目录
- 写在开头
- 1. 地理编码基础
- 1.1 地理编码的基本原理
- 1.1.1 坐标系统
- 1.1.2 地名解析
- 1.1.3 编码算法
- 1.2 Python中使用地理编码的基础知识
- 1.2.1 百度地图API
- 1.2.2 高德地图API
- 1.2.3 腾讯地图API
- 1.3 Python中实现代码
- 2. 逆地理编码
- 2.1 利用Python进行逆地理编码
- 2.1.1 获取高德地图开发者密钥
- 2.1.2 使用高德地图API进行逆地理编码
- 2.2 Python中实现代码
- 写在最后
写在开头
地理空间数据科学作为一个不断发展的领域,涉及着前沿问题和多元化的研究方向。本文将深入探讨该领域的最新进展,以及如何在Python中运用深度学习等技术解决地理问题的实际案例。
1. 地理编码基础
1.1 地理编码的基本原理
地理编码是通过坐标将地球表面上的点转换为可读的地址或地名的过程。在中国,主要的地理编码服务提供商有百度地图、高德地图和腾讯地图。了解地理编码的基本原理有助于理解数据的转换过程。
1.1.1 坐标系统
地理编码依赖于坐标系统,通常使用经度和纬度表示地球上的点。在中国,常用的坐标系有WGS-84、GCJ-02和BD-09。其中,WGS-84为全球卫星定位系统使用的坐标系,GCJ-02为中国国测局制定的坐标系,而BD-09是在GCJ-02基础上由百度进行的扩展。
1.1.2 地名解析
地名解析是地理编码的关键步骤,它涉及将抽象的坐标映射为人类可读的地址。在中国,地名解析需要充分理解中文地理信息数据库,将坐标与地名、行政区划等信息相匹配。
1.1.3 编码算法
不同的地理编码服务商采用不同的编码算法。百度地图使用BD-09坐标系,高德地图使用GCJ-02坐标系,腾讯地图也采用自家坐标系。这些算法确保地理编码结果的准确性和一致性。
1.2 Python中使用地理编码的基础知识
1.2.1 百度地图API
百度地图API提供了全面的地理编码服务,包括正地理编码和逆地理编码。使用前需要在百度开放平台注册开发者账号,创建应用并获取API密钥。
1.2.2 高德地图API
高德地图API同样提供了丰富的地理编码服务。在使用前,需要在高德开放平台注册开发者账号,创建应用并获取Key。
1.2.3 腾讯地图API
腾讯地图API包括地理编码和逆地理编码服务。在开始之前,需要在腾讯位置服务注册账号,创建应用并获取Key。
1.3 Python中实现代码
以下是在Python中使用高德地图API进行地理编码的详细示例:
单个地址
import requests
def geocode(address, api_key):
base_url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/geo"
params = {
'address': address,
'key': api_key,
'output': 'json'
}
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)
data = response.json()
if data['status'] == '1' and int(data['count']) > 0:
location = data['geocodes'][0]['location'].split(',')
latitude, longitude = float(location[1]), float(location[0])
return latitude, longitude
else:
return None
address = "广州市广州塔"
api_key = "your_api_key" # 替换成你的高德API Key
result = geocode(address, api_key)
if result:
print(f"经纬度:{result[0]}, {result[1]}")
else:
print("地理编码失败,请检查输入地址或API Key是否正确。")
运行上面的代码,得到下面的输出:

列表形式
当我们以列表形式输入多个地理位置时,可以使用下面的代码:
import requests
def geocode(address, api_key):
base_url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/geo"
params = {
'address': address,
'key': api_key,
'output': 'json'
}
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)
data = response.json()
if data['status'] == '1' and int(data['count']) > 0:
location = data['geocodes'][0]['location'].split(',')
latitude, longitude = float(location[1]), float(location[0])
return latitude, longitude
else:
return None
def batch_geocode(addresses, api_key):
coordinates_list = []
for address in addresses:
result = geocode(address, api_key)
if result:
coordinates_list.append(result)
return coordinates_list
addresses_list = ["广州市广州塔", "北京天安门", "上海陆家嘴"]
api_key = "your_api_key" # 替换成你的高德API Key
coordinates_result = batch_geocode(addresses_list, api_key)
if coordinates_result:
for i, coordinates in enumerate(coordinates_result):
print(f"{addresses_list[i]} 的经纬度:{coordinates[0]}, {coordinates[1]}")
else:
print("地理编码失败,请检查输入地址或API Key是否正确。")
pandas集成
当我们输入的地理位置是pandas中的某个列时,可以使用下面的代码进行调用:
import requests
import pandas as pd
def geocode(address, api_key):
base_url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/geo"
params = {
'address': address,
'key': api_key,
'output': 'json'
}
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)
data = response.json()
if data['status'] == '1' and int(data['count']) > 0:
location = data['geocodes'][0]['location'].split(',')
latitude, longitude = float(location[1]), float(location[0])
return latitude, longitude
else:
return None
def batch_geocode(df, address_column, api_key):
coordinates_list = []
for _, row in df.iterrows():
address = row[address_column]
result = geocode(address, api_key)
if result:
coordinates_list.append(result)
else:
coordinates_list.append((None, None)) # 添加空坐标,表示失败
# 将结果增加到 DataFrame 中
df[['Latitude', 'Longitude']] = pd.DataFrame(coordinates_list, columns=['Latitude', 'Longitude'])
# 示例DataFrame,包含一个地址列
data = {'Address': ["广州市广州塔", "北京天安门", "上海陆家嘴"]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
api_key = "your_api_key" # 替换成你的高德API Key
batch_geocode(df, 'Address', api_key)
# 打印包含经纬度信息的DataFrame
print(df)
2. 逆地理编码
逆地理编码在中国境内的应用涉及将经纬度坐标转换为具体的省市区等地理位置信息。中国地理广阔,拥有复杂的地名体系,因此在进行逆地理编码时,需考虑特定的地理情境。
2.1 利用Python进行逆地理编码
2.1.1 获取高德地图开发者密钥
首先,为了使用高德地图的逆地理编码服务,需要在高德开发者平台注册并获取API密钥。这个密钥将用于向高德地图API发起请求。
2.1.2 使用高德地图API进行逆地理编码
在Python中,可以通过requests库向高德地图API发起HTTP请求。以下是一个详细的实现代码:
单坐标输入:
import requests
def amap_reverse_geocoding(api_key, latitude, longitude):
# 构建请求URL
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/regeo?output=json&key={api_key}&location={longitude},{latitude}'
# 发起请求
response = requests.get(url)
result = response.json()
# 解析结果
if result['status'] == '1' and result['info'] == 'OK':
address = result['regeocode']['formatted_address']
return address
else:
return '逆地理编码失败'
# 替换为您的高德地图API密钥
api_key = "your_api_key" # 替换成你的高德API Key
# 例如,广州市广州塔的坐标
latitude, longitude = 23.106414, 113.324553
# 进行逆地理编码
result_address = amap_reverse_geocoding(api_key, latitude, longitude)
print(f'坐标 ({latitude}, {longitude}) 的地理位置为:{result_address}')
运行上述代码后,输出如下:

元组的列表形式:
当输入的经纬度数据为元组的列表形式时,我们需要对代码进行修改以支持批量的逆地理编码。以下是修改后的代码:
import requests
def amap_batch_reverse_geocoding(api_key, coordinates_list):
addresses = [] # 用于存储逆地理编码结果
for coordinate in coordinates_list:
latitude, longitude = coordinate
# 构建请求URL
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/regeo?output=json&key={api_key}&location={longitude},{latitude}'
# 发起请求
response = requests.get(url)
result = response.json()
# 解析结果
if result['status'] == '1' and result['info'] == 'OK':
address = result['regeocode']['formatted_address']
addresses.append(address)
else:
addresses.append('逆地理编码失败')
return addresses
# 替换为您的高德地图API密钥
api_key = 'Your_Amap_API_Key'
# 例如,批量处理多个坐标
coordinates = [(39.908715, 116.397389), (31.230416, 121.473701), (23.12911, 113.264385)]
# 进行批量逆地理编码
result_addresses = amap_batch_reverse_geocoding(api_key, coordinates)
# 打印结果
for i, coordinate in enumerate(coordinates):
print(f'坐标 {coordinate} 的地理位置为:{result_addresses[i]}')
pandas的集成:
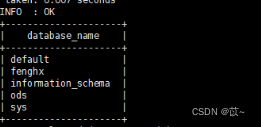
当我们需要利用pandas读取某些存储在表格或数据库里的坐标数据时,常会遇到下面这种形式:

针对上面这种形式的数据,我们可以使用下面的代码:
import requests
import pandas as pd
def amap_batch_reverse_geocoding(api_key, coordinates_df):
addresses = [] # 用于存储逆地理编码结果
for index, row in coordinates_df.iterrows():
latitude, longitude = row['Latitude'], row['Longitude']
# 构建请求URL
url = f'https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/regeo?output=json&key={api_key}&location={longitude},{latitude}'
# 发起请求
response = requests.get(url)
result = response.json()
# 解析结果
if result['status'] == '1' and result['info'] == 'OK':
address = result['regeocode']['formatted_address']
addresses.append(address)
else:
addresses.append('逆地理编码失败')
return addresses
# 替换为您的高德地图API密钥
api_key = 'Your_Amap_API_Key'
# 例如,创建一个包含经纬度的DataFrame
data = {'Latitude': [39.908715, 31.230416, 23.12911],
'Longitude': [116.397389, 121.473701, 113.264385]}
coordinates_df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 进行批量逆地理编码
result_addresses = amap_batch_reverse_geocoding(api_key, coordinates_df)
# 将逆地理编码结果添加到DataFrame中
coordinates_df['Address'] = result_addresses
# 打印结果
print(coordinates_df)
在实际应用中,需要注意异常处理、错误日志记录等工作,以保障系统的稳定性和可靠性。
2.2 Python中实现代码
逆地理编码的实现代码应该结合具体的地理编码服务商和坐标信息。上述示例中使用了高德地图API,但根据项目需求,可能会选择其他地理编码服务商。此代码应该能够轻松嵌入到您的空间数据分析流程中,并确保准确获取地理位置信息。逆地理编码是空间数据分析中解决实际问题的重要步骤,通过Python的灵活性和丰富的库支持,我们能够更便捷地进行相关操作。
写在最后
在文章的尾声,我们将为读者推荐深入学习地理空间数据科学的前沿资料。这包括学术期刊、在线课程和开源项目,帮助读者不仅了解当前研究状况,还能够不断跟进领域最新动态,保持在地理空间数据科学领域的领先地位。