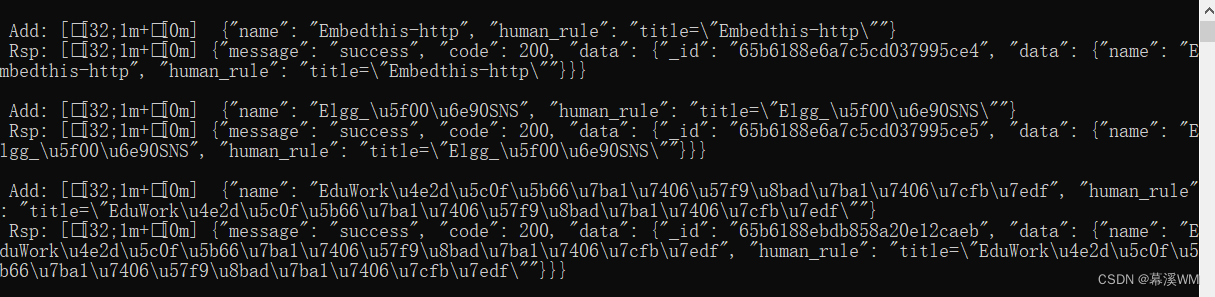
LegacyContext
- 老的 contextAPI 也就是我们使用 childContextTypes 这种声明方式
- 来从父节点为它的子树提供 context 内容的这么一种方式
- 遗留的contextAPI 在 react 17 被彻底移除了,就无法使用了
- 那么为什么要彻底移除这个contextAPI的使用方式呢?
- 因为它对性能的影响会比较的大,它会影响整个子树的一个更新过程
- 它嵌套的context提供者是需要进行一个数据的合并的
- 嵌套组件中,如果父子两者都提供相同的变量,会进行一个合并
- 越接近里层,越会被选择
- 也就是说在孙子消费变量的时候,选择父亲的,舍弃爷爷的
2 )源码
定位到 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.js#L1522
在这里,有这个判断 if ( oldProps === newProps && !hasLegacyContextChanged() && updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime ) {}
看到有
import {
hasContextChanged as hasLegacyContextChanged
} from './ReactFiberContext';
关注 hasLegacyContextChanged 基于此,定位到 (packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberContext.js#L115)[https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v16.6.3/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberContext.js#L115]
// 要去推入 stack 的值的时候,就要去创建这么一个 cursor 来标记不同类型的一个值
function hasContextChanged(): boolean {
return didPerformWorkStackCursor.current;
}
回顾到 context-stack 中
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberContext.js#L36
// A cursor to the current merged context object on the stack.
// 用来记录我们当前的我们更新到某一个节点之后,它应该可以拿到的context对应的所有值
let contextStackCursor: StackCursor<Object> = createCursor(emptyContextObject);
// A cursor to a boolean indicating whether the context has changed.
// 代表着我们在更新到某一个节点的时候,它这个context是否有变化这么一个情况
let didPerformWorkStackCursor: StackCursor<boolean> = createCursor(false);
再次回到 ReactFiberBeginWork.js 中的 if ( oldProps === newProps && !hasLegacyContextChanged() && updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime ) {}
对于在 beginWork 中的 context 操作,可以看上述判断成立的条件下的代码,即便有符合跳过更新的操作,依然 需要 push 和 pop 操作
进入代码
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case ClassComponent: {
const Component = workInProgress.type;
// 如果当前组件是一个 provider 则进行 push 操作
if (isLegacyContextProvider(Component)) {
pushLegacyContextProvider(workInProgress);
}
break;
}
}
-
跟遗留的 contextAPI 有关,通过 legency 标志,如果一个组件能够作为一个 context 的提供者
-
那么它肯定是一个
ClassComponent, 因为要通过 getchildcontext 这么一个方法来声明我们子树当中提供了哪些 concontext -
最主要的就是来看在classcomponent的更新过程当中,如果它是一个contextprovider,那么它要执行的操作是
pushLegacyContextProvider -
进入
isLegacyContextProvider, 看到它是isContextProvider的别名// 这个 type 就是组件实例,这个 childContextTypes function isContextProvider(type: Function): boolean { // 通过判断应用中声明的 class 上面是否有这个属性 const childContextTypes = type.childContextTypes; return childContextTypes !== null && childContextTypes !== undefined; }- 通过声明的这个class给它挂载 childContextTypes 来表示它是一个context的提供者
- 只有声明了这个之后,它才会作为一个context的provider来提供子树上面的context
- 如果不这么声明,即便在class里面提供了 getChildContext 这个方法,还是拿不到对应的context
-
进入
pushLegacyContextProvider它是pushContextProvider的别名function pushContextProvider(workInProgress: Fiber): boolean { const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // We push the context as early as possible to ensure stack integrity. // If the instance does not exist yet, we will push null at first, // and replace it on the stack later when invalidating the context. const memoizedMergedChildContext = (instance && instance.__reactInternalMemoizedMergedChildContext) || emptyContextObject; // Remember the parent context so we can merge with it later. // Inherit the parent's did-perform-work value to avoid inadvertently blocking updates. previousContext = contextStackCursor.current; // 获取之前的 context 挂载到全局变量上 push(contextStackCursor, memoizedMergedChildContext, workInProgress); push( didPerformWorkStackCursor, didPerformWorkStackCursor.current, workInProgress, ); return true; }
以上是可以跳出当前组件的更新的一个处理情况
如果我们可以跳出组件的更新,也就是代表着当前这个 classComponent,它的state它的props都应该是没有任何变化的
这个时候, 当然是可以直接使用保存在它上面原始的 context 的对象
如果它是一个需要更新的 classComponent,需要看一下 updateClassComponent 这个更新方法
function updateClassComponent(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: any,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
) {
// Push context providers early to prevent context stack mismatches.
// During mounting we don't know the child context yet as the instance doesn't exist.
// We will invalidate the child context in finishClassComponent() right after rendering.
let hasContext;
if (isLegacyContextProvider(Component)) {
hasContext = true;
pushLegacyContextProvider(workInProgress);
} else {
hasContext = false;
}
prepareToReadContext(workInProgress, renderExpirationTime);
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
let shouldUpdate;
if (instance === null) {
if (current !== null) {
// An class component without an instance only mounts if it suspended
// inside a non- concurrent tree, in an inconsistent state. We want to
// tree it like a new mount, even though an empty version of it already
// committed. Disconnect the alternate pointers.
current.alternate = null;
workInProgress.alternate = null;
// Since this is conceptually a new fiber, schedule a Placement effect
workInProgress.effectTag |= Placement;
}
// In the initial pass we might need to construct the instance.
constructClassInstance(
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
mountClassInstance(
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
shouldUpdate = true;
} else if (current === null) {
// In a resume, we'll already have an instance we can reuse.
shouldUpdate = resumeMountClassInstance(
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
} else {
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
return finishClassComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
shouldUpdate,
hasContext,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
-
一进来就调用了
isLegacyContextProvider方法- 就是如果它是一个contextprovider,那么它要进行 push 操作
pushLegacyContextProvider
- 就是如果它是一个contextprovider,那么它要进行 push 操作
-
接下去, 它调用了一个方法,叫做
prepareToReadContext这么一个方法- 这个方法和新的contextAPI有关,先跳过
-
接下去基本上没有跟 context 相关的内容了,这里进入
finishClassComponentfunction finishClassComponent( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, Component: any, shouldUpdate: boolean, hasContext: boolean, renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, ) { // Refs should update even if shouldComponentUpdate returns false markRef(current, workInProgress); const didCaptureError = (workInProgress.effectTag & DidCapture) !== NoEffect; if (!shouldUpdate && !didCaptureError) { // Context providers should defer to sCU for rendering if (hasContext) { invalidateContextProvider(workInProgress, Component, false); } return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork( current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime, ); } const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // Rerender ReactCurrentOwner.current = workInProgress; let nextChildren; if ( didCaptureError && typeof Component.getDerivedStateFromError !== 'function' ) { // If we captured an error, but getDerivedStateFrom catch is not defined, // unmount all the children. componentDidCatch will schedule an update to // re-render a fallback. This is temporary until we migrate everyone to // the new API. // TODO: Warn in a future release. nextChildren = null; if (enableProfilerTimer) { stopProfilerTimerIfRunning(workInProgress); } } else { if (__DEV__) { ReactCurrentFiber.setCurrentPhase('render'); nextChildren = instance.render(); if ( debugRenderPhaseSideEffects || (debugRenderPhaseSideEffectsForStrictMode && workInProgress.mode & StrictMode) ) { instance.render(); } ReactCurrentFiber.setCurrentPhase(null); } else { nextChildren = instance.render(); } } // React DevTools reads this flag. workInProgress.effectTag |= PerformedWork; if (current !== null && didCaptureError) { // If we're recovering from an error, reconcile without reusing any of // the existing children. Conceptually, the normal children and the children // that are shown on error are two different sets, so we shouldn't reuse // normal children even if their identities match. forceUnmountCurrentAndReconcile( current, workInProgress, nextChildren, renderExpirationTime, ); } else { reconcileChildren( current, workInProgress, nextChildren, renderExpirationTime, ); } // Memoize state using the values we just used to render. // TODO: Restructure so we never read values from the instance. workInProgress.memoizedState = instance.state; // The context might have changed so we need to recalculate it. if (hasContext) { invalidateContextProvider(workInProgress, Component, true); } return workInProgress.child; }hasContext是否是一个 contextProvider- 如果是 true, 则执行
invalidateContextProvider(workInProgress, Component, false);function invalidateContextProvider( workInProgress: Fiber, type: any, didChange: boolean, ): void { const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; invariant( instance, 'Expected to have an instance by this point. ' + 'This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.', ); // 如果有变化 if (didChange) { // Merge parent and own context. // Skip this if we're not updating due to sCU. // This avoids unnecessarily recomputing memoized values. const mergedContext = processChildContext( workInProgress, type, previousContext, ); instance.__reactInternalMemoizedMergedChildContext = mergedContext; // Replace the old (or empty) context with the new one. // It is important to unwind the context in the reverse order. pop(didPerformWorkStackCursor, workInProgress); pop(contextStackCursor, workInProgress); // Now push the new context and mark that it has changed. push(contextStackCursor, mergedContext, workInProgress); push(didPerformWorkStackCursor, didChange, workInProgress); } else { pop(didPerformWorkStackCursor, workInProgress); push(didPerformWorkStackCursor, didChange, workInProgress); } }- 通过
processChildContext计算出新的 context 并挂载到__reactInternalMemoizedMergedChildContext - 之后,pop 2次,push 2次 来处理了栈内的顺序
- 进入
processChildContext看下这个方法function processChildContext( fiber: Fiber, type: any, parentContext: Object, ): Object { const instance = fiber.stateNode; const childContextTypes = type.childContextTypes; // TODO (bvaughn) Replace this behavior with an invariant() in the future. // It has only been added in Fiber to match the (unintentional) behavior in Stack. // 这个属性一定是 function 才能生效 if (typeof instance.getChildContext !== 'function') { if (__DEV__) { const componentName = getComponentName(type) || 'Unknown'; if (!warnedAboutMissingGetChildContext[componentName]) { warnedAboutMissingGetChildContext[componentName] = true; warningWithoutStack( false, '%s.childContextTypes is specified but there is no getChildContext() method ' + 'on the instance. You can either define getChildContext() on %s or remove ' + 'childContextTypes from it.', componentName, componentName, ); } } return parentContext; } let childContext; if (__DEV__) { ReactCurrentFiber.setCurrentPhase('getChildContext'); } startPhaseTimer(fiber, 'getChildContext'); childContext = instance.getChildContext(); // 执行这个 提供的api, 获取数据 stopPhaseTimer(); if (__DEV__) { ReactCurrentFiber.setCurrentPhase(null); } for (let contextKey in childContext) { invariant( contextKey in childContextTypes, '%s.getChildContext(): key "%s" is not defined in childContextTypes.', getComponentName(type) || 'Unknown', contextKey, ); } // 忽略 if (__DEV__) { const name = getComponentName(type) || 'Unknown'; checkPropTypes( childContextTypes, childContext, 'child context', name, // In practice, there is one case in which we won't get a stack. It's when // somebody calls unstable_renderSubtreeIntoContainer() and we process // context from the parent component instance. The stack will be missing // because it's outside of the reconciliation, and so the pointer has not // been set. This is rare and doesn't matter. We'll also remove that API. ReactCurrentFiber.getCurrentFiberStackInDev, ); } // 最终是两者 merge return {...parentContext, ...childContext}; }- 其实,这个 processChildContext 非常简单,获取 context,合并 context
- 这里的 parentContext 是传入的 previousContext, 这个是上面调用 pushContextProvider 时设置的全局变量
contextStackCursor.current - 也就是 父组件中 提供的 context 对象,最终都是为了合并
- 通过
-
总结来说,父子孙三个组件,在更新子组件的时候,先去push了一个它之前存在的这个属性
-
因为我们不知道这个组件它是否要更新,不管它是否要更新,都要先都要执行 push 的一个操作
-
所以,先 push 一个老的值进去再说, 然后到后面,如果发现这个组件它是要更新的,就调用这个
invalidateContextProvider方法 -
调用了这个方法之后, 根据传进来的
didChange,如果是 true 表示要更新,要重新去计算一个新的合并过的这个context, 即mergedContext给它推入到栈里面 -
对于子组件来说,它的所有子树所获取到的context肯定是经过子组件,和上层的父组件合并的 context 了, 也就是
contextStackCursor这里 -
同时对于
didPerformWorkStackCursor来说,因为didChange是 true,它的 current 肯定也是 true -
如果
didChange是 false,这个时候不需要改变contextStackCursor- 因为 push 的本来就是上面的那个值,也就是上一次计算出来的这个值
- 就是保存在
__reactInternalMemoizedMergedChildContext这上面的值 - 因为它本身没有变化,不需要去改动它,而对于
didPerformWorkStackCursor来说,需要去改变它 - didChange 变成false,我没有更新,不能继续存之前的那个值, 因为之前的那个值可能是更新过了,它可能是 true
- 我这次发现这个组件是不需要更新的, 要把它改成 false
- 在一开始,这个方法就是叫做 hasContextChaned 的这个方法,它是用来判断这个组件
- 是否可以跳过更新的一个非常关键的一个值, 如果它返回的一直是 true
- 会导致我们每一个组件都需要去更新,而最终导致整个性能变得非常的差
- 所以这就是
didPerformWorkStackCursor它的一个作用
-
老的 context api当中的 push 操作是比较复杂的,要进行一个 context 的合并这么一个过程
-
到这里为止,将context的合并,并让它入栈
-
注意,还有一种情况是这样的,父子孙三层组件,有一个子组件没有儿子组件
-
也就是有多个子组件,其中有的子组件没有下层组件,这时候这类子组件拿到的是父组件原来的,而非合并过的
-
看下具体的代码处理, 比如说我们随便挑一个 class component,更新过程当中调用的方法, 如
updateClassInstance这个方法// Invokes the update life-cycles and returns false if it shouldn't rerender. function updateClassInstance( current: Fiber, workInProgress: Fiber, ctor: any, newProps: any, renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, ): boolean { const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // ... 跳过很多代码 const contextType = ctor.contextType; // 注意这里 let nextContext; if (typeof contextType === 'object' && contextType !== null) { nextContext = readContext(contextType); } else { // 注意这个 else, 这个是重点 const nextUnmaskedContext = getUnmaskedContext(workInProgress, ctor, true); nextContext = getMaskedContext(workInProgress, nextUnmaskedContext); } // ... 跳过很多代码 return shouldUpdate; } -
这里有一个在
ctor.contextType在 classComponent 上面去读取这个属性 -
注意,这里
contextType和contextTypes的区别- 后者在应用中,我们自己的代码里用于设定接收上层属性的
- 前者就是要去读取某一个新的 contextAPI 它的 provider 上面提供的属性
- 也就是说可以这么设置
Child.contextType = Consumer - 两者共同存在,则后者老的失效
- 也就是说,如果 孙组件使用了 新的 contextType 这个api, 后面同时定义的 contextTypes 相关的会失效
-
对于react来说,它即将把所有context相关的东西呢都放在新的contextAPI里面
- 所以如果我们优先使用了 contextType 这种新的 context API 的使用方式
- 就直接默认只使用新的 context
- 而只有在没有使用这个新的 context API 的时候才会去使用老的 context API
- 这个时候我们就会去调用一个叫做
getUnmaskedContext(workInProgress, ctor, true) - 这个方法来去读取用在这一个组件上面它所对应的context属性
function getUnmaskedContext( workInProgress: Fiber, Component: Function, didPushOwnContextIfProvider: boolean, ): Object { if (didPushOwnContextIfProvider && isContextProvider(Component)) { // If the fiber is a context provider itself, when we read its context // we may have already pushed its own child context on the stack. A context // provider should not "see" its own child context. Therefore we read the // previous (parent) context instead for a context provider. return previousContext; } return contextStackCursor.current; }didPushOwnContextIfProvider传进来的时候是 true- 代表是否已经 push 了自己的 contextProvider,对于我们自己是一个 contextProvider 的一个情况
- 在调用update之前,那么肯定是已经调用过push了, 如果提供了 context,这个值就是true
- 而后面还需要判断它是否是一个 contextProvider,如果这两个条件都符合,返回的是 previousContext
- 这个 previousContext 就是之前在调用 push 操作的时候,即
pushContextProvider,给它赋值的这个值 - 就比如说在更新 子组件 的过程中,执行 updateClassComponent
- 先 push 了自己的 contextProvider, 这个时候赋值给了 previousContext
- 它等于 push 之前的那个context,就是 父组件提供的 context
- 对于 子组件 更新的过程当中使用的 context,肯定不能使用自己提供的这个 value
- 子组件提供的value是给自己子树,也就是孙组件及之后使用的
- 子组件要用context的话,应该是去读取父组件提供的 context
- 子组件要去获取父组件提供的context,要去调用
getUnmaskedContext这个方法 - 而如果组件同时是一个provider,那它肯定已经push过了,所以组件必须返回 previousContext 才行
- 同样,如果组件不是一个 contextprovider,当然没有执行过push,只需要执行当前这个cursor即可
- 进入
getMaskedContextfunction getMaskedContext( workInProgress: Fiber, unmaskedContext: Object, ): Object { const type = workInProgress.type; const contextTypes = type.contextTypes; if (!contextTypes) { return emptyContextObject; } // Avoid recreating masked context unless unmasked context has changed. // Failing to do this will result in unnecessary calls to componentWillReceiveProps. // This may trigger infinite loops if componentWillReceiveProps calls setState. const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; if ( instance && instance.__reactInternalMemoizedUnmaskedChildContext === unmaskedContext ) { return instance.__reactInternalMemoizedMaskedChildContext; } // 注意,这里是核心 const context = {}; for (let key in contextTypes) { context[key] = unmaskedContext[key]; } if (__DEV__) { const name = getComponentName(type) || 'Unknown'; checkPropTypes( contextTypes, context, 'context', name, ReactCurrentFiber.getCurrentFiberStackInDev, ); } // Cache unmasked context so we can avoid recreating masked context unless necessary. // Context is created before the class component is instantiated so check for instance. if (instance) { cacheContext(workInProgress, unmaskedContext, context); } return context; }- 这个方法是在组件的父组件中所有合并过的 context 中获得当前组件需要读取的属性
- 也就是说当前组件需要什么指定什么,context中就返回什么
-
以上,就是对于一个 Class Component,要使用老的contextAPI, 如何去提供这个context以及它如何去获取这个context的一个过程
-
以上是 push 操作,那什么时候才会 pop 呢?
-
在
completeUnitOfWork的时候,在 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCompleteWork.js#L540function completeWork( current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, ): Fiber | null { const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps; // ... 跳过很多代码 switch (workInProgress.tag) { // ... 跳过很多代码 case ClassComponent: { const Component = workInProgress.type; if (isLegacyContextProvider(Component)) { popLegacyContext(workInProgress); } break; } // ... 跳过很多代码 } // ... 跳过很多代码 }- 对于 classComponent,如果它是一个 provider,它必须要
popLegacyContext别名是popContext// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberContext.js#L124 function popContext(fiber: Fiber): void { pop(didPerformWorkStackCursor, fiber); pop(contextStackCursor, fiber); }- 就把两个 cursor 给它 pop 一下
- 在这里回到之前的push进行一下对比
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberContext.js#L215 function pushContextProvider(workInProgress: Fiber): boolean { // ... 跳过很多代码 push(contextStackCursor, memoizedMergedChildContext, workInProgress); push( didPerformWorkStackCursor, didPerformWorkStackCursor.current, workInProgress, ); return true; }- 这里先push的是
contextStackCursor再push的是didPerformWorkStackCursor
- 这里先push的是
- 回到pop, 先pop的是
didPerformWorkStackCursor再pop的是contextStackCursor - 这就是我之前说过的,push 是按哪个顺序, pop的时候,必须要反过来去做
- 这样的话,在 context-stack 中的 valueStack 里面存储的值对应的cursor的位置才是能真正对应起来
- 对于在 completeWork 里面,我们只需要去执行
popLegacyContext这个操作就可以了
- 对于 classComponent,如果它是一个 provider,它必须要
-
还是用之前的 Fiber 树来举例子
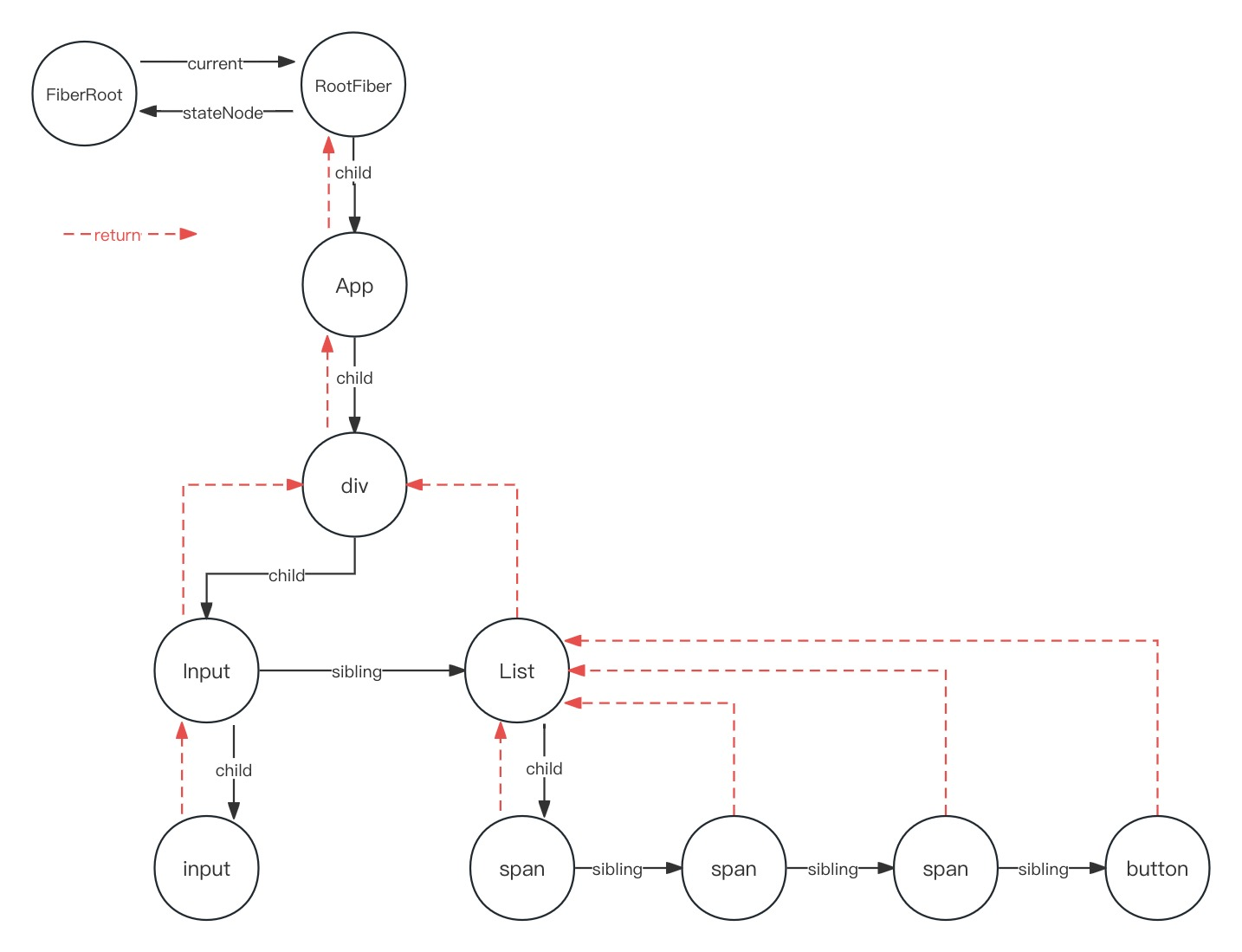
- 假设整个树形结构下面的每一个节点,它都是一个classcomponent
- 这个时候我们更新,然后 App 和 这个 div,它都提供了
childContextTypes - 这个时候对于 input 这个 classcomponent,它要更新的过程中肯定要获取
- 这个App和和div提供的context合并之后的那个对象,对App更新的过程中,它调用了push
- 然后在div执行更新的时候,它先去获取App push 的那个 context 作为它更新的时候要用的那个context
- 它自己也要去push一个context,push的时候要跟App提供的context进行一个合并
- 这个时候游标已经到了第二个context了, 第一个context是App提供的, 第二个是App和和div合并的
- 这两个值都是在stack栈里面有存着的,只不过现在的
contextStackCursor这个游标 - 指向的是div它合并过之后的那个context,这个context是提供给Input渲染更新的时候,它要获取的那个值
- 就这么一层一层下来之后,到最后更新 input 这个节点的时候,它拿到的context是上面这三个组件,它合并过的 context
- 对于List的更新,它不需要Input合并进去,它只需要App和div它们合并之后的那个 context 对象
- 这个就是我们在 completeUnitOfWork 的时候,要去pop这个stack
- 在input节点执行 completeUnitOfWork 的时候
- 要 pop input节点及以上提供的context合并之后的一个值
- 对应 cursor 指向 App, div, Input 合并后的 context
- 在Input节点执行 completeUnitOfWork 的时候
- 要 pop Input节点及以上提供的context合并之后的一个值
- 对应 cursor 指向 App 和 div 合并后的 context
- 在Input发现sibling节点 List,要对这个兄弟节点执行 beginWork,也就是更新的流程
- 这个时候 List 拿到的这个 context,也就是 App 和 div合并之后的节点
- 所以这就是在 beginWork 的时候,要对 classcomponent 进行一个push的操作
- 等到要去 completeUnitOfWork 的时候,执行到每个节点,要执行对应的pop
- 所以这个时候就可以对节点 push 和 pop 的位置可以一一对应起来
- 这样的话就不会造成整个stack里面的这个顺序混淆
- 在input节点执行 completeUnitOfWork 的时候
- 这就是对于 childContextTypes 这种context提供的方式的一个使用的过程
- 这个 API 最终被删除了,因为前面谈到的性能问题,以上是它的整体原理