异步请求
-
同步发送请求过程如下

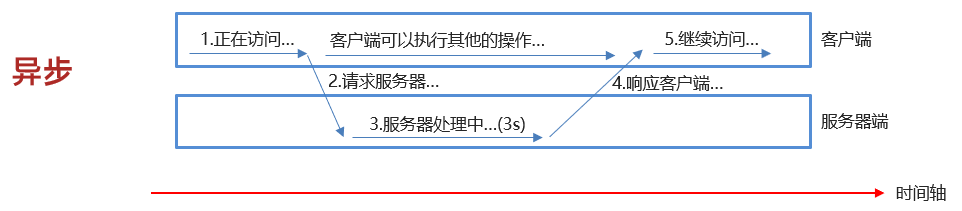
浏览器页面在发送请求给服务器,在服务器处理请求的过程中,浏览器页面不能做其他的操作。只能等到服务器响应结束后才能,浏览器页面才能继续做其他的操作。
-
异步发送请求过程如下浏览器页面发送请求给服务器,在服务器处理请求的过程中,浏览器页面还可以做其他的操作。
Ajax
我们先来看一下axios的基础版本ajax,这里大家了解即可!
//2. 发送ajax请求
//2.1. 创建核心对象
var xhttp;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
// code for IE6, IE5
xhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
//2.2. 发送请求
xhttp.open("GET", "http://localhost:8080/ajax-demo/selectUserServlet);
xhttp.send();
//2.3. 获取响应
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
//处理响应的结果
}
};
可以看出,前端给后端发送请求,主要由三部分组成:
- 创建对象
- 调用方法,发送请求
- 调用方法,获取响应
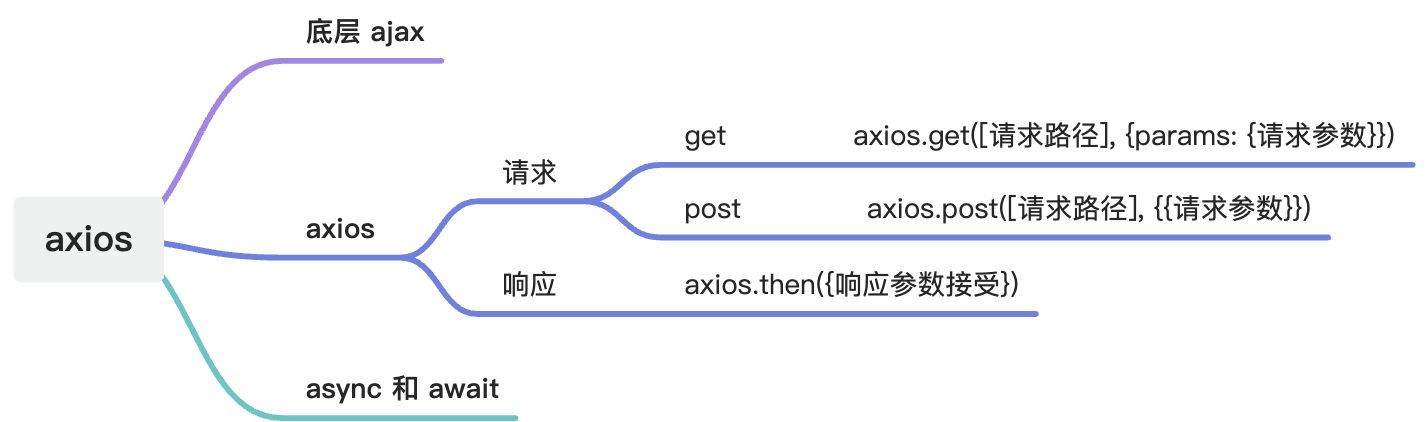
Axios
其实,axios是由ajax封装得来的,他简化了ajax的重复工作,使我们工作更简单
入门案例
我们以get请求为例来来研究axios的使用
方法一:
this.$axios.get('http://localhost:8080/goods.json?id=1',{
params: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
},err=>{
console.log(err);
})
方法二:
this.$axios({
method: 'get',
url: 'http://localhost:8080/goods.json?id=1',
params: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
},err=>{
console.log(err);
})
可以看到,axios的请求依旧由 请求 和 响应 来组成,而对象的创建这种重复不变的工作由axios来封装完成
在日常代码编写中,方式一更常用
这里我们其实可以优化,将 this.$ 来省略
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/goods.json?id=1',{
params: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
},err=>{
console.log(err);
})
这里的请求中,我们主要指定请求后端路径
这里的响应中,我们使用.then来访问,使用res=>{ }来获取响应的数据
相信到了这里,大家对axios的基础使用有了基本的了解,接下来,我们就好好研究一下我们的 请求 和 响应 这两大板块
请求方式
axios可以请求的5种方法:
- get:获取数据,请求指定的信息,返回实体对象
- post:向指定资源提交数据(例如表单提交或文件上传)
- put:更新数据,从客户端向服务器传送的数据取代指定的文档的内容
- patch:更新数据,是对put方法的补充,用来对已知资源进行局部更新
- delete:请求服务器删除指定的数据
get
我们的入门案例中就使用的是get请求
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/goods.json?id=1',{
params: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
post
方法一:注意这里参数传递不写params
axios.post('/url',{
id:1
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
方法二:注意这里参数传递是data
axios({
method: 'post',
url: '/url',
data: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
form-data请求
let data = {
//请求参数
}
let formdata = new FormData();
for(let key in data){
formdata.append(key,data[key]);
}
axios.post('/goods.json',formdata).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
put
axios.put('/url',{
id:1
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
patch请求
axios.patch('/url',{
id:1
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
delete
参数以明文形式提交
this.$axios.delete('/url',{
params: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
参数以封装对象的形式提交
axios.delete('/url',{
data: {
id:1
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
axios({
method: 'delete',
url: '/url',
params: { id:1 }, //以明文方式提交参数
data: { id:1 } //以封装对象方式提交参数
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
all 并发请求(了解)
并发请求:同时进行多个请求,并统一处理返回值
this.$axios.all([
this.$axios.get('/goods.json'),
this.$axios.get('/classify.json')
]).then(
this.$axios.spread((goodsRes,classifyRes)=>{
console.log(goodsRes.data);
console.log(classifyRes.data);
})
)
响应
这里我们只要了解使用
- res => {} 接受参数
- err => {} 接受参数
async和await
参考帖子:async和await
async/await 出现的原因
Promise 的编程模型依然充斥着大量的 then 方法,虽然解决了回调地狱的问题,但是在语义方面依然存在缺陷,代码中充斥着大量的 then 函数,这就是 async/await 出现的原因。async/await 让代码更少,更简洁。
入门案例
这里我们还是以 get 请求为例
// vue2 格式
async sendReq() {
const resp = await axios.get('http://localhost:8080/goods');
}
// vue3格式
const sendReq = async () => {
const resp = await axios.get('http://localhost:8080/goods');
}
写法说明:
- await 等待请求返回值,使用遍历接受返回值,我们使用响应值的时候可以直接使用resp这个接受变量来获取
- await等待谁呢?等待async修饰的异步函数,所以有await一定有async,并且作用在函数上
后续的深入原理教程我们下期再见!