路径总和 II
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
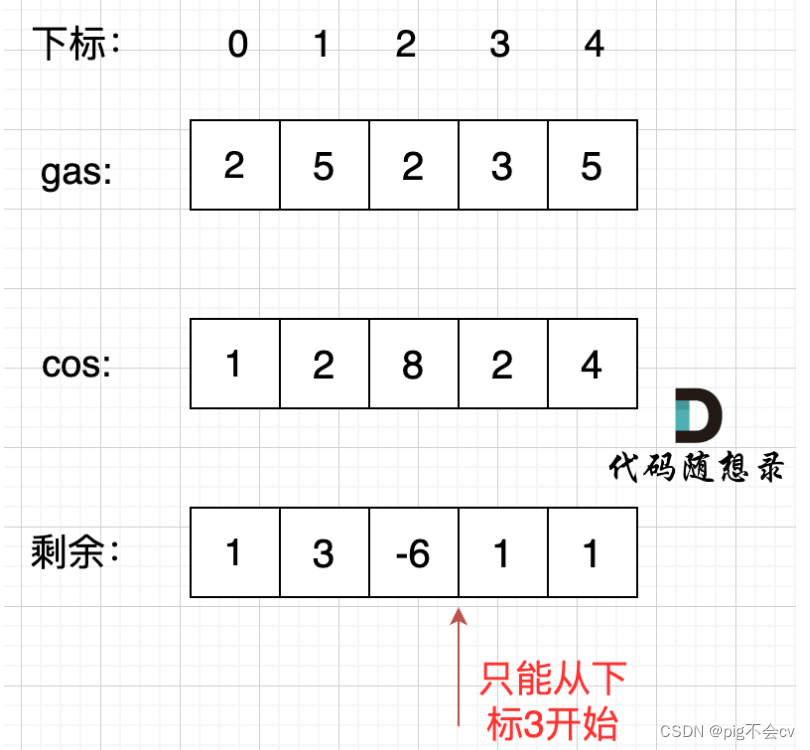
思路:深度优先遍历,递归回溯。这里要用到双端队列Deque
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return res;
}
dfs(root,targetSum);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null ) {
return;
}
path.add(root.val);
targetSum -=root.val;
if(root.left == null && root.right ==null && targetSum == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
dfs(root.left,targetSum);
dfs(root.right,targetSum);
path.pollLast();
}
}
第二次写:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root,targetSum);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
if(root == null) {
return ;
}
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null ) {
if(targetSum == root.val) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
}
dfs(root.left,targetSum-root.val);
dfs(root.right,targetSum-root.val);
path.pollLast();
}
}