排序算法:交换类排序,插入类排序、选择类排序、归并类排序
交换类排序:冒泡排序、快速排序
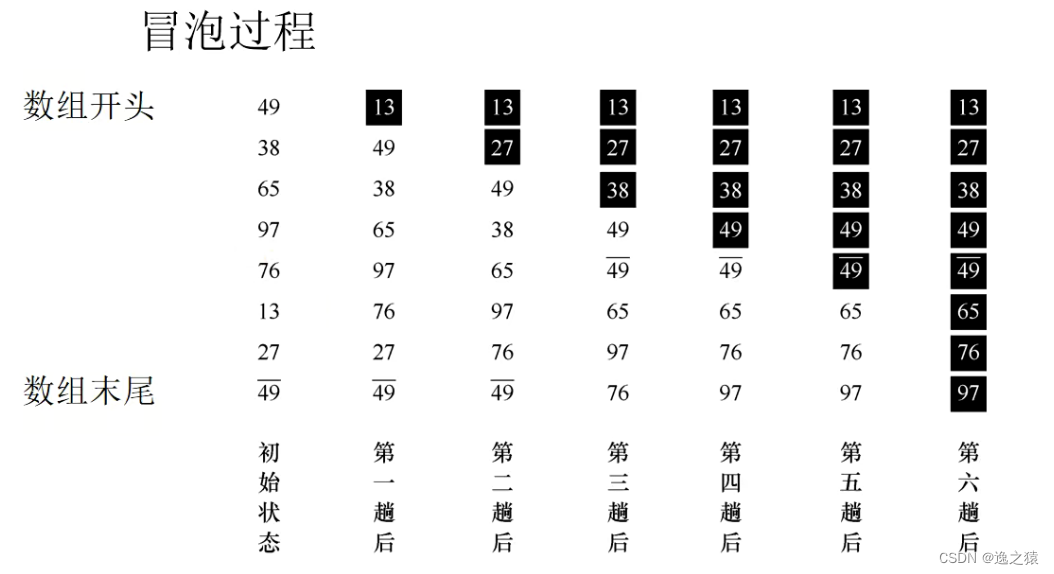
一、冒泡排序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType *elem; //整形指针,申请的堆空间的起始地址存入elem
int TableLen; //存储动态数组里边元素的个数
}SSTable;
void ST_Init(SSTable &ST,int len){
ST.TableLen=len;
ST.elem=(ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*ST.TableLen);
int i;
srand(time(NULL)); //随机数生成
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
ST.elem[i]=rand()%100;
}
}
void ST_print(SSTable ST){
int i;
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
printf("%3d",ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void swap(ElemType &a,ElemType &b){
ElemType tmp;
tmp=a;
a=b;
b=tmp;
}
//两层循环
//优先写内层循环,再写外层循环
void BubbleSort(ElemType A[],int n){
int i,j;
bool flag;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){ //控制的是有序数的数目
flag=false;
for(j=n-1;j>i;j--){ //内层控制比较和交换
if(A[j-1]>A[j]){
swap(A[j-1],A[j]);
flag=true;
}
}
if(flag==false){ //如果一趟没有发生任何交换,说明数组有序,提前结束排序
return;
}
}
}
int main(){
SSTable ST;
ST_Init(ST,10);
ST_print(ST);
BubbleSort(ST.elem,10);
ST_print(ST);
return 0;
} 时间复杂度:内层是j>i,外层是从0到n-1,运行的总次数是1+2+3+4+...+n-1,即O()
空间复杂度:O(1),没有使用额外空间,不会因为n的变化而变化
如果数组本身有序,最好的时间复杂度是O(n)
二、快速排序
核心:分治思想
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType *elem; //整形指针,申请的堆空间的起始地址存入elem
int TableLen; //存储动态数组里边元素的个数
}SSTable;
void ST_Init(SSTable &ST,int len){
ST.TableLen=len;
ST.elem=(ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*ST.TableLen);
int i;
srand(time(NULL)); //随机数生成
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
ST.elem[i]=rand()%100;
}
}
void ST_print(SSTable ST){
int i;
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
printf("%3d",ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void swap(ElemType &a,ElemType &b){
ElemType tmp;
tmp=a;
a=b;
b=tmp;
}
int Partition(ElemType A[],int low,int high){
ElemType pivot=A[low]; //拿最左边的作为分割值,并存储下来
while(low<high){
while(low<high&&A[high]>=pivot){ //从后往前遍历,找到一个比分割值小的
--high;
}
A[low]=A[high];
while(low<high&&A[low]<=pivot){
++low;
}
A[high]=A[low];
}
A[low]=pivot;
return low; //返回分割值所在的下标
}
//递归实现
void QuickSort(ElemType A[],int low,int high){
if(low<high){
int pivotpos=Partition(A,low,high);
QuickSort(A,low,pivotpos-1);
QuickSort(A,pivotpos+1,high);
}
}
int main(){
SSTable ST;
ST_Init(ST,10);
ST_print(ST);
QuickSort(ST.elem,0,9);
ST_print(ST);
return 0;
}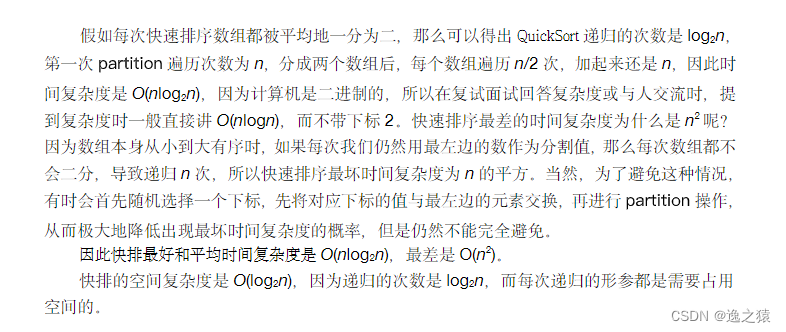 空间复杂度与n有关
空间复杂度与n有关
三、插入排序
插入排序:直接插入排序、折半插入排序、希尔排序
直接插入排序
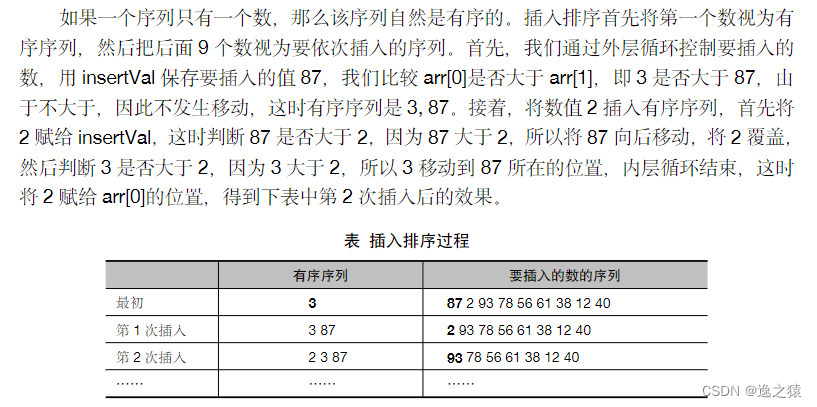
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType *elem; //整形指针,申请的堆空间的起始地址存入elem
int TableLen; //存储动态数组里边元素的个数
}SSTable;
void ST_Init(SSTable &ST,int len){
ST.TableLen=len;
ST.elem=(ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*ST.TableLen);
int i;
srand(time(NULL)); //随机数生成
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
ST.elem[i]=rand()%100;
}
}
void ST_print(SSTable ST){
int i;
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
printf("%3d",ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void InsertSort(ElemType *arr,int n){
int i,j,insertVal;
for(i=1;i<n;i++){ //控制要插入的数
insertVal=arr[i]; //先保存要插入的值
//内层控制比较,往后覆盖
for(j=i-1;j>=0&&arr[j]>insertVal;j--){
arr[j+1]=arr[j];
}
arr[j+1]=insertVal;
}
}
int main(){
SSTable ST;
ST_Init(ST,10);
ST_print(ST);
InsertSort(ST.elem,10);
ST_print(ST);
return 0;
}