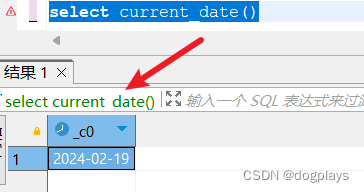
4.5线性回归
线性回归是解决回归问题的常用模型。
实例:简单线性回归
def skLearn13():
'''
线性回归
:return:
'''
#简单的一元一次方程
#斜率为a,截距为b
#y=ax+b
#创建线性数据
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
x = 10 * rng.rand(50)
y = 2*x - 5 + rng.randn(50)
#绘制数据集
plt.scatter(x,y)
#使用线性回归模型
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
#拟合数据
model.fit(x[:,np.newaxis],y)
#获取训练的斜率和截距
print(model.coef_)
print(model.intercept_)
#构建测试数据
xtest = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
ymodel = model.predict(xtest[:,np.newaxis])
#绘制预测线
plt.plot(xtest,ymodel)
#显示图片
plt.show()
实例2:多项式基函数
将线性回归模型转换为非线性回归模型。
y=a0+a1x1+a2x2+a3x3………
将一个变量x,转换为多维的x1,x2,x3等;
def skLearn14():
'''
多项式基函数
:return:
'''
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
x = np.array([2,3,4])
print(x)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(3,include_bias=False)
#转换为多维数据
#获取1,2,3次方数据矩阵
x_trans = poly.fit_transform(x[:,np.newaxis])
print(x_trans)
#使用管道,组合多个操作
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
#使用5次方多项式
model = make_pipeline(PolynomialFeatures(5),LinearRegression())
#构建数据
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
x_data = rng.rand(50) * 10
y_data = np.sin(x_data) + 0.2 * rng.randn(50)
#拟合数据
model.fit(x_data[:,np.newaxis],y_data)
#预测数据
x_test = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
y_model = model.predict(x_test[:,np.newaxis])
#绘制数据图及预测图
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data)
plt.plot(x_test,y_model)
#显示图片
plt.show()
实例3:正则化
当基函数过于灵活,相邻基函数相互影响会导致模型过拟合。为了抑制模型波动,引入正则化机制。常用的正则化:岭回归;Lasso正则化
注意:Lasso倾向于构建稀疏矩阵,将模型系数置为0,所以效果差异大。
def skLearn15():
'''
正则化,避免多项式次数过多导致过拟合
:return:
'''
#使用管道,组合多个操作
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
#使用5次方多项式
model = make_pipeline(PolynomialFeatures(10),LinearRegression())
#构建数据
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
x_data = rng.rand(50) * 30
y_data = np.sin(x_data) + 0.2 * rng.randn(50)
#拟合数据
model.fit(x_data[:,np.newaxis],y_data)
#预测数据
x_test = np.linspace(0,30,1000)
y_model = model.predict(x_test[:,np.newaxis])
#使用岭回归
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
model_rid = make_pipeline(PolynomialFeatures(10),Ridge(alpha=0.1))
#拟合数据
model_rid.fit(x_data[:,np.newaxis],y_data)
#测试数据
y_model_rid = model_rid.predict(x_test[:,np.newaxis])
#使用Lasso正则化
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
model_lasso = make_pipeline(PolynomialFeatures(10),Lasso(alpha=0.001))
#拟合数据
model_lasso.fit(x_data[:,np.newaxis],y_data)
#测试数据
y_model_lasso = model_lasso.predict(x_test[:,np.newaxis])
#绘制数据图及预测图
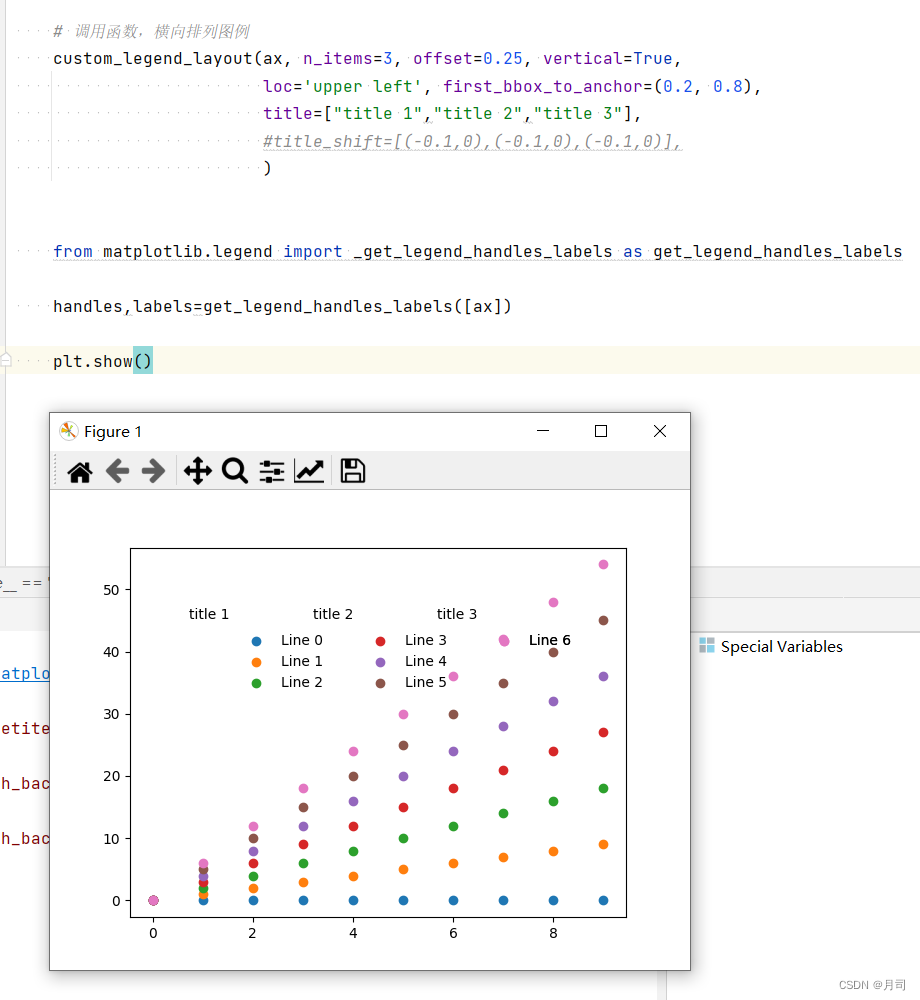
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data)
plt.plot(x_test,y_model,label='base line',color='k')
plt.plot(x_test,y_model_rid,label='rid line',color='g')
plt.plot(x_test,y_model_lasso,label='lasso line',color='r')
plt.legend()
#显示图片
plt.show()






![[创业之路-88/管理者与领导者-128]:企业运行分层模型、研发管理全视野](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f8afbb0f6ca34aec89f4079f1a12e00c.png)