文章目录
- 前言
- 一、场景描述
- 二、加锁
- 1.synchronized
- 2.ReentrantLock
- 三、扩展
- 1.ThreadLocal
- 总结
前言
在多线程场景下,多个线程同时对共享变量进行操作是存在风险的,这时候就需要加锁来保证数据的正确性。
一、场景描述
我这里有5个无人机,准备卖到乌克兰,奈何买家太多了,应酬不来,就挂到了网上,先到先得。
卖方
@Controller
public class StudentLockController {
private static int number=5;
public boolean get(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
if(number>0){
try {
//模拟业务处理时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(name+"业务处理成功");
number--;
return true;
}
System.out.println(name+"业务处理失败");
return false;
}
public int size(){
return number;
}
}
买方
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootStart.class)
public class SpringbootStartTest {
@Autowired
private StudentLockController studentLockController;
@Test
public void test(){
normal();
}
public void normal(){
int count=10;
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(count);
Future<Boolean> submit = null;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
submit = threadPool.submit(() -> studentLockController.get());
}
try {
submit.get();
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
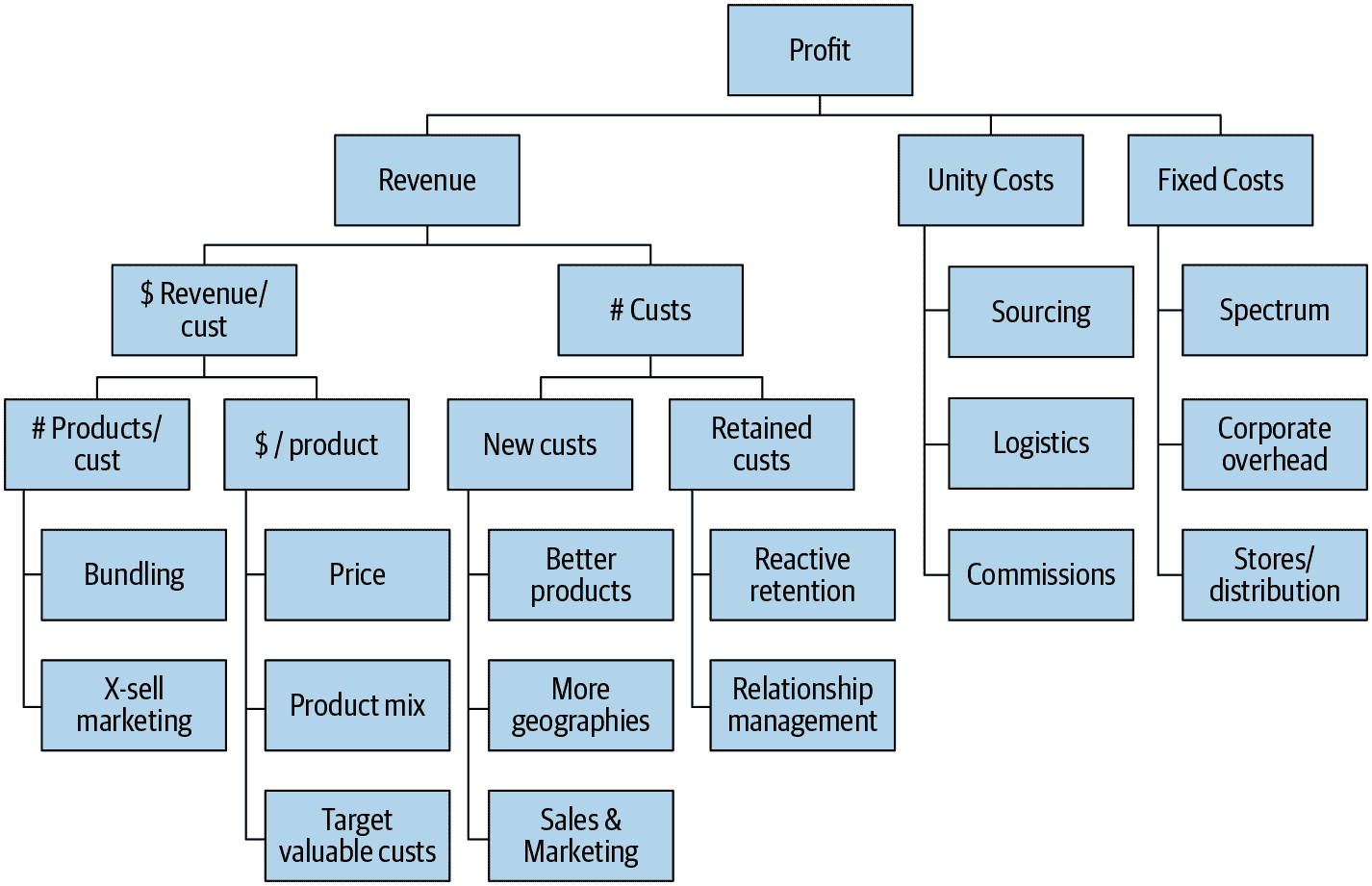
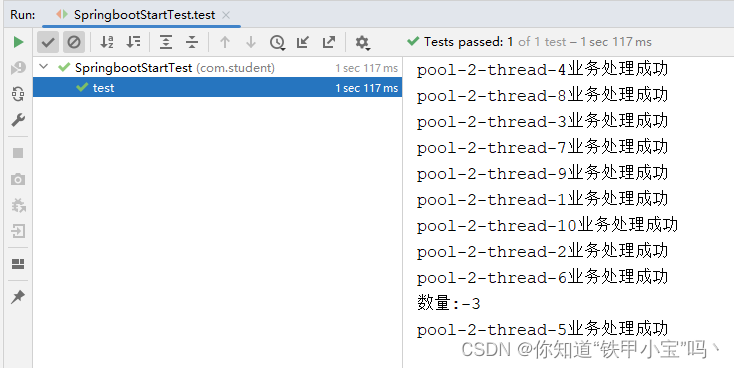
System.out.println("数量:"+studentLockController.size());
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
来了10个买家,都抢上了,这库存就5个了肯定不够,这样不行,得重新抢,我加个锁让他们排队去
二、加锁
1.synchronized
public synchronized boolean get(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
if(number>0){
try {
//模拟业务处理时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(name+"业务处理成功");
number--;
return true;
}
System.out.println(name+"业务处理失败");
return false;
}
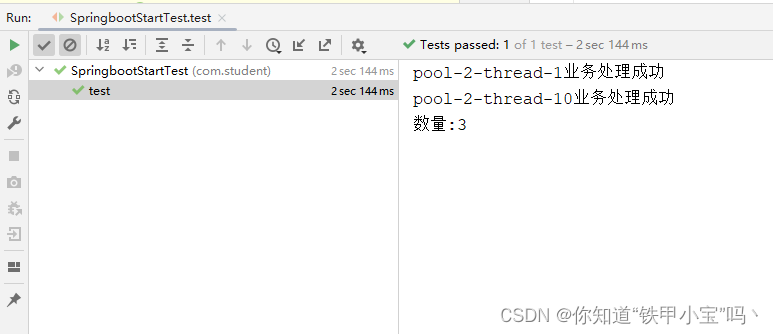
给这个方法加个锁,但这个锁范围太大了,导致我库存没卖完,这不耽误挣钱了嘛,那哪行,继续改。
2.ReentrantLock
@Controller
public class StudentLockController {
private static int number=5;
private ReentrantLock rl=new ReentrantLock();
public boolean get(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
while (!rl.tryLock()){
try {
//获取锁等待时间
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
};
try {
if(number>0){
//模拟业务处理时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(name+"业务处理成功");
number--;
return true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(rl.isLocked()){
rl.unlock();
}
}
System.out.println(name+"业务处理失败");
return false;
}
public int size(){
return number;
}
}
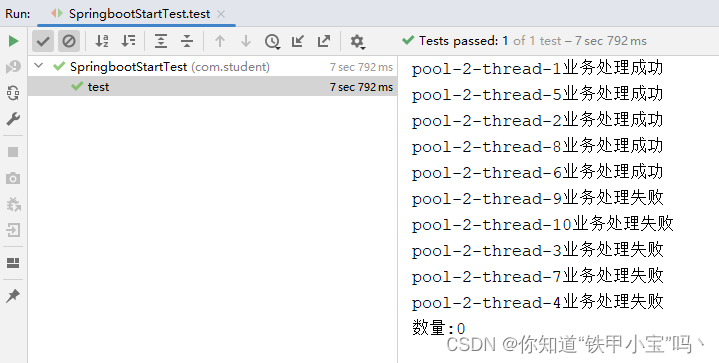
嗯,东西都卖出去了,没货了就失败了,这个能挣大钱了,ReentrantLock这个好👍
三、扩展
每个买家购买物品之前需要登陆,一个买家账户会开启一个专门的线程来维护,买家有3次用户名、密码失败的次数,这就需要控制每个线程拥有单独的变量,ThreadLocal可以为每个线程开辟单独的工作空间。
1.ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(0);
Integer count = threadLocal.get();
if(count >=3){
System.out.println("已经达到最大重试次数,请联系管理员进行重置!");
}
threadLocal.remove();
总结
回到顶部
加锁是为了保证多线程下数据的安全,但是锁过多和范围过大会影响程序性能,增加服务的处理时间,所以,使用锁要考虑当前的业务场景是否合适。