文章目录
- 一、栈(Stack)
- 1.概念
- 2.栈的使用
- 3.栈的模拟实现
- 1、定义接口
- 2、定义栈
- 3、成员
- 4、构造方法
- 5、判断空间是否满 full
- 6、入栈 push
- 7、出栈 pop
- 8、获取栈顶元素 peek
- 9、获取栈中有效元素个数 size
- 10、检测栈是否为空 empty
- 完整代码
- 4.练习
- 1、有效括号
- 2、逆波兰表达式求值
- 3、栈的压入,弹出序列
- 4、最小栈
- 5. 概念区分
- 二、队列
- 1.概念
- 2.队列的使用
- 3.模拟实现
- 1、成员
- 2、入队列 offer
- 3、出队列 poll
- 4、获取队头元素 peek
- 5、获取队列中有效元素个数 size
- 6、检查队列是否为空 isEmpty
- 完整代码
- 三、其他队列
- 1.循环队列
- 设计循环队列
- 2.双端队列
- 3.练习
一、栈(Stack)
1.概念
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。

2.栈的使用
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| Stack() | 构造一个空的栈 |
| E push(E e) | 将e入栈 |
| E pop() | 将栈顶元素出栈 |
| E peek() | 获取栈顶元素 |
| int size() | 获取栈中有效元素个数 |
| boolean empty() | 检查栈是否为空 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s =new Stack<>();
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
System.out.println(s.size());
System.out.println(s.peek());
s.pop();
System.out.println(s.pop());
if(s.empty())
{
System.out.println("栈空");
}
else
{
System.out.println(s.size());
}
}

3.栈的模拟实现
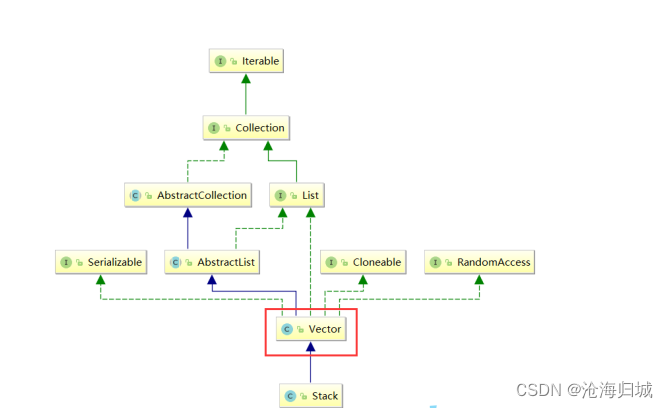
从上图中可以看到,Stack继承了Vector,Vector和ArrayList类似,都是动态的顺序表,不同的是Vector是线程安全的。
1、定义接口
public interface IStack {
void push(int x);
int pop();
int peek();
int size();
boolean empty();
//判断是否满
boolean full();
}
2、定义栈
public class MyStack implements IStack{
@Override
public void push(int x) {
}
@Override
public int pop() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int peek() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public boolean empty() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean full() {
return false;
}
}
3、成员
存储数据的数组:
private int usedSize;
有效数据的个数:
private int usedSize;
默认大小:
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
4、构造方法
public MyStack()
{
elem =new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
5、判断空间是否满 full
@Override
public boolean full() {
if(usedSize ==elem.length)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
6、入栈 push
@Override
public void push(int x) {
if(full())
{
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,elem.length*2);
}
elem[usedSize++] =x;
}
7、出栈 pop
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException(String msg)
{
super(msg);
}
}
-------------------------------------
@Override
public int pop() {
if(empty())
{
//抛异常
throw new EmptyException("栈空,出栈异常");
}
int old = elem[usedSize--];
//如果是引用就需要置空
return old;
}
8、获取栈顶元素 peek
@Override
public int peek() {
if(empty())
{
//抛异常
throw new EmptyException("栈空");
}
return elem[usedSize-1];
}
9、获取栈中有效元素个数 size
@Override
public int size() {
return usedSize;
}
10、检测栈是否为空 empty
@Override
public boolean empty() {
return usedSize==0;
}
完整代码
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException(String msg)
{
super(msg);
}
}
----------------------------
public interface IStack {
void push(int x);
int pop();
int peek();
int size();
boolean empty();
//判断是否满
boolean full();
}
----------------------------------
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyStack implements IStack{
private int [] elem;
private int usedSize;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
public MyStack()
{
elem =new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
@Override
public boolean full() {
if(usedSize ==elem.length)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void push(int x) {
if(full())
{
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,elem.length*2);
}
elem[usedSize++] =x;
}
@Override
public int pop() {
if(empty())
{
//抛异常
throw new EmptyException("栈空,出栈异常");
}
int old = elem[usedSize--];
return old;
}
@Override
public int peek() {
if(empty())
{
//抛异常
throw new EmptyException("栈空");
}
return elem[usedSize-1];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return usedSize;
}
@Override
public boolean empty() {
return usedSize==0;
}
}
4.练习
1、有效括号
有效括号
开一个栈,遇到左括号进栈,遇到右括号检查栈顶和遇到右括号是否匹配。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> st = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++)
{
char c =s.charAt(i);
if(c=='('||c=='{'||c=='[')
{
st.push(c);
}
else
{
if(c==')'&&!st.empty())
{
if(st.peek()!='(')
{
return false;
}
st.pop();
}
else if(c=='}'&&!st.empty())
{
if(st.peek()!='{')
{
return false;
}
st.pop();
}
else if(c==']'&&!st.empty())
{
if(st.peek()!='[')
{
return false;
}
st.pop();
}
else {
return false;
}
}
}
if(st.empty())
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
2、逆波兰表达式求值
逆波兰表达式
判断是操作数还是算符,如果是操作数转Int存在栈,不是就按算符进行运算。
class Solution {
boolean isOperation(String s)
{
if(s.equals("+")||s.equals("-")||s.equals("*")||s.equals("/"))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer > st = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0;i<tokens.length;i++)
{
String s = tokens[i];
if(isOperation(s))
{
int right = 0;
int left=0 ;
if(st.size()>=2)
{
right = st.pop();
left = st.pop();
}
if(s.equals("+"))
{
st.push(left+right);
}
else if(s.equals("-"))
{
st.push(left-right);
}
else if(s.equals("*"))
{
st.push(left*right);
}
else if(s.equals("/"))
{
st.push(left/right);
}
}
else
{
int temp = Integer.parseInt(s);
st.push(temp);
}
}
return st.peek();
}
}
3、栈的压入,弹出序列
栈的压入,弹出序列
先创建一个栈模拟压入,循环检查是否可以出栈,如果符合就出栈,不符合继续压入,直到全部压入但不能出栈,即为不符合弹出序列。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pushV int整型一维数组
* @param popV int整型一维数组
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();
int cur1= 0;
int cur2 =0;
int len = pushV.length;
while(cur1<len||cur2<len)
{
if(cur1<len)
{
st.push(pushV[cur1]);
}
while(cur2<len)
{
if(!st.empty()&&st.peek()==popV[cur2])
{
st.pop();
cur2++;
}
else {
if(cur1<len)
{
break;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
cur1++;
}
return st.empty();
}
}
4、最小栈
最小栈
开两个栈,一个存最小值的栈,一个就是普通的栈。在入栈的时候,判断存最小值的栈是否为空,空就同时入这两个栈,不为空就要比较存最小值的栈上面的值和新入的值,如果比最小栈的值还小或等于就同时入两栈,否则只入普通栈。
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack =new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
if(minStack.empty())
{
minStack.push(val);
}
else
{
if(minStack.peek()>=val)
{
minStack.push(val);
}
}
}
public void pop() {
if(minStack.peek().equals(stack.peek()))
{
minStack.pop();
}
stack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
5. 概念区分
栈、虚拟机栈、栈帧有什么区别?
栈:数据结构
虚拟机栈:JVM划分的一款内存而已
栈帧:调用方法的时候会在虚拟机当中给这个方法开辟一块内存
二、队列
1.概念
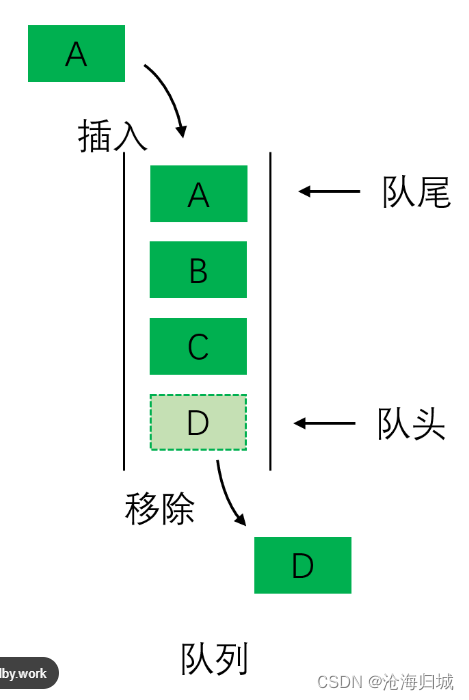
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端就进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear)
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)
2.队列的使用
在Java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表实现的。
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| boolean offer(E e) | 入队列 |
| E poll() | 出队列 |
| peek() | 获取队头元素 |
| int size() | 获取队列中有效元素个数 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 检查队列是否为空 |
注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
System.out.println(queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.peek());
queue.poll();
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
}

3.模拟实现
1、成员
双向链表节点
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val)
{
this.val =val;
}
}
头尾引用
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
节点个数
public int size;
2、入队列 offer
boolean offer(int val)
{
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
if(head==null)
{
head = node;
last = node;
}
else
{
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
size++;
return true;
}
3、出队列 poll
public int poll()
{
if(head==null){
return -1;
}
int ret = head.val;
if(head.next==null)
{
head =null;
last = null;
return ret;
}
head.next.prev = null;
head = head.next;
return ret;
}
4、获取队头元素 peek
public int peek()
{
if(head==null)
{
return -1;
}
return head.val;
}
5、获取队列中有效元素个数 size
public int size()
{
return size;
}
6、检查队列是否为空 isEmpty
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return size==0;
}
完整代码
package queuedemo;
import java.util.List;
public class MyLinkQueue {
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val)
{
this.val =val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
public int size;
boolean offer(int val)
{
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
if(head==null)
{
head = node;
last = node;
}
else
{
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
size++;
return true;
}
public int poll()
{
if(head==null){
return -1;
}
size--;
int ret = head.val;
if(head.next==null)
{
head =null;
last = null;
return ret;
}
head.next.prev = null;
head = head.next;
return ret;
}
public int peek()
{
if(head==null)
{
return -1;
}
return head.val;
}
public int size()
{
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return size==0;
}
}
三、其他队列
1.循环队列
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列通常使用数组实现。
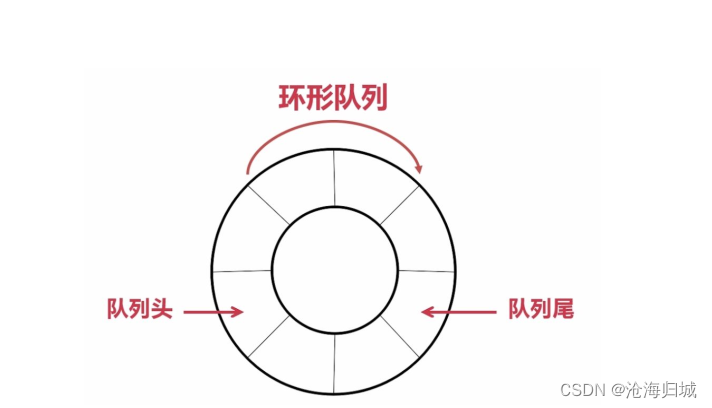
问题:
如何判断是空还是满?
解决空还是满有很多种方案:
1.使用usedSize进行记录
2.浪费一个空间来表示满
3.使用标记
如何从7下标来到0下标?
(队尾指针+1)%len
设计循环队列
设计循环队列
class MyCircularQueue {
public int [] elem;
int front = 0;
int rear = 0;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
elem = new int[k+1];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull())
{
return false;
}
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty())
{
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty())
{
return-1;
}
return elem[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty())
{
return -1;
}
int temp = (rear-1+elem.length)%elem.length;
return elem[temp];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front==rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)%elem.length==front;
}
}
2.双端队列
双端队列(deque)是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以从队尾出队和入队。
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();//双端队列的线性实现
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();//双端队列的链式实现
3.练习
队列实现栈
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> que1;
Queue<Integer> que2;
public MyStack() {
que1 = new LinkedList<>();
que2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(que1.isEmpty()&&que2.isEmpty())
{
que1.offer(x);
}
else
{
if(que1.isEmpty())
{
que2.offer(x);
}
else
{
que1.offer(x);
}
}
}
public int pop() {
int size ;
if(que1.isEmpty())
{
size = que2.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size-1;i++)
{
que1.offer(que2.poll());
}
return que2.poll();
}
else
{
size = que1.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size-1;i++)
{
que2.offer(que1.poll());
}
return que1.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(que1.isEmpty())
{
int size = que2.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size-1;i++)
{
que1.offer(que2.poll());
}
int ret =que2.poll();
que1.offer(ret);
return ret;
}
else
{
int size = que1.size();
for(int i = 0;i<size-1;i++)
{
que2.offer(que1.poll());
}
int ret =que1.poll();
que2.offer(ret);
return ret;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return que2.isEmpty()&&que1.isEmpty();
}
}
栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();//入队列
stack2 = new Stack<>();//出列
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty())
{
while(!stack1.isEmpty())
{
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(stack2.isEmpty())
{
while(!stack1.isEmpty())
{
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack2.isEmpty()&&stack1.isEmpty();
}
}