目录
- 一、程序及输出
- 1.1 全局变量检测增强
- 1.2 函数检测增强
- 1.3 类型转换检测增强
- 1.4 struct增强
- 1.5 bool类型扩展
- 1.6 三目运算符增强
- 1.7 const增强
- 1.7.1 全局Const对比
- 1.7.2 局部Const对比
- 1.7.3 Const变量初始化数组
- 1.7.3 Const修饰变量的链接性
- 二、分析总结
一、程序及输出
1.1 全局变量检测增强
c 正常编译输出。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
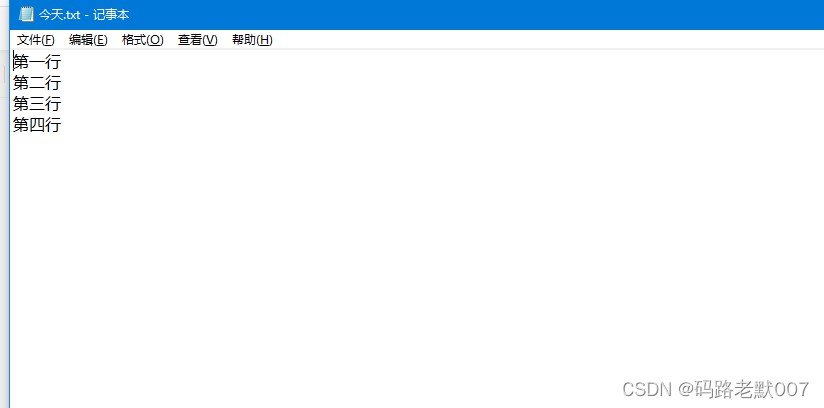
//1、全局变量检测增强
int a;
int a = 10;
int main(){
printf(" %d\n",a);
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
c++ 会检测出重定义
1.2 函数检测增强
c 正常编译输出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
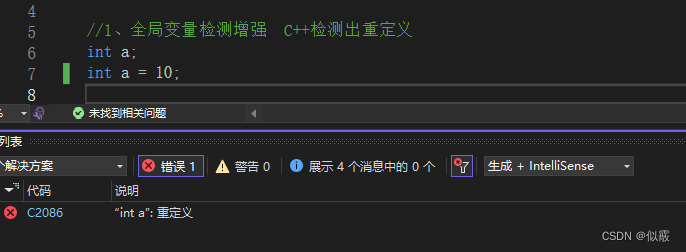
getRectS( w , h)
{
return w *h;
}
void test01()
{
printf("%d\n", getRectS(10, 10, 10));
}
int main(){
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}

c++ 返回值检测、形参类型检测、函数调用参数个数检测
1.3 类型转换检测增强
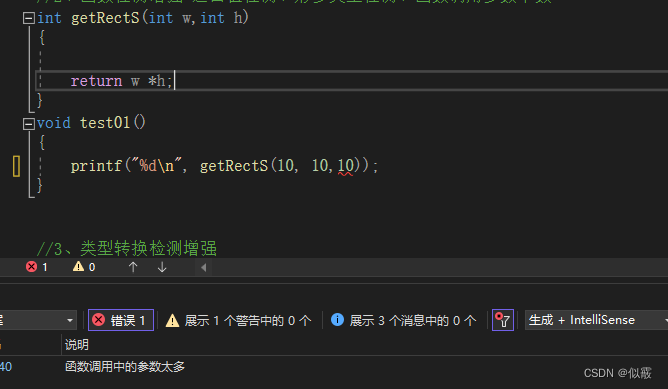
c 类型检测不严谨 malloc 返回类型void*,正常编译通过。
void test02()
{
char * p = malloc(64);
}
c++ 必须进行类型转换才能通过。
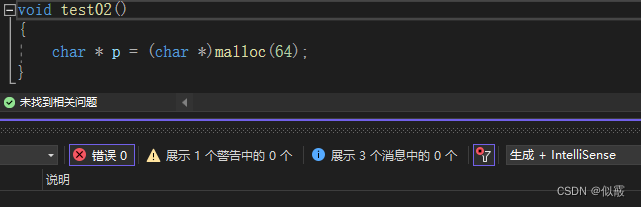
1.4 struct增强
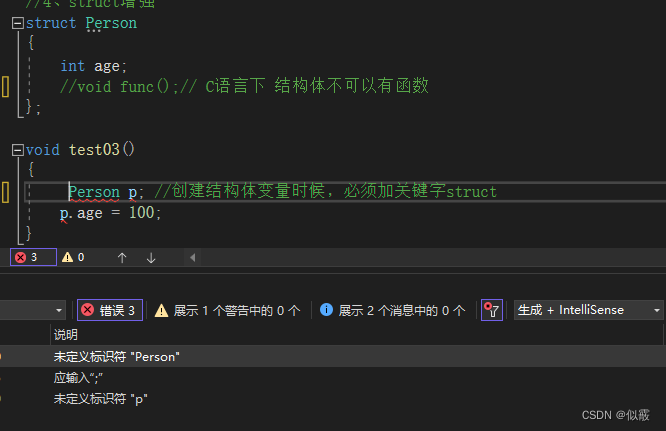
c 结构体中不能有函数

c 创建结构体变量必须加关键字struct
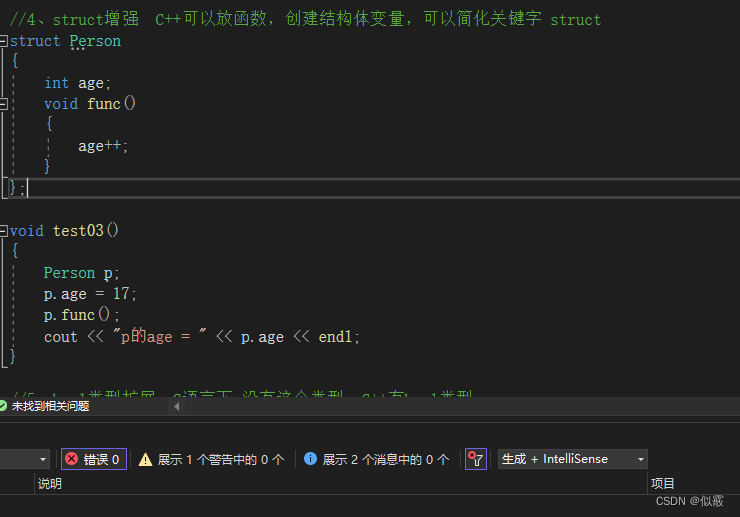
c++ 可以放函数,创建结构体变量,可以简化关键字 struct
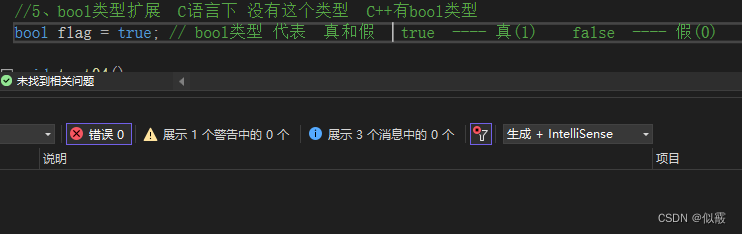
1.5 bool类型扩展
c 没有bool类型
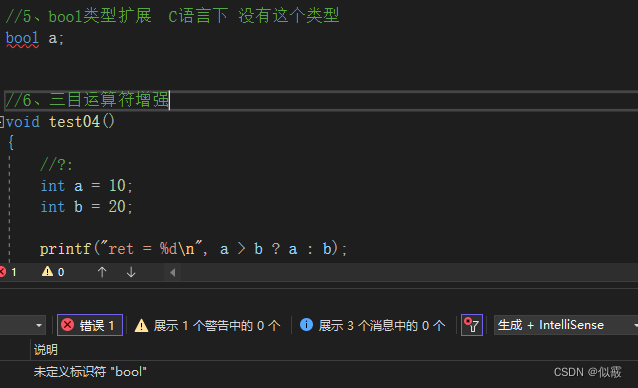
c++ 有bool类型
1.6 三目运算符增强
c 三目运算符变量作为左值不可修改。
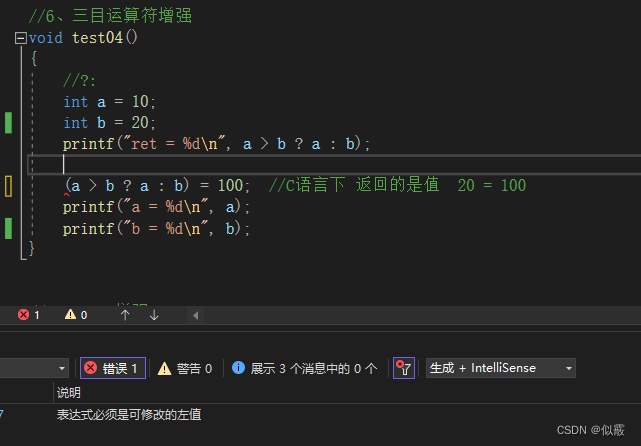
c++ 三目运算符增强,返回变量作为左值可被修改。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void test05()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
printf("ret = %d\n", a > b ? a : b);
(a < b ? a : b )= 100; // C++下返回的是变量 b = 100
printf("a = %d\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
}
int main(){
test05();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}

1.7 const增强
1.7.1 全局Const对比
c 不可修改
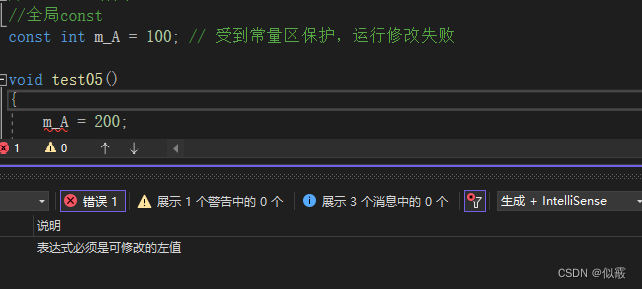
使用指针修改
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
const int m_A = 100; // 受到常量区保护,运行修改失败
void test05()
{
int * r = &m_A;
*r = 200;
printf("m_A = %d\n",m_A);
}
int main(){
test05();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
输出: 退出,没有修改成功

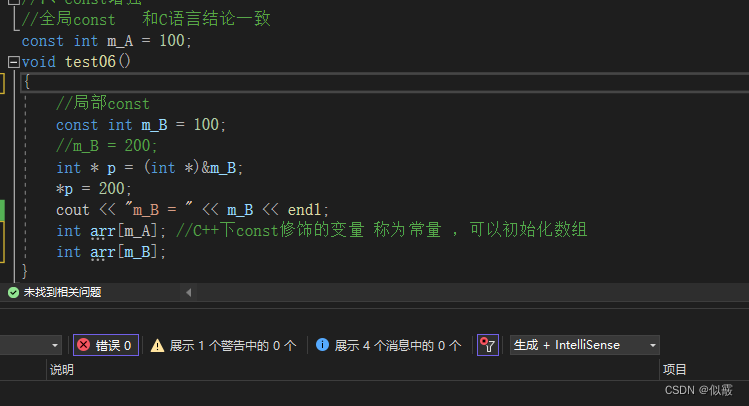
c++ 与C结论一致
1.7.2 局部Const对比
c 可以被修改
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void test05()
{
//局部const
const int m_B = 100; //分配到栈上
//m_B = 200; //直接修改会报错
int * p = &m_B; //指针修改成功
*p = 200;
printf("%d\n", m_B);
}
int main(){
test05();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
输出:

c++ 修改失败
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void test06()
{
//局部const
const int m_B = 100;
//m_B = 200;//直接修改会报错
int * p = (int *)&m_B;//指针修改失败
*p = 200;
cout << "m_B = " << m_B << endl;
}
int main(){
test06();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
输出:

1.7.3 Const变量初始化数组
c 初始化失败 C语言下Const修饰的是伪常量
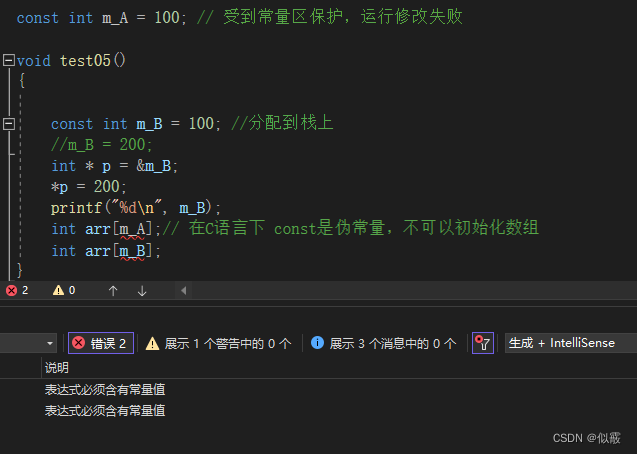
c++ 初始化成功 :C++下const修饰的变量 称为常量 ,可以初始化数组
1.7.3 Const修饰变量的链接性
c 下const修饰全局变量默认是外部链接属性
主文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
extern const int g_a;
printf("g_a = %d\n", g_a);
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
另外一个.c文件
const int g_a = 100;
输出:

解析:
extern 关键字用于声明一个外部变量
c 下const修饰全局变量默认是外部链接属性,所以.c文件定义的变量没有使用extern 关键字,但是主文件能够通过extern关键字链接到真正需要的变量,体现了const修饰全局变量默认是外部链接属性这一特点。
c++下const修饰全局变量默认是内部链接属性
主文件
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
extern const int g_b ;
cout << "g_b = " << g_b << endl;;
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
另外一个.cpp文件
extern const int g_b = 1000;
输出:

解析:
extern 关键字用于声明一个外部变量
两个文件都加了extern ,定义是在主文件里定义的,但是初始化却是在另一个.cpp文件初始化的,因为c++中const修饰全局变量默认是内部链接属性,所以外部文件初始化时需要使用extern关键字声明,如果去掉会编译报错。
二、分析总结
C++对C语言增强和扩展如下:
1.
全局变量检测增强C++检测出重定义
2.函数检测增强返回值检测、形参类型检测、函数调用参数个数检测
3.类型转换检测增强类型转换检测更严谨
4.struct增强C++可以放函数,创建结构体变量,可以简化关键字 struct
5.bool类型扩展扩展添加bool类型
6.三目运算符增强返回变量作为左值可被修改
7.const增强c++下const修饰是真常量,且可以用来初始化数组
8.Const修饰变量的链接性c 下const修饰全局变量默认是外部链接属性, c++下const修饰全局变量默认是内部链接属性