React中的核心对象
- 在React应用中,有很多特定的对象或数据结构.了解这些内部的设计,可以更容易理解react运行原理
- 列举从react启动到渲染过程出现频率较高,影响范围较大的对象,它们贯穿整个react运行时
- 如 ReactElement 对象
- 如 Fiber 对象
- 其他过程的重要对象
- 如事件对象(位于react-dom/events保障react应用能够响应ui交互)
- 如 ReactContext, ReactProvider, ReactConsumer对象等
ReactElement对象
-
入口函数
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementByld('root'); -
可以简单的认为,包括
<App/>及其所有子节点都是ReactElement对象(在render之后才会生成子节点) -
每个ReactElement对象的区别在于type不同,其type定义在shared包中
-
所有采用jsx语法书写的节点,都会被编译器转换,最终会以
React.createElement(..)的方式 -
创建出来一个与之对应的ReactElement对象
-
ReactElement对象的数据结构如下,定义在:
packages/shared/ReactElementType.js/** * Copyright (c) Meta Platforms, Inc. and affiliates. * * This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. * * @flow */ export type ReactElement = { $$typeof: any, type: any, key: any, ref: any, props: any, // ReactFiber _owner: any, // __DEV__ _store: {validated: boolean, ...}, }; -
特别关注 key 和 type 这两个属性
- key 属性在reconciler阶段会用到
- 所有的ReactElement对象都有key属性
- 且其默认值是null
- 后续在diff算法中会使用到
- type 属性决定了节点的种类
- 它的值可以是字符串(代表div,span等dom节点),函数(代表function,class等节点)
- 或者react内部定义的节点类型(portal,context,fragment等)
- 在reconciler阶段,会根据type执行不同的逻辑
- 如type是一个字符串类型,则直接使用.
- 如type是一个ReactComponent类型,则会调用其render方法获取节点.
- 如type是一个function类型,则会调用该方法获取子节点
- key 属性在reconciler阶段会用到
-
ReactElement 的工厂方法如下,定义在:
packages/react/src/ReactElementProd.js/** * Factory method to create a new React element. This no longer adheres to * the class pattern, so do not use new to call it. Also, instanceof check * will not work. Instead test $$typeof field against Symbol.for('react.element') to check * if something is a React Element. * * @param {*} type * @param {*} props * @param {*} key * @param {string|object} ref * @param {*} owner * @param {*} self A *temporary* helper to detect places where `this` is * different from the `owner` when React.createElement is called, so that we * can warn. We want to get rid of owner and replace string `ref`s with arrow * functions, and as long as `this` and owner are the same, there will be no * change in behavior. * @param {*} source An annotation object (added by a transpiler or otherwise) * indicating filename, line number, and/or other information. * @internal */ function ReactElement(type, key, ref, owner, props) { const element = { // This tag allows us to uniquely identify this as a React Element $$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE, // Built-in properties that belong on the element type: type, key: key, ref: ref, props: props, // Record the component responsible for creating this element. _owner: owner, }; if (__DEV__) { // The validation flag is currently mutative. We put it on // an external backing store so that we can freeze the whole object. // This can be replaced with a WeakMap once they are implemented in // commonly used development environments. element._store = {}; // To make comparing ReactElements easier for testing purposes, we make // the validation flag non-enumerable (where possible, which should // include every environment we run tests in), so the test framework // ignores it. Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', { configurable: false, enumerable: false, writable: true, value: false, }); // debugInfo contains Server Component debug information. Object.defineProperty(element, '_debugInfo', { configurable: false, enumerable: false, writable: true, value: null, }); if (Object.freeze) { Object.freeze(element.props); Object.freeze(element); } } return element; } -
举一个App组件的例子
class App extends React.Component { render() { return ( <div className="app"> <header>header</header> <Content /> <footer>footer</footer> </div> ) } } class Content extends React.Component { render() { return ( <React.Fragment> <p>1</p> <p>2</p> <p>3</p> </React.Fragment> ); } } export default App; -
这个代码,对应着 ReactElement 树结构如下
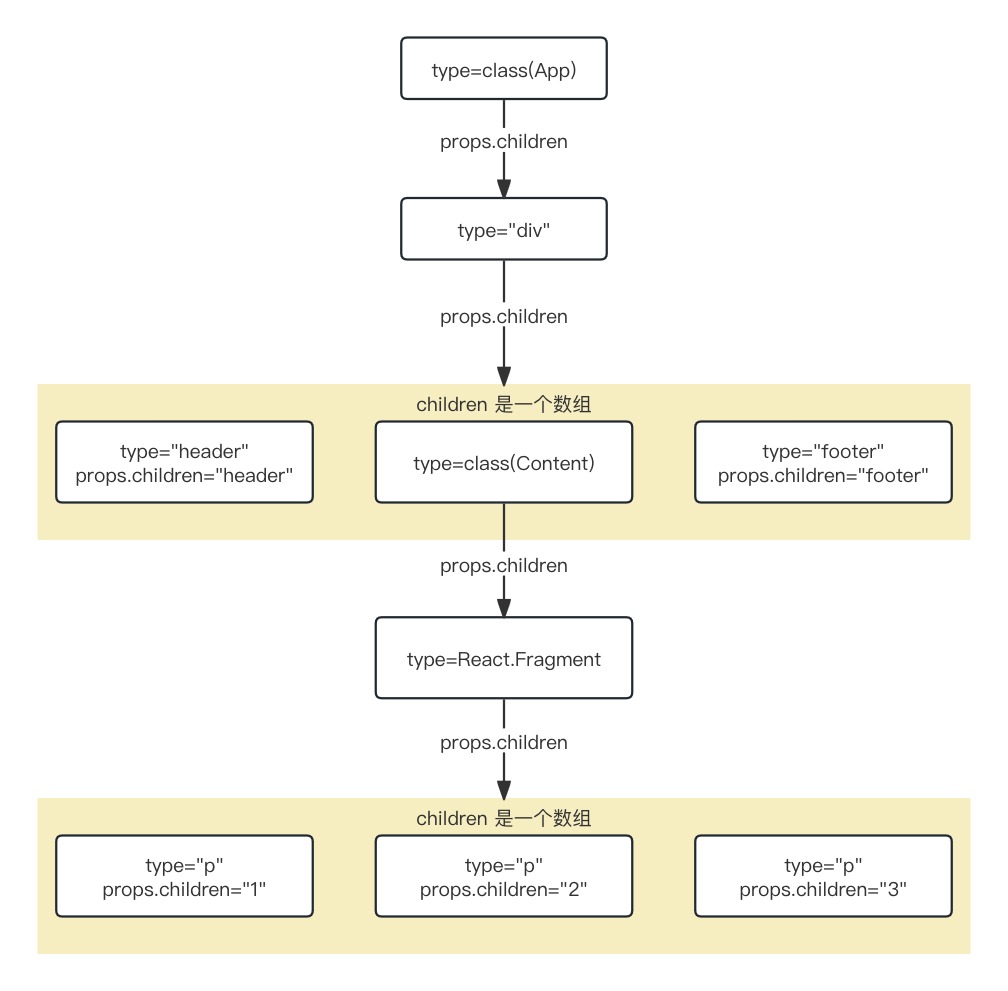
- class和function类型的组件,其子节点是在render之后(reconciler阶段)才生成的
- 此处只是单独表示 ReactElement 的数据结构
- 父级对象和子级对象之间是通过props.children属性进行关联的(与fiber树不同)
- ReactElement虽然不能算是一个严格的树,也不能算是一个严格的链表
- 它的生成过程是自顶向下的,是所有组件节点的总和
- ReactElement树(暂且用树来表述)和fiber树是以props.children为单位先后交替生成的
- 当ReactElement树构造完毕,fiber树也随后构造完毕
- reconciler阶段会根据ReactElement的类型生成对应的fiber节点
- 注意,不是一一对应
- 比如,Fragment类型的组件在生成fiber节点的时候会略过
Fiber对象
-
react-reconciler包是react应用的中枢
-
连接渲染器(react-dom)和调度中心(scheduler),同时自身也负责fiber树的构造
-
先看数据结构,其type类型的定义在 ReactInternalTypes.js 中
// A Fiber is work on a Component that needs to be done or was done. There can // be more than one per component. export type Fiber = { // These first fields are conceptually members of an Instance. This used to // be split into a separate type and intersected with the other Fiber fields, // but until Flow fixes its intersection bugs, we've merged them into a // single type. // An Instance is shared between all versions of a component. We can easily // break this out into a separate object to avoid copying so much to the // alternate versions of the tree. We put this on a single object for now to // minimize the number of objects created during the initial render. // Tag identifying the type of fiber. tag: WorkTag, // Unique identifier of this child. key: null | string, // The value of element.type which is used to preserve the identity during // reconciliation of this child. elementType: any, // The resolved function/class/ associated with this fiber. type: any, // The local state associated with this fiber. stateNode: any, // Conceptual aliases // parent : Instance -> return The parent happens to be the same as the // return fiber since we've merged the fiber and instance. // Remaining fields belong to Fiber // The Fiber to return to after finishing processing this one. // This is effectively the parent, but there can be multiple parents (two) // so this is only the parent of the thing we're currently processing. // It is conceptually the same as the return address of a stack frame. return: Fiber | null, // Singly Linked List Tree Structure. child: Fiber | null, sibling: Fiber | null, index: number, // The ref last used to attach this node. // I'll avoid adding an owner field for prod and model that as functions. ref: | null | (((handle: mixed) => void) & {_stringRef: ?string, ...}) | RefObject, refCleanup: null | (() => void), // Input is the data coming into process this fiber. Arguments. Props. pendingProps: any, // This type will be more specific once we overload the tag. memoizedProps: any, // The props used to create the output. // A queue of state updates and callbacks. updateQueue: mixed, // The state used to create the output memoizedState: any, // Dependencies (contexts, events) for this fiber, if it has any dependencies: Dependencies | null, // Bitfield that describes properties about the fiber and its subtree. E.g. // the ConcurrentMode flag indicates whether the subtree should be async-by- // default. When a fiber is created, it inherits the mode of its // parent. Additional flags can be set at creation time, but after that the // value should remain unchanged throughout the fiber's lifetime, particularly // before its child fibers are created. mode: TypeOfMode, // Effect flags: Flags, subtreeFlags: Flags, deletions: Array<Fiber> | null, // Singly linked list fast path to the next fiber with side-effects. nextEffect: Fiber | null, // The first and last fiber with side-effect within this subtree. This allows // us to reuse a slice of the linked list when we reuse the work done within // this fiber. firstEffect: Fiber | null, lastEffect: Fiber | null, lanes: Lanes, childLanes: Lanes, // This is a pooled version of a Fiber. Every fiber that gets updated will // eventually have a pair. There are cases when we can clean up pairs to save // memory if we need to. alternate: Fiber | null, // Time spent rendering this Fiber and its descendants for the current update. // This tells us how well the tree makes use of sCU for memoization. // It is reset to 0 each time we render and only updated when we don't bailout. // This field is only set when the enableProfilerTimer flag is enabled. actualDuration?: number, // If the Fiber is currently active in the "render" phase, // This marks the time at which the work began. // This field is only set when the enableProfilerTimer flag is enabled. actualStartTime?: number, // Duration of the most recent render time for this Fiber. // This value is not updated when we bailout for memoization purposes. // This field is only set when the enableProfilerTimer flag is enabled. selfBaseDuration?: number, // Sum of base times for all descendants of this Fiber. // This value bubbles up during the "complete" phase. // This field is only set when the enableProfilerTimer flag is enabled. treeBaseDuration?: number, // Conceptual aliases // workInProgress : Fiber -> alternate The alternate used for reuse happens // to be the same as work in progress. // __DEV__ only _debugInfo?: ReactDebugInfo | null, _debugOwner?: Fiber | null, _debugIsCurrentlyTiming?: boolean, _debugNeedsRemount?: boolean, // Used to verify that the order of hooks does not change between renders. _debugHookTypes?: Array<HookType> | null, };- fiber.tag
- 表示fiber类型,根据 ReactElement 组件的type进行生成,在react内部共定义了25种tag
- fiber.key
- ReactElement 组件的key一致
- fiber.elementType
- 一般来讲和ReactElement组件的type一致
- fiber.type
- 一般来讲和fiber.elementType一致.一些特殊情形下,比如在开发环境下为了兼容热更新 (HotReloading)
- 会对 function, class, ForwardRef类型的 ReactElement做一定的处理
- 这种情况会区别于fiber.elementType
- fiber.stateNode
- 与fiber关联的局部状态节点
- 比如:HostComponent 类型指向与fiber节点对应的dom节点
- 根节点 fiber.stateNode 指向的是 FiberRoot
- class 类型节点其 stateNode 指向的是 class 实例
- fiber.return
- 指向父节点
- fiber.child
- 指向第一个子节点
- fiber.sibling
- 指向下一个兄弟节点
- fiber.index
- fiber在兄弟节点中的索引,如果是单节点默认为0.
- fiber.ref
- 指向在ReactElement组件上设置的ref
- string类型的ref除外,这种类型的ref已经不推荐使用
- reconciler阶段会将string类型的ref转换成一个function类型
- fiber.pendingProps
- 输入属性,从 ReactElement对象传的props
- 用于和 fiber.memoizedProps 比较可以得出属性是否变动
- fiber.memoizedProps
- 上一次生成子节点时用到的属性,生成子节点之后保持在内存中
- 向下生成子节点之前叫做pendingProps
- 生成子节点之后会把pendingProps赋值给 memoizedProps用于下一次比较
- pendingProps和memoizedProps比较可以出属性是否变动
- fiber.updateQueue
- 存储update更新对象的队列,每一次发起更新,都需要在该队列上创建一个update对象
- fiber.memoizedState
- 上一次生成子节点之后保持在内存中的局部状态
- fiber.dependencies
- 该fiber节点所依赖的(contexts, events)等
- fiber.mode
- 二进制位 Bitfield, 继承至父节点,影响本fiber节点及其子树中所有节点
- 与react应用的运行模式有关(有ConcurrentMode, NoMode等选项)
- fiber.flags
- 标志位,副作用标记(在16.x版本中叫做effectTag)
- 在 ReactFiberFlags.js中定义了所有的标志位
- reconciler阶段会将所有拥有flags标记的节点添加到副作用链表中,等待commit阶段的处理
- fiber.subtreeFlags
- subtreeFlags是一个二进制形式的属性,它代表了Fiber节点子树的操作依据
- 换句话说,它包含了有关该节点及其所有子节点的更新信息。这是React内部用于优化和协调更新的重要机制之一
- 具体来说,subtreeFlags可能包含各种标志,这些标志指示了哪些子节点需要更新、哪些操作正在进行中、哪些操作已经完成等
- React使用这些标志来有效地管理组件的更新过程,确保只更新实际发生变化的部分,从而提高性能和效率
- 需要注意的是,subtreeFlags是React内部使用的属性,对于大多数开发者来说,通常不需要直接与之交互
- React的公开API和抽象层使得开发者可以专注于编写组件逻辑,而无需关心底层的更新和渲染机制
- fiber.deletions
- 存储将要被删除的子节点.默认未开启,
- fiber.nextEffect
- 单向链表,指向下一个有副作用的fiber节点
- fiber.firstEffect
- 指向副作用链表中的第一个fiber节点
- fiber.lastEffect
- 指向副作用链表中的最后一个fiber节点.
- fiber.lanes
- 本fiber节点所属的优先级,创建fiber的时候设置
- fiber.childLanes
- 子节点所属的优先级
- fiber.alternate
- 指向内存中的另一个fiber,每个被更新过fiber节点在内存中都是成对出现(current 和 workInProgress)
- fiber.tag
- 绘制与ReactElement对应的一棵Fiber树
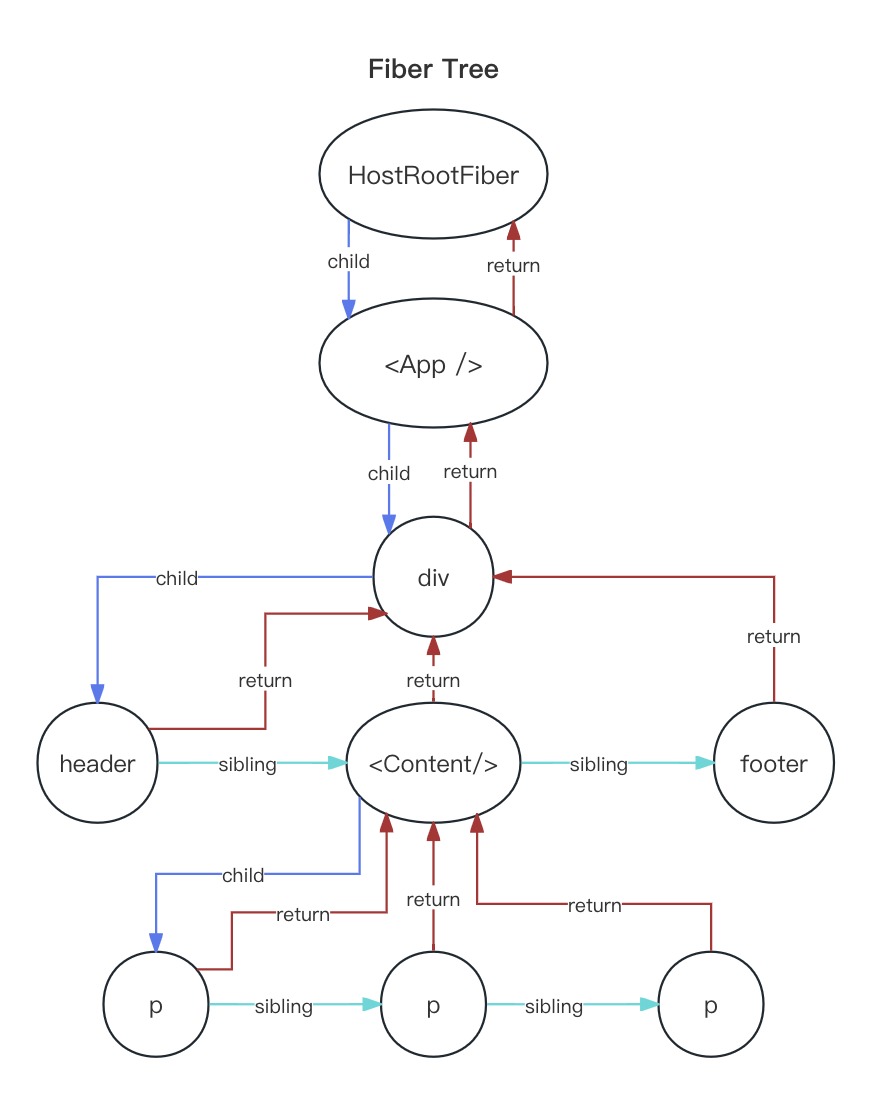
- 这里的fiber树只是为了和上面的ReactElement树对照
- 其中
<App/>,<Content/>为ClassComponent类型的fiber节点 - 其余节点都是普通 HostComponent 类型节点
<Content/>的子节点在ReactElement树中是React.Fragment- 但是在 fiber 树中 React.Fragment并没有与之对应的fiber节点
- reconciler阶段对此类型节点做了单独处理
- 所以ReactElement节点和fiber节点不是一对一匹配