- SqlAlchemy使用教程(一) 原理与环境搭建
- SqlAlchemy使用教程(二) 入门示例及编程步骤
- SqlAlchemy使用教程(三) CoreAPI访问与操作数据库详解
- SqlAlchemy使用教程(四) MetaData 与 SQL Express Language 的使用
- SqlAlchemy使用教程(五) ORM API 编程入门
本章内容,稍微有些复杂,建议腾出2小时空闲时间,冲杯咖啡或泡杯茶 😃 , 慢慢看,在电脑上跑下代码,可以加深理解.
六、表间关系的定义与CRUD操作
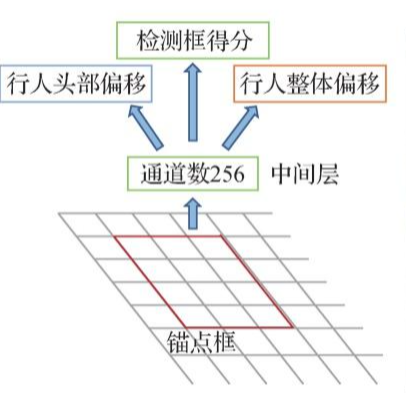
表间关系主要包括:一对多,一对一,多对多。其中一对多关系中也隐含了多对一关系。
表间关系是数据库操作中的重要技术点,非常有必要理解与掌握。
1、 一对多表间关系的定义
一对多表间关系实现语法
以一对多关系为例,
- 子表侧,与父表是一对多关系,
- 父表侧,可以反向查询子表数据,与子表是多对一关系。
class Parent(Base):
__tablename__ = "parent_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
children: Mapped[List["Child"]] = relationship(back_populates="parent")
class Child(Base):
__tablename__ = "child_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
parent_id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("parent_table.id"))
parent: Mapped["Parent"] = relationship(back_populates="children")
说明:
1)在子表中添加外键字段,以及relationship()引用,
2)在父表中添加relationship()引用,用于反向查询。
示例代码
父表:company, 子表 person, 表结构类定义如下。
from sqlalchemy.orm import DeclarativeBase, Session
from sqlalchemy.orm import Mapped, mapped_column
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
from sqlalchemy import ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy import String, Integer
from typing import List
class Base(DeclarativeBase):
pass
class Company(Base):
__tablename__ = "company"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(Integer, primary_key=True)
company_name: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(30), index=True)
persons: Mapped[List['Person']] = relationship(
back_populates="company", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f"Company(id={self.id}, company_name={self.company_name})"
class Person(Base):
__tablename__ = "person"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(30))
age: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(Integer)
company_id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("company.id"))
company: Mapped['Company'] = relationship(back_populates="persons")
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f"Person(id={self.id}, name={self.name})"
说明:
1)从子表视角看,1个人只属于1个Company; 但1个Company 对应多个人,因此在父表则,relationship() 左侧的类型注解为 List[‘Person’], 也可以用Set[‘Person’]
2)父表中添加删除依赖,cascade=“all, delete-orphan”,即子表中不存在对父表记录的引用时,才能删除,以保证数据的完整性。
3)当前版本可能存在bug, 官方文档中的示例中有的字段使用简化写法(右侧未给出mapped_column()),sqlite3运行是没有问题的,但mysql, postgresql创建表时会丢弃简化写法的字段,导致后续insert等操作失败。 因此请严格请勿采有简化写法。
多对一关系的实现语法
当不需要反向查询时,则父表与子表形成Many to One 多对一关系, 在父表则添加子表的外键与relationship()引用,子表无须做额外配置
class Parent(Base):
__tablename__ = "parent_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
child_id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("child_table.id"))
child: Mapped["Child"] = relationship()
class Child(Base):
__tablename__ = "child_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
如果允许 child_id空值,则将改字段的类型注解修改为
from typing import Optional
......
child_id: Mapped[Optional[int]] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("child_table.id"))
对于3.10+版本,类型注解支持 | 操作符
child_id: Mapped[int | None] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("child_table.id"))
child: Mapped[Child | None] = relationship(back_populates="parents")
2、 插入数据与多表联合查询
1)在数据库创建表
# 创建数据库连接引擎对象
engine = create_engine(
"mysql+mysqlconnector://root:Admin&123@localhost:3306/testdb")
# 将DDL语句映射到数据库表,如果数据库表不存在,则创建该表
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
# 打印创建创建的表
Print(Base.metadata.tables)
2)插入数据
基本步骤包括:
(1)为测试方便,先写1个get_or_create()函数,如果插入对象在数据库中已存在则不插入,以方便连续测试。
(2)创建session对象
(3)先创建父表对象并插入
(4)创建子表对象并插入
(5)用多表查询方法检查结果
Step-1: 自定义create_or_create()函数
官方提供的upsert方法不通用。下面函数是通用的,
def get_or_create(session, model, defaults=None, **kwargs):
"""如果不存在则创建,如果存在则返回
输入参数:
session: sqlalchemy session
model: 自定义的ORM类
defaults: 有默认值的字段
kwargs: 其他字段(必须包含主要字段)
返回值:
instance: 返回的实例
"""
instance = session.query(model).filter_by(**kwargs).first()
if instance:
print("instance already exists", instance)
return instance
else:
params = dict((k, v) for k, v in kwargs.items()
if not isinstance(v, ClauseElement))
if defaults:
params.update(defaults)
instance = model(**params)
session.add(instance)
session.commit()
print("instance inserted", instance)
return instance
Step-2: 向两个关联表插入数据
用with 语句创建session对象,插入操作顺序,先父表再子表
with Session(engine) as session:
# 插入数据
get_or_create(session, Company, company_name="蜀汉")
get_or_create(session, Company, company_name="曹魏")
get_or_create(session, Company, company_name="东吴")
stmt = select(Company)
results = session.scalars(stmt)
print(results.all())
# insert data in person table
company_shu = session.scalars(select(Company).where(
Company.company_name == "蜀汉")).first()
get_or_create(session, Person, name="刘备",
age=42, company=company_shu)
get_or_create(session, Person, name="关羽",
age=40, company=company_shu)
get_or_create(session, Person, name="张飞", age=38, company=company_shu)
company_wei = session.scalars(select(Company).where(
Company.company_name == "曹魏")).first()
get_or_create(session, Person, name="张辽", age=40, company=company_wei)
get_or_create(session, Person, name="曹操", age=38, company=company_wei)
company_wu = session.scalars(select(Company).where(
Company.company_name == "东吴")).first()
get_or_create(session, Person, name="周瑜", age=30, company=company_wu)
3) 多表联合查询
# select with Join 多表查询
stmt = select(Person).join(Person.company).where(
Company.company_name == "蜀汉").order_by(Person.age)
results = session.scalars(stmt)
# 遍历结果
for r in results:
print(r.name, r.age, r.company.company_name)
Output:
instance inserted Company(id=1, company_name=蜀汉)
instance inserted Company(id=2, company_name=曹魏)
instance inserted Company(id=3, company_name=东吴)
[Company(id=1, company_name=蜀汉), Company(id=2, company_name=曹魏), Company(id=3, company_name=东吴)]
instance inserted Person(id=1, name=刘备)
instance inserted Person(id=2, name=关羽)
instance inserted Person(id=3, name=张飞)
instance inserted Person(id=4, name=张辽)
instance inserted Person(id=5, name=曹操)
instance inserted Person(id=6, name=周瑜)
张飞 38 蜀汉
关羽 40 蜀汉
刘备 42 蜀汉
删除数据
当删除父表记录时,子表中应无对此数据的引用,否则无法删除。
3、 一对一关系
从外键角度看,一对一关系也是一对多关系。实现时,
- 在父表中收集子表数据时,类型注解不使用集合类型即可。
- 子表中relationship()方法中添加single_parent=True.
class Parent(Base):
__tablename__ = "parent_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
child: Mapped["Child"] = relationship(back_populates="parent")
# 一对多时,使用child: Mapped[List["Child"]]
class Child(Base):
__tablename__ = "child_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
parent_id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("parent_table.id"))
parent: Mapped["Parent"] = relationship(back_populates="child",single_parent=True)
4、 多对多关系
多对多关系特点:
1)父表与子表,子表与父表之间均为多对多关系。
2)通常使用1张中间表, 与父表、子表均实现1对多关系。
(当然有的ORM模型将中间表的创建隐藏起来,但在数据库中还是可以看到)
多对多关系定义示例
from __future__ import annotations
from sqlalchemy import Column
from sqlalchemy import Table
from sqlalchemy import ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy import Integer
from sqlalchemy.orm import Mapped
from sqlalchemy.orm import mapped_column
from sqlalchemy.orm import DeclarativeBase
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
class Base(DeclarativeBase):
pass
# note for a Core table, we use the sqlalchemy.Column construct,
# not sqlalchemy.orm.mapped_column
association_table = Table(
"association_table",
Base.metadata,
Column("left_id", ForeignKey("left_table.id")),
Column("right_id", ForeignKey("right_table.id")),
)
class Parent(Base):
__tablename__ = "left_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
children: Mapped[List[Child]] = relationship(
secondary=association_table, back_populates="parents"
)
class Child(Base):
__tablename__ = "right_table"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True)
parents: Mapped[List[Parent]] = relationship(
secondary=association_table, back_populates="children"
)
多对多关系的查询、插入操作与一对多查询相似。 需要注意的是删除操作。
从多对多关系中删除数据
用SQL来实现时,需要先从父表与子表删除数据,再从中间表删除。ORM API 可以自动完成这个过程。 如要删除子表的某条记录。
myparent.children.remove(somechild)
注:通过session.delete(somechild)时,MySql可能会报错,我遇到的原因有多种,不建议使用。
同样,如果要删除父表中的1条记录:
mychild.parent.remove(someparent)