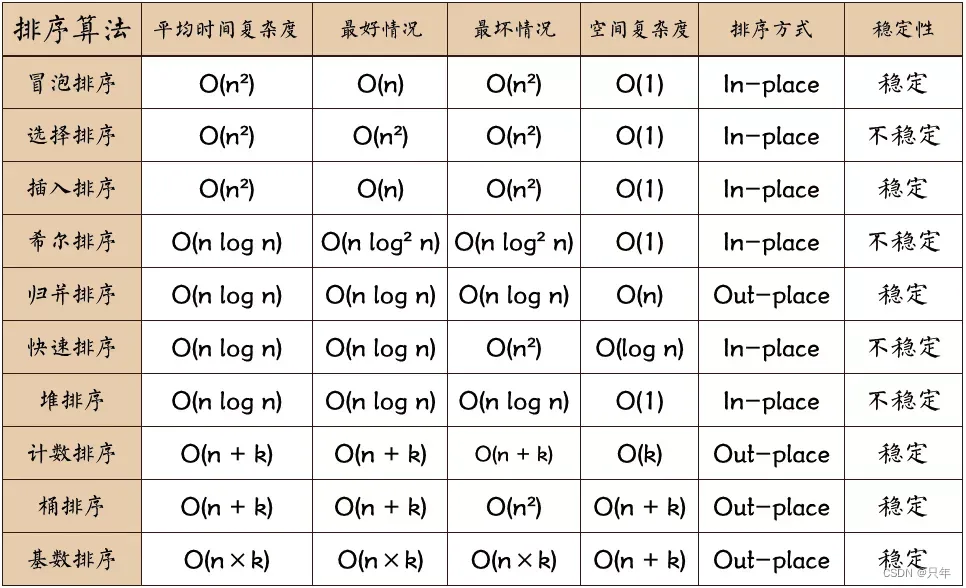
一、比较排序
1.1 交换排序
数组两元素交换位置
public class ArrayUtil {
/**
* 交换数组中的两个元素
* @param array 数组
* @param ele1Idx 元素1的索引下标
* @param ele2Idx 元素1的索引下表
*/
public static void swap(int[] array, int ele1Idx, int ele2Idx) {
int tmp = array[ele1Idx];
array[ele1Idx] = array[ele2Idx];
array[ele2Idx] = tmp;
}
}
1.1.1 冒泡排序
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new BubbleSort().bubbleSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void bubbleSort(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
ArrayUtil.swap(nums, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
}
}
1.1.2 快速排序
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new QuickSort().quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void quickSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) return;
int i = start, j = end, base = nums[start];
while (i < j) {
while (j >= 0 && nums[j] >= base) j--;
while (i < j && nums[i] <= base) i++;
if (i < j) {
ArrayUtil.swap(nums, i, j);
}
}
ArrayUtil.swap(nums, start, i);
quickSort(nums, start, i - 1);
quickSort(nums, i + 1, end);
}
}
1.2 插入排序
1.2.1 简单插入排序
public class InsertionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new InsertionSort().insertionSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void insertionSort(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
int j, temp = nums[i];
for (j = i; j > 0 && nums[j - 1] > temp; j--) {
nums[j] = nums[j - 1];
}
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
1.2.2 希尔排序
public class ShellSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new ShellSort().shellSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void shellSort(int[] nums) {
// 缩小增量排序
for (int gap = nums.length / 2; gap >= 1; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < nums.length; i++) {
int j, temp = nums[i];
for (j = i; j >= gap && nums[j - gap] > temp; j-=gap) {
nums[j] = nums[j - gap];
}
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
1.3 选择排序
1.3.1 简单选择排序
public class SelectionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new SelectionSort().selectionSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void selectionSort(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
ArrayUtil.swap(nums, i, j);
}
}
}
}
}
1.3.2 堆排序
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new HeapSort().headSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void headSort(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
buildHeap(nums, n);
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
swap(nums, i, 0);
heapify(nums, i, 0);
}
}
private void buildHeap(int[] tree, int n) {
int lastNodeIndex = n - 1;
int parentNodeIndex = (lastNodeIndex - 1) / 2;
for (int i = parentNodeIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(tree, n, i);
}
}
private void heapify(int[] tree, int n, int i) {
if (i > n) {
return;
}
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
int max = i;
if (l < n && tree[l] > tree[max]) {
max = l;
}
if (r < n && tree[r] > tree[max]) {
max = r;
}
if (max != i) {
swap(tree, max, i);
heapify(tree, n, max);
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
}
1.4 归并排序
1.4.1 二路归并排序
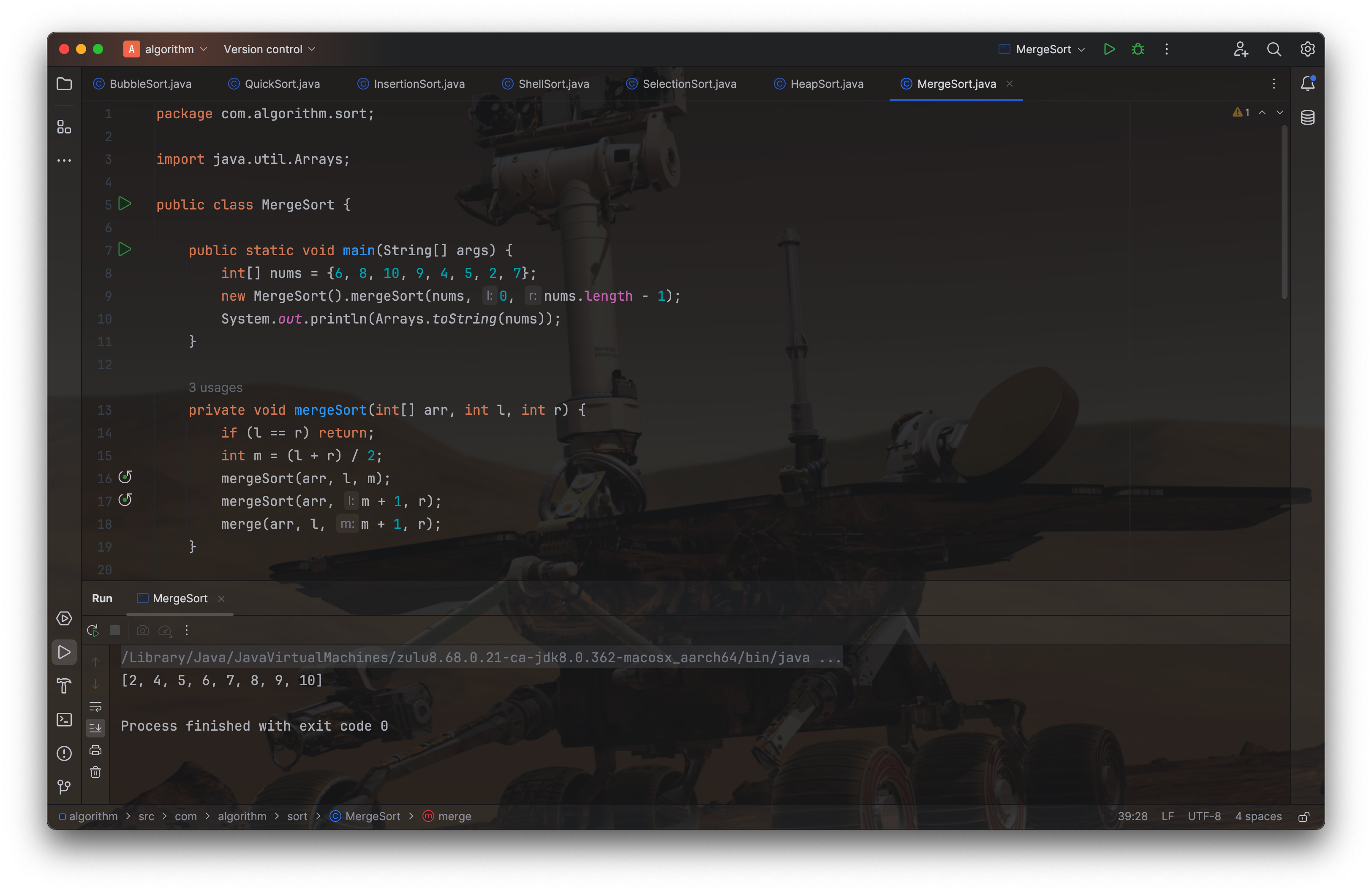
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {6, 8, 10, 9, 4, 5, 2, 7};
new MergeSort().mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
}
private void mergeSort(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return;
int m = (l + r) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, l, m);
mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r);
merge(arr, l, m + 1, r);
}
private void merge(int[] arr, int l, int m, int r) {
int lSize = m - l;
int rSize = r - m + 1;
int[] lArr = new int[lSize];
int[] rArr = new int[rSize];
// 1.fill in the left sub array
if (m - l >= 0) System.arraycopy(arr, l, lArr, 0, lSize);
// 2.fill in the right sub array
if (r + 1 - m >= 0) System.arraycopy(arr, m, rArr, 0, rSize);
// 3.merge into the original array
int i = 0, j = 0, k = l;
while (i < lSize && j < rSize) {
if (lArr[i] < rArr[j]) {
arr[k++] = lArr[i++];
} else {
arr[k++] = rArr[j++];
}
}
while (i < lSize) {
arr[k++] = lArr[i++];
}
while (j < rSize) {
arr[k++] = rArr[j++];
}
}
}
1.4.2 多路归并排序
待更新...
二、非比较排序
2.1 计数排序
public class CountingSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new CountingSort().countingSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
public void countingSort(int[] nums) {
int[] mm = getMaxMin(nums);
int[] cnt = new int[mm[1] - mm[0] + 1];
for (int num : nums) {
cnt[num - mm[0]] += 1;
}
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt[i]; j++) {
nums[idx++] = i + mm[0];
}
}
}
private static int[] getMaxMin(int[] nums) {
int max = nums[0], min = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) max = nums[i];
if (nums[i] < min) min = nums[i];
}
return new int[]{min, max};
}
}

2.2 桶排序
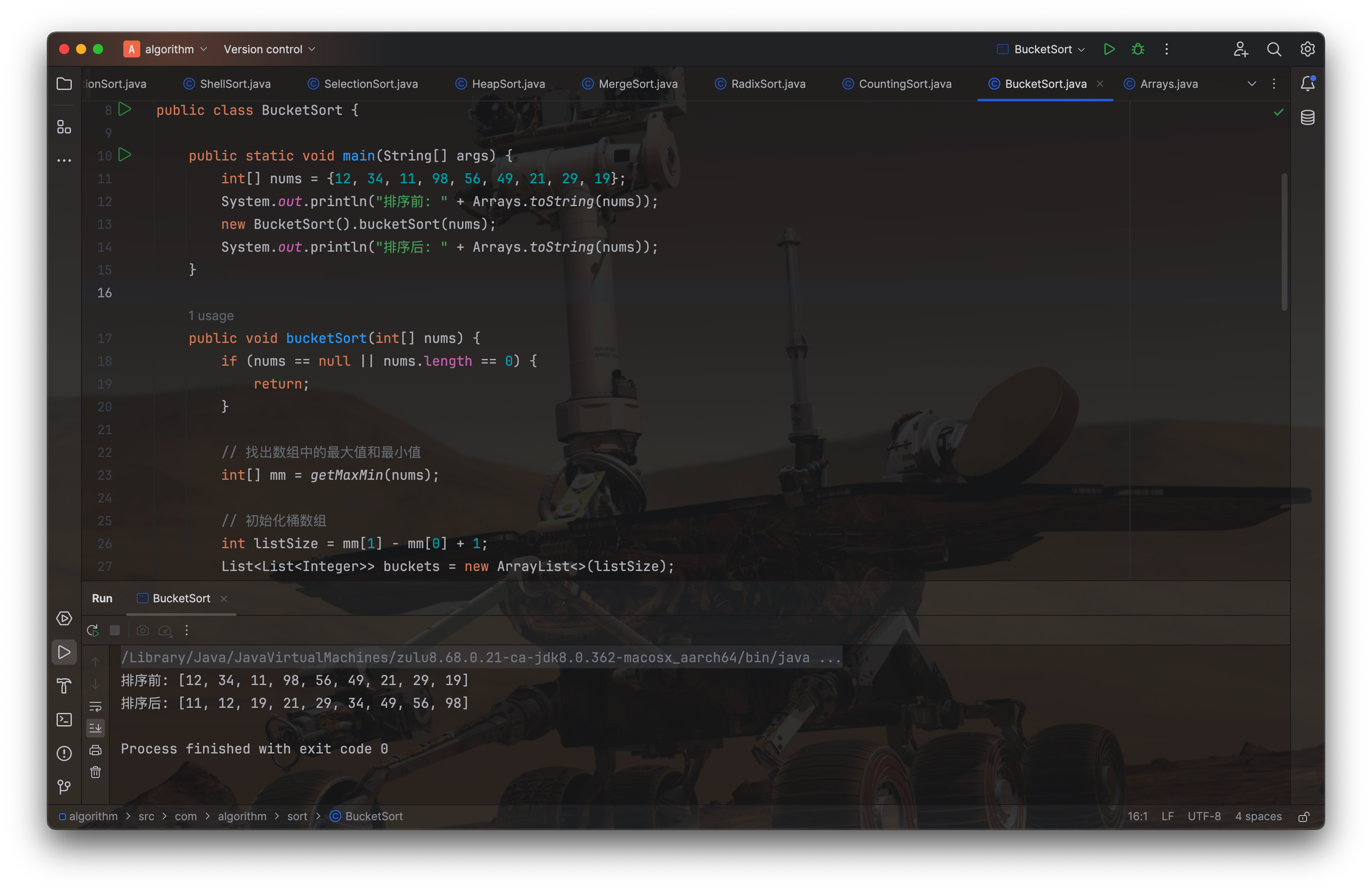
public class BucketSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new BucketSort().bucketSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
public void bucketSort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return;
}
// 找出数组中的最大值和最小值
int[] mm = getMaxMin(nums);
// 初始化桶数组
int listSize = mm[1] - mm[0] + 1;
List<List<Integer>> buckets = new ArrayList<>(listSize);
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++) {
buckets.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// 将数据分配到桶中
for (int num : nums) {
buckets.get(num - mm[0]).add(num);
}
// 对每个桶进行排序,这里使用了简单的Insertion Sort
for (List<Integer> numList : buckets) {
if (!numList.isEmpty()) {
Collections.sort(numList);
}
}
// 从桶中收集已排序的数据
int k = 0;
for (List<Integer> bucket : buckets) {
for (Integer value : bucket) {
nums[k++] = value;
}
}
}
private static int[] getMaxMin(int[] nums) {
int max = nums[0], min = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) max = nums[i];
if (nums[i] < min) min = nums[i];
}
return new int[]{min, max};
}
}
2.3 基数排序
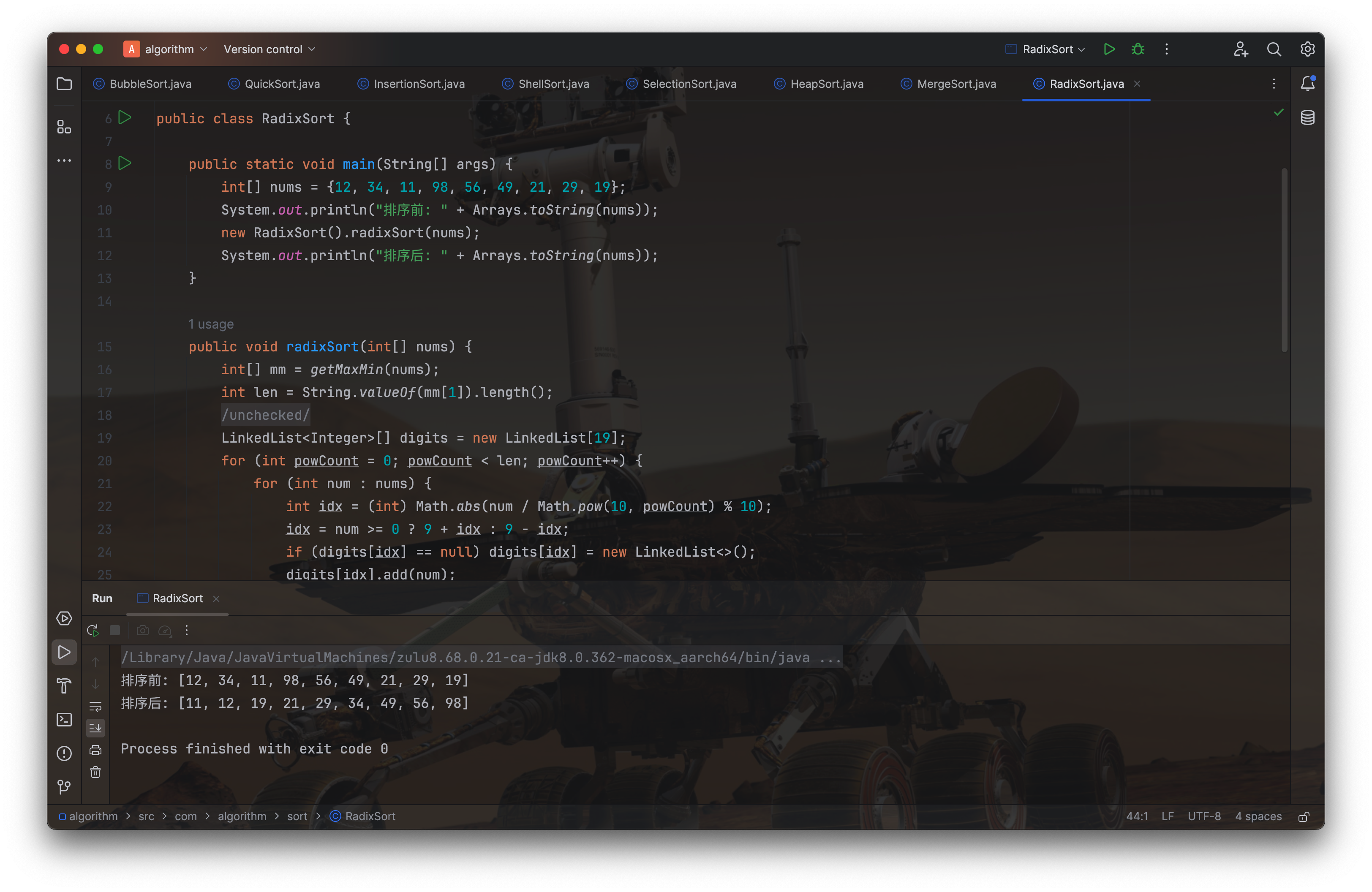
public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {12, 34, 11, 98, 56, 49, 21, 29, 19};
System.out.println("排序前: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
new RadixSort().radixSort(nums);
System.out.println("排序后: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
public void radixSort(int[] nums) {
int[] mm = getMaxMin(nums);
int len = String.valueOf(mm[1]).length();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
LinkedList<Integer>[] digits = new LinkedList[19];
for (int powCount = 0; powCount < len; powCount++) {
for (int num : nums) {
int idx = (int) Math.abs(num / Math.pow(10, powCount) % 10);
idx = num >= 0 ? 9 + idx : 9 - idx;
if (digits[idx] == null) digits[idx] = new LinkedList<>();
digits[idx].add(num);
}
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < digits.length; j++) {
while (digits[j] != null && !digits[j].isEmpty()) {
nums[i++] = digits[j].removeFirst();
}
}
}
}
private static int[] getMaxMin(int[] nums) {
int max = nums[0], min = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) max = nums[i];
if (nums[i] < min) min = nums[i];
}
return new int[]{min, max};
}
}






![[HCIE]防火墙基础配置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/271fca66d0834f1183b65c86cbafda3d.png)