[a2#38436,b2#38437,c2#38438,d2#38439,e2#38440,f2#38441] parquet




![练习 2 Web [ACTF2020 新生赛]BackupFile 1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7beef1165993494f84db210c5e94a35a.png)