VideoCapture类介绍
OpenCV-Python 中的 VideoCapture 类是一个用于捕获视频的类,它可以从摄像头、视频文件或者设备上捕获视频。主要方法有:
class VideoCapture:
# Functions
@_typing.overload
def __init__(self) -> None: ...
@_typing.overload
def __init__(self, filename: str, apiPreference: int = ...) -> None: ...
@_typing.overload
def __init__(self, filename: str, apiPreference: int, params: _typing.Sequence[int]) -> None: ...
@_typing.overload
def __init__(self, index: int, apiPreference: int = ...) -> None: ...
@_typing.overload
def __init__(self, index: int, apiPreference: int, params: _typing.Sequence[int]) -> None: ...
@_typing.overload
def open(self, filename: str, apiPreference: int = ...) -> bool: ...
@_typing.overload
def open(self, filename: str, apiPreference: int, params: _typing.Sequence[int]) -> bool: ...
@_typing.overload
def open(self, index: int, apiPreference: int = ...) -> bool: ...
@_typing.overload
def open(self, index: int, apiPreference: int, params: _typing.Sequence[int]) -> bool: ...
def isOpened(self) -> bool: ...
def release(self) -> None: ...
def grab(self) -> bool: ...
@_typing.overload
def retrieve(self, image: cv2.typing.MatLike | None = ..., flag: int = ...) -> tuple[bool, cv2.typing.MatLike]: ...
@_typing.overload
def retrieve(self, image: UMat | None = ..., flag: int = ...) -> tuple[bool, UMat]: ...
@_typing.overload
def read(self, image: cv2.typing.MatLike | None = ...) -> tuple[bool, cv2.typing.MatLike]: ...
@_typing.overload
def read(self, image: UMat | None = ...) -> tuple[bool, UMat]: ...
def set(self, propId: int, value: float) -> bool: ...
def get(self, propId: int) -> float: ...
def getBackendName(self) -> str: ...
def setExceptionMode(self, enable: bool) -> None: ...
def getExceptionMode(self) -> bool: ...
@staticmethod
def waitAny(streams: _typing.Sequence[VideoCapture], timeoutNs: int = ...) -> tuple[bool, _typing.Sequence[int]]: ...
OpenCV: cv::VideoCapture Class Reference (C++类)
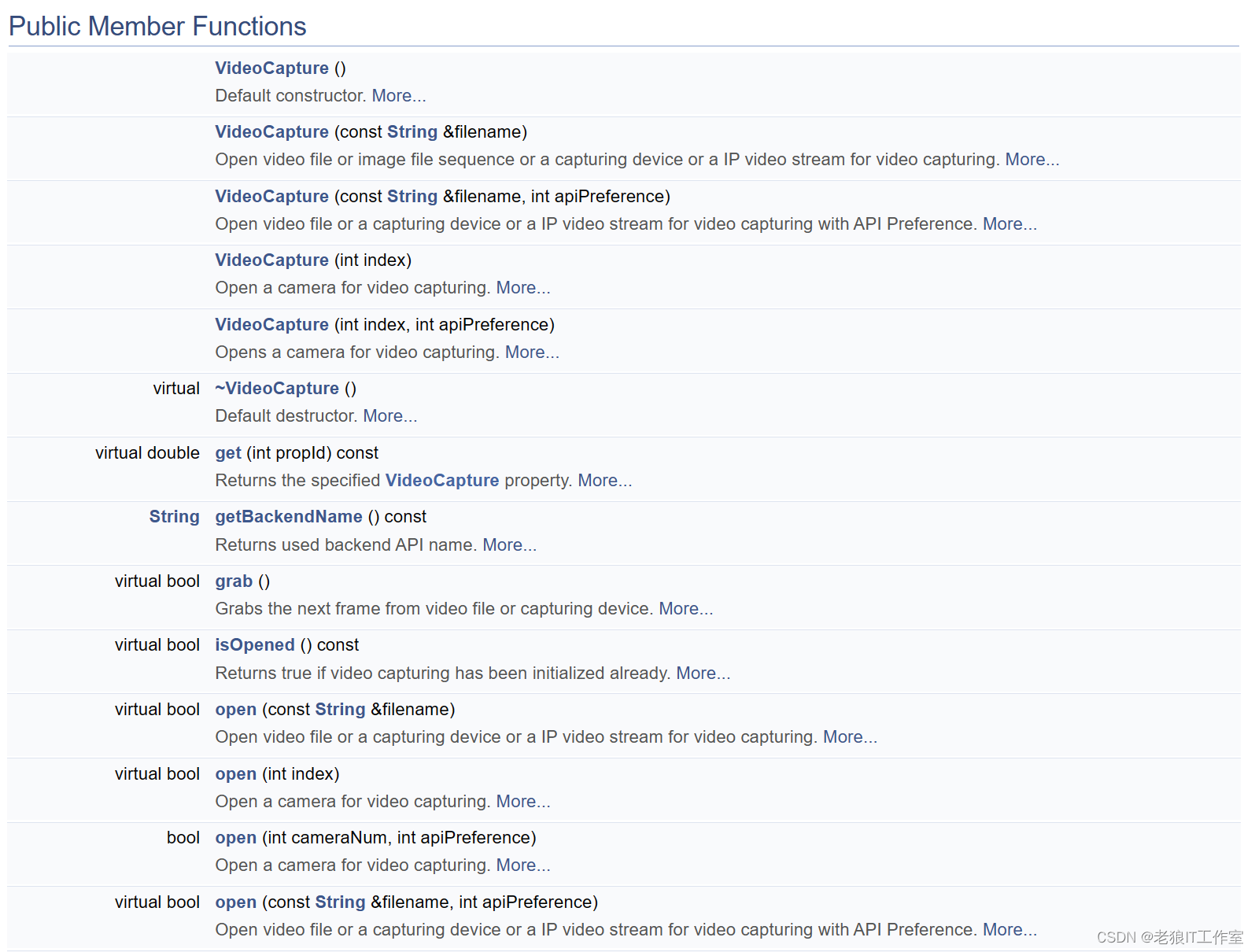
VideoCapture(string 或者int)
构造函数,传入一个字符串参数或者整形参数,可以是摄像头设备的 ID、视频文件的路径或者设备名称。
open(string 或者int)
如何构造函数没有指定设备ID或者视频文件路径,可以通过open来传入一个字符串参数或者整型参数,可以是摄像头设备的 ID、视频文件的路径或者设备名称。
isOpened()
检查是否成功打开了视频源。
read(Mat&)
从视频源中读取一帧图像,并将其存储在传入的 Mat 对象中。如果读取失败,返回 false。
release()
释放 VideoCapture 对象占用的资源。
grab()
获取下一帧图像。
retrieve(Mat&)
从视频源中读取一帧图像,并将其存储在传入的 Mat 对象中。如果读取失败,返回 false。
使用该函数前必须先调用grab()函数,否则将会返回空对象。grab() + retrieve()想结合可以代替read方法。
set(int, float)
设置视频源的属性,如分辨率、帧率等。
get(int)
获取视频源的属性值。
关于视频属性ID
OpenCV: cv::VideoCapture Class Reference

OpenCV: Flags for video I/O

使用案例
import cv2
# 创建 VideoCapture 对象
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 检查是否成功打开摄像头
if not cap.isOpened():
print("无法打开摄像头")
else:
# 读取摄像头的属性信息
print('frame width:', cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
print('frame height:', cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
print('fps:', cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
print('fourcc:', cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC))
# 循环读取摄像头的每一帧图像
while True:
# 读取一帧图像
ret, frame = cap.read()
# 如果读取失败,跳出循环
if not ret:
break
# 在窗口中显示图像
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
# 按下 'q' 键退出循环
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# 释放资源
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()在这个例子中,我们首先创建了一个 VideoCapture 对象,然后在一个循环中不断读取摄像头的图像并显示在窗口中,直到按下 'q' 键退出循环。最后释放 VideoCapture 对象占用的资源。








![[前 10 名] 最佳 Android 数据恢复软件免费下载](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/7c62d4914ef8a266a01275c829b4e36d.jpeg)
