一、PFH特征描述符可视化
C++
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d_omp.h>//使用OMP需要添加的头文件
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
#include <pcl/features/3dsc.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_plotter.h>// 直方图的可视化
#include <pcl/visualization/histogram_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/features/pfh.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//------------------加载点云数据-----------------
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("pcd/pig_view1.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//需使用绝对路径
{
PCL_ERROR("Could not read file\n");
}
//--------------------计算法线------------------
pcl::NormalEstimationOMP<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> n;//OMP加速
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
//建立kdtree来进行近邻点集搜索
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
n.setNumberOfThreads(8);//设置openMP的线程数
n.setInputCloud(cloud);
n.setSearchMethod(tree);
n.setKSearch(20);
n.compute(*normals);//开始进行法向计算
// ------------------3DSC图像计算------------------
pcl::PFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::PFHSignature125> pfh;
pfh.setInputCloud(cloud);
pfh.setInputNormals(normals);
pfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfh_images(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());
pfh.setRadiusSearch(15);
pfh.compute(*pfh_images);
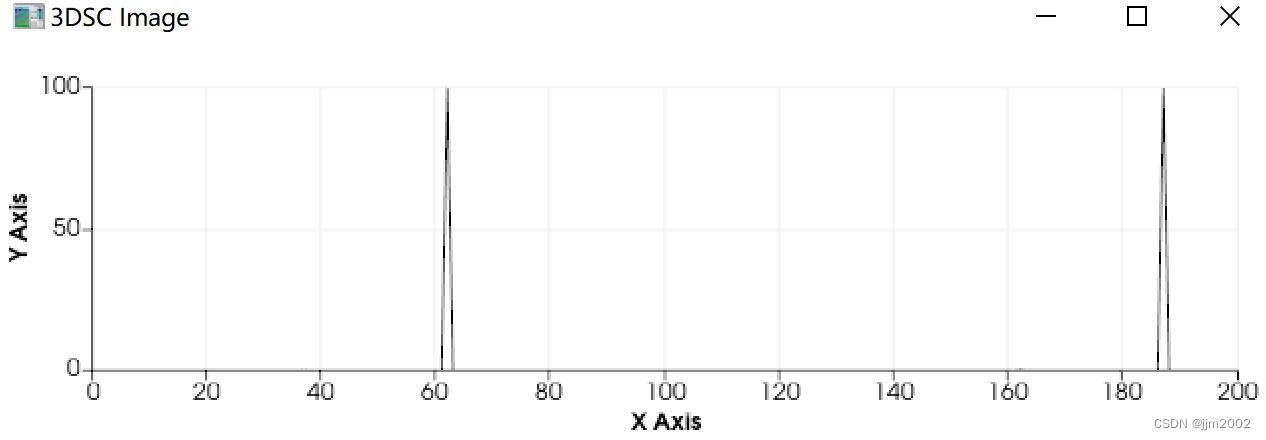
cout << "PFH图像计算计算完成" << endl;
// 显示和检索第一点的自旋图像描述符向量。
pcl::PFHSignature125 first_descriptor = pfh_images->points[0];
cout << first_descriptor << endl;
pcl::visualization::PCLPlotter plotter;
plotter.addFeatureHistogram(*pfh_images, 200); //设置的横坐标长度,该值越大,则显示的越细致
plotter.setWindowName("3DSC Image");
plotter.plot();
return 0;
}关键代码解析:
pcl::PFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::PFHSignature125> pfh;
pfh.setInputCloud(cloud);
pfh.setInputNormals(normals);
pfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfh_images(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());
pfh.setRadiusSearch(15);
pfh.compute(*pfh_images);-
pcl::PFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::PFHSignature125> pfh;- 这一行定义了一个PFH特征估计器对象
pfh,并指定了输入点云类型为pcl::PointXYZ,输入法向量类型为pcl::Normal,以及输出特征类型为pcl::PFHSignature125。
- 这一行定义了一个PFH特征估计器对象
-
pfh.setInputCloud(cloud);- 将点云数据设置为PFH估计器的输入。
cloud是一个指向pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>类型的指针,表示原始点云数据。
- 将点云数据设置为PFH估计器的输入。
-
pfh.setInputNormals(normals);- 将法向量数据设置为PFH估计器的输入。
normals是一个指向pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>类型的指针,表示点云中每个点的法向量数据。
- 将法向量数据设置为PFH估计器的输入。
-
pfh.setSearchMethod(tree);- 设置搜索方法。
tree是一个用于加速邻域搜索的数据结构,例如kd-tree或octree。这个参数可以根据点云的大小和分布来调整,以获得更好的性能。
- 设置搜索方法。
-
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfh_images(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());- 创建一个指向
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>类型的智能指针pfh_images,用于存储计算得到的PFH特征。
- 创建一个指向
-
pfh.setRadiusSearch(15);- 设置用于计算PFH特征的邻域搜索半径。较小的半径会考虑较近的邻居点,而较大的半径会考虑更远的邻居点。这个参数需要根据点云的密度和特征的分布来调整。
-
pfh.compute(*pfh_images);- 运行PFH特征的计算过程。该方法会根据输入的点云和法向量数据以及设置的搜索参数来计算每个点的PFH特征,并将结果存储在
pfh_images中。
- 运行PFH特征的计算过程。该方法会根据输入的点云和法向量数据以及设置的搜索参数来计算每个点的PFH特征,并将结果存储在
-
cout << "PFH图像计算计算完成" << endl;- 打印消息,指示PFH特征计算完成。
-
pcl::PFHSignature125 first_descriptor = pfh_images->points[0];- 提取第一个点的PFH特征描述符。这里假设点云中至少有一个点。
-
cout << first_descriptor << endl;- 打印第一个点的PFH特征描述符。
-
pcl::visualization::PCLPlotter plotter;- 创建一个PCL绘图器对象,用于可视化PFH特征。
-
plotter.addFeatureHistogram(*pfh_images, 200);- 向绘图器中添加PFH特征的直方图。第二个参数指定了横坐标的长度,该值越大,显示的越细致。
-
plotter.setWindowName("3DSC Image");- 设置绘图窗口的名称。
-
plotter.plot();- 显示绘图器中的图像。
总的来说,这段代码的作用是计算并可视化点云的PFH特征。参数的设置会直接影响特征的计算和可视化效果,因此需要根据具体的数据和需求进行调整。
结果:
二、PFH对应关系可视化
C++
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d_omp.h>
#include <pcl/registration/correspondence_estimation.h>
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/registration/transformation_estimation_svd.h>
#include <pcl/keypoints/sift_keypoint.h>
#include <pcl/features/pfh.h>
using namespace std;
namespace pcl
{
template<>
struct SIFTKeypointFieldSelector<PointXYZ>
{
inline float
operator () (const PointXYZ& p) const
{
return p.z;
}
};
}
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> pointcloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal> pointnormal;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125> pfhFeature;
pfhFeature::Ptr compute_pfh_feature(pointcloud::Ptr input_cloud, pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree)
{
pointnormal::Ptr normals(new pointnormal);
pcl::NormalEstimationOMP<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> n;
n.setInputCloud(input_cloud);
n.setNumberOfThreads(5);
n.setSearchMethod(tree);
n.setKSearch(10);
n.compute(*normals);
pcl::PFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::PFHSignature125> pfh;
pfh.setInputCloud(input_cloud);
pfh.setInputNormals(normals);
pfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfh_fe_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());
pfh.setRadiusSearch(10);
pfh.compute(*pfh_fe_ptr);
return pfh_fe_ptr;
}
void extract_keypoint(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr& cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr& keypoint)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithScale> result;
const float min_scale = 5.f;
const int n_octaves = 3;
const int n_scales_per_octave = 15;
const float min_contrast = 0.01f;
pcl::SIFTKeypoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointWithScale> sift;
sift.setInputCloud(cloud);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
sift.setSearchMethod(tree);
sift.setScales(min_scale, n_octaves, n_scales_per_octave);
sift.setMinimumContrast(min_contrast);
sift.compute(result);
cout << "Extracted " << result.size() << " keypoints" << endl;
copyPointCloud(result, *keypoint);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pointcloud::Ptr source_cloud(new pointcloud);
pointcloud::Ptr target_cloud(new pointcloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("pcd/pig_view1.pcd", *source_cloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("pcd/pig_view2.pcd", *target_cloud);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr s_k(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr t_k(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
extract_keypoint(source_cloud, s_k);
extract_keypoint(target_cloud, t_k);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pfhFeature::Ptr source_pfh = compute_pfh_feature(s_k, tree);
pfhFeature::Ptr target_pfh = compute_pfh_feature(t_k, tree);
pcl::registration::CorrespondenceEstimation<pcl::PFHSignature125, pcl::PFHSignature125> crude_cor_est;
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::Correspondences> cru_correspondences(new pcl::Correspondences);
crude_cor_est.setInputSource(source_pfh);
crude_cor_est.setInputTarget(target_pfh);
crude_cor_est.determineCorrespondences(*cru_correspondences);
Eigen::Matrix4f Transform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
pcl::registration::TransformationEstimationSVD<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ, float>::Ptr trans(new pcl::registration::TransformationEstimationSVD<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ, float>);
trans->estimateRigidTransformation(*source_cloud, *target_cloud, *cru_correspondences, Transform);
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("v1"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ>target_color(target_cloud, 255, 0, 0);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(target_cloud, target_color, "target cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "target cloud");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ>input_color(source_cloud, 0, 255, 0);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(source_cloud, input_color, "input cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "input cloud");
viewer->addCorrespondences<pcl::PointXYZ>(s_k, t_k, *cru_correspondences, "correspondence");
//viewer->initCameraParameters();
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(1000));
}
return 0;
}
关键代码解析:
我之前在SIFT 3D关键点检测以及SAC-IA粗配准-CSDN博客
和Spin Image自旋图像描述符可视化以及ICP配准-CSDN博客以及本章第一部分已经解释了大部分函数,这里就不赘述了
结果:
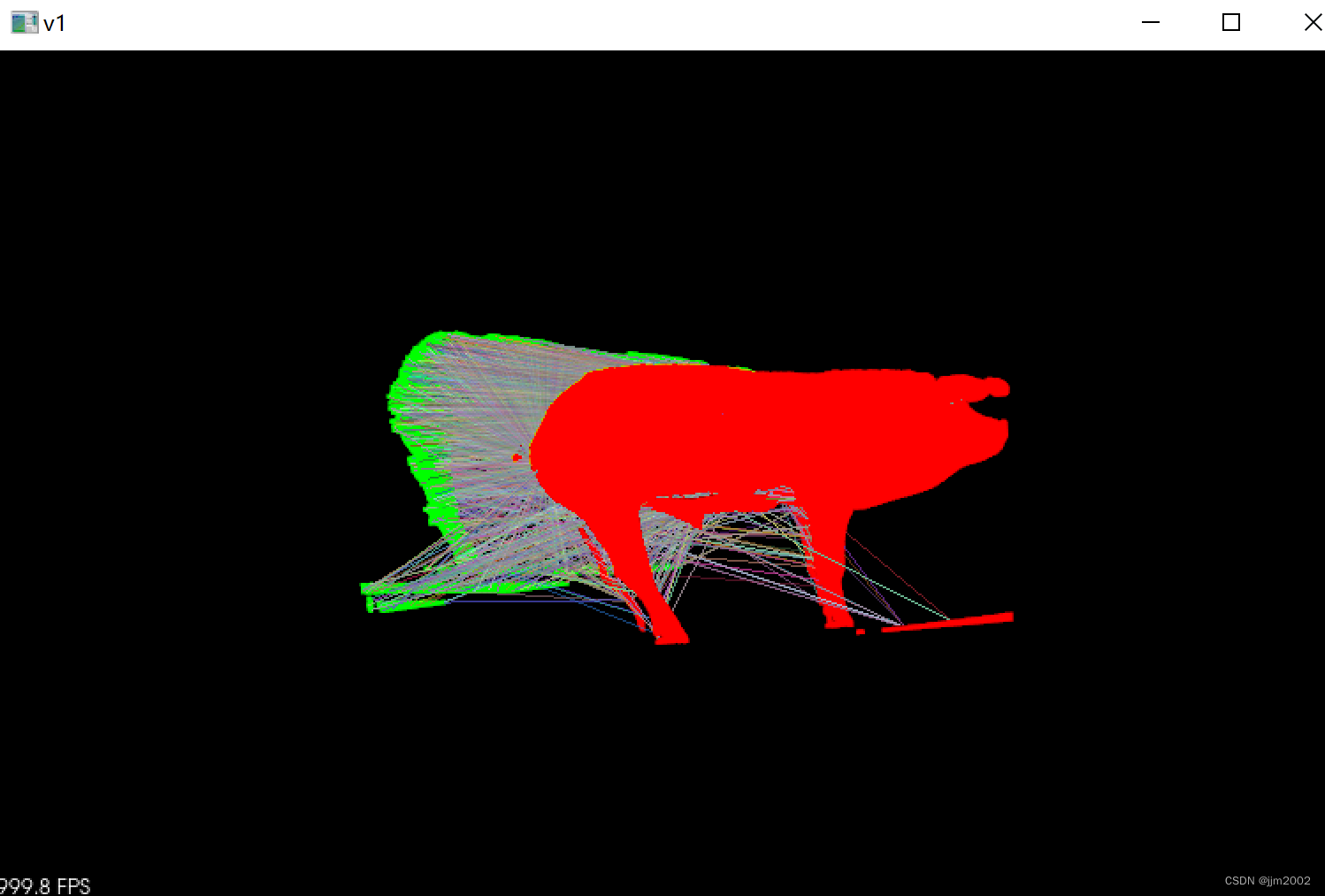

三、PFH结合ICP配准
C++
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d_omp.h>
#include <pcl/registration/icp.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
#include <pcl/registration/ia_ransac.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_plotter.h>
#include <pcl/features/pfh.h>
#include <pcl/keypoints/sift_keypoint.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PFHSignature125 PFHT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PFHT> PointCloudPFH;
typedef pcl::search::KdTree<PointT> Tree;
namespace pcl
{
template<>
struct SIFTKeypointFieldSelector<PointXYZ>
{
inline float
operator () (const PointXYZ& p) const
{
return p.z;
}
};
}
// 关键点提取
void extract_keypoint(PointCloud::Ptr& cloud, PointCloud::Ptr& keypoint, Tree::Ptr& tree)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithScale> result;
const float min_scale = 5.f;
const int n_octaves = 3;
const int n_scales_per_octave = 15;
const float min_contrast = 0.01f;
pcl::SIFTKeypoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointWithScale> sift;
sift.setInputCloud(cloud);
sift.setSearchMethod(tree);
sift.setScales(min_scale, n_octaves, n_scales_per_octave);
sift.setMinimumContrast(min_contrast);
sift.compute(result);
copyPointCloud(result, *keypoint);
}
// 法线计算和 计算特征点的Spinimage描述子
void computeKeyPointsPFH(PointCloud::Ptr& cloud_in, PointCloud::Ptr& key_cloud, PointCloudPFH::Ptr& dsc, Tree::Ptr& tree)
{
pcl::NormalEstimationOMP<PointT, pcl::Normal> n;//OMP加速
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
n.setNumberOfThreads(6);//设置openMP的线程数
n.setInputCloud(key_cloud);
n.setSearchSurface(cloud_in);
n.setSearchMethod(tree);
//n.setKSearch(10);
n.setRadiusSearch(0.3);
n.compute(*normals);
pcl::PFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::PFHSignature125> pfh;
pfh.setInputCloud(key_cloud);
pfh.setInputNormals(normals);
pfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfh_fe_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());
pfh.setRadiusSearch(10);
pfh.compute(*dsc);
}
// 点云可视化
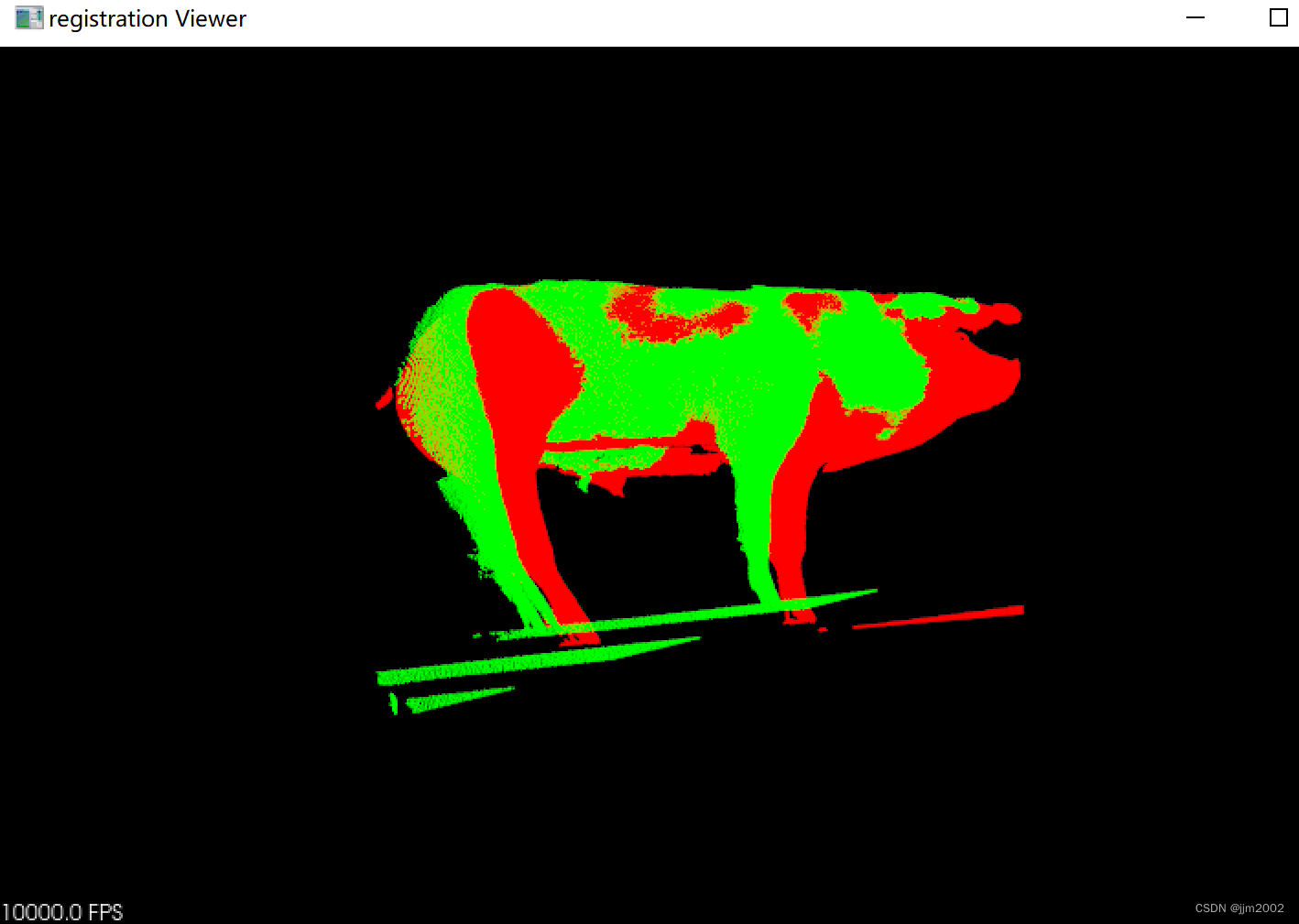
void visualize_pcd(PointCloud::Ptr icp_result, PointCloud::Ptr cloud_target)
{
//创建初始化目标
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("registration Viewer");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> final_h(icp_result, 0, 255, 0);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> tgt_h(cloud_target, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_target, tgt_h, "tgt cloud");
viewer.addPointCloud(icp_result, final_h, "final cloud");
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
}
int main()
{
// 加载源点云和目标点云
PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new PointCloud);
PointCloud::Ptr cloud_target(new PointCloud);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("pcd/pig_view1.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
PCL_ERROR("加载点云失败\n");
}
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("pcd/pig_view2.pcd", *cloud_target) == -1)
{
PCL_ERROR("加载点云失败\n");
}
visualize_pcd(cloud, cloud_target);
//关键点
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr keypoints1(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr keypoints2(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
Tree::Ptr tree(new Tree);
extract_keypoint(cloud, keypoints1, tree);
extract_keypoint(cloud_target, keypoints2, tree);
cout << "SIFT 3D完成!" << endl;
cout << "cloud的关键点的个数:" << keypoints1->size() << endl;
cout << "cloud_target的关键点的个数:" << keypoints2->size() << endl;
// 使用SpinImage描述符计算特征
PointCloudPFH::Ptr source_features(new PointCloudPFH);
PointCloudPFH::Ptr target_features(new PointCloudPFH);
computeKeyPointsPFH(cloud, keypoints1, source_features, tree);
computeKeyPointsPFH(cloud_target, keypoints2, target_features, tree);
cout << "PFH完成!" << endl;
//SAC配准
pcl::SampleConsensusInitialAlignment<PointT, PointT, PFHT> scia;
scia.setInputSource(keypoints1);
scia.setInputTarget(keypoints2);
scia.setSourceFeatures(source_features);
scia.setTargetFeatures(target_features);
scia.setMinSampleDistance(7); // 设置样本之间的最小距离
scia.setNumberOfSamples(100); // 设置每次迭代计算中使用的样本数量(可省),可节省时间
scia.setCorrespondenceRandomness(6);// 在选择随机特征对应时,设置要使用的邻居的数量;
PointCloud::Ptr sac_result(new PointCloud);
scia.align(*sac_result);
Eigen::Matrix4f sac_trans;
sac_trans = scia.getFinalTransformation();
cout << "SAC配准完成!" << endl;
//icp配准
PointCloud::Ptr icp_result(new PointCloud);
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointT, PointT> icp;
icp.setInputSource(keypoints1);
icp.setInputTarget(keypoints2);
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(20);
icp.setMaximumIterations(35); // 最大迭代次数
icp.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-10); // 两次变化矩阵之间的差值
icp.setEuclideanFitnessEpsilon(0.01);// 均方误差
icp.align(*icp_result, sac_trans);
cout << "ICP配准完成!" << endl;
// 输出配准结果
std::cout << "ICP converged: " << icp.hasConverged() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Transformation matrix:\n" << icp.getFinalTransformation() << std::endl;
Eigen::Matrix4f icp_trans;
icp_trans = icp.getFinalTransformation();
cout << icp_trans << endl;
使用创建的变换对未过滤的输入点云进行变换
pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud, *icp_result, icp_trans);
visualize_pcd(icp_result, cloud_target);
return 0;
}
关键代码解析:
我之前在SIFT 3D关键点检测以及SAC-IA粗配准-CSDN博客
和Spin Image自旋图像描述符可视化以及ICP配准-CSDN博客以及本章第一部分已经解释了大部分函数,这里就不赘述了
结果: