note
- function call本质:准确识别用户的语义,将其转为结构化的指令,其中通过LLM理解指令和上下文判断需要调用哪个函数、抽取出input中函数所需的参数。是用户和界面交互方式产生质变的一个trick。
- 所以为了提高模型准确识别和调用函数的能力,如agenttuning就是利用多个agent任务交互轨迹,对LLM进行sft微调,
文章目录
- note
- 一、function call
- 1. function call的使用例子
- 2. 注意事项
- 3. glm3中的function call
- (1)定义好工具描述信息
- (2)demo中的回答
- 4. gpt的function call
- (1)调用示例
- (2)Function Calling 接口说明
- 二、微调chatglm3
- 1. ChatGLM3 对话格式
- (1)整体结构
- (2)对话头
- 2. 样例场景
- (1)多轮对话
- (2)工具调用
- (3)代码执行
- 3. 如何微调
- (1)数据格式
- 4. glm3-6b的多轮对话微调
- 三、AgentTuning微调
- 1. 数据层面
- 2. 实验细节
- 3. 实验结果:
- 四、GLM4-all tools
- Reference
一、function call
1. function call的使用例子
gpt中的function call可以让开发者在调用 GPT-4 和 GPT-3.5-turbo 模型时,描述函数并让模型智能地输出一个包含调用这些函数所需参数的 JSON 对象。这种功能可以更可靠地将 GPT 的能力与外部工具和 API 进行连接,从而实现以下应用:
- 创建聊天机器人:开发者可以通过调用外部工具,如 ChatGPT 插件,回答问题,或者将查询「北京的天气如何?」转换为调用
getCurrentWeather(location: string)的函数。 - 将自然语言转换为 API 调用或数据库查询:例如,将查询「这个月我的前十个客户是谁?」转换为调用
get_customers_by_revenue(start_date, end_date, limit)的内部 API 调用,或者将查询「上个月 Acme 公司下了多少订单?」转换为使用 sql_query(query)的 SQL 查询。 - 从文本中提取结构化数据:开发者可以定义一个名为
extract_people_data(people)的函数,以提取在维基百科文章中提到的所有人物。
(1)获取天气,通过curl方式调用,
curl https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions -u :$OPENAI_API_KEY -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the weather like in Boston?"}
],
"functions": [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
}'
# 返回结果:
get_current_weather("Boston")
(2)判断用户之间的关系:通过python http调用,这个例子有两个参数
import requests
import json
url = "请求地址"
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer API Key'
}
data = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "李华和小王是不是认识?"},
],
"functions": [
{
"name": "get_connection",
"description": "判断用户1和用户2 是否为朋友关系",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"user_id1": {
"type": "string",
"description": "用户ID 1"
},
"user_id2": {
"type": "string",
"description": "用户ID 2"
},
},
"required": ["user_id1", "user_id2"]
}
}
]
}
data = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data).json()
data
# 返回结果为:
get_connection("李华", "小王")
2. 注意事项
- 当通过英文进提问时, Function calling的效果更好。因为 Function calling本身也是通过大模型进行预测的。
- 通过API访问时候, Function calling效果更好,也更加容易生成函数调用结果,而不是纯对话内容。
- 在对话时可以传入多个待选的函数,GPT会选择其中一个,并生成其对应的参数。
- GPT可以为一个函数生成对应的多个传参,但无法同时生成多个函数调用逻辑。
- Function calling比较适合结合函数 & 参数定义(数值、浮点数、布尔型、日期)生成调用,并不擅长为list参数生成具体的取值。
3. glm3中的function call
(1)定义好工具描述信息
tools = [
{
"name": "track",
"description": "追踪指定股票的实时价格",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"symbol": {
"description": "需要追踪的股票代码"
}
},
"required": ['symbol']
}
},
{
"name": "text-to-speech",
"description": "将文本转换为语音",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"text": {
"description": "需要转换成语音的文本"
},
"voice": {
"description": "要使用的语音类型(男声、女声等)"
},
"speed": {
"description": "语音的速度(快、中等、慢等)"
}
},
"required": ['text']
}
}
]
system_info = {"role": "system", "content": "Answer the following questions as best as you can. You have access to the following tools:", "tools": tools}
(2)demo中的回答

背后的调用返回结果如下图(当需要调用工具的case):
(1)可以看到下面第二个Output结果含get_weather函数名、第二行是将调用的函数及其传参,但是注意这里写死了tool_call,参数部分是从大模型结果得到的
(2)工具调用结果通过 <|observation|> 返回给模型
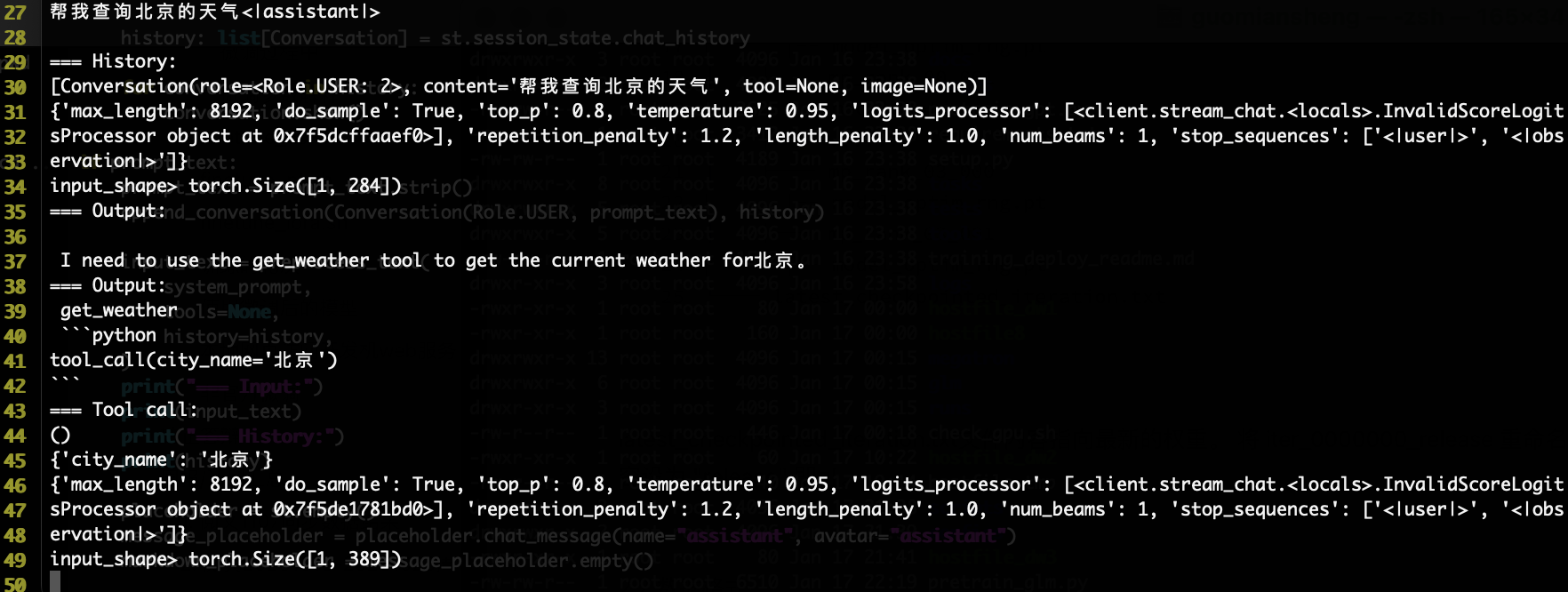
其中get_weather函数是我们事先定义好的:
@register_tool
def get_weather(
city_name: Annotated[str, 'The name of the city to be queried', True],
) -> str:
"""
Get the current weather for `city_name`
"""
if not isinstance(city_name, str):
raise TypeError("City name must be a string")
key_selection = {
"current_condition": ["temp_C", "FeelsLikeC", "humidity", "weatherDesc", "observation_time"],
}
import requests
try:
resp = requests.get(f"https://wttr.in/{city_name}?format=j1")
resp.raise_for_status()
resp = resp.json()
ret = {k: {_v: resp[k][0][_v] for _v in v} for k, v in key_selection.items()}
except:
import traceback
ret = "Error encountered while fetching weather data!\n" + traceback.format_exc()
return str(ret)
(3)模型调用工具时给出 <|observation|> 作为结束 token。因此,需要检查 <|user|> 与 <|observation|> 两种终止token 并作不同处理。如何提取参数:
eval(),方便但需要注意安全性问题,最好在隔离环境中运行- 手动解析 AST
- 限制能够执行的代码
- Transformers Agents:限制执行的代码只能调用工具和 print 函数https://hugqingface.co/docs/transformers/transformers agents#code-execution
比如在glm3源码中process_response函数中使用eval()字符串表达式,直接执行前面字符串提出的tool_call(symbol='10111'),并且tool_call函数这里也定义好了,所以通过执行eval后返回{'symbol': '10111'}字典:
- Transformers Agents:限制执行的代码只能调用工具和 print 函数https://hugqingface.co/docs/transformers/transformers agents#code-execution
def process_response(output: str, use_tool: bool = False) -> Union[str, dict]:
content = ""
for response in output.split("<|assistant|>"):
metadata, content = response.split("\n", maxsplit=1)
if not metadata.strip():
content = content.strip()
content = content.replace("[[训练时间]]", "2023年")
else:
# 如果使用工具调用
if use_tool:
content = "\n".join(content.split("\n")[1:-1])
def tool_call(**kwargs):
return kwargs
parameters = eval(content)
content = {
"name": metadata.strip(),
"arguments": json.dumps(parameters, ensure_ascii=False)
}
else:
content = {
"name": metadata.strip(),
"content": content
}
return content
注意:glm3工具调用只支持chat,不支持stream_chat方法。
4. gpt的function call
(1)调用示例
- 增加了
functions参数,即带有函数描述信息 - 增加了
function_call参数:none:告诉gpt不要调用我们自己任何的函数auto:让gpt自行决定是否调用、调用什么函数具体函数名:让gpt只考虑是否调用xx具体函数
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Boston?"}],
functions=[
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
],
function_call="auto",
)
(2)Function Calling 接口说明
- chat接口的messages参数数组除了原有的system、user、assisant,新增了role参数选项function。chat接口新增functions参数,格式为数组,意味着可以传入一组函数定义,模型将智能选择用哪个
- 每个function支持三个参数:name(函数名)、description(函数功能说明)和parameters(模型输出的数据格式说明)
- chat接口新增了function_call参数,默认值为none,可设置为auto。chat接口的function_call用于决定是否启用函数式回答。如果值为none,则不需要传入functions参数,如果值为auto,你需要提供一些函数供模型选择。只有在function_call为auto,且functions包含函数数组,且模型根据你的函数功能说明匹配到函数时,返回的message中才会包含function_call
- 调用本地函数执行后,需要将结果传回给模型以生成自然语言回复。此时,应在请求的messages中添加一个role为assisant的message,包含function_call信息(即模型返回的数据),同时需要添加一个role为function的数据,包含本地函数执行的结果
二、微调chatglm3
关于glm3的微调:
- 与此前的做法不同,chatglm3-6b 推荐使用多轮对话格式进行微调
- 即将多个不同角色的对话内容直接拼接进行 teacher-forcing
- Special token 的加入使得多轮训练变得容易
- 不再特殊区别 prompt 和 response
- 需正确配置
loss_mask,即哪些 token 的预测需要模型学习 - loss_mask 的配置依据是推理时的行为
- 模型自己生成的 token 需要计算 loss
- 推理系统插入的 token 无需计算 loss
1. ChatGLM3 对话格式
为了避免用户输入的注入攻击,以及统一 Code Interpreter,Tool & Agent 等任务的输入,ChatGLM3 采用了全新的对话格式。
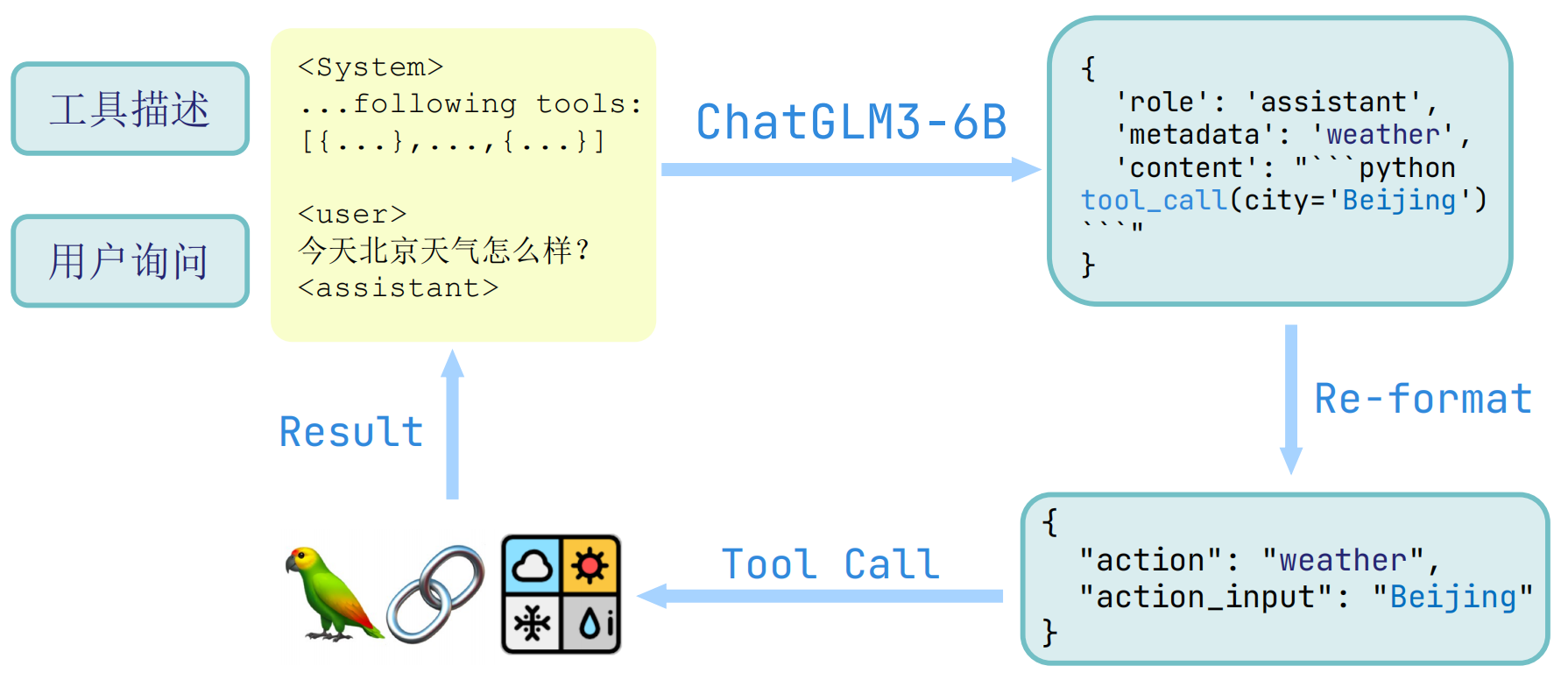
(1)整体结构
ChatGLM3 对话的格式由若干对话组成,其中每个对话包含对话头和内容,一个典型的多轮对话结构如下
<|system|>
You are ChatGLM3, a large language model trained by Zhipu.AI. Follow the user's instructions carefully. Respond using markdown.
<|user|>
Hello
<|assistant|>
Hello, I'm ChatGLM3. What can I assist you today?
(2)对话头
对话头占完整的一行,格式为
<|role|>{metadata}
其中 <|role|> 部分使用 special token 表示,无法从文本形式被 tokenizer 编码以防止注入。metadata 部分采用纯文本表示,为可选内容。
<|system|>:系统信息,设计上可穿插于对话中,但目前规定仅可以出现在开头<|user|>:用户- 不会连续出现多个来自
<|user|>的信息
- 不会连续出现多个来自
<|assistant|>:AI 助手- 在出现之前必须有一个来自
<|user|>的信息
- 在出现之前必须有一个来自
<|observation|>:外部的返回结果- 必须在
<|assistant|>的信息之后
- 必须在
2. 样例场景
(1)多轮对话
- 有且仅有
<|user|>、<|assistant|>、<|system|>三种 role
<|system|>
You are ChatGLM3, a large language model trained by Zhipu.AI. Follow the user's instructions carefully. Respond using markdown.
<|user|>
Hello
<|assistant|>
Hello, I'm ChatGLM3. What can I assist you today?
(2)工具调用
- <|assistant|>{metadata}:
- 工具调用:{metadata} 为调用的工具名
- 例如 <|assistant|>test_tool 表示模型希望调用
test_tool工具
<|system|>
Answer the following questions as best as you can. You have access to the following tools:
[
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string"},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
]
<|user|>
今天北京的天气怎么样?
<|assistant|>
好的,让我们来查看今天的天气
<|assistant|>get_current_weather
```python
tool_call(location="beijing", unit="celsius")
```
<|observation|>
{"temperature": 22}
<|assistant|>
根据查询结果,今天北京的气温为 22 摄氏度。
-
tool_registry模式在tool_registry.py中定义工具

-
除了正常使用 <|assistant|> 进行对话外,模型在感到需要调用工具时会生成
<|assistant|>{metadata},其中 metadata 为调用的工具名 -
对话内容为 Python 代码,最终调用
tool_call函数传参数 -
例如:(增加了额外换行以提升可读性)

-
工具调用结果通过 <|observation|> 返回给模型。例如:

-
模型调用工具时给出 <|observation|> 作为结束 token。因此,需要检查 <|user|> 与 <|observation|> 两种终止token 并作不同处理。如:


(3)代码执行
- 有
<|user|>、<|assistant|>、<|system|>、<|observation|>四种 role。其中<|assistant|>的 metadata 只有 interpreter。
- Code Interpreter: 固定为 <|assistant|>interpreter
<|system|>
你是一位智能AI助手,你叫ChatGLM3,你连接着一台电脑,但请注意不能联网。在使用Python解决任务时,你可以运行代码并得到结果,如果运行结果有错误,你需要尽可能对代码进行改进。你可以处理用户上传到电脑上的文件,文件默认存储路径是/mnt/data/。
<|user|>
#File: /mnt/data/metadata.jsonl
#Size: 35380
#File uploaded
文件中是否存在缺失值或异常值?
<|assistant|>
首先,我将读取您提供的文件,并查看其内容以确定是否存在缺失值或异常值。
我们从加载文件开始:
<|assistant|>interpreter
```python
import json
# Load the uploaded file
data = []
with open("/mnt/data/metadata.jsonl", 'r') as file:
for line in file:
data.append(json.loads(line))
# Display the first few records to get a sense of the data
data[:5]
```
<|observation|>
```result
[{'file_name': 'aceinthehole.png',
'name': 'Ace in the Hole',
'type': 'survivor',
'description': 'Lady Luck always seems to be throwing something good your way.'},
{'file_name': 'adrenaline.png',
'name': 'Adrenaline',
'type': 'survivor',
'description': 'You are fuelled by unexpected energy when on the verge of escape.'},
{'file_name': 'aftercare.png',
'name': 'Aftercare',
'type': 'survivor',
'description': "Unlocks potential in one's aura reading ability."},
{'file_name': 'agitation.png',
'name': 'Agitation',
'type': 'killer',
'description': 'You get excited in anticipation of hooking your prey.'},
{'file_name': 'alert.png',
'name': 'Alert',
'type': 'survivor',
'description': 'Your acute senses are on high alert.'}]
```
<|assistant|>
该文件看起来包含有关某些条目的元数据,每个条目有以下字段:
- `file_name`: 文件名称
- `name`: 名称
- `type`: 类型(例如 "survivor" 或 "killer")
- `description`: 描述
接下来,我将检查这些字段是否存在缺失值。
<|assistant|>interpreter
```python
# Check for missing values in each column
missing_values = {key: sum(1 for item in data if key not in item) for key in data[0].keys()}
missing_values
```
<|observation|>
```result
{'file_name': 0, 'name': 0, 'type': 0, 'description': 0}
```
<|assistant|>
每个字段都没有缺失值。这意味着每个条目都完整。
接下来,我们可以检查是否存在任何潜在的异常值。这通常需要更深入的分析和对数据的了解,但我可以从一些基本的统计和分布开始进行检查。为了这样做,我们可以查看“type”字段的值分布,看看是否有任何意外的类别。
<|assistant|>interpreter
```python
# Check the distribution of values in the 'type' column
type_distribution = {key: sum(1 for item in data if item['type'] == key) for key in set(item['type'] for item in data)}
type_distribution
```
<|observation|>
```result
{'survivor': 116, 'killer': 103}
```
<|assistant|>
“type”字段有两个值:“survivor”和“killer”。其中,“survivor”有116个条目,而“killer”有103个条目。
从这个初步的检查中,我们没有发现任何明显的异常值。
如果您有任何特定的标准或其他字段需要检查,我可以为您提供更详细的分析。您还希望我检查什么呢?
<|user|>
帮我画一个爱心
<|assistant|>interpreter
```python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 爱心形状的参数方程
def heart(t):
x = 16 * np.sin(t) ** 3
y = 13 * np.cos(t) - 5 * np.cos(2 * t) - 2 * np.cos(3 * t) - np.cos(4 * t)
return x, y
t = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 1000)
x, y = heart(t)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.plot(x, y, color='red')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
```
<|observation|>
```result
【image】
```
<|assistant|>
这是一个爱心形状。我使用了参数方程来描述这个形状,并使用matplotlib进行了绘制。如果您有任何其他需求或问题,请随时告诉我。
<|user|> # End
3. 如何微调
包括全量微调和 P-Tuning v2两种方案。
格式上,提供多轮对话微调样例和输入输出格式微调样例。
(1)数据格式
多轮对话微调示例采用 ChatGLM3 对话格式约定,对不同角色添加不同 loss_mask 从而在一遍计算中为多轮回复计算 loss。

对于数据文件,样例采用如下格式
[
{
"tools": [
// available tools, format is not restricted
],
"conversations": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "<system prompt text>"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "<user prompt text>",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "<assistant response text>"
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "<name of the tool to be called",
"parameters": {
"<parameter_name>": "<parameter_value>"
},
"observation": "<observation>" // don't have to be string
}
]
}
// ...
]
- 关于工具描述的 system prompt 无需手动插入,预处理时会将 tools 字段使用
json.dumps(..., ensure_ascii=False)格式化后插入为首条 system prompt。 - 每种角色可以附带一个 bool 类型的 loss 字段,表示该字段所预测的内容是否参与 loss 计算。若没有该字段,样例实现中默认对 system, user 不计算 loss,其余角色则计算 loss。
- tool 并不是 ChatGLM3 中的原生角色,这里的 tool 在预处理阶段将被自动转化为一个具有工具调用 metadata 的 assistant 角色(默认计算 loss)和一个表示工具返回值的 observation 角色(不计算 loss)。
栗子如下:高亮部分为需要计算loss的token,<|assistant|> 后的内容和角色 token 都需要计算 loss。

4. glm3-6b的多轮对话微调
有且仅有 <|user|>、<|assistant|>、<|system|> 三种 role
<|system|>
You are ChatGLM3, a large language model trained by Zhipu.AI. Follow the user's instructions carefully. Respond using markdown.
<|user|>
Hello
<|assistant|>
Hello, I'm ChatGLM3. What can I assist you today?
具体用到的dataset如下:
class MultiTurnDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data: List[dict], tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizer, max_seq_length: int):
super(MultiTurnDataset, self).__init__()
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_seq_length = max_seq_length
self.data = data
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, i) -> dict:
data_item = self.data[i]
tokens, loss_masks = format_conversation(data_item, self.tokenizer, CONVERSATOIN_KEY, TOOL_DESC_KEY)
# labels are used inside the model
target_based_loss_mask = [False] + loss_masks[:-1]
labels = [(t if m else -100) for t, m in zip(tokens, target_based_loss_mask)]
tokens = tokens[:self.max_seq_length]
labels = labels[:self.max_seq_length]
tokens += [self.tokenizer.pad_token_id] * (self.max_seq_length - len(tokens))
labels += [-100] * (self.max_seq_length - len(labels))
assert len(tokens) == len(labels), f"length mismatch: {len(tokens)} vs {len(labels)}"
return {
"input_ids": tokens,
"labels": labels
}
三、AgentTuning微调
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.12823.pdf
Github地址:https://github.com/THUDM/AgentTuning
1. 数据层面
(1)数据——AgentInstruction数据集构建有三个主要阶段:指令构建、轨迹交互和轨迹过滤。整个过程使用GPT-3.5(GPT-3.5-turbo-0613)和GPT4(GPT-4-0613)实现完全自动化,使该方法能够轻松扩展到新的Agent任务。
- 任务包括AlfWorld、WebShop、Mind2Web、知识图、操作系统、数据库。
2. 实验细节
模型:Llama 2(Llama-2-{7,13,70}b-chat)
学习率:7B和13B模型的学习率为5e-5,70B模型为1e-5;
批次大小:设置了批次大小为64;
序列长度:序列长度为4096;
优化器:我们使用AdamW优化器,其中余弦学习调度器具有2%的预热步骤。
高效训练:tensor并行和pipeline并行
混合训练:使用基础模型
π
θ
\pi_\theta
πθ,表示为给定input和x时得到模型结果y的概率分布
π
θ
(
y
∣
x
)
\pi_\theta(y\mid x)
πθ(y∣x));AgentInstruct 数据集 Dagent 和通用数据集 Dgeneral的数量比为
η
\eta
η,目标是找到最佳的策略
π
θ
(
y
∣
x
)
\pi_\theta(y\mid x)
πθ(y∣x),通过最小化损失函数:
J
(
θ
)
=
η
⋅
E
(
x
,
y
)
∼
D
agent
[
log
π
θ
(
y
∣
x
)
]
+
(
1
−
η
)
⋅
E
(
x
,
y
)
∼
D
general
[
log
π
θ
(
y
∣
x
)
]
J(\theta)=\eta \cdot \mathbb{E}_{(x, y) \sim \mathcal{D}_{\text {agent }}}\left[\log \pi_\theta(y \mid x)\right]+(1-\eta) \cdot \mathbb{E}_{(x, y) \sim \mathcal{D}_{\text {general }}}\left[\log \pi_\theta(y \mid x)\right]
J(θ)=η⋅E(x,y)∼Dagent [logπθ(y∣x)]+(1−η)⋅E(x,y)∼Dgeneral [logπθ(y∣x)]
注:虽然直觉上代理数据越多则代理能力越强,但是实验发现仅在代理数据上sft后模型泛化能力比混合训练情况差,实验结果
η
\eta
η为0.2的效果最好。
3. 实验结果:
对于大多数held-in任务,Llama 2的性能几乎为零,这表明Llama 2完全无法处理这些任务。然而,AgentLM的基本错误明显较少,这表明该方法有效地激活了模型的Agent能力。并且70BAgentLM的总体性能接近GPT-4。

四、GLM4-all tools
GLM-4 实现自主根据用户意图,自动理解、规划复杂指令,自由调用网页浏览器、Code Interpreter代码解释器和多模态文生图大模型,以完成复杂任务。即只需一个指令,GLM-4会自动分析指令,结合上下文选择决定调用合适的工具。

All Tools - Function Call。GLM-4 能够根据用户提供的Function描述,自动选择所需 Function并生成参数,以及根据 Function 的返回值生成回复;同时也支持一次输入进行多次 Function 调用,支持包含中文及特殊符号的 Function 名字。这一方面GLM-4 All Tools 与 GPT-4 Turbo 相当。
Reference
[1] 当MLG邂逅AI,Copilot模式将成就「Growth Automation」时代
[2] 大模型下半场,关于Agent的几个疑问
[3] LLM-Native产品的变与不变
[4] 聊聊我对AI Agents技术的一些看法.小夕
[5] Agent = LLM+Planning+Feedback+Tool use
[6] ChatGLM团队发布AI Agent能力评测工具AgentBench:GPT-4一骑绝尘,开源模型表现非常糟糕
[7] 从 GPTs 聊到 Agent、LLMOps 以及开源的新机会.质朴发言
[8] chatglm3.0发布,对应的权重,部署代码管上:
模型:https://huggingface.co/THUDM/chatglm3-6b-base
模型:https://huggingface.co/THUDM/chatglm3-6b
[9] chatglm 32k版本:https://huggingface.co/THUDM/chatglm3-6b-32k
[10] 低成本部署:https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3/blob/main/DEPLOYMENT.md
工具调用:https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3/blob/main/tool_using/README.md
github:https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3
[11] 智谱AI推出第三代基座大模型
[12] https://modelscope.cn/models/ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b/summary
[13] 北大校友“炼丹”分享:OpenAI如何训练千亿级模型?
[14] 大模型工具调用(function call)原理及实现:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/663770472
[15] 万字解析 AI Agent:如何重构千亿美金市场,掀起软件生产革命?
[16] Langchain-Chatchat项目:5.1-ChatGLM3-6B工具调用
[17] 智谱ChatGLM3魔搭最佳实践教程
[18] ChatGLM3 的工具调用(FunctionCalling)实现原理
[19] XAgent:地址:🔗 https://github.com/OpenBMB/XAgent
案例展示地址:🔗 https://x-agent.net/
博客地址:🔗 https://blog.x-agent.net
[20] Function Call: Chat 应用的插件基石与交互技术的变革黎明
[21] https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling
[22] Automated Multi Agent Chat
[23] 从第一性原理看大模型Agent技术
[24] 智谱AI推出新一代基座模型 GLM-4
[25] https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3/tree/main/finetune_demo
[26] 使用docker运行chatglm3对外的http服务,使用python代码执行函数调用,查询北京天气
[27] 大模型工具调用(function call)原理及实现
[28] ToolAlpaca: Generalized Tool Learning for Language Models with 3000 Simulated Cases
[29] 【LangChain笔记11】打造属于自己的AutoGPT,利用LangChain和GPT最新0613构建工具组合助手
[30] 易懂的OpenAI Function Call功能说明
[31] OpenAI 最新发布的 Function calling 到底是什么
[32] 用户交互-Function Call 到底是什么
[33] https://github.com/THUDM/AgentTuning
[34] LLM之Agent(五)| AgentTuning:清华大学与智谱AI提出AgentTuning提高大语言模型Agent能力
[35] ChatGLM3 tool_registry.py 代码解析
[36] LLMs之ChatGLM3:ChatGLM3/ChatGLM3-6B的简介—“对话格式”功能介绍(推理系统如何解析参数/采用Python代码形式/编写工具调用的代码/Manual Mode)、推理演示