目录
一、Nginx相关介绍
1. 概述
2. 优缺点
3. 零拷贝技术
4. I/O模型相关概念
5. 网络I/O模型
5.1 阻塞型I/O模型
5.2 非阻塞型I/O模型
5.3 多路复用I/O型
5.4 信号驱动式I/O模型
5.5 异步I/O模型
6. 事件驱动模型
7. Nginx与Apache区别
二、Nginx部署和使用
1. yum安装
2. 编译安装
3. 创建Nginx 自启动文件
4. 信号使用命令及平滑升级
4.1 信号
5. 热升级nginx1.18至nginx1.20
6. 回滚
一、Nginx相关介绍
1. 概述
Nginx(发音为"engine-x")是一个高性能的开源Web服务器,反向代理服务器以及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器。Nginx专为性能优化而设计,可以处理高并发连接,并且占用系统资源较少。它也被广泛用作负载均衡器和HTTP缓存。Nginx的设计目标之一是解决C10k问题,即同时连接数超过1万的情况下仍能保持高性能。
2. 优缺点
优点:
① 高并发能力: 能够处理大量并发连接,适合高流量的网站和应用程序
② 低系统资源消耗: 相比其他Web服务器,Nginx占用更少的系统资源,表现出更好的性能
③ 灵活的配置选项: 允许管理员根据需要进行高度定制,满足各种复杂的部署需求
④ 可扩展性: 支持动态模块加载,可以根据需要添加额外的功能和扩展
缺点:
① 不适合处理动态内容: 相比Apache等服务器,Nginx在处理动态内容时效率稍低。
② 学习曲线: 对于初学者来说,可能需要一些时间来熟悉Nginx的配置和工作原理。
③ 缺少内置的支持: 相比一些其他服务器,Nginx在某些方面可能需要依赖第三方模块来实现特定功能。
3. 零拷贝技术
在传统的数据传输过程中,数据通常需要经过多次复制。比如,当数据从磁盘读取到内存时,首先将数据读入内核缓冲区,然后再从内核缓冲区复制到用户空间的应用程序缓冲区。零拷贝技术通过避免或减少数据在内存和设备之间的多次复制来提高效率。具体做法包括直接内存访问(DMA)、文件映射(mmap)和发送文件(sendfile)等。
4. I/O模型相关概念
同步/异步(消息反馈机制):关注的是消息通信机制,即调用者在等待一件事情的处理结果时,被调用者是否提供完成状态的通知
- 同步:被调用者不提供事件的处理结果,需要调用者主动询问事情是否处理完成
- 异步:被调用者通过状态、通知或回调机制主动通知调用者被调用者的运行状态
阻塞/非阻塞:关注调用者在等待结果返回之前所处的状态
- 阻塞:指IO操作需要彻底完成后才返回到用户空间,调用结果返回之前,调用者被挂起,干不了别的事情
- 非阻塞:指IO操作被调用后立即返回给用户一个状态值,而无需等到IO操作彻底完成,在最终的调用结果返回之前,调用者不会被挂起,可以去做别的事情
5. 网络I/O模型
5.1 阻塞型I/O模型
Linux操作系统默认是阻塞型I/O模型。阻塞IO模型是最简单的I/O模型,用户线程在内核进行IO操作时被阻塞用户线程通过系统调用read发起I/O读操作,由用户空间转到内核空间。内核等到数据包到达后,然后将接收的数据拷贝到用户空间,完成read操作用户需要等待read将数据读取到buffer(缓存区)后,才继续处理接收的数据。整个I/O请求的过程中,用户线程是被阻塞的,这导致用户在发起IO请求时,不能做任何事情,对CPU的资源利用率不够。
- 优点:程序简单,在阻塞等待数据期间进程/线程挂起,基本不会占用 CPU 资源
- 缺点:每个连接需要独立的进程/线程单独处理,当并发请求量大时为了维护程序,内存、线程切换开销较大,apache 的preforck使用的是这种模式。
5.2 非阻塞型I/O模型
用户线程发起IO请求时立即返回。但并未读取到任何数据,用户线程需要不断地发起IO请求,直到数据到达后,才真正读取到数据,继续执行。即 “轮询”机制存在两个问题:如果有大量文件描述符都要等,那么就得一个一个的read。这会带来大量的Context Switch(read是系统调用,每调用一次就得在用户态和核心态切换一次)。轮询的时间不好把握。这里是要猜多久之后数据才能到。等待时间设的太长,程序响应延迟就过大;设的太短,就会造成过于频繁的重试,干耗CPU而已,是比较浪费CPU的方式,一般很少直接使用这种模型,而是在其他IO模型中使用非阻塞IO这一特性。
5.3 多路复用I/O型
I/O multiplexing 主要包括:select,poll,epoll三种系统调用,select/poll/epoll的好处就在于单个process就可以同时处理多个网络连接的IO。它的基本原理就是select/poll/epoll这个function会不断的轮询所负责的所有socket,当某个socket有数据到达了,就通知用户进程。当用户进程调用了select,那么整个进程会被block,而同时,kernel会“监视”所有select负责的socket,当任何一个socket中的数据准备好了,select就会返回。这个时候用户进程再调用read操作,将数据从kernel拷贝到用户进程。Apache prefork是此模式的select,work是poll模式。
5.4 信号驱动式I/O模型
通过系统调用 sigaction ,并注册一个信号处理的回调函数,该调用会立即返回,然后主程序可以继续向下执行,当有I/O操作准备就绪,即内核数据就绪时,内核会为该进程产生一个SIGIO 信号,并回调注册的信号回调函数,这样就可以在信号回调函数中系统调用 recvfrom 获取数据,将用户进程所需要的数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间。
此模型的优势在于等待数据报到达期间进程不被阻塞。用户主程序可以继续执行,只要等待来自信号处理函数的通知。在信号驱动式 I/O 模型中,应用程序使用套接口进行信号驱动 I/O,并安装一个信号处理函数,进程继续运行并不阻塞当数据准备好时,进程会收到一个 SIGIO 信号,可以在信号处理函数中调用 I/O 操作函数处理数据。
- 优点:线程并没有在等待数据时被阻塞,内核直接返回调用接收信号,不影响进程继续处理其他请求因此可以提高资源的利用率
- 缺点:信号I/O在大量IO操作时可能会因为信号队列溢出导致没法通知
5.5 异步I/O模型
异步I/O 与 信号驱动I/O最大区别在于,信号驱动是内核通知我们何时开始一个I/O操作,而异步I/O是由内核通知我们I/O操作何时完成,两者有本质区别,相当于不用去饭店场吃饭,直接点个外卖,把等待上菜的时间也给省了。所有事情都交给内核处理。
6. 事件驱动模型
Nginx支持在多种不同的操作系统实现不同的事件驱动模型,但是其在不同的操作系统甚至是不同的系统版本上面的实现方式不同。
① select:select库是在linux和windows平台都基本支持的 事件驱动模型库,并且在接口的定义也基本相同,只是部
分参数的含义略有差异,最大并发限制1024,是最早期的事件驱动模型。
② poll:在Linux 的基本驱动模型,windows不支持此驱动模型,是select的升级版,取消了最大的并发限制,在编
译nginx的时候可以使用--with-poll_module和--without-poll_module这两个指定是否编译select
库。
③ epoll:epoll是库是Nginx服务器支持的最高性能的事件驱动库之一,是公认的非常优秀的事件驱动模型,它和select和poll有很大的区别,epoll是poll的升级版,但是与poll有很大的区别.
epoll的处理方式是创建一个待处理的事件列表,然后把这个列表发给内核,返回的时候在去轮训检查这个表,以判断事件是否发生,epoll支持一个进程打开的最大事件描述符的上限是系统可以打开的文件的最大数,同时epoll库的I/O效率不随描述符数目增加而线性下降,因为它只会对内核上报的“活跃”的描述符进行操作。
7. Nginx与Apache区别
① 性能和并发处理
Nginx:采用事件驱动的架构,能够高效地处理大量并发连接;在高并发情况下表现出色,占用较少的系统资源
Apache:传统多进程模型,在高并发情况下性能可能受限,消耗较多的系统资源
② 静态内容处理
Nginx:擅长处理静态文件,能够快速、高效地提供静态内容
Apache:在处理静态文件时效率稍低,尤其在高并发环境下表现不如Nginx
③ 动态内容处理
Nginx:对于动态内容的处理相对有限,通常需要结合后端应用服务器(如uWSGI、FastCGI等)来处理动态请求
Apache:擅长处理动态内容,支持多种编程语言和模块,如mod_php、mod_perl等
④ 配置语法和灵活性
Nginx:配置文件语法简洁清晰,支持动态模块加载,允许管理员根据需要进行高度定制
Apache:配置文件相对复杂,但更加灵活,允许管理员通过.htaccess文件进行目录级别的配置
⑤ 虚拟主机支持
Nginx:能够支持虚拟主机配置,但相对Apache的虚拟主机配置更为简洁
Apache:以在同一台服务器上托管多台域名的网站
⑥ 模块和扩展性
Nginx:支持丰富的第三方模块,但相比Apache模块生态系统规模较小
Apache:拥有庞大的模块生态系统,支持广泛的功能和扩展
⑦ 适用场景
Nginx:更适合作为反向代理、负载均衡器以及高性能Web服务器使用
Apache:适合处理动态内容、具有灵活的配置需求,并且需要强大的模块支持的场景
综合来看,Nginx擅长处理高并发、静态内容,以及作为反向代理和负载均衡器;而Apache则更适合处理动态内容、拥有复杂配置需求和强大的模块支持的场景。
二、Nginx部署和使用
1. yum安装
① 使用yum部署Nginx需要先安装epel-release扩展包
[root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release -y #安装epel额外源
[root@localhost ~]# yum install nginx -y #安装nginx② 使用yum安装的nginx配置文件位置在:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf;默认根目录在:/usr/share/nginx/html;默认日志文件在:/var/log/nginx/路径下
2. 编译安装
① 访问官网下载安装包,优先选择偶数版本下载,较为稳定。下载到本地可以使用xshell工具传输到Linux系统中或者使用wget工具复制链接下载。

[root@localhost ~]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
#新建nginx用户便于管理
[root@localhost opt]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz② 安装编译需要的依赖环境和工具,进入对应的目录进行解压编译
[root@localhost opt]# tar xf nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz #解压
[root@localhost opt]# cd nginx-1.24.0/
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE man README src
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# yum install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel -y
#安装依赖包
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# ./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx \
> --user=nginx \
> --group=nginx \
> --with-http_ssl_module \
> --with-http_v2_module \
> --with-http_realip_module \
> --with-http_stub_status_module \
> --with-http_gzip_static_module \
> --with-pcre \
> --with-stream \
> --with-stream_ssl_module \
> --with-stream_realip_module
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# make -j 2 && make install
#2u编译;执行文件安装
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# chown -R nginx.nginx /apps/nginx
#修改权限③ 创建软链接并关闭防火墙
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# ln -s /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/sbin/
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# setenforce 0 ④ 启动关闭nginx查看进程
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 4664 0.0 0.0 20580 616 ? Ss 15:52 0:00 nginx: master process nginx
nobody 4665 0.0 0.0 23108 1372 ? S 15:52 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 4675 0.0 0.0 112824 984 pts/0 S+ 15:53 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#nginx: master主进程
#nginx: worker子进程
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# killall nginx #停止nginx
⑤ 文件夹功能介绍
[root@localhost nginx-1.24.0]# ll /apps/nginx/
总用量 4
drwxr-xr-x. 2 nginx nginx 4096 2月 20 16:36 conf
drwxr-xr-x. 2 nginx nginx 40 2月 20 16:36 html
drwxr-xr-x. 2 nginx nginx 58 2月 20 16:43 logs
drwxr-xr-x. 2 nginx nginx 19 2月 20 16:36 sbin- conf:保存nginx所有的配置文件,其中nginx.conf是nginx服务器的最核心最主要的配置文件,其他的.conf则是用来配置nginx相关的功能的,例如fastcgi功能使用的是fastcgi.conf和fastcgi_params两个文件,配置文件一般都有个样板配置文件,是文件名.default结尾,使用的使用将其复制为并将default去掉即可。
- html目录中保存了nginx服务器的web文件,但是可以更改为其他目录保存web文件,另外还有一个50x的web文件是默认的错误页面提示页面。
- logs:用来保存nginx服务器的访问日志错误日志等日志,logs目录可以放在其他路径,比如/var/logs/nginx里面。
- sbin:保存nginx二进制启动脚本,可以接受不同的参数以实现不同的功能。
3. 创建Nginx 自启动文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=nginx - high performance web server
Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/
After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/apps/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
#注意文件位置,如果不对 启动不了
ExecStart=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#注意启动文件位置
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID
LimitNOFILE=100000
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
#重新加载配置
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable --now nginx
#开机自启并立即启动
4. 信号使用命令及平滑升级
4.1 信号
nginx 命令支持向其发送信号,实现不同功能;nginx 当做单独命令使用有以下选项:
| 选项 | 说明 |
| nginx -?,-h | 帮助 |
| nginx -v | 显示版本号 |
| nginx -V | 查看安装了哪些模块 |
| nginx -t | 测试配置文件是否有语法错误 |
| nginx -s | 发送信号 后面可以跟stop、reload、quit、reopen |
| nginx -p | 指定运行目录 |
| nginx -c | 使用指定的配置文件 |
| nginx -g | 指定配置指令 |
① 显示版本号
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.24.0② 显示编译详细情况 模块等信息
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.24.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module③ 发送信号
[root@localhost ~]# pstree -p | grep nginx
|-nginx(5367)---nginx(5368)
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s stop #立即关闭nginx
[root@localhost ~]# pstree -p | grep nginx
[root@localhost ~]#
nginx -s quit #优雅退出,不影响业务的状态下退出
nginx -s reload #重新加载
USR1分割日志:
192.168.190.100:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@localhost ~]# cd /apps/nginx/logs/
[root@localhost logs]# ls
access.log error.log nginx.pid
[root@localhost logs]# ll | grep access.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 2月 20 16:41 access.log
19.168.190.101:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.190.100
192.168.190.100:
[root@localhost logs]# ll | grep access.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 92 2月 20 18:04 access.log #产生日志
192.168.190.100:
[root@localhost logs]# mv access.log access.log.bak
[root@localhost logs]# touch access.log
[root@localhost logs]# ls
access.log access.log.bak error.log nginx.pid
[root@localhost logs]# ll | grep access.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 2月 20 18:07 access.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 92 2月 20 18:04 access.log.bak
[root@localhost logs]# nginx -s reopen
#重新打开日志文件,否则依然写入.bak,或者kill -s USR1 主进程号
192.168.190.101:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.190.100
192.168.1901.100:
[root@localhost logs]# ll | grep access.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 nginx root 92 2月 20 18:11 access.log #此时日志已写入新文件
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 92 2月 20 18:04 access.log.bak④ 指定配置,不以配置文件中的为准
[root@localhost ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
3 #worker_processes 1; #避免冲突注释此行
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -g 'worker_processes 2;'
[root@localhost ~]# pstree -p | grep nginx
|-nginx(6068)-+-nginx(6069)
| `-nginx(6070)
⑤ 检查语法格式
nginx -t5. 热升级nginx1.18至nginx1.20
① 修改配置文件nginx.conf
[root@localhost sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
#先查看是否开启nginx
[root@localhost ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 2;
#开启双核,最大性能为8核
[root@localhost ~]#nginx -s reload
#重新加载配置文件
[root@localhost ~]#ps aux | grep nginx
#查看多了一个worker进程② 下载新版本安装包,重新编译安装
[root@localhost ~]#wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz -P /usr/local/src/
#下载安装包到/usr/local/src/目录
[root@localhost ~]#cd /usr/local/src/
[root@localhost src]#ls
nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]#tar xf nginx-1.20.2.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]#cd nginx-1.20.2/
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]#ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE man README src
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# ./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
#重新编译
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE Makefile man objs README src
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# make
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# cd objs/
#此文件夹中有新版本的nginx运行程序
[root@localhost objs]# ls
autoconf.err Makefile nginx nginx.8 ngx_auto_config.h ngx_auto_headers.h ngx_modules.c ngx_modules.o src
[root@localhost objs]# ./nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.20.2
#查看版本③ 拷贝新版本至原安装路径
[root@localhost objs]# mv /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx.bak
#将低版本的nginx主程序改名
[root@localhost objs]# cp nginx /apps/nginx/sbin/
#将新版本拷入原安装路径
[root@localhost objs]# cd /apps/nginx/sbin/
[root@localhost sbin]# ls
nginx nginx.bak
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# ll /apps/nginx/sbin/
总用量 15308
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 7896080 2月 20 21:15 nginx
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 nginx nginx 7774624 2月 20 20:52 nginx.bak
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.20.2
#nginx文件为新版本
[root@localhost sbin]# /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
#检查下语法问题④ 生成新进程
[root@localhost nginx-1.20.2]# kill -USR2 `cat /apps/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`
#发送 2 信号
[root@localhost sbin]# pstree -p | grep nginx
|-nginx(5073)-+-nginx(8717)-+-nginx(8718)
| | `-nginx(8719)
| |-nginx(5623)
| `-nginx(5624)
[root@localhost sbin]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 5073 0.0 0.1 46344 2020 ? Ss 22:33 0:00 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginx 5623 0.0 0.1 48856 2092 ? S 22:37 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 5624 0.0 0.1 48856 2084 ? S 22:37 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 8717 0.0 0.1 46220 3368 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginx 8718 0.0 0.1 48756 1992 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 8719 0.0 0.1 48756 1992 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: worker process
#生成新的master8717
[root@localhost ~]# cd /apps/nginx/logs
[root@localhost logs]# ls
access.log error.log nginx.pid nginx.pid.oldbin
[root@localhost logs]# cat nginx.pid
8717 #新的master进程
[root@localhost logs]# cat nginx.pid.oldbin
5073 #旧的master进程⑤ 优雅的退出旧进程,不影响真正使用的用户
192.168.190.102:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /apps/nginx/html
[root@localhost html]# ls
50x.html index.html
#会有新老两个进程
[root@localhost html]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/apps/nginx/html/m.img bs=1G count=10
#生成大文件
[root@localhost html]# ll -h
总用量 1.1G
-rw-r--r--. 1 nginx nginx 494 2月 20 20:52 50x.html
-rw-r--r--. 1 nginx nginx 612 2月 20 20:52 index.html
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1.0G 2月 20 22:06 m.img
192.168.190.101:
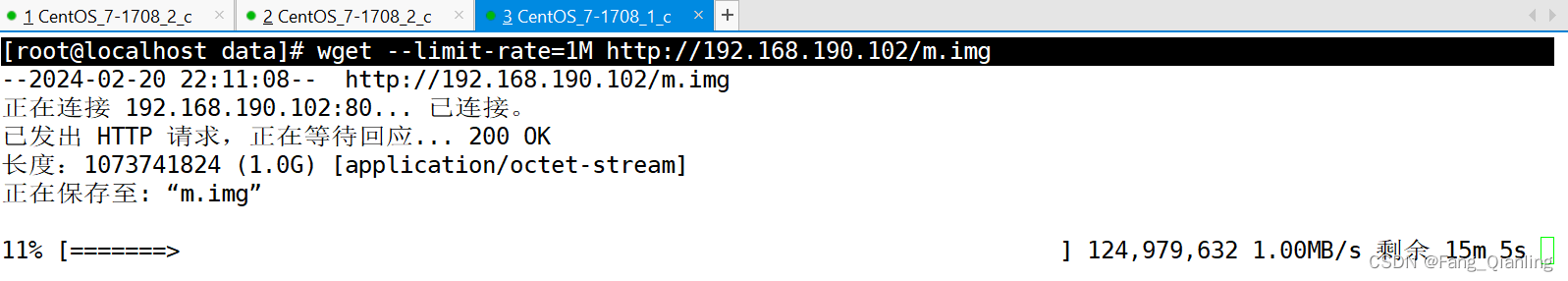
[root@localhost data]# wget --limit-rate=1M http://192.168.190.102/m.img
#下载文件
192.168.190.102:
[root@localhost html]# kill -WINCH `cat /apps/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin`
#优雅关闭旧进程的worker进程,此时旧进程不会再接收新的任务,后期可以直接退出
192.168.190.101:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.190.102 -I
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.20.2
#新版本接替接收任务,即升级成功
优雅关闭旧进程的worker进程,查看是否影响当前任务:
注意:当旧进程任务结束后可以优雅的退出: kill -quit 旧master pid;或者直接关闭:kill 旧master pid;或者此时将无法回滚。
6. 回滚
当发现新版本有异常,可以通过回滚解决。
① 查看当前worker进程
[root@localhost ~]# pstree -p | grep nginx
|-nginx(5073)---nginx(8717)-+-nginx(8718)
| `-nginx(8719)
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 5073 0.0 0.1 46344 2020 ? Ss 22:33 0:00 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
root 8717 0.0 0.1 46220 3368 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginx 8718 0.0 0.1 48756 1992 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 8719 0.0 0.1 48756 1992 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: worker process
#旧的两个worker进程已关闭
② 唤醒旧进程
[root@localhost ~]# pstree -p | grep nginx
|-nginx(5073)-+-nginx(8717)-+-nginx(8718)
| | `-nginx(8719)
| |-nginx(8786)
| `-nginx(8787)
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | grep -v grep | grep nginx
root 5073 0.0 0.1 46344 2052 ? Ss 22:33 0:00 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
root 8717 0.0 0.1 46220 3368 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginx 8718 0.0 0.1 48756 1992 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 8719 0.0 0.1 48756 1992 ? S 22:43 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 8786 0.0 0.1 48856 2120 ? S 22:49 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 8787 0.0 0.1 48856 2120 ? S 22:49 0:00 nginx: worker process
#此时查旧的两个worker进程恢复③ 修改nginx.bak文件名回滚版本
192.168.190.102:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /apps/nginx/sbin/
[root@localhost sbin]# ls
nginx nginx.bak
#这里的nginx版本为1.20.2,nginx.bak版本为1.18.0
[root@localhost sbin]# mv nginx nginx.1.20.2
[root@localhost sbin]# mv nginx.bak nginx
[root@localhost sbin]# systemctl start nginx
192.168.190.100:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.190.102 -I
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.18.0
#已回滚至1.18.0