题目:
A priority encoder is a combinational circuit that, when given an input bit vector, outputs the position of the first 1 bit in the vector. For example, a 8-bit priority encoder given the input 8’b10010000 would output 3’d4, because bit[4] is first bit that is high.
Build a 4-bit priority encoder. For this problem, if none of the input bits are high (i.e., input is zero), output zero. Note that a 4-bit number has 16 possible combinations.

解题:
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos );
always@(*)
begin
case(in)
4'b0000:pos = 2'd00;
4'b0001:pos = 2'd00;
4'b0010:pos = 2'd01;
4'b0011:pos = 2'd00;
4'b0100:pos = 2'd02;
4'b0101:pos = 2'd00;
4'b0110:pos = 2'd01;
4'b0111:pos = 2'd00;
4'b1000:pos = 2'd03;
4'b1001:pos = 2'd00;
4'b1010:pos = 2'd01;
4'b1011:pos = 2'd00;
4'b1100:pos = 2'd02;
4'b1101:pos = 2'd00;
4'b1110:pos = 2'd01;
4'b1111:pos = 2'd00;
default:pos = 2'd00;
endcase
end
endmodule
结果正确:
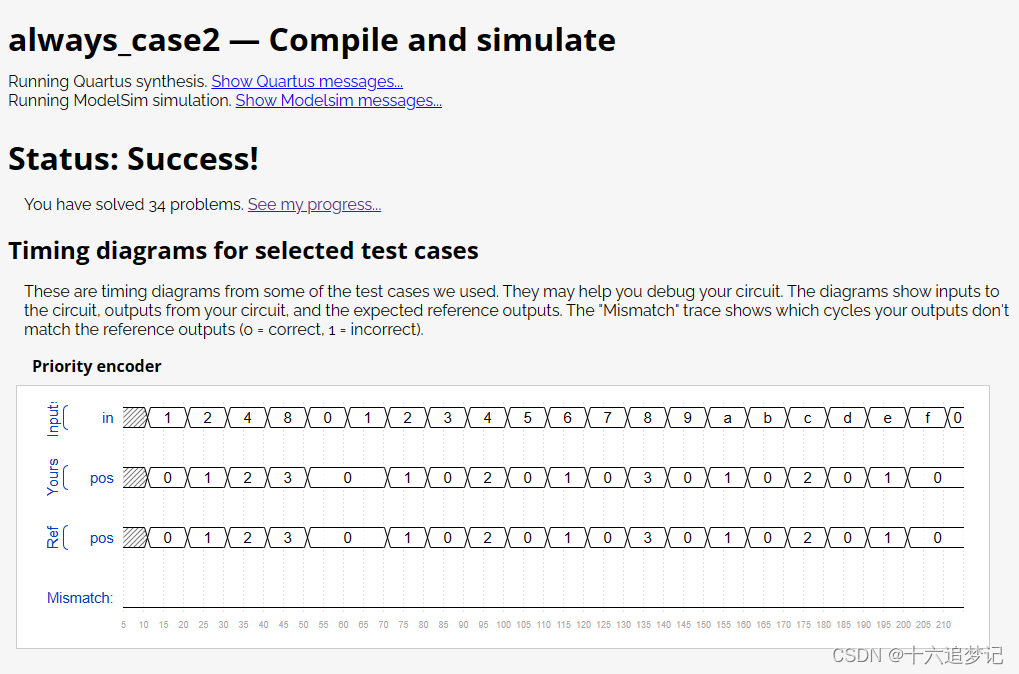
答案:
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos
);
always @(*) begin // Combinational always block
case (in)
4'h0: pos = 2'h0; // I like hexadecimal because it saves typing.
4'h1: pos = 2'h0;
4'h2: pos = 2'h1;
4'h3: pos = 2'h0;
4'h4: pos = 2'h2;
4'h5: pos = 2'h0;
4'h6: pos = 2'h1;
4'h7: pos = 2'h0;
4'h8: pos = 2'h3;
4'h9: pos = 2'h0;
4'ha: pos = 2'h1;
4'hb: pos = 2'h0;
4'hc: pos = 2'h2;
4'hd: pos = 2'h0;
4'he: pos = 2'h1;
4'hf: pos = 2'h0;
default: pos = 2'b0; // Default case is not strictly necessary because all 16 combinations are covered.
endcase
end
// There is an easier way to code this. See the next problem (always_casez).
endmodule
注意:
本题一开始没理解题目意思,比较迷,还是需要先把题目意思理解才会写。4位优先编码器

![[ECE] P2.3Determine t_P_LH and t_P_HL from the oscilloscope](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2d6c748baac941818c67c7447ac9a300.png)