对象序列化
- 12.16对象序列化
- 12.16.1 基本概念与 Serializable 接口
- 12.16.2 对象输出流ObjectOutputStream
- 【例12.71】将Person类的对象保存在文件之中
- 12.16.3 对象输入流 Objectinputstream
- 12.16.4 Externalizable 接口
- 【例12.73】修改Person类并实现Extemalizable接口
- 【例12.74】序列化和反序列化Person对象
- 12.16.5 transient 关键字
- 【例12.75】 Person中的name属性不希望被序列化
- 【例12.76】重新保存再读取对象
- 12.16.6 序列化一组对象
- 【例12.77】序列化多个Person对象
12.16对象序列化
12.16.1 基本概念与 Serializable 接口

class Person implements Serializable
{
private String name =null;
private int age =0 ;
public Person(String name,int age)
{
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return "name:" + this.name + " \t" + "age:" + this.age ;
}
}

12.16.2 对象输出流ObjectOutputStream
一个对象如果想要进行输出,则必须使用ObjectOutputStream类,此类定义如下:
public class ObjectOutputStream extends Outputstream implements Objectoutput,ObjectStreamConstants ObjectOutputStream类属于Outputstream的子类,此类的常用方法如表12-25所示。
表 12-25 ObjectOutputStream 常用方法
序 号 方法或常量 类 型 描 述
1 public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException 构造 传入输出的对象
2 public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException 普通 输出对象
此类的使用形式与PrintStream非常相似,在实例化时也需要传入一个Outputstream的子类对象,然后根据传入的Outputstream子类的对象不同,输出的位置也不同。
【例12.71】将Person类的对象保存在文件之中
package jiaqi;
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable
{
private String name =null;
private int age =0 ;
public Person(String name,int age)
{
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return "name:" + this.name + " \t" + "age:" + this.age ;
}
}
public class demo439_1 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
File f =new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt");
//对象输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
//输出对象
// oos.writeObject(new Person("杜变成",3222));
oos.writeObject(new Person("杜艳贺",3));
oos.close();
}
}

12.16.3 对象输入流 Objectinputstream
使用ObjectI叩utStream可以直接把被序列化好的对象反序列化。ObjectlnputStream的定义如下:
public class ObjectlnputStream extends Inputstream implements Objectinput, ObjectStreamConstants ObjectlnputStream类也是InputStream的子类,与PrintStream类的使用类似,此类同样需要接收InputStream类的实例才可以实例化。主要操作方法如表12-26所示。
表12-26 ObjectlnputStream的主要操作方法
序 号 方法或常量 类 型 描 述
1 public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException 构造 构造输入对象
2 public final Object readObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFound Exception 普通 从指定位置读取对象
下面使用对象输入流将12.16.2节保存在文件中的对象读取出来,此过程有时也称为反序列化。
【例12.72】从文件中将Person对象反序列化(读取)
package jiaqi;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class demo441_1 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("d:"+ File.separator +"test.txt")));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(obj);
ois.close();
}
}
12.16.4 Externalizable 接口


【例12.73】修改Person类并实现Extemalizable接口
【例12.74】序列化和反序列化Person对象
package jiaqi;
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Externalizable
{
private String name =null;
private int age =0 ;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age)
{
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return "name:" + this.name + " \t" + "age:" + this.age ;
}
//反序列化
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
this.age = (int)in.readInt();
}
//序列化
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException
{
out.writeInt(this.age);
}
}
public class demo443_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
start();
end();
}
public static void start() throws Exception
{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt")));
oos.writeObject(new Person("du",5));
oos.close();
}
public static void end()throws Exception
{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt")));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(obj);
ois.close();
}
}

12.16.5 transient 关键字
Serializable接口实现的操作实际上是将一个对象中的全部属性进行序列化,当然也可以使用Extemalizable接口以实现部分属性的序列化,但这样操作比较麻烦。
当使用Serializable接口实现序列化操作时,如果一个对象中的某个属性不希望被序列化的话,则可以使用transient关键字进行声明,代码如下所示。
【例12.75】 Person中的name属性不希望被序列化
【例12.76】重新保存再读取对象
package jiaqi;
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable
{
private transient String name =null;
private int age =0 ;
public Person(String name,int age)
{
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return "name:" + this.name + " \t" + "age:" + this.age ;
}
}
public class demo445_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
start();
end();
}
public static void start() throws Exception
{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt")));
oos.writeObject(new Person("du",5));
oos.close();
}
public static void end()throws Exception
{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt")));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(obj);
ois.close();
}
}
12.16.6 序列化一组对象
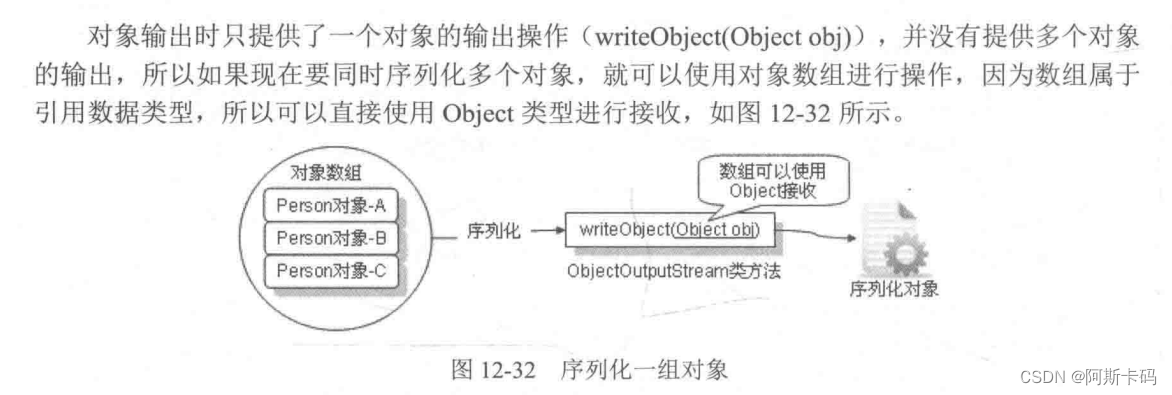
【例12.77】序列化多个Person对象
package jiaqi;
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable
{
private String name = null;
private int age = 0;
public Person(String name,int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString()
{
return "name:" + this.name + " \t" + "age:" + this.age ;
}
}
public class demo446_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
Person per[] = {new Person("name3",9),new Person("name4",10),new Person("name5",11),new Person("name6",12)};
start(per);
Object obj[] = end();
for(int i=0;i<obj.length;i++)
{
Person p = (Person)obj[i];
System.out.println(p);
}
}
public static void start(Person obj[]) throws Exception
{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt")));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object[] end()throws Exception
{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"test.txt")));
Object obj[] = (Object[])ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return obj;
}
}