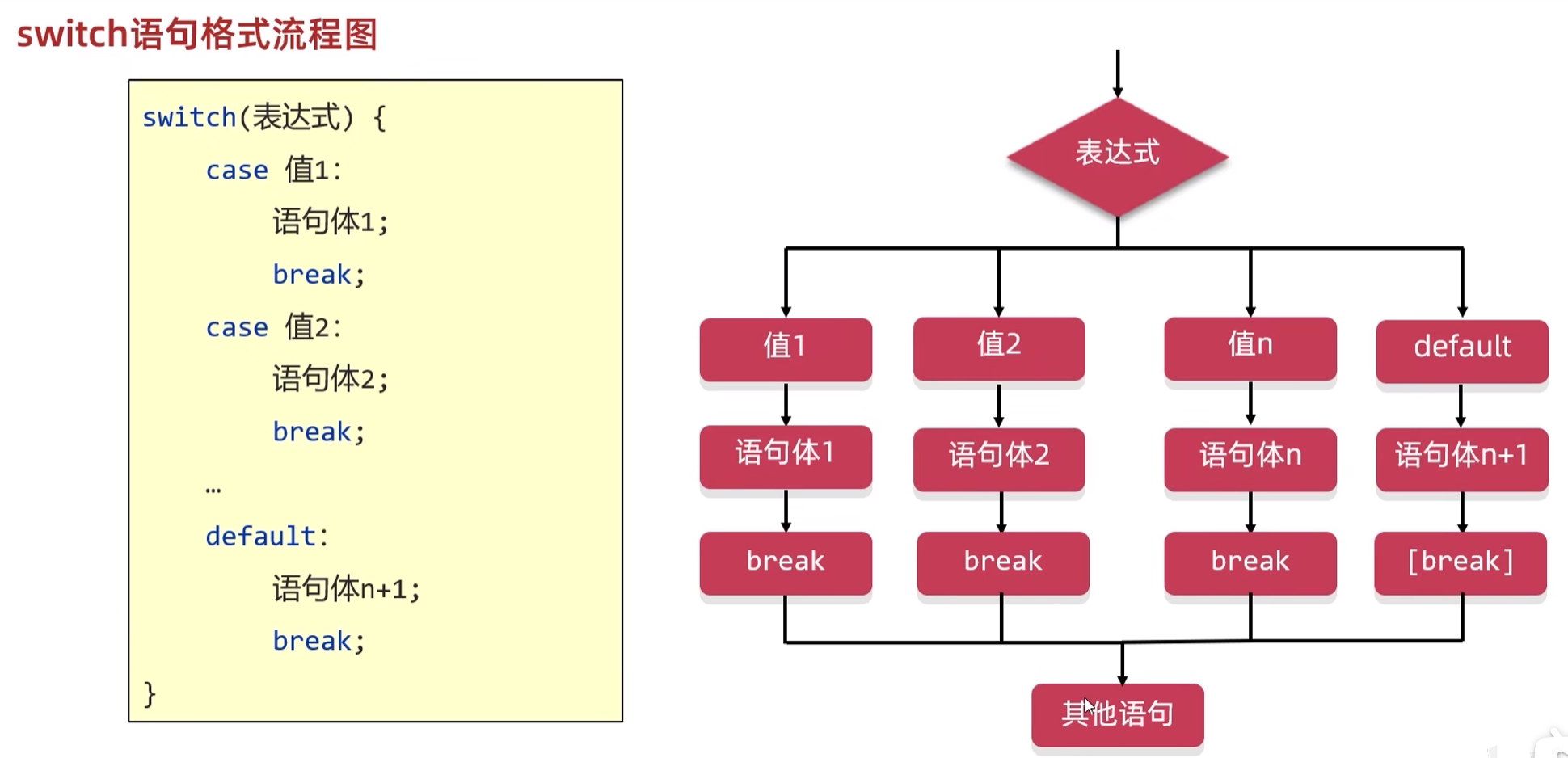
switch语句格式
switch(表达式) {
case 值1:
语句体1;
break;
case 值2:
语句体2;
break;
...
default:
语句体n+1;
break;
}
- 执行流程:
- 首先计算表达式的值。
- 依次和
case后面的值进行比较,如果有对应的值,就会执行相应的语句,在执行的过程中,遇到break就会解释。 - 如果所有的
case后面的值和表达式的值都不匹配,就会执行default里面的语句体,然后结束整个switch语句。

代码演示
public class SwitchDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//兰州拉面、武汉热干面、北京炸酱面、陕西油泼面
//1.定义变量记录我心里想吃的面
//2.拿着这个面利用switch跟四种面条匹配
String noodles = "海鲜龙虾面";
switch (noodles) {
case "兰州拉面":
System.out.println("吃兰州拉面");
break;
case "武汉热干面":
System.out.println("吃武汉热干面");
break;
case "北京炸酱面":
System.out.println("吃北京炸酱面");
break;
case "陕西油泼面":
System.out.println("吃陕西油泼面");
break;
default:
System.out.println("吃方便面");
break;
}
}
}
练习
运动计划
需求:键盘录入星期数,显示今天的减肥活动。
周一:跑步
周二:游泳
周三:慢走
周四:动感单车
周五:拳击
周六:爬山
周日:好好吃一顿
代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入今天是星期几");
String day = sc.next();
switch (day) {
case "周一":
System.out.println("跑步");
break;
case "周二":
System.out.println("游泳");
break;
case "周三":
System.out.println("慢走");
break;
case "周四":
System.out.println("动感单车");
break;
case "周五":
System.out.println("拳击");
break;
case "周六":
System.out.println("爬山");
break;
case "周日":
System.out.println("好好吃一顿");
break;
default:
System.out.println("狠狠地颓废一周");
break;
}
}
}
另
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入今天是星期几");
int week = sc.nextInt();
switch (day) {
case 1:
System.out.println("跑步");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("游泳");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("慢走");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("动感单车");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("拳击");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("爬山");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("好好吃一顿");
break;
default:
System.out.println("狠狠地颓废一周");
break;
}
}
}
switch的扩展知识点和练习
1.default的位置和省略
/*
default的位置和省略
1.位置:default不一定是写在最下面的,我们也可以写在任意位置。只是习惯写在最下面
2.省略:default可以省略,语法不会有问题,但是不建议省略。
*/
public class SwitchDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 100;
switch (number) {
case 1:
System.out.println("number的值为1");
break;
case 10:
System.out.println("number的值为10");
break;
case 20:
System.out.println("number的值为20");
break;
/*default:
System.out.println("number的值不是1,10或者20");
break;*/
}
}
}
2.case穿透
/*
case穿透:break省略了导致的。
执行流程:
首先还是会用小括号中表达式中的值与下面每一个case进行匹配;
如果匹配上了,就会执行对应的语句体,如果此时发现了break,那么结束整个switch语句。
如果没有发现break,那么程序会执行下一个语句体。一直直到遇到下一个break或者右大括号为止。
*/
public class SwitchDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
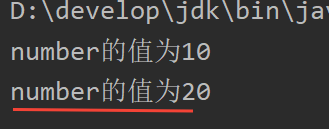
int number = 10;
switch (number) {
case 1:
System.out.println("number的值为1");
break;
case 10:
System.out.println("number的值为10");
//break;
case 20:
System.out.println("number的值为20");
break;
default:
System.out.println("number的值不是1,10或者20");
//break;
}
}
}
output
3.switch函数在JDK12之后的新特性。
//1.简化格式
int number = 1;
switch (number) {
case 1 -> {
System.out.println("一");
}
case 2 -> {
System.out.println("二");
}
case 3 -> {
System.out.println("三");
}
default -> {
System.out.println("没有这种选项");
}
}
//2.如果{}中只有一行代码,可以省略大括号。
int number = 1;
switch (number) {
case 1 -> System.out.println("一");
case 2 -> System.out.println("二");
case 3 -> System.out.println("三");
default -> System.out.println("没有这种选项");
}
其实,还可以对switch赋值变量去接收switch的结果,稍微有点难,在之后学完方法再来讨论。
/*
switch新特性
JDK12
*/
public class SwitchDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:
// 1 2 3 一 二 三
/*int number = 1;
switch (number) {
case 1:
System.out.println("一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("三");
break;
default:
System.out.println("没有这种选项");
break;
}*/
/*int number = 1;
switch (number) {
case 1 -> {
System.out.println("一");
}
case 2 -> {
System.out.println("二");
}
case 3 -> {
System.out.println("三");
}
default -> {
System.out.println("没有这种选项");
}
}*/
int number = 1;
switch (number) {
case 1 -> System.out.println("一");
case 2 -> System.out.println("二");
case 3 -> System.out.println("三");
default -> System.out.println("没有这种选项");
}
}
}
4.switch和if第三种格式各自的使用场景
练习
休息日和工作日
需求:键盘录入星期数,输出工作日、休息日。
(1-5)工作日,(6-7)休息日。
switch语句写法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
需求:键盘录入星期数,输出工作日、休息日。
(1-5) 工作日,(6-7)休息日。
*/
//分析:
//1.键盘录入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入星期数");
int day = sc.nextInt();
//2.用switch语句进行选择
switch (day) {
case 1:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("休息日");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("休息日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("再想想?");
break;
}
语句重复了,可以用
case穿透简化代码!
//2.用switch语句进行选择
switch (day) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
System.out.println("休息日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("再想想?");
break;
}
还可以进一步再简化
//2.用switch语句进行选择
switch (day) {
case 1,2,3,4,5:
System.out.println("工作日");
break;
case 6,7:
System.out.println("休息日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("再想想?");
break;
}
emm,其实还能简化(利用
JDK12的新特性)
//2.用switch语句进行选择
switch (day) {
case 1,2,3,4,5 -> System.out.println("工作日");
case 6,7 -> System.out.println("休息日");
default -> System.out.println("再想想?");
}
机票业务
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
在实际开发中,如果我们需要在多种情况下选择其中一个,就可以使用switch语句
当我们拨打了某些服务电话时,一般都会有按键选择。
假设我们现在拨打了一个机票预定电话。
电话中语音提示:
1机票查询
2机票预定
3机票改签
4退出服务
其他按键也是退出服务。请使用switch模拟该业务逻辑。
*/
//分析:
//1.键盘录入我们的选择
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入数字获取服务");
int number = sc.nextInt();
//2.根据选择执行不同的代码逻辑
switch (number) {
case 1 -> System.out.println("机票查询");
case 2 -> System.out.println("机票预定");
case 3 -> System.out.println("机票改签");
//case 4 -> System.out.println("退出服务");
default -> System.out.println("退出服务");
}
}
}