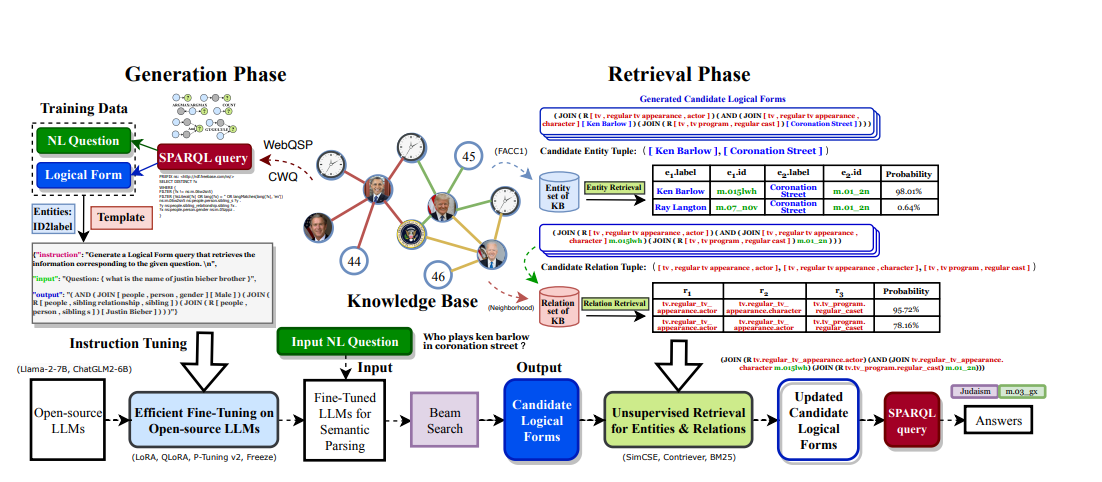
一、VFH特征识别
C++
recognize_objects.h
#pragma once
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/common/common.h>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/console/print.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/features/vfh.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <boost/filesystem.hpp>
#include <flann/flann.h>
#include <flann/io/hdf5.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/algorithm/string/replace.hpp>
// Define vfh_model type for storing data file name and histogram data
typedef std::pair<std::string, std::vector<float> > vfh_model;
// This function estimates VFH signatures of an input point cloud
// Input: File path
// Output: VFH signature of the object
void estimate_VFH(const boost::filesystem::path& path, pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308>& signature)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>());
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>(path.string(), *cloud) == -1) //* load the file
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file %s \n", path.string());
return;
}
// Estimate point cloud normals
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr normalTree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);
ne.setSearchMethod(normalTree);
ne.setRadiusSearch(0.03);
ne.compute(*normals);
// Estimate VFH signature of the point cloud
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::VFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::VFHSignature308> vfh;
vfh.setInputCloud(cloud);
vfh.setInputNormals(normals);
vfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
vfh.compute(signature);
}
// This function checks if the file already contains a VFH signature
// Input: File path
// Output: true if file contains VFH signature, false if file does not contain VFH signature
bool checkVFH(const boost::filesystem::path& path)
{
int vfh_idx;
try
{
// Read point cloud header
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin;
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type; unsigned int idx;
r.readHeader(path.string(), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);
// Check if there is VFH field in the cloud header
vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex(cloud, "vfh");
if (vfh_idx == -1)
return (false);
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != 1)
return (false);
}
catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&)
{
return (false);
}
return (true);
}
// This function loads VFH signature histogram into a vfh model
// Input: File path
// Output: A boolean that returns true if the histogram is loaded successfully and a vfh_model data that holds the histogram information
bool loadHist(const boost::filesystem::path& path, vfh_model& vfh)
{
int vfh_idx;
// Read file header to check if the file contains VFH signature
try
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin;
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type; unsigned int idx;
r.readHeader(path.string(), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);
vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex(cloud, "vfh");
if (vfh_idx == -1)
{
return (false);
}
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != 1)
return (false);
}
catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&)
{
return (false);
}
// Treat the VFH signature as a single Point Cloud and load data from it
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> point;
pcl::io::loadPCDFile(path.string(), point);
vfh.second.resize(308);
std::vector <pcl::PCLPointField> fields;
pcl::getFieldIndex(point, "vfh", fields);
// Fill vfh_model.second with histogram data
for (size_t i = 0; i < fields[vfh_idx].count; ++i)
{
vfh.second[i] = point.points[0].histogram[i];
}
// Put file path in vfh_model.first
vfh.first = path.string();
return (true);
}
// This gets PCD file names from a directory and passes them to histogram loader one by one
// then pushes the results into a vfh_model vector to keep them in a data storage
// Input: Training data set file path
// Output: A vfh_model vector that contains all VFH signature information
void loadData(const boost::filesystem::path& base_dir, std::vector<vfh_model>& models)
{
if (!boost::filesystem::exists(base_dir) && !boost::filesystem::is_directory(base_dir))
return;
else
{
// Iterate through the data set directory to read VFH signatures
for (boost::filesystem::directory_iterator i(base_dir); i != boost::filesystem::directory_iterator(); i++)
{
// If read path is a directory, then print path name on console and call data loader again
if (boost::filesystem::is_directory(i->status()))
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << i->path();
pcl::console::print_highlight("Loading %s (%lu models loaded so far).\n", ss.str().c_str(), (unsigned long)models.size());
loadData(i->path(), models);
}
// If read path is a file with *.pcd extension, then check if it contains VFH signature
// If not, then estimate VFH signature of it
// Either way, pass the file to histogram loader since it can differentiate between files with VFH signatures and files without them
if (boost::filesystem::is_regular_file(i->status()) && boost::filesystem::extension(i->path()) == ".pcd")
{
vfh_model m;
std::string str = i->path().string();
if (!checkVFH(str))
{
str.replace(str.find(".pcd"), 4, "_vfh.pcd");
if (!boost::filesystem::exists(str))
{
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> signature;
estimate_VFH(i->path().string(), signature);
pcl::io::savePCDFile(str, signature);
}
}
if (loadHist(i->path().string(), m))
{
models.push_back(m);
std::cout << m.first << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
}
// This function visualizes given k point cloud arguments on a PCL_Viewer
// It shows distances of candidates from the query object at the left bottom corner of each window
// If the distance is smaller than a given threshold then the distances are shown in green, else they are shown in red
// Inputs: Main function arguments, candidate count (k), threshold value, vfh_model vector that contains VFH signatures
// from the data set, indices of candidates and distances of candidates
void visualize(int argc, char** argv, int k, double thresh, std::vector<vfh_model> models, flann::Matrix<int> k_indices, flann::Matrix<float> k_distances)
{
// Load the results
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer p(argc, argv, "VFH Cluster Classifier");
int y_s = (int)floor(sqrt((double)k));
int x_s = y_s + (int)ceil((k / (double)y_s) - y_s);
double x_step = (double)(1 / (double)x_s);
double y_step = (double)(1 / (double)y_s);
pcl::console::print_highlight("Preparing to load ");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", k);
pcl::console::print_info(" files (");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", x_s);
pcl::console::print_info("x");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", y_s);
pcl::console::print_info(" / ");
pcl::console::print_value("%f", x_step);
pcl::console::print_info("x");
pcl::console::print_value("%f", y_step);
pcl::console::print_info(")\n");
int viewport = 0, l = 0, m = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
std::string cloud_name = models.at(k_indices[0][i]).first;
boost::replace_last(cloud_name, "_vfh", "");
p.createViewPort(l * x_step, m * y_step, (l + 1) * x_step, (m + 1) * y_step, viewport);
l++;
if (l >= x_s)
{
l = 0;
m++;
}
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
pcl::console::print_highlight(stderr, "Loading "); pcl::console::print_value(stderr, "%s ", cloud_name.c_str());
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(cloud_name, cloud) == -1)
break;
// Convert from blob to PointCloud
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_xyz;
pcl::fromPCLPointCloud2(cloud, cloud_xyz);
if (cloud_xyz.points.size() == 0)
break;
pcl::console::print_info("[done, ");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", (int)cloud_xyz.points.size());
pcl::console::print_info(" points]\n");
pcl::console::print_info("Available dimensions: ");
pcl::console::print_value("%s\n", pcl::getFieldsList(cloud).c_str());
// Demean the cloud
Eigen::Vector4f centroid;
pcl::compute3DCentroid(cloud_xyz, centroid);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_xyz_demean(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::demeanPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_xyz, centroid, *cloud_xyz_demean);
// Add to renderer*
p.addPointCloud(cloud_xyz_demean, cloud_name, viewport);
// Check if the model found is within our inlier tolerance
std::stringstream ss;
ss << k_distances[0][i];
if (k_distances[0][i] > thresh)
{
p.addText(ss.str(), 20, 30, 1, 0, 0, ss.str(), viewport); // display the text with red
// Create a red line
pcl::PointXYZ min_p, max_p;
pcl::getMinMax3D(*cloud_xyz_demean, min_p, max_p);
std::stringstream line_name;
line_name << "line_" << i;
p.addLine(min_p, max_p, 1, 0, 0, line_name.str(), viewport);
p.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_LINE_WIDTH, 5, line_name.str(), viewport);
}
else
p.addText(ss.str(), 20, 30, 0, 1, 0, ss.str(), viewport);
// Increase the font size for the score*
p.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_FONT_SIZE, 18, ss.str(), viewport);
// Add the cluster name
p.addText(cloud_name, 20, 10, cloud_name, viewport);
}
// Add coordinate systems to all viewports
p.addCoordinateSystem(0.1, "global", 0);
p.spin();
}
// This function finds the k nearest neighbors of the query object and returns their indices in the K-d tree and distances from the query object
// Inputs: K-d tree, query object model, desired candidate count (k)
// Outputs: K-d tree indices of candidates, Distances of candidates from the query object
inline void nearestKSearch(flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> >& index, const vfh_model& model,
int k, flann::Matrix<int>& indices, flann::Matrix<float>& distances)
{
// Query point
flann::Matrix<float> p = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[model.second.size()], 1, model.second.size());
memcpy(&p.ptr()[0], &model.second[0], p.cols * p.rows * sizeof(float));
indices = flann::Matrix<int>(new int[k], 1, k);
distances = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[k], 1, k);
index.knnSearch(p, indices, distances, k, flann::SearchParams(512));
delete[] p.ptr();
}recognize_objects.cpp
#include "recognize_objects.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int k = 6;
double thresh = DBL_MAX;
std::string model_dir = "vfh_training_data";
std::string inputname = "pcd/pig_view1.pcd";
std::vector<vfh_model> models;
flann::Matrix<int> k_indices;
flann::Matrix<float> k_distances;
/*if (argc < 2) {
PCL_ERROR("Usage: %s [-i <inputname>] [-m <model_dir>] [-k <neighbors>] [-t <threshold>]\n", argv[0]);
return(-1);
}*/
// Parse console inputs
/*pcl::console::parse_argument(argc, argv, "-i", inputname);
pcl::console::parse_argument(argc, argv, "-m", model_dir);
pcl::console::parse_argument(argc, argv, "-k", k);
pcl::console::parse_argument(argc, argv, "-t", thresh);*/
vfh_model histogram;
std::string str = inputname;
// Check if the query object has VFH signature, if not estimate signature and save it in a file
if (!checkVFH(inputname))
{
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> signature;
estimate_VFH(str, signature);
str.replace(str.find(".pcd"), 4, "_vfh.pcd");
pcl::io::savePCDFile(str, signature);
}
// Load VFH signature of the query object
if (!loadHist(str, histogram))
{
pcl::console::print_error("Cannot load test file %s\n", inputname);
return (-1);
}
// Load training data
loadData(model_dir, models);
// Convert data into FLANN format
flann::Matrix<float> data(new float[models.size() * models[0].second.size()], models.size(), models[0].second.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < data.rows; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j < data.cols; ++j)
data[i][j] = models[i].second[j];
// Place data in FLANN K-d tree
flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > index(data, flann::LinearIndexParams());
index.buildIndex();
// Search for query object in the K-d tree
nearestKSearch(index, histogram, k, k_indices, k_distances);
// Print closest candidates on the console
std::cout << "The closest " << k << " neighbors for " << inputname << " are: " << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
pcl::console::print_info(" %d - %s (%d) with a distance of: %f\n",
i, models.at(k_indices[0][i]).first.c_str(), k_indices[0][i], k_distances[0][i]);
// Visualize closest candidates on the screen
visualize(argc, argv, k, thresh, models, k_indices, k_distances);
return 0;
}编译过程的问题:
PCL中有1个位置有一个bug以及c++17已经抛弃了的两处STL函数,会提示错误,这时,需要修改后才能通过编译。(以下都是我自己的文件路径)
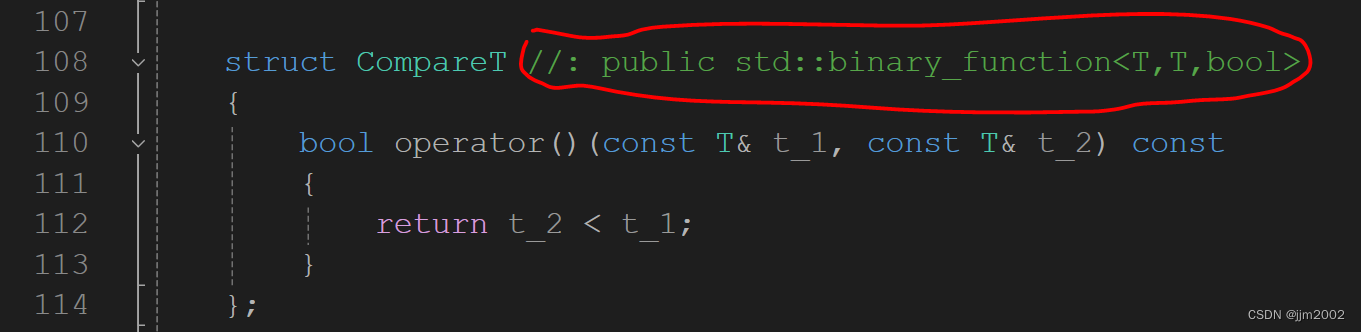
1.文件路径:C:\Compiler\PCL\PCL 1.14.0\3rdParty\FLANN\include\flann\algorithms\dist.h
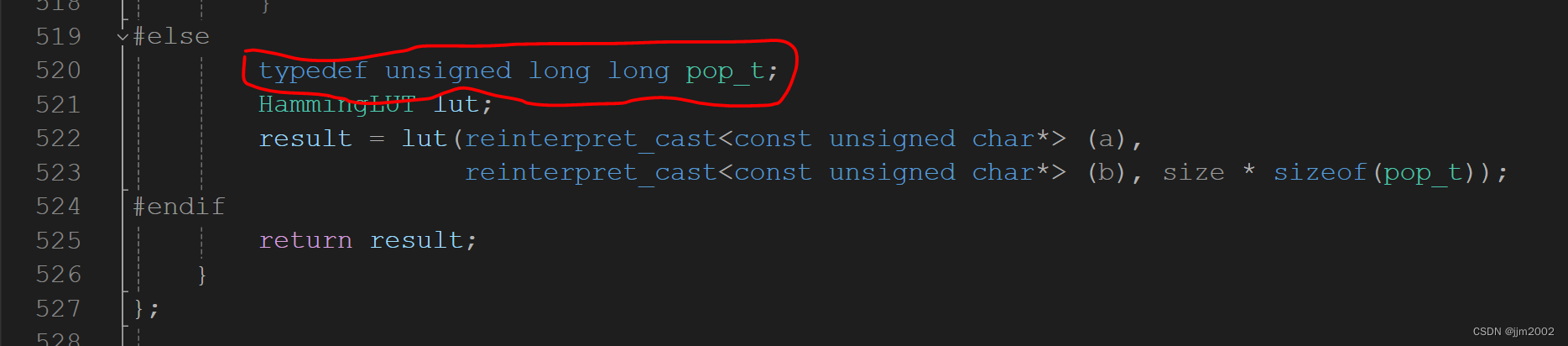
2.文件路径:C:\Compiler\PCL\PCL 1.14.0\3rdParty\FLANN\include\flann\util\heap.h
这里注释掉
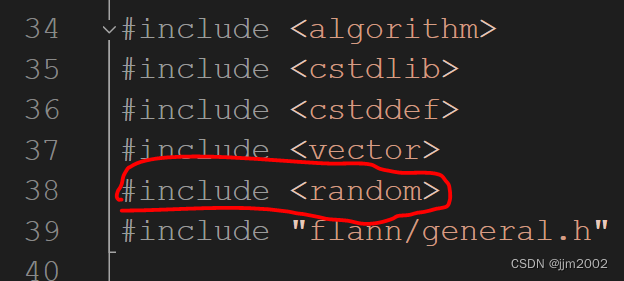
3.文件路径:C:\Compiler\PCL\PCL 1.14.0\3rdParty\FLANN\include\flann\util\random.h
增加头文件:
注释掉:
std::random_shuffle(vals_.begin(), vals_.end(), generator);增加:
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 g(rd());
std::shuffle(vals_.begin(), vals_.end(), g);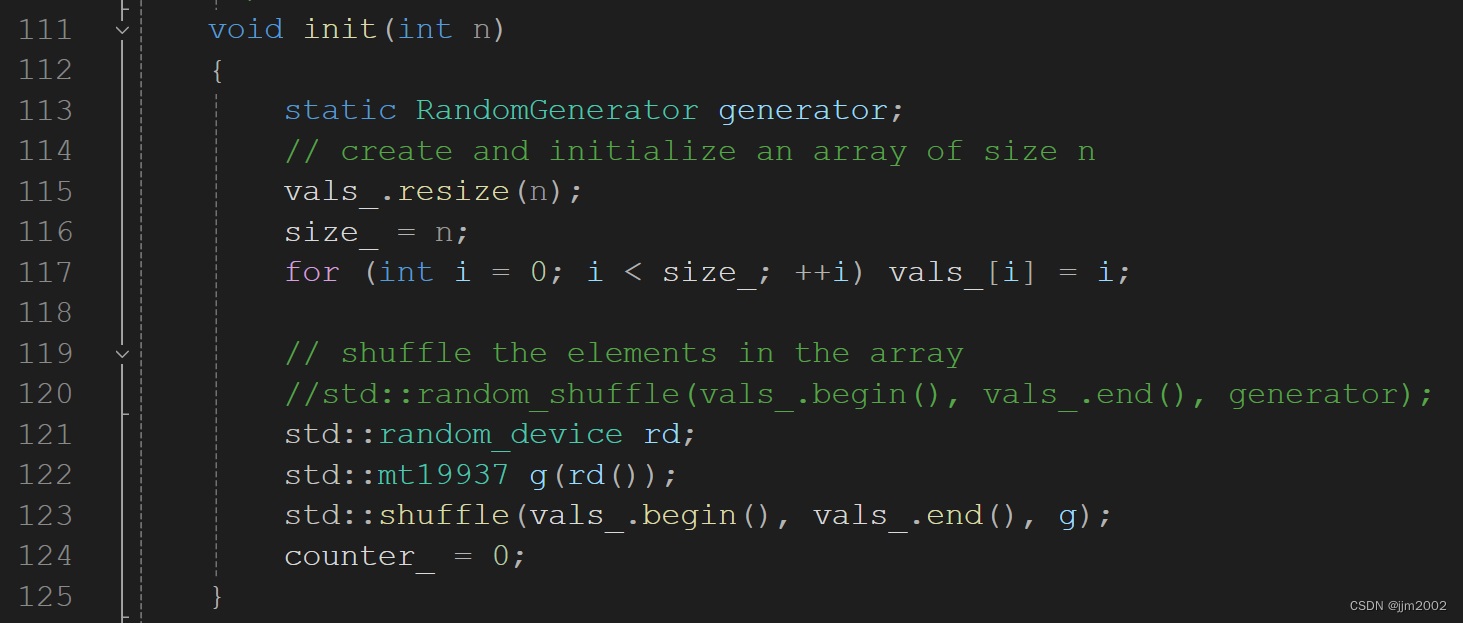
4.文件路径:C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include\flann\algorithms\kdtree_index.h
增加头文件:
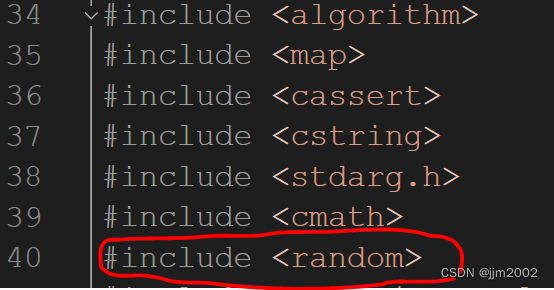
for循环上面增加 :
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 g(rd());for循环里面增加 :
std::shuffle(vals_.begin(), vals_.end(), g);for循环里面注释 :
std::random_shuffle(ind.begin(), ind.end());
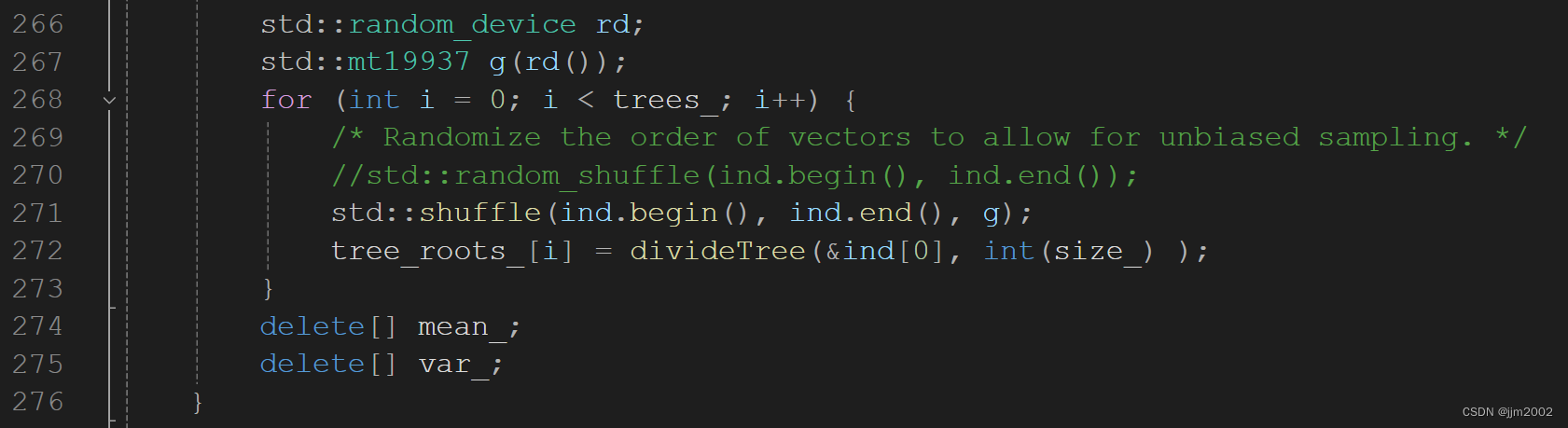
5.文件路径:C:\PCL1.12.1\3rdParty\FLANN\include\flann\util\lsh_table.h
增加头文件:
注释掉:
std::random_shuffle(indices.begin(), indices.end());
增加:
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 g(rd());
std::shuffle(indices.begin(), indices.end(), g);
6.安装HDF5
官网网址:Download HDF5® - The HDF Group
如果网速太慢,我这里有下载好的HDF5的C++安装包资源-CSDN文库
解压之后:
双击运行 ,基本上一直下一步就行了,中间有一步可以修改安装路径,安装完成。
在visual studio22里找到你之前配置好PCL环境的项目,而且已经放入我上述 recognize_objects.cpp和 recognize_objects.h,然后在该项目的包含目录里增加C:\Compiler\Format\HDF5\include,库目录里增加C:\Compiler\Format\HDF5\lib,附加依赖项增加hdf5.lib和hdf5_cpp.lib
7.完成上述步骤之后就可以运行了
关键代码解析:
typedef std::pair<std::string, std::vector<float> > vfh_model;
void estimate_VFH(const boost::filesystem::path& path, pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308>& signature)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>());
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>(path.string(), *cloud) == -1) //* load the file
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file %s \n", path.string());
return;
}
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr normalTree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);
ne.setSearchMethod(normalTree);
ne.setRadiusSearch(0.03);
ne.compute(*normals);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::VFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::VFHSignature308> vfh;
vfh.setInputCloud(cloud);
vfh.setInputNormals(normals);
vfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
vfh.compute(signature);
}
bool checkVFH(const boost::filesystem::path& path)
{
int vfh_idx;
try
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin;
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type; unsigned int idx;
r.readHeader(path.string(), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);
vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex(cloud, "vfh");
if (vfh_idx == -1)
return (false);
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != 1)
return (false);
}
catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&)
{
return (false);
}
return (true);
}-
typedef std::pair<std::string, std::vector<float> > vfh_model;: 定义了一个vfh_model类型,它是一个包含字符串和浮点数向量的 pair,用于表示 VFH 特征模型。 -
void estimate_VFH(const boost::filesystem::path& path, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308>& signature): 这是一个函数,用于估计输入点云的 VFH 特征。-
const boost::filesystem::path& path: 输入参数,表示点云文件的路径。 -
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308>& signature: 输出参数,存储计算得到的 VFH 特征。 -
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);: 创建一个指向点云的智能指针cloud,用于存储加载的点云数据。 -
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>());: 创建一个指向法线的智能指针normals,用于存储估计的法线信息。 -
pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>(path.string(), *cloud) == -1: 通过 PCL 加载点云文件,如果加载失败则输出错误信息。 -
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;: 创建法线估计对象ne。 -
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);: 设置法线估计的输入点云。 -
ne.setSearchMethod(normalTree);: 设置法线估计的搜索方法,这里使用了 KD 树。 -
ne.setRadiusSearch(0.03);: 设置法线估计的搜索半径。 -
ne.compute(*normals);: 计算法线并存储在normals中。 -
pcl::VFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::VFHSignature308> vfh;: 创建 VFH 估计对象vfh。 -
vfh.setInputCloud(cloud);: 设置 VFH 估计的输入点云。 -
vfh.setInputNormals(normals);: 设置 VFH 估计的输入法线。 -
vfh.setSearchMethod(tree);: 设置 VFH 估计的搜索方法,这里同样使用了 KD 树。 -
vfh.compute(signature);: 计算 VFH 特征并存储在signature中。
-
-
bool checkVFH(const boost::filesystem::path& path): 这是一个函数,用于检查点云文件是否包含 VFH 特征。-
const boost::filesystem::path& path: 输入参数,表示点云文件的路径。 -
int vfh_idx;: 存储 VFH 特征的字段索引。 -
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;: 存储点云数据的 PCLPointCloud2 对象。 -
pcl::PCDReader r;: 创建 PCD 读取对象r。 -
r.readHeader(path.string(), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);: 读取点云文件的头信息。 -
vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex(cloud, "vfh");: 获取 VFH 特征的字段索引。 -
if (vfh_idx == -1) return (false);: 如果 VFH 特征索引为 -1,表示未找到 VFH 特征字段,返回 false。 -
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != 1) return (false);: 如果点云数据不是单帧(width * height 不等于 1),返回 false。 -
return (true);: 如果以上条件都满足,返回 true,表示点云包含 VFH 特征。
-
这些函数主要用于加载点云、估计 VFH 特征以及检查点云是否包含 VFH 特征。参数的设置主要包括法线估计的搜索半径、VFH 估计的搜索方法等,这些参数的选择需要根据点云数据的性质和具体应用场景进行调整。例如,搜索半径的大小会影响法线和 VFH 特征的计算精度,需要根据点云的密度和噪声程度来确定。
bool loadHist(const boost::filesystem::path& path, vfh_model& vfh)
{
int vfh_idx;
try
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
int version;
Eigen::Vector4f origin;
Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;
pcl::PCDReader r;
int type; unsigned int idx;
r.readHeader(path.string(), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);
vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex(cloud, "vfh");
if (vfh_idx == -1)
{
return (false);
}
if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != 1)
return (false);
}
catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&)
{
return (false);
}
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> point;
pcl::io::loadPCDFile(path.string(), point);
vfh.second.resize(308);
std::vector <pcl::PCLPointField> fields;
pcl::getFieldIndex(point, "vfh", fields);
for (size_t i = 0; i < fields[vfh_idx].count; ++i)
{
vfh.second[i] = point.points[0].histogram[i];
}
vfh.first = path.string();
return (true);
}这段代码是一个函数,名为 loadHist,其目的是从指定路径加载包含 VFH(Viewpoint Feature Histogram)数据的点云文件,并将加载的数据存储到自定义结构 vfh_model 中。下面是对代码的逐行解析:
-
函数签名:
bool loadHist(const boost::filesystem::path& path, vfh_model& vfh)
-
参数:
path:类型为boost::filesystem::path的引用,表示点云文件的路径。vfh:类型为vfh_model的引用,用于存储加载后的 VFH 数据。
-
函数体:
int vfh_idx;:声明了一个整型变量vfh_idx,用于存储 VFH 字段在点云数据中的索引。try { ... } catch (const pcl::InvalidConversionException&) { ... }:使用try-catch块捕获可能的异常,包括文件读取过程中的无效转换异常。如果出现异常,函数将返回false。pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;:声明了一个pcl::PCLPointCloud2类型的变量cloud,用于存储点云数据。int version;、Eigen::Vector4f origin;、Eigen::Quaternionf orientation;、int type;、unsigned int idx;:声明了一些其他变量,用于存储点云数据的版本、原点、方向、类型等信息。r.readHeader(path.string(), cloud, origin, orientation, version, type, idx);:使用 PCL 中的readHeader函数读取点云文件的头部信息,并将信息存储到相应的变量中。vfh_idx = pcl::getFieldIndex(cloud, "vfh");:获取 VFH 字段在点云数据中的索引,并存储到vfh_idx中。if (vfh_idx == -1) { return false; }:如果 VFH 字段在点云数据中不存在,则返回false。if ((int)cloud.width * cloud.height != 1) return false;:确保点云数据是一维的,即宽度乘以高度等于 1。如果不是,则返回false。pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308> point;:声明了一个类型为pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308>的点云变量point,用于存储加载的点云数据。pcl::io::loadPCDFile(path.string(), point);:使用 PCL 中的loadPCDFile函数加载点云文件到point变量中。vfh.second.resize(308);:调整vfh结构体中的second成员的大小为 308,以存储 VFH 数据。std::vector<pcl::PCLPointField> fields;:声明了一个std::vector类型的变量fields,用于存储点云数据的字段信息。pcl::getFieldIndex(point, "vfh", fields);:获取 VFH 字段的信息,并存储到fields变量中。for (size_t i = 0; i < fields[vfh_idx].count; ++i) { vfh.second[i] = point.points[0].histogram[i]; }:遍历 VFH 字段中的直方图数据,将其存储到vfh结构体的second成员中。vfh.first = path.string();:将点云文件的路径存储到vfh结构体的first成员中。return true;:返回true,表示加载成功。
-
参数设置及影响:
path参数用于指定点云文件的路径。调用该函数时,需要提供有效的点云文件路径。vfh参数用于存储加载后的 VFH 数据。调用该函数时,需要传递一个vfh_model类型的变量的引用,以便在函数内部存储加载后的数据。
-
影响:
- 如果加载成功,函数会将点云文件中的 VFH 数据存储到
vfh结构体中,并返回true。 - 如果加载失败(例如,无法读取文件、文件中不存在 VFH 数据等),则函数将返回
false。
- 如果加载成功,函数会将点云文件中的 VFH 数据存储到
void loadData(const boost::filesystem::path& base_dir, std::vector<vfh_model>& models)
{
if (!boost::filesystem::exists(base_dir) && !boost::filesystem::is_directory(base_dir))
return;
else
{
for (boost::filesystem::directory_iterator i(base_dir); i != boost::filesystem::directory_iterator(); i++)
{
if (boost::filesystem::is_directory(i->status()))
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << i->path();
pcl::console::print_highlight("Loading %s (%lu models loaded so far).\n", ss.str().c_str(), (unsigned long)models.size());
loadData(i->path(), models);
}
if (boost::filesystem::is_regular_file(i->status()) && boost::filesystem::extension(i->path()) == ".pcd")
{
vfh_model m;
std::string str = i->path().string();
if (!checkVFH(str))
{
str.replace(str.find(".pcd"), 4, "_vfh.pcd");
if (!boost::filesystem::exists(str))
{
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> signature;
estimate_VFH(i->path().string(), signature);
pcl::io::savePCDFile(str, signature);
}
}
if (loadHist(i->path().string(), m))
{
models.push_back(m);
std::cout << m.first << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
}
base_dir:这是一个boost::filesystem::path类型的引用,表示要加载数据的基本目录。models:这是一个std::vector<vfh_model>类型的引用,用于存储加载的数据模型。
现在让我们逐行解析代码:
-
if (!boost::filesystem::exists(base_dir) && !boost::filesystem::is_directory(base_dir)):这一行检查指定的base_dir是否存在且是否是一个目录。如果base_dir既不存在也不是目录,则函数直接返回,不执行后续操作。 -
for (boost::filesystem::directory_iterator i(base_dir); i != boost::filesystem::directory_iterator(); i++):这一行通过遍历指定目录base_dir中的文件和子目录来实现。 -
if (boost::filesystem::is_directory(i->status())):在循环中,对于每个目录项,首先检查是否是一个目录。如果是目录,则递归调用loadData函数,加载子目录中的数据。 -
if (boost::filesystem::is_regular_file(i->status()) && boost::filesystem::extension(i->path()) == ".pcd"):对于每个文件项,检查是否是一个常规文件且是否是以 ".pcd" 为扩展名的文件。 -
vfh_model m;:在满足条件的情况下,创建一个名为m的vfh_model对象,用于存储加载的模型数据。 -
std::string str = i->path().string();:获取当前文件的路径并将其转换为std::string类型。 -
if (!checkVFH(str)):调用checkVFH函数检查是否存在与当前文件相关联的 VFH(Viewpoint Feature Histogram)文件。如果不存在,将生成该文件。 -
str.replace(str.find(".pcd"), 4, "_vfh.pcd");:将当前文件的扩展名从 ".pcd" 替换为 "_vfh.pcd",以获取相关的 VFH 文件路径。 -
if (!boost::filesystem::exists(str)):检查生成的 VFH 文件是否已经存在,如果不存在,则执行以下操作。 -
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308> signature;:声明一个pcl::PointCloud类型的对象signature,用于存储 VFH 特征。 -
estimate_VFH(i->path().string(), signature);:调用estimate_VFH函数计算当前文件的 VFH 特征。 -
pcl::io::savePCDFile(str, signature);:将计算得到的 VFH 特征保存到生成的 VFH 文件中。 -
if (loadHist(i->path().string(), m)):尝试加载当前文件的直方图数据到m中。 -
models.push_back(m);:将加载的模型数据m添加到models向量中。 -
std::cout << m.first << std::endl;:打印加载的模型的第一个元素到控制台。
关于参数设置和影响:
base_dir参数用于指定要加载数据的基本目录。models参数用于存储加载的数据模型。- 修改
base_dir可以改变加载数据的根目录。 - 修改
models可以改变加载的数据存储方式,例如,可以将加载的模型数据存储到其他容器或者进行其他处理。
void visualize(int argc, char** argv, int k, double thresh, std::vector<vfh_model> models, flann::Matrix<int> k_indices, flann::Matrix<float> k_distances)
{
// Load the results
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer p(argc, argv, "VFH Cluster Classifier");
int y_s = (int)floor(sqrt((double)k));
int x_s = y_s + (int)ceil((k / (double)y_s) - y_s);
double x_step = (double)(1 / (double)x_s);
double y_step = (double)(1 / (double)y_s);
pcl::console::print_highlight("Preparing to load ");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", k);
pcl::console::print_info(" files (");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", x_s);
pcl::console::print_info("x");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", y_s);
pcl::console::print_info(" / ");
pcl::console::print_value("%f", x_step);
pcl::console::print_info("x");
pcl::console::print_value("%f", y_step);
pcl::console::print_info(")\n");
int viewport = 0, l = 0, m = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
std::string cloud_name = models.at(k_indices[0][i]).first;
boost::replace_last(cloud_name, "_vfh", "");
p.createViewPort(l * x_step, m * y_step, (l + 1) * x_step, (m + 1) * y_step, viewport);
l++;
if (l >= x_s)
{
l = 0;
m++;
}
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud;
pcl::console::print_highlight(stderr, "Loading "); pcl::console::print_value(stderr, "%s ", cloud_name.c_str());
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(cloud_name, cloud) == -1)
break;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_xyz;
pcl::fromPCLPointCloud2(cloud, cloud_xyz);
if (cloud_xyz.points.size() == 0)
break;
pcl::console::print_info("[done, ");
pcl::console::print_value("%d", (int)cloud_xyz.points.size());
pcl::console::print_info(" points]\n");
pcl::console::print_info("Available dimensions: ");
pcl::console::print_value("%s\n", pcl::getFieldsList(cloud).c_str());
Eigen::Vector4f centroid;
pcl::compute3DCentroid(cloud_xyz, centroid);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_xyz_demean(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::demeanPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_xyz, centroid, *cloud_xyz_demean);
p.addPointCloud(cloud_xyz_demean, cloud_name, viewport);
std::stringstream ss;
ss << k_distances[0][i];
if (k_distances[0][i] > thresh)
{
p.addText(ss.str(), 20, 30, 1, 0, 0, ss.str(), viewport);
pcl::PointXYZ min_p, max_p;
pcl::getMinMax3D(*cloud_xyz_demean, min_p, max_p);
std::stringstream line_name;
line_name << "line_" << i;
p.addLine(min_p, max_p, 1, 0, 0, line_name.str(), viewport);
p.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_LINE_WIDTH, 5, line_name.str(), viewport);
}
else
p.addText(ss.str(), 20, 30, 0, 1, 0, ss.str(), viewport);
p.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_FONT_SIZE, 18, ss.str(), viewport);
p.addText(cloud_name, 20, 10, cloud_name, viewport);
}
p.addCoordinateSystem(0.1, "global", 0);
p.spin();
}
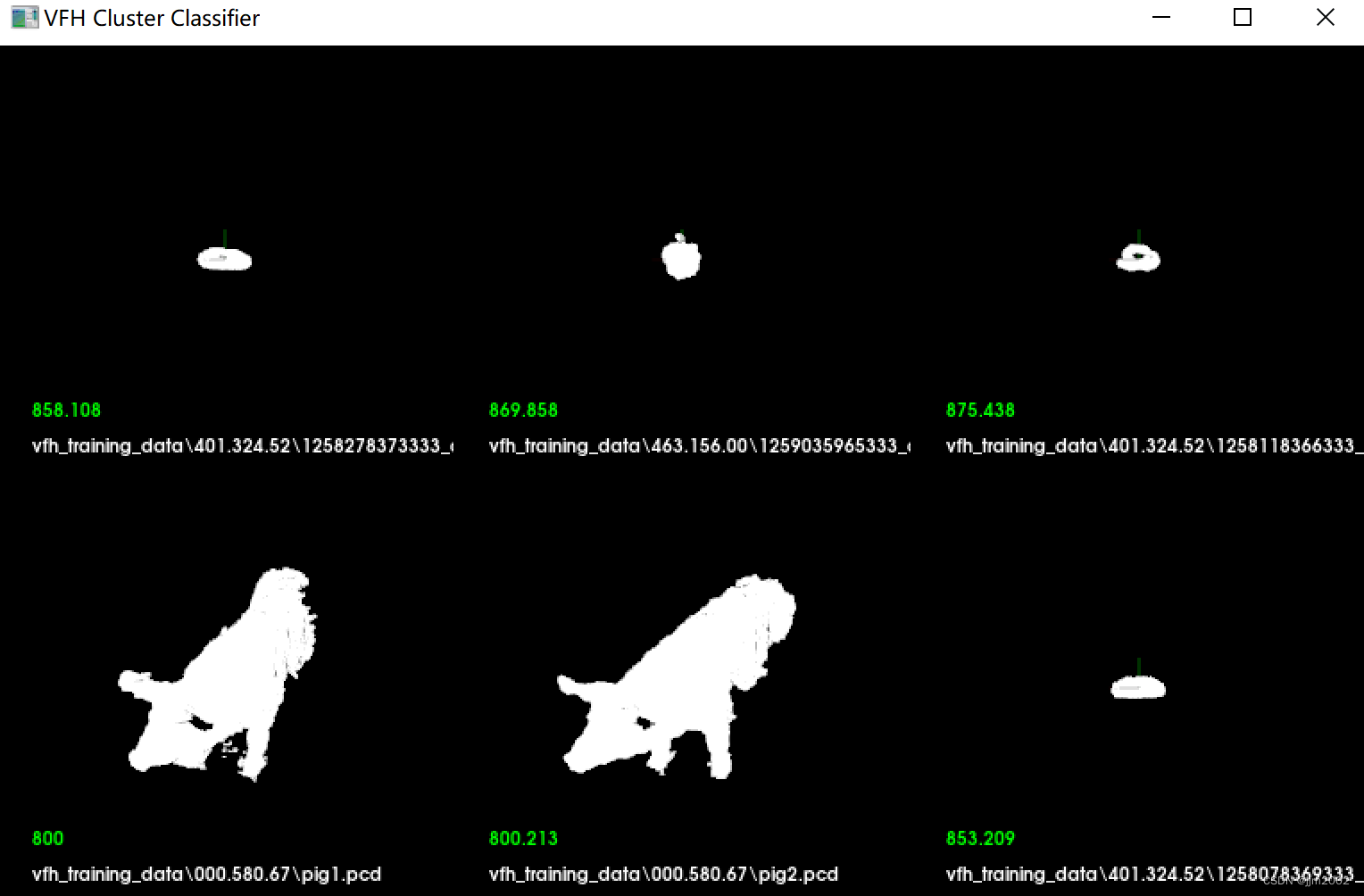
这段代码是一个PCL(Point Cloud Library)程序,用于可视化点云匹配结果。通过VFH(Viewpoint Feature Histogram)特征模型与已知模型数据库的匹配,选出k个最相似的模型,并在一个PCLVisualizer窗口中可视化显示。
代码参数如下:
-
argc,argv:命令行参数的数量和值,用于初始化PCLVisualizer。 -
k:要显示的最相似模型的数量。 -
thresh:距离阈值,用于决定是否在模型上绘制文本和线条。 -
models:一个结构体vector,包含数据库中所有模型的名称和对应的VFH特征。 -
k_indices:FLANN库输出的最近邻索引,这里表示最相似模型的索引。 -
k_distances:FLANN库输出的最近邻距离,表示每个最相似模型与查询模型的距离。
代码逻辑如下:
-
初始化PCLVisualizer对象
p。 -
根据
k的值计算可视化窗口网格的大小(x_s,y_s)和步长(x_step,y_step)。 -
循环
k次,每次处理一个最相似的模型:-
获取模型名称并加载对应的点云文件。
-
创建一个新的视图端口,用于显示当前模型的点云。
-
将加载的点云转换为
PointXYZ类型,并居中处理。 -
将处理过的点云添加到对应的视图端口中。
-
如果当前模型与查询模型的距离大于
thresh阈值,则在视图端口中添加一条红色线段和红色文本。否则,添加绿色文本。 -
设置文本的字体大小。
-
添加模型的名称作为文本。
-
-
在可视化窗口中添加一个全局坐标系。
-
启动可视化并等待用户交互。
调整参数会产生以下影响:
-
k的值会改变显示的模型数量。如果k太大,窗口中的模型可能会太密集,难以查看;如果k太小,可能无法显示足够的匹配结果。 -
thresh阈值会影响哪些模型会在视图端口中被突出显示。阈值太大,可能会有过多的模型被突出显示;阈值太小,则可能没有模型被突出显示。 -
models、k_indices、k_distances是根据点云匹配结果提供的,通常不会手动调整,但如果匹配算法或数据发生变化,这些值也会相应变化,影响可视化结果。
请注意,代码中可能会有错误处理不足(如在加载点云失败后直接使用break退出循环),在实际使用中可能需要更健壮的错误处理机制。此外,这段代码假定了k_indices和k_distances有足够的结果来支持k个最相似模型的显示,这在实际应用中可能需要确保。
inline void nearestKSearch(flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> >& index, const vfh_model& model,
int k, flann::Matrix<int>& indices, flann::Matrix<float>& distances)
{
flann::Matrix<float> p = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[model.second.size()], 1, model.second.size());
memcpy(&p.ptr()[0], &model.second[0], p.cols * p.rows * sizeof(float));
indices = flann::Matrix<int>(new int[k], 1, k);
distances = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[k], 1, k);
index.knnSearch(p, indices, distances, k, flann::SearchParams(512));
delete[] p.ptr();
}-
inline void nearestKSearch(flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> >& index, const vfh_model& model, int k, flann::Matrix<int>& indices, flann::Matrix<float>& distances): 这是函数的声明,它接受一个FLANN索引(index)、一个包含模型数据的结构体(model)、一个整数k(指定要搜索的最近邻的数量)、两个用于存储搜索结果的矩阵indices和distances。 -
flann::Matrix<float> p = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[model.second.size()], 1, model.second.size());: 在这一行中,创建了一个flann::Matrix<float>对象p,用于存储模型数据。这里使用new分配了一块内存来存储模型数据,其大小为model.second.size()个float元素。这个model参数似乎是一个结构体,其中的.second成员存储了模型数据。 -
memcpy(&p.ptr()[0], &model.second[0], p.cols * p.rows * sizeof(float));: 这一行通过memcpy函数将模型数据从model结构体中的.second成员复制到了矩阵p中。这样做是为了将数据转换为FLANN库中使用的矩阵格式。 -
indices = flann::Matrix<int>(new int[k], 1, k);: 这里创建了一个flann::Matrix<int>对象indices,用于存储搜索结果中的最近邻的索引。同样使用new分配了一块大小为k的内存来存储索引。 -
distances = flann::Matrix<float>(new float[k], 1, k);: 这里创建了一个flann::Matrix<float>对象distances,用于存储搜索结果中最近邻的距离。同样使用new分配了一块大小为k的内存来存储距离。 -
index.knnSearch(p, indices, distances, k, flann::SearchParams(512));: 这一行调用了FLANN库中的knnSearch函数来执行最近邻搜索。它传递了模型数据矩阵p、最近邻的索引矩阵indices、最近邻的距离矩阵distances、要搜索的最近邻数量k,以及一些搜索参数(例如,flann::SearchParams(512),这可能是一个搜索参数对象,但具体的含义取决于FLANN库的文档或者实现)。 -
delete[] p.ptr();: 最后,释放了先前为模型数据分配的内存。
参数的设置和影响:
index: 这是一个FLANN索引对象,用于加速最近邻搜索。model: 包含模型数据的结构体或类对象。k: 指定要搜索的最近邻的数量。indices: 用于存储最近邻的索引的矩阵。distances: 用于存储最近邻的距离的矩阵。flann::SearchParams(512): 这可能是一个FLANN库中的搜索参数对象,其具体含义需要查阅FLANN库的文档来确定。
根据FLANN库的实现和所处理的数据类型,不同的参数设置可能会影响搜索的速度、准确性和内存占用等方面。
#include "recognize_objects.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int k = 6;
double thresh = DBL_MAX;
std::string model_dir = "vfh_training_data";
std::string inputname = "pcd/pig_view1.pcd";
std::vector<vfh_model> models;
flann::Matrix<int> k_indices;
flann::Matrix<float> k_distances;
vfh_model histogram;
std::string str = inputname;
if (!checkVFH(inputname))
{
pcl::PointCloud <pcl::VFHSignature308> signature;
estimate_VFH(str, signature);
str.replace(str.find(".pcd"), 4, "_vfh.pcd");
pcl::io::savePCDFile(str, signature);
}
if (!loadHist(str, histogram))
{
pcl::console::print_error("Cannot load test file %s\n", inputname);
return (-1);
}
loadData(model_dir, models);
flann::Matrix<float> data(new float[models.size() * models[0].second.size()], models.size(), models[0].second.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < data.rows; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j < data.cols; ++j)
data[i][j] = models[i].second[j];
flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > index(data, flann::LinearIndexParams());
index.buildIndex();
nearestKSearch(index, histogram, k, k_indices, k_distances);
std::cout << "The closest " << k << " neighbors for " << inputname << " are: " << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
pcl::console::print_info(" %d - %s (%d) with a distance of: %f\n",
i, models.at(k_indices[0][i]).first.c_str(), k_indices[0][i], k_distances[0][i]);
visualize(argc, argv, k, thresh, models, k_indices, k_distances);
return 0;
}-
int k = 6;: 定义了用于最近邻搜索的邻居数量,这里设置为6。 -
double thresh = DBL_MAX;: 定义了阈值,默认为DBL_MAX,表示没有特定的距离阈值。 -
std::string model_dir = "vfh_training_data";: 定义了存储训练模型数据的目录,默认为"vfh_training_data"。 -
std::string inputname = "pcd/pig_view1.pcd";: 定义了输入点云文件的路径,默认为"pcd/pig_view1.pcd"。 -
std::vector<vfh_model> models;: 定义了存储训练模型的容器。 -
flann::Matrix<int> k_indices;: 定义了一个矩阵,用于存储最近邻的索引。 -
flann::Matrix<float> k_distances;: 定义了一个矩阵,用于存储最近邻的距离。 -
vfh_model histogram;: 定义了一个VFH特征模型,用于存储输入点云的VFH特征。 -
std::string str = inputname;: 将输入文件路径赋给str,用于后续的文件处理。 -
if (!checkVFH(inputname)) { /* ... */ }: 如果输入点云文件的VFH特征不存在,则通过estimate_VFH函数计算VFH特征并保存到文件中。 -
if (!loadHist(str, histogram)) { /* ... */ }: 如果加载VFH特征失败,则输出错误信息并返回。 -
loadData(model_dir, models);: 加载训练数据,将训练模型的VFH特征存储到models容器中。 -
flann::Matrix<float> data(new float[models.size() * models[0].second.size()], models.size(), models[0].second.size());: 创建一个矩阵data,用于存储训练模型的VFH特征数据。 -
for (size_t i = 0; i < data.rows; ++i) for (size_t j = 0; j < data.cols; ++j) data[i][j] = models[i].second[j];: 将训练模型的VFH特征数据填充到矩阵data中。 -
flann::Index<flann::ChiSquareDistance<float> > index(data, flann::LinearIndexParams());: 使用FLANN库创建索引结构,采用卡方距离(ChiSquareDistance)作为距离度量。 -
index.buildIndex();: 建立FLANN索引,以加速最近邻搜索。 -
nearestKSearch(index, histogram, k, k_indices, k_distances);: 调用先前解析的nearestKSearch函数,搜索输入VFH特征的最近邻。 -
输出最近邻的信息到控制台。
-
visualize(argc, argv, k, thresh, models, k_indices, k_distances);: 调用一个名为visualize的函数,可能用于可视化结果,传递了一些参数,包括阈值、训练模型、最近邻的索引和距离等。
这段代码的参数设置主要包括最近邻的数量k、阈值thresh、模型目录model_dir、输入点云文件路径inputname等。影响主要体现在最近邻搜索的准确性和速度上,以及可视化函数中的可视化效果。在调用FLANN库的函数时,距离度量的选择、搜索参数的设置等也会影响搜索结果的质量和性能。
结果:
PCL使用K-4PCS\SAC\ICP\NDT\GICP进行点云配准-CSDN博客