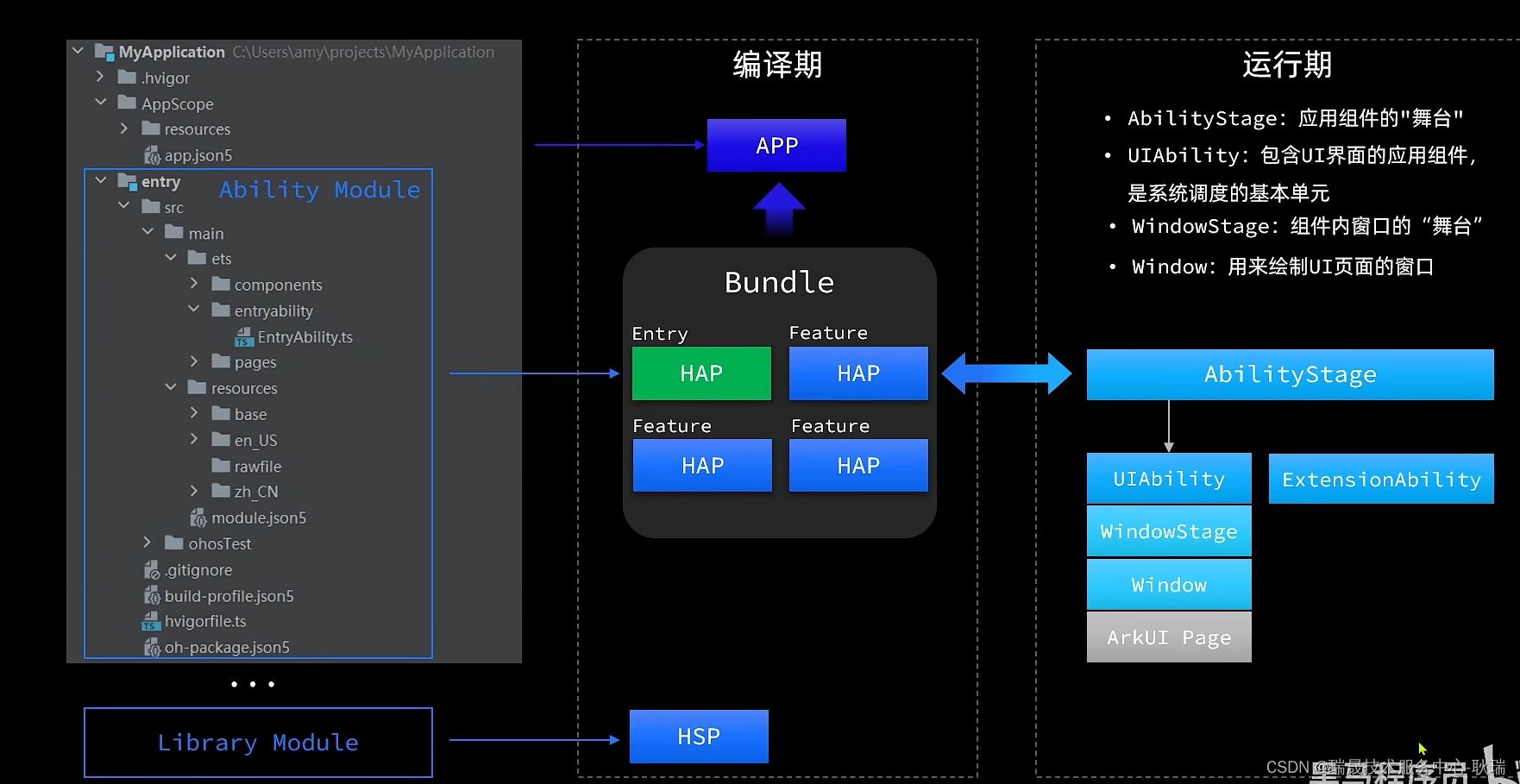
1.公共服务器
学习物联网就离不开服务器,如果你资金充足的话,可以自己购买或者租用一个服务器。本次我选择,使用免费的公共MQTT服务器。它的端口及Broker信息如下:
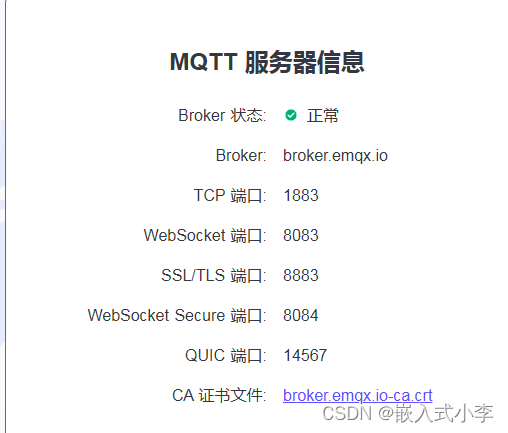
网址为:
免费的公共 MQTT 服务器 | EMQ (emqx.com)![]() https://www.emqx.com/zh/mqtt/public-mqtt5-broker
https://www.emqx.com/zh/mqtt/public-mqtt5-broker
2.MQTT 调试工具
为了弄清楚,你的数据是否成功发送到了对应的服务器上,你需要使用一个mqtt调试工具。你可以设置它的服务器地址,端口号,发布主题,订阅主题,这样就能调试了。你在MQTT调试工具上的订阅主题设置为ESP8266上的发布主题,就可以看到从ESP8266传输过来的数据!
这里我直接给出我用的mqtt调试工具的安装包: 【免费】MQTT调试助手物联网必备资源-CSDN文库![]() https://download.csdn.net/download/guangali/88865017
https://download.csdn.net/download/guangali/88865017
3.代码设计
简单介绍一下代码的重要部分吧

首先,前三行是导入头文件, 紧接着的就是你使用的WIFI名称和密码,mqtt服务器地址(我使用的是这个地址,也是一个公共服务器,你可以跟我用一样的)。第7行是ESP8266的发布主题,8行是ESP8266的订阅主题。 发布主题的名字和订阅主题的名字你可以设置为任意的,只要记得如何区分就行。
接下来是WIFI设置,不用改
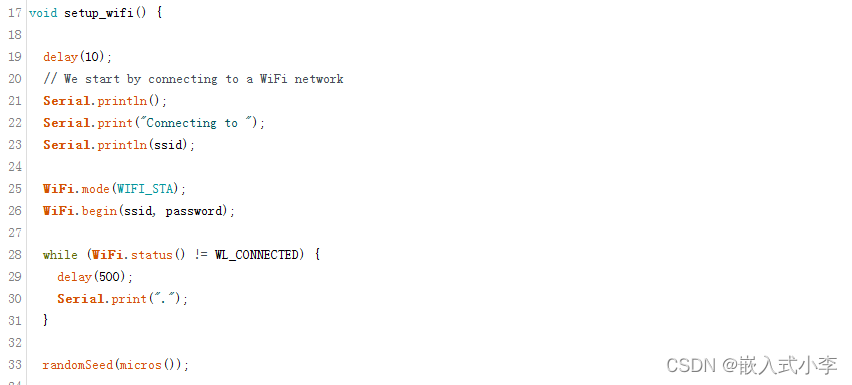
下面是回调函数,当服务器给ESP8266发数据时,8266就执行这里面的函数。这里面使用了json解析的库函数,所以要安装json第三方库。
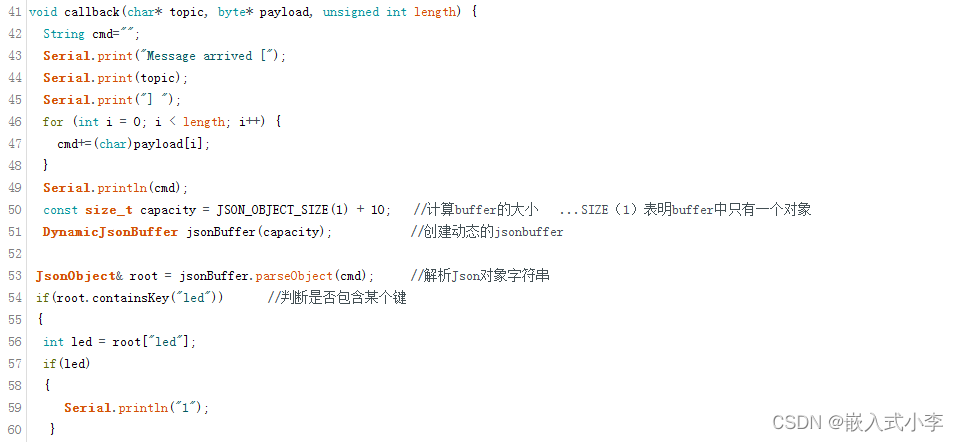
这函数里面,我实现的功能是:
发送“led”: 1 时,打印1,发送 “led”: 0 时,打印2.
实现了这个功能以后,稍加修改,就可以实现通过手机APP控制单片机上任意设备的功能!
WIFI重连函数

代码的主题部分:
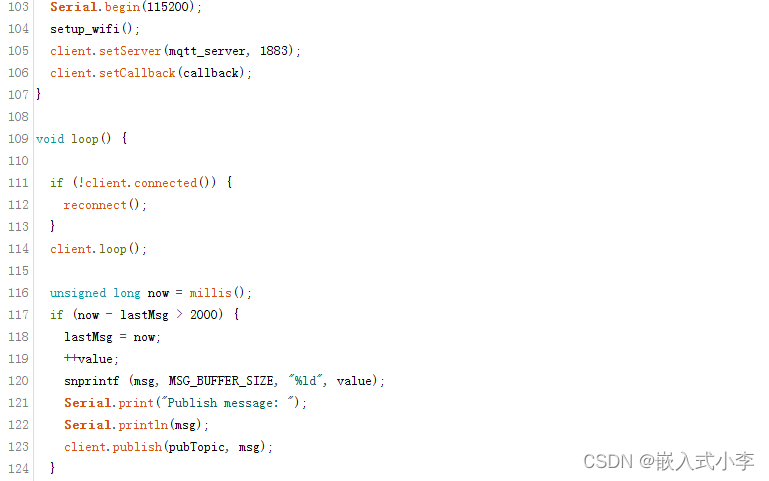
串口波特率设置的为115200,服务器端口号设置为1883. 这里实现的功能是,每隔两秒钟,就给服务器发送自增的数字。
完整代码如下:
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
const char* ssid = "lig"; //WIFI名称
const char* password = "1521"; //WIFI密码 这里改成你自己的WIFI名称和密码
const char* mqtt_server = "broker-cn.emqx.io"; //mqtt服务器地址 (IP/域名)这里可以不改
const char *pubTopic="my_pubtopic";
const char *subTopic="my_subtopic"; //订阅的主题
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient client(espClient);
unsigned long lastMsg = 0;
#define MSG_BUFFER_SIZE (50)
char msg[MSG_BUFFER_SIZE];
int value = 0;
void setup_wifi() {
delay(10);
// We start by connecting to a WiFi network
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
randomSeed(micros());
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
String cmd="";
Serial.print("Message arrived [");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print("] ");
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
cmd+=(char)payload[i];
}
Serial.println(cmd);
const size_t capacity = JSON_OBJECT_SIZE(1) + 10; //计算buffer的大小 ...SIZE(1)表明buffer中只有一个对象
DynamicJsonBuffer jsonBuffer(capacity); //创建动态的jsonbuffer
JsonObject& root = jsonBuffer.parseObject(cmd); //解析Json对象字符串
if(root.containsKey("led")) //判断是否包含某个键
{
int led = root["led"];
if(led)
{
Serial.println("1");
}
else
Serial.println("2");
}
if(root.containsKey("beep")) //判断是否包含某个键
{
int beep = root["beep"];
if(beep)
{
Serial.println("3");
}
else
Serial.println("4");
}
}
void reconnect() {
// Loop until we're reconnected
while (!client.connected()) {
Serial.print("Attempting MQTT connection...");
// Create a random client ID
String clientId = "ESP8266Client-";
clientId += String(random(0xffff), HEX);
// Attempt to connect
if (client.connect(clientId.c_str())) {
Serial.println("connected");
// Once connected, publish an announcement...
client.publish(pubTopic, "hello world"); //发布的主题
// ... and resubscribe
client.subscribe(subTopic); //设置订阅的主题
} else {
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(client.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
// Wait 5 seconds before retrying
delay(5000);
}
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
setup_wifi();
client.setServer(mqtt_server, 1883);
client.setCallback(callback);
}
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()) {
reconnect();
}
client.loop();
unsigned long now = millis();
if (now - lastMsg > 2000) {
lastMsg = now;
++value;
snprintf (msg, MSG_BUFFER_SIZE, "%ld", value);
Serial.print("Publish message: ");
Serial.println(msg);
client.publish(pubTopic, msg);
}
}4.功能验证
打开MQTT调试助手,进入设置界面
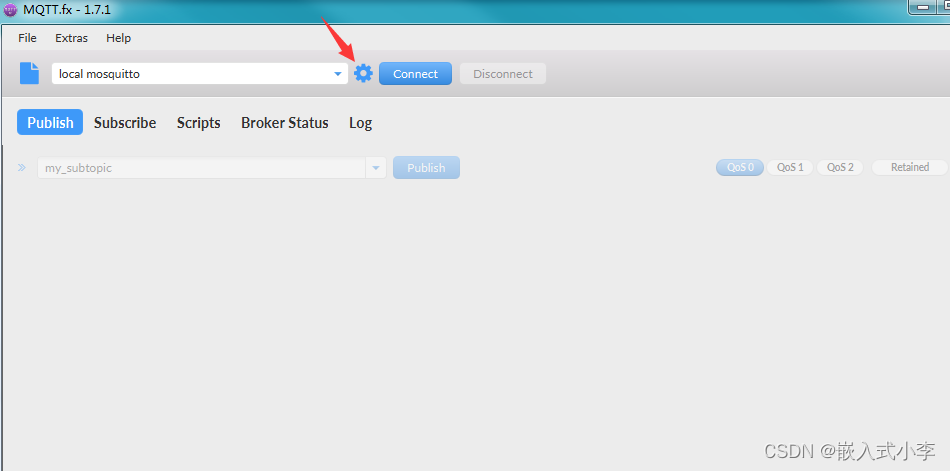
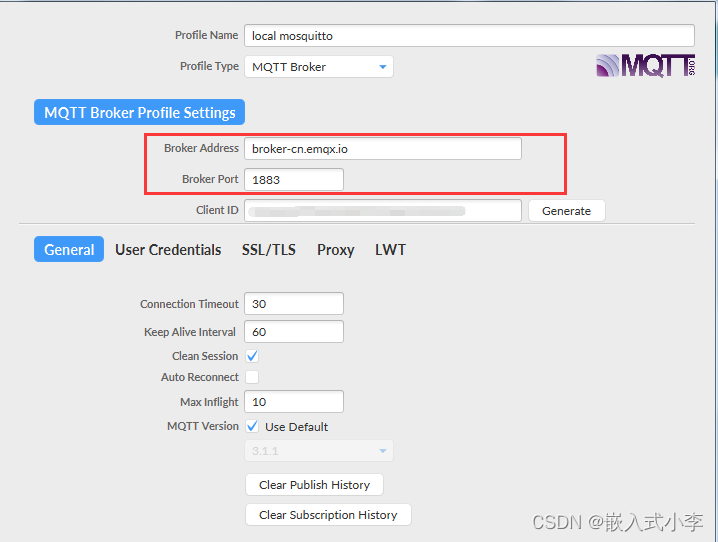
服务器地址和端口号很重要,设置为和你8266代码里面一样的
设置成功后点击连接
将服务器的发布主题设置为8266上的订阅主题,这样,只要你一发布内容,服务器就会自动推送给8266,8266就可以接收数据了。
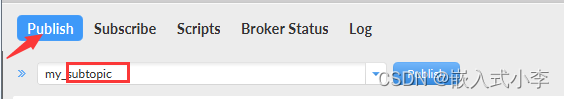
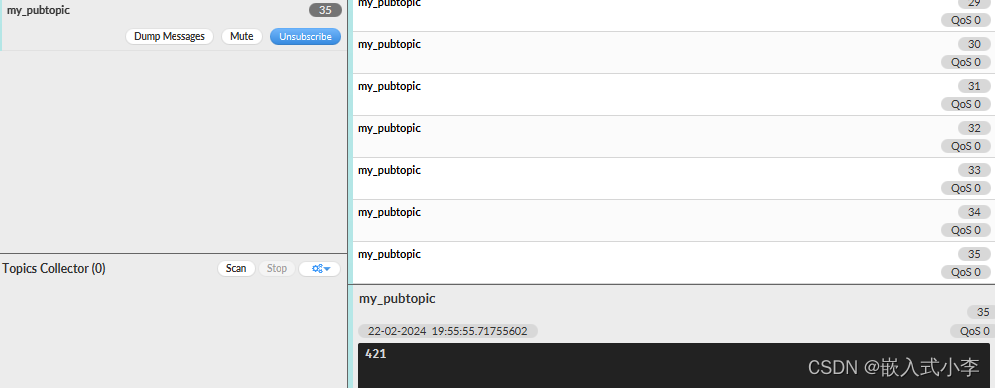
同理,将服务器的订阅主题设置为8266的发布主题,这样服务器就能接收到8266上发的数据。
服务器接收的数据如下:
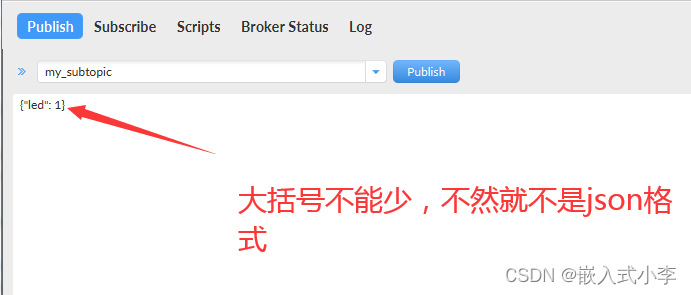
通过服务器发布消息: (必须为json格式)
8266做出相关反应:
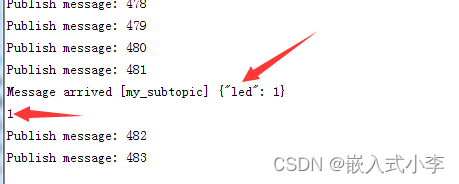
可见,8266正确接收并解析了相关消息。
5.总结
至此,已经完成了,8266向服务器发送消息,可解析服务器下发的消息。ESP8266智能家居项目已经完成了将近一半。试想一下,如果你可以开发一款APP,并且APP上订阅的主题就是8266发布的主题,APP上发布的主题就是8266上订阅的主题,并且8266通过串口和单片机通讯,这样就可以让单片机测量到的温度、湿度、光照等信息显示在手机APP上,并且手机给单片机下发的开灯、开蜂鸣器、开窗等指令也能被识别并执行!