跟着施磊老师学C++
下载:GitHub - nlohmann/json: JSON for Modern C++
在single_include/nlohmann里头有一个json.hpp,把它放到我们的项目中就可以了
#include "json.hpp"
using json = nlohmann::json;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/*
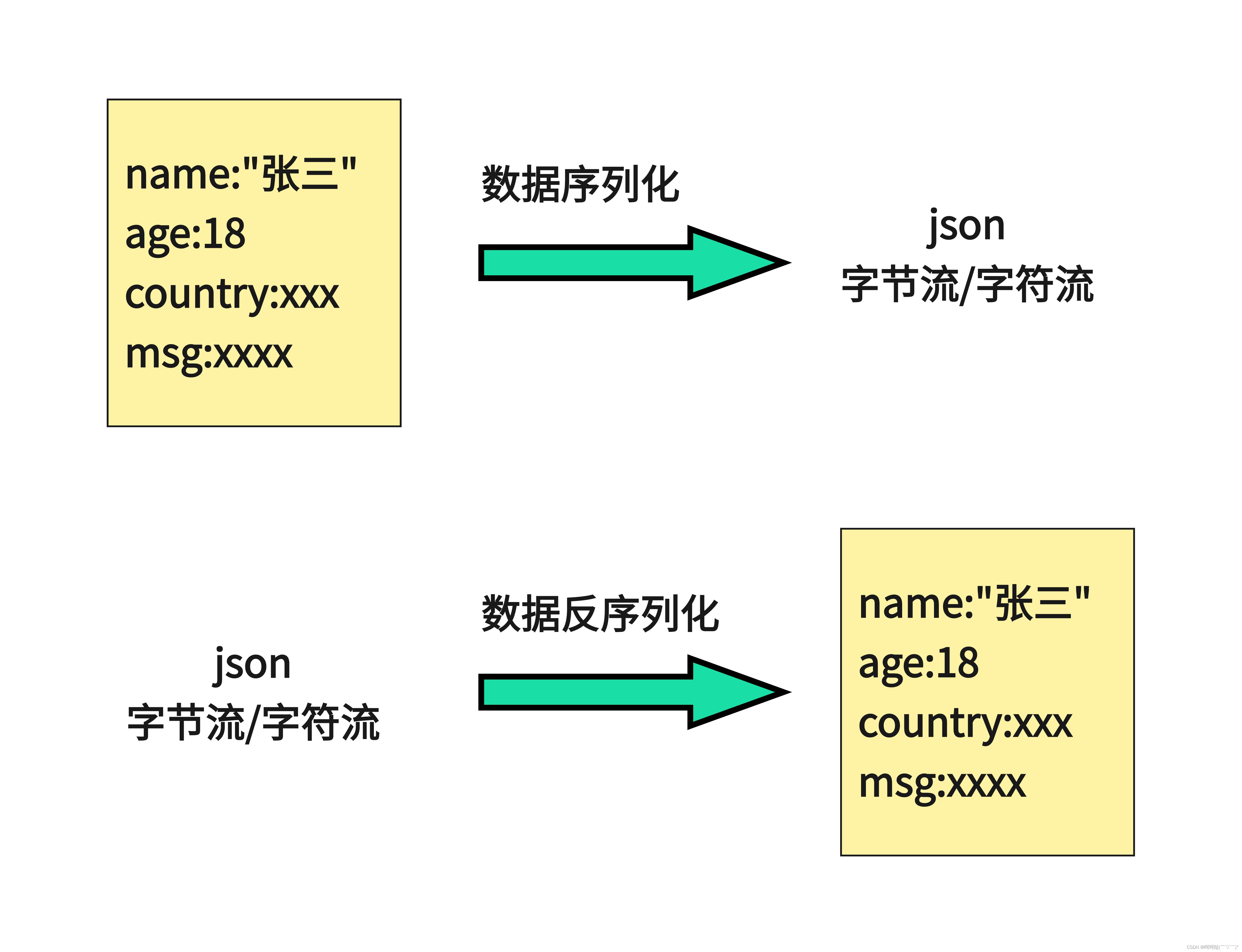
Json数据序列化
:就是把我们想要打包的数据,或者对象,直接处理成Json字符串
*/
// json序列化示例1
string func1() { 普通数据序列化
json js;
js["msg_type"] = 2;
js["from"] = "呵呵哒";
js["to"] = "小比尔";
js["msg"] = "hello,what are you doing now?";
std::cout << js << std::endl;
// {"from":"呵呵哒","msg":"hello,what are you doing now?","msg_type":2,"to":"小比尔"}
string sendBuf = js.dump();
// cout << sendBuf.c_str() << endl;
return sendBuf;
}
// json 序列化示例2 普通数据序列化
string func2() {
json js;
// 添加数组
js["id"] = {1,2,3,4,5};
// 添加key-value
js["name"] = "张三";
// 添加对象
js["msg"]["张三"] = "hello world";
js["msg"]["李四"] = "hello china";
// 上面等同于下面这句一次性添加数组对象
js["msg"] = {{"张三","hello world"},{"李四","hello china"}};
std::cout << js << std::endl;
// {"id":[1,2,3,4,5],"msg":{"张三":"hello world","李四":"hello china"},"name":"张三"}
string sendBuf = js.dump();
// cout << sendBuf.c_str() << endl;
return sendBuf;
}
// json序列化示例代码3 容器序列化
string func3() {
json js;
// 直接序列化一个vector容器
vector<int> vec;
vec.push_back(1);
vec.push_back(2);
vec.push_back(5);
js["list"] = vec;
// 直接序列化一个map容器
map<int,string> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1,"刘备"));
m.insert(make_pair(2,"关羽"));
m.insert(make_pair(3,"张飞"));
js["hero"] = m;
std::cout << js << std::endl;
// {"hero":[[1,"刘备"],[2,"关羽"],[3,"张飞"]],"list":[1,2,5]}
string sendBuf = js.dump();// json数据对象 => 序列化 json字符串
// cout << sendBuf.c_str() << endl;
// 输出:{"hero":[[1,"刘备"],[2,"关羽"],[3,"张飞"]],"list":[1,2,5]}
return sendBuf;
}
// 直接反序列化取得数据 func1
void test1() {
string recvBuf = func1();
// 数据的反序列化 json字符串 => 反序列化 数据对象(看作容器,方便访问)
json jsbuf = json::parse(recvBuf);
cout<<jsbuf["msg_type"]<<endl;
cout<<jsbuf["from"]<<endl;
cout<<jsbuf["to"]<<endl;
cout<<jsbuf["msg"]<<endl;
}
// 直接反序列化取得数据 func2
void test2() {
string recvBuf = func2();
// 数据的反序列化 json字符串 => 反序列化 数据对象(看作容器,方便访问)
json jsbuf = json::parse(recvBuf);
cout<<jsbuf["id"]<<endl;
cout<<jsbuf["name"]<<endl;
cout<<jsbuf["msg"]<<endl;
auto arr = jsbuf["id"];
for(auto it = arr.begin(); it != arr.end(); it++) {
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
// auto msgmap = jsbuf["msg"];
// for(auto it = msgmap.begin(); it != msgmap.end(); it++) {
// cout<<it.key()<<" => "<<it.value()<<endl;
// }
map<string,string> msgmap = jsbuf["msg"];
for(auto &mp : msgmap) {
cout<<mp.first<<" => "<<mp.second<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
// 直接反序列化出对象 func3
void test3() {
string recvBuf = func3();
// 数据的反序列化 json字符串 => 反序列化 数据对象(看作容器,方便访问)
json jsbuf = json::parse(recvBuf);
cout<<jsbuf["list"]<<endl;
cout<<jsbuf["hero"]<<endl;
vector<int> vec = jsbuf["list"];// js 对象里面的数组类型,直接放入vector容器当中
for(auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); it++) {
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
map<int,string> mymap = jsbuf["hero"];
for(auto &mp:mymap) {
cout<<mp.first<<" => "<<mp.second<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
test2();
test3();
return 0;
}