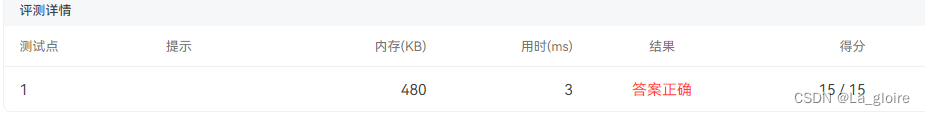
对于输入的若干学生的信息,按学号顺序从小到大建立有序链表,最后遍历链表,并按顺序输出学生信息。
输入格式:
首先输入一个正整数T,表示测试数据的组数,然后是T组测试数据。每组测试数据首先输入一个正整数n,表示学生的个数。然后输入n行信息,分别是学生的学号和姓名,其中,学号是8位的正整数(保证各不相同),姓名是长度不超过10且不含空格的字符串。
输出格式:
对于每组测试,按顺序输出学生信息,学号和姓名之间留一个空格(参看输出样例)。
输入样例:
1
3
20220108 Zhangsan
20210328 Lisi
20210333 Wangwu
输出样例:
20210328 Lisi
20210333 Wangwu
20220108 Zhangsan代码呈现
//C语言
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
//定义学生结构体
struct Student
{
char code[9];//学号
char name[11];//名字
struct Student* next;//指向下一个节点的指针
};
//写一个函数创建新节点
struct Student* creatNode(char code[],char name[])
{
//分配内存空间
struct Student* newNode = (struct Student*)malloc(sizeof(struct Student));
strcpy(newNode->code,code);//复制学号
strcpy(newNode->name,name);//复制姓名
newNode->next = NULL;//将next指针初始化为NULL,表示链表的结束
return newNode;
}
//插入节点到有序链表中
struct Student* insertNode(struct Student* head,struct Student* newNode)
{
if(head == NULL || strcmp(newNode->code,head->code) < 0)
{
//如果链表为空或者新节点的学号小于头节点的学号,将新节点插入到头部
newNode->next = head;
return newNode;//返回新节点为头部
}
struct Student* curr = head;//辅助节点
while(curr->next != NULL && strcmp(newNode->code,curr->next->code) > 0)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
newNode->next = curr->next;
curr->next = newNode;
return head;
}
//遍历链表并输出学生信息
void traverseList(struct Student* head)
{
struct Student* curr = head;
while(curr != NULL)
{
printf("%s %s\n",curr->code,curr->name);
curr = curr->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int T;//测试数据的个数
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int n;//学生个数
scanf("%d",&n);
struct Student* head = NULL;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
char code[9];
char name[11];
scanf("%s%s",code,name);
struct Student* newNode = creatNode(code,name);
head = insertNode(head,newNode);
}
traverseList(head);
//释放链表内存空间
struct Student* curr = head;
while(curr != NULL)
{
struct Student* temp = curr;
curr = curr->next;
free(temp);
}
}
return 0;
}测试点