本篇文章发表于ICLR 2024。
文章链接:https://openreview.net/attachment?id=rp0EdI8X4e&name=pdf
一、概述
这篇文章也是CBMs“大家庭”的一员。众所周知,CBMs需要大量的人工annotation,Label-Free CBM借用pre-trained多模态模型自动生成concepts在一定程度上解决了这一问题。但使用pre-trained模型存在unstable的问题,因此作者在Label-Free CBM的基础上提出了更加stable的模型——Faithful Vision-Language Concept (FVLC) models。
作者指出,faithful concept应该具备四个特性:
- Faithful concept应该尽可能与original concept一致:Significant overlap between the top-k indices of the “faithful concept” and the original concept, ensuring interpretability.
- 在concept generation过程中可以抵抗噪声和干扰:Inherent stability, with the concept vector remaining robust against random noise and perturbations during LLM concept set generation.
- 预测结果要与vanilla CBMs保持一致:A prediction distribution close to that of the vanilla CBMs, preserving its outstanding performance.
- Output distribution具备稳定性(stable):Stable output distribution, remaining robust during self-supervised learning and LLM concept set generation, even in the presence of perturbations.
二、方法
在具体介绍本文提出的方法之前,我们先来回顾一些知识点。
1. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs)
首先是概念瓶颈模型CBMs,这一部分已经写过很多篇博客了。如果大家对CBMs熟悉的话,应该知道CBMs有两大主要缺点:1. 因为原始数据特征的不完全提取而导致的性能损失; 2. 需要大量的人工标注。针对这两个问题,已经有大量文献提出了潜在的解决方法,比如SENN、PCBM、Label-Free CBM等。
回顾一下CBMs的notation:We consider a classification task with a concept set denoted as and a training dataset represented as
, where for
,
is the feature vector,
denotes the label, where
corresponds to the number of classes, and
denotes the concept vector whose
-th entry represents the weight of the concept
. In CBMs, we aim to learn two representations, one transforms from the input space to the concept space, which is represented by
. The other one maps from the concept space to the prediction space, which can be denoted by
. For any input
, we aim to make its predicted concept vector
and prediction
to be close to its underlying ones.
2. Label-free CBMs
Label-free CBMs有四个步骤:
Step 1: Concept set creation and filtering.
询问GPT-3一系列问题并做筛选,产生概念集合 ;
Step 2 and 3: Learning the Concept Bottleneck Layer (CBL).
学习从特征空间到概念空间的prejection weights 。具体的做法是首先使用CLIP生成concept activation matrix
,其中
与
分别为CLIP中的image encoder与text encoder,矩阵
的行代表不同的图片,列代表不同的概念,其中的元素代表图片 i 中概念 j 的存在情况(表示为乘积)。
是一个
的矩阵,代表了特征空间到概念空间的映射,
。用
表示我们关注的神经元,所有图片在该神经元上对应的activation pattern可以表示为
,优化目标是使得第 i 个神经元与第 i 个concept尽可能对齐/匹配,由以下式子给出:
Step 4: After successfully learning the Concept Bottleneck Layer, the next step involves training the final predictor using the fully connected layer.
学习从概念到类别的映射 ,
接下来介绍本文提出的FVLC。
3. Faithful Vision-Language Concept
由于Label-free CBMs概念集合的产生依赖于GPT-3,因此可能会引入不稳定(instability)和扰动(perturbation)。此外,不仅概念会被干扰,输入图片也会不可避免地存在被干扰的风险,因此在以上情况下更需要保持概念的stability,也就是所谓的“faithful concept”。
那么什么是faithful concept?由上所述我们可以知道,faithful concept要具备当输入或概念集本身被扰动时概念向量仍然能够保持稳定的能力。我们应该对此进行合理的定义。(图片截取自原论文)
定义一:


两个概念向量按激活值从大到小的顺序排列后前 k 个concepts的overlap程度
此处是为了后面比较faithful concepts与original concepts之间的差异所作出的定义。
(注: 是一个包含了concept索引的集合,而并不是具体的concept,因此后面对concept进行perturbation后,对于stable and faithful concept而言,这个索引集
是不会发生太大变化的,即使concept本身发生了变化。)
定义二:
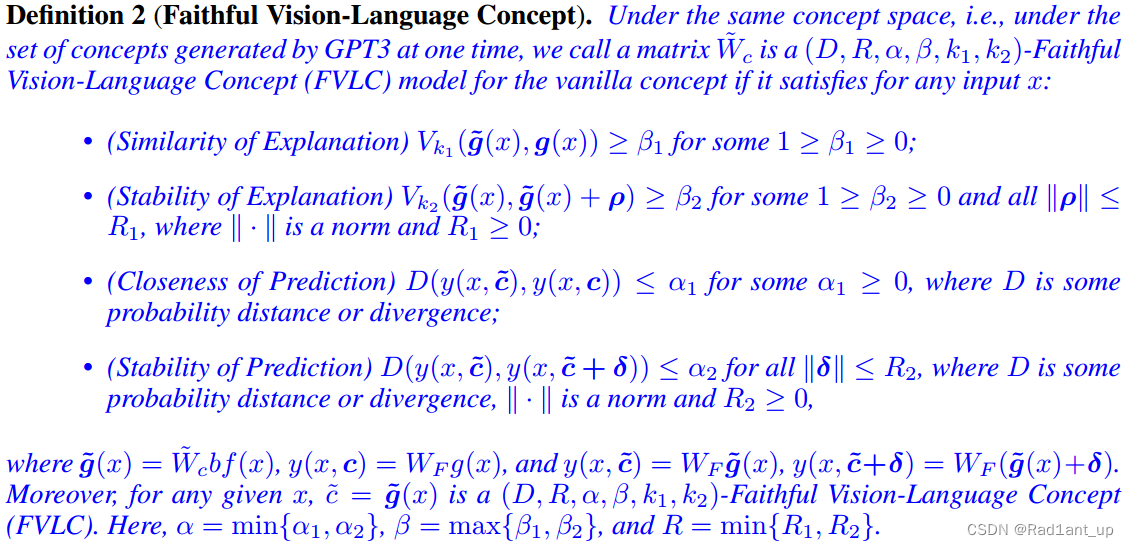
- Similarity of Explanation: faithful concept
与original concept
的 top-k1 overlap 程度大于等于
,易知
对应于二者的top-k1 concepts完全相同。这一点是为了保证faithful concept要尽可能与original concept在前 k1 个concepts上保持一致;
- Stability of Explanation: 进行
的扰动后的概念
与扰动前的概念
的top-k2 overlap程度大于等于
,易知
对应于二者完全相同。这一点是为了保证扰动后概念向量仍然不会发生太大变化(具体来说是扰动后概念的rank尽可能与原来保持一致);
- Closeness of Prediction: 用faithful concept与original concept产生的结果要尽可能一致,
代表某种距离度量比如KL散度,
时对应于二者的预测结果完全一致;
- Stability of Prediction: 对faithful concept进行扰动
后的预测结果不会发生太大变化,
时对应于二者的预测结果完全一致;
整体上,我们可以说:
4. FVLC Framework
这一节的写作上有点乱,领会精神吧......
Sensitivity: 除了上面讨论的similarity与stability,sensitivity敏感性指的是,当我们排除掉(exclude)关键的concep时预测应该表现出敏感性,而对其进行微小扰动时应该表现出稳定性。
让我们再次回到定义二,总结一下各个参数的理想值应该是什么:
Top-k approach: 尽可能接近于1;
Stability: 应该尽可能大,
尽可能接近于1;
Prediction: 应该尽可能大,
尽可能接近于0;
网络整体示意图:

整体的做法和Label-free CBM基本是一致的,只是使用 来限制网络以产生faithful concepts。总体的目标函数为:
这四项分别对应于:prediction closeness,concept similarity,prediction stability,concept stability。
可以使用PSGD解决这个优化问题,但是因为top-k overlap function 是不可微的,所以要用surrogate loss来替代。
具体来说,只优化前k个entries并简单地使用使得它们尽可能接近,见下:

(然而,从交集变为的“逐点匹配”,虽然使损失函数可微了,但对concept的rank也进行了限制。也就是说,如果是使用原本的交集操作,只要top-k中的concepts存在就行了,对顺序没有要求——比如perturbation之前top-k concepts的indices是{1,3,5,7},perturbation之后是{3,1,7,5},交集的结果是二者“完全重合”,但用
则不是。)
从而,放宽后的目标函数变为:
三、实验及结果
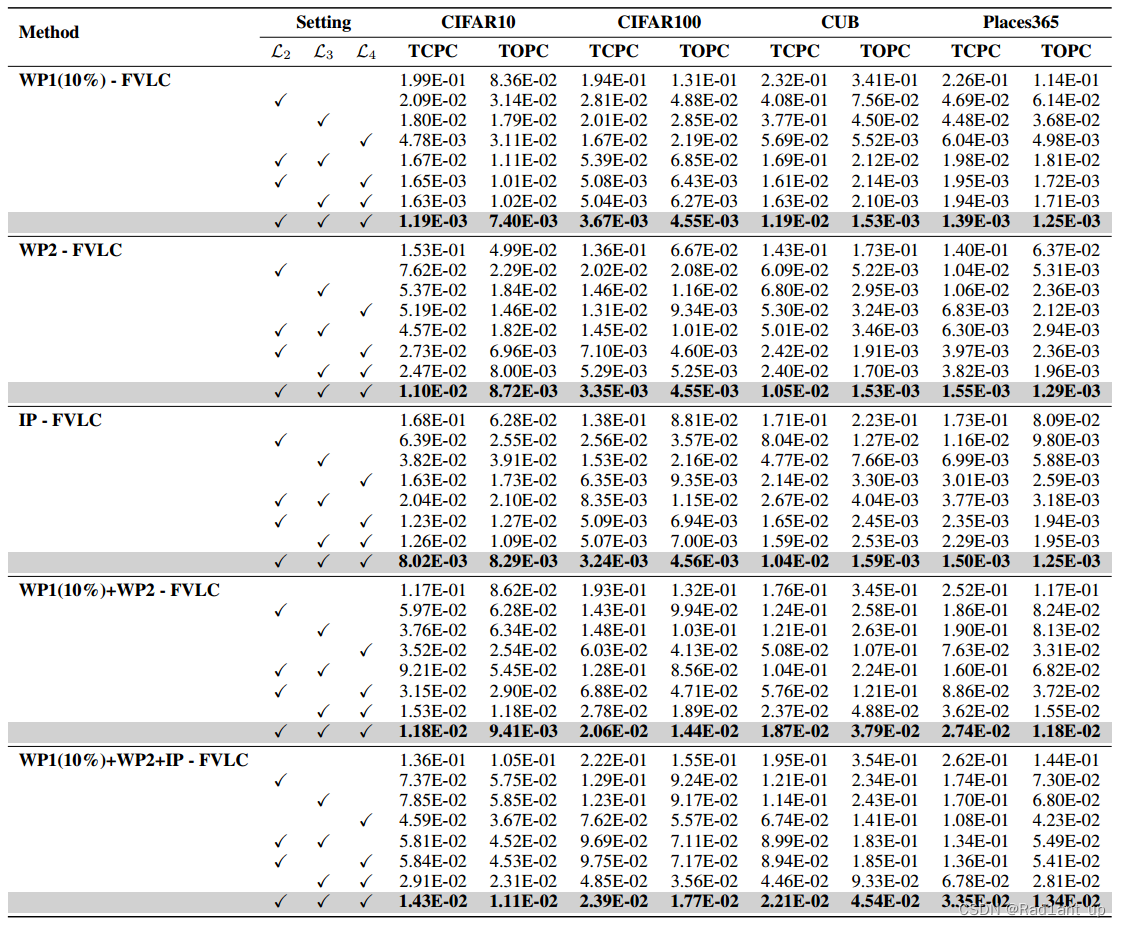
Datasets: CIFAR-10、CIFAR-100 、CUB和Places365.
Addition of perturbations:
- Word perturbation 1 (WP1): 将full concepts输入到GPT-3并让其将5%或10%的单词替换为同义词;
- Word perturbation 2 (WP2)选择text encoder的最后一层embedding,添加噪声:
;
- Input perturbation (IP): 向输入图像中添加高斯噪声
。
Evaluation Metrics: Total Concept Perturbation Change (TCPC) and Total Output Perturbation Change (TOPC).
Results:
Utility evaluation:

第一行standard指的是没有concept bottleneck layer的黑盒模型;
结果显示在各种扰动下FVLC的表现都是最好的。
Stability evaluation:

perturbation不会引起concept与prediction的较大变化;
Ablation Study: