继续上一节的内容,本节是苍穹外卖后端开发的最后一节,本节学习Apache POI,完成工作台、数据导出功能。
目录
- 工作台
- Apache POI
- 入门案例
- 导出运营数据Excel报表
工作台
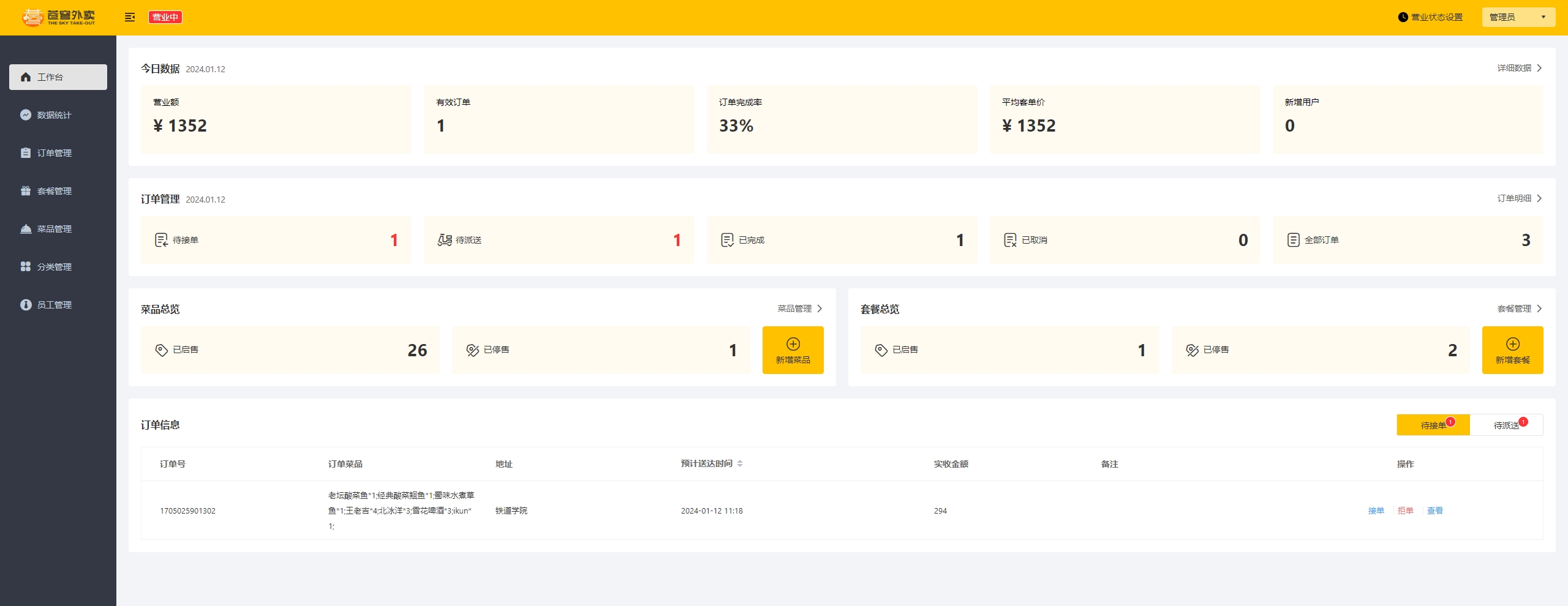
工作台是系统运营的数据看板,并提供快捷操作入口,可以有效提高商家的工作效率。
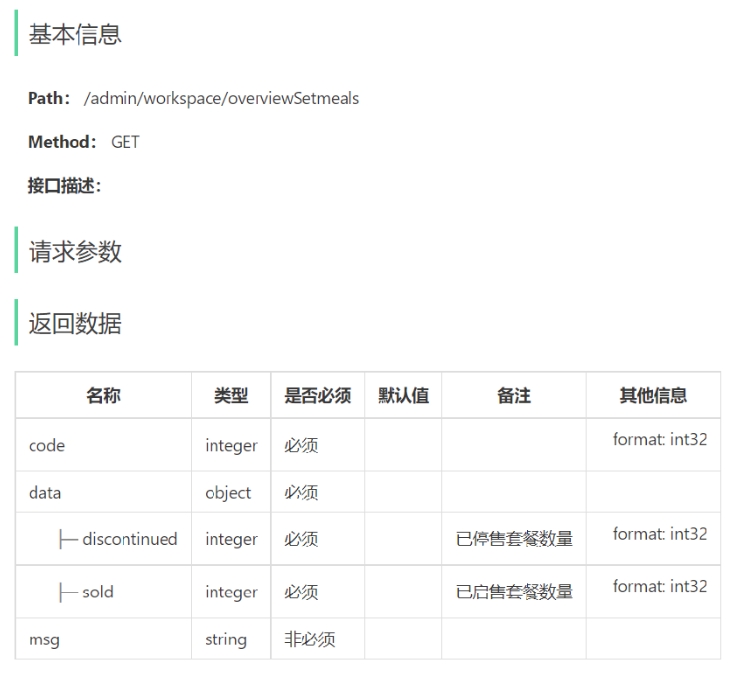
工作台展示的数据:今日数据、订单管理、菜品总览、套餐总览、订单信息
营业额:已完成订单的总金额
有效订单:已完成订单的数量
订单完成率:有效订单数 / 总订单数 * 100%
平均客单价:营业额 / 有效订单数
新增用户:新增用户的数量
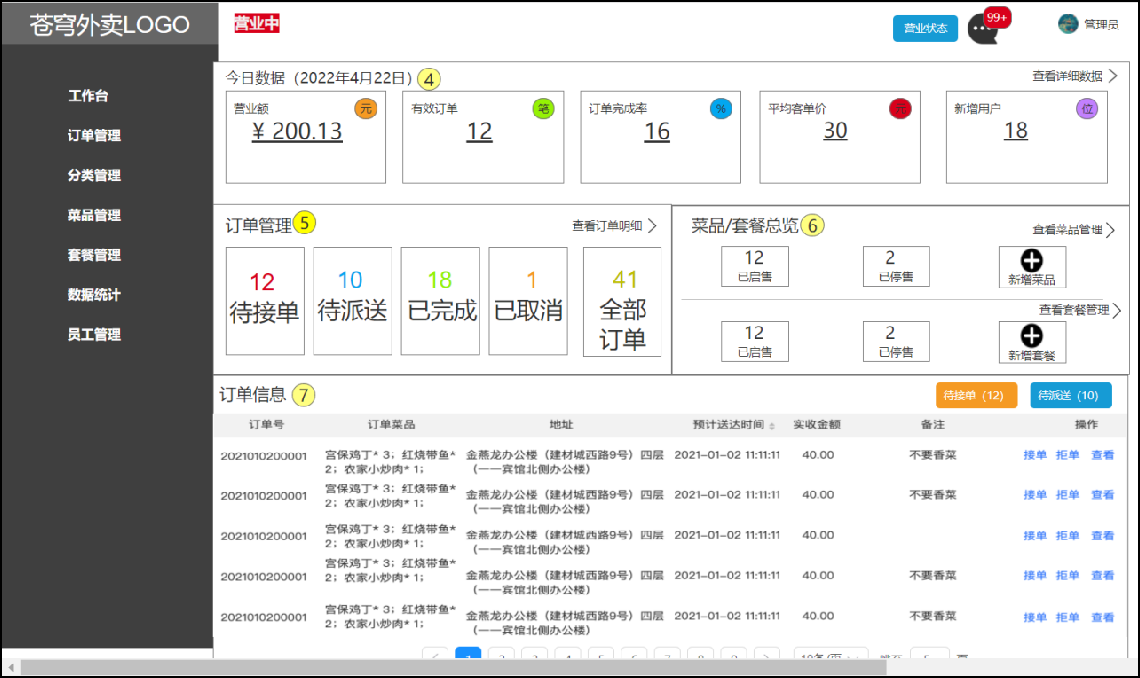
通过上述原型图分析,共包含6个接口。今日数据接口、订单管理接口、菜品总览接口、套餐总览接口、订单搜索(已完成)、各个状态的订单数量统计(已完成)
1). 今日数据的接口设计
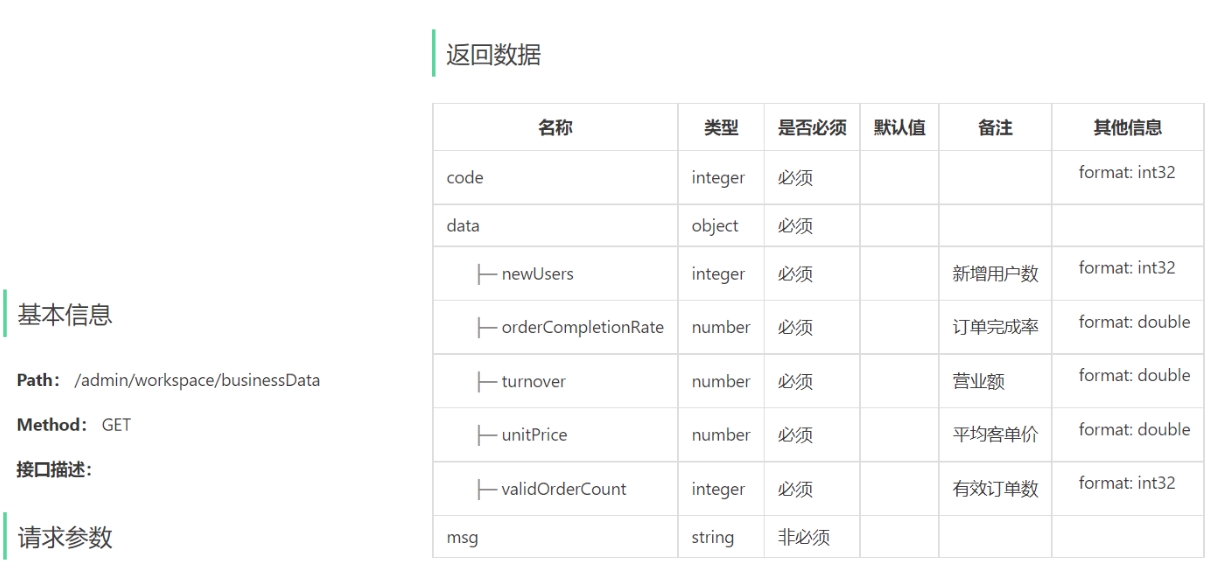
2). 订单管理的接口设计
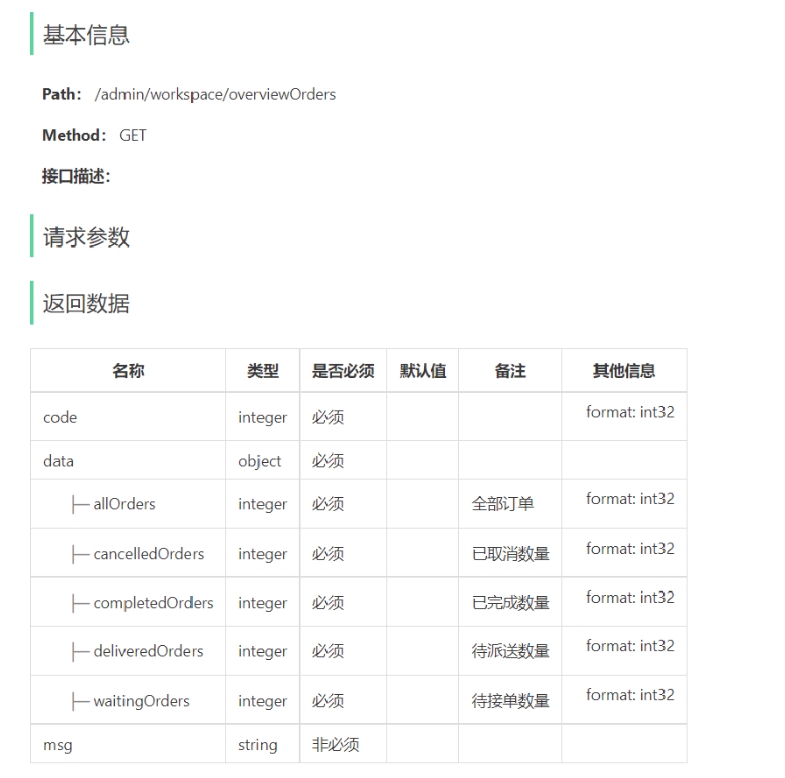
3). 菜品总览的接口设计
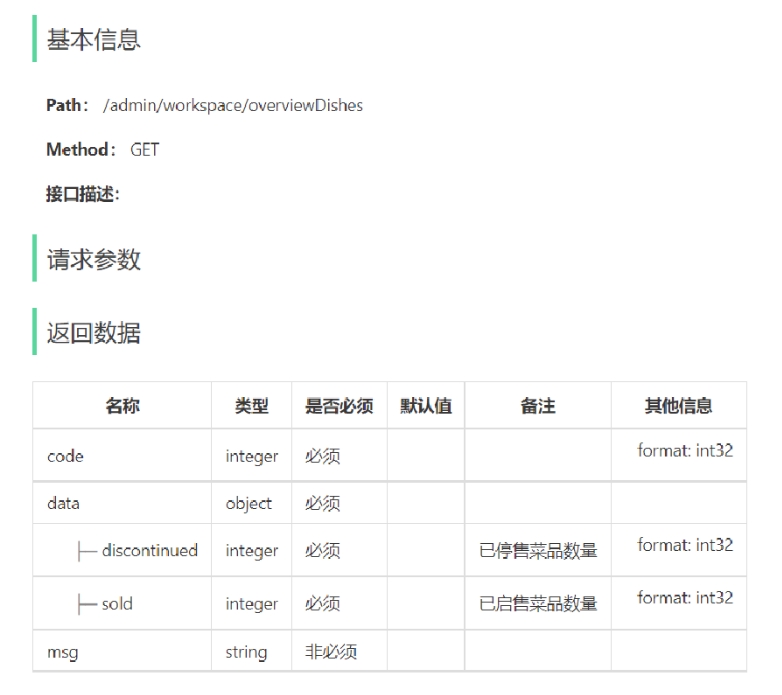
4). 套餐总览的接口设计
Controller层
添加controller.admin.WorkSpaceController.java
/**
* 工作台
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/admin/workspace")
@Slf4j
@Api(tags = "工作台相关接口")
public class WorkSpaceController {
@Autowired
private WorkspaceService workspaceService;
/**
* 工作台今日数据查询
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/businessData")
@ApiOperation("工作台今日数据查询")
public Result<BusinessDataVO> businessData(){
//获得当天的开始时间
LocalDateTime begin = LocalDateTime.now().with(LocalTime.MIN);
//获得当天的结束时间
LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.now().with(LocalTime.MAX);
BusinessDataVO businessDataVO = workspaceService.getBusinessData(begin, end);
return Result.success(businessDataVO);
}
/**
* 查询订单管理数据
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/overviewOrders")
@ApiOperation("查询订单管理数据")
public Result<OrderOverViewVO> orderOverView(){
return Result.success(workspaceService.getOrderOverView());
}
/**
* 查询菜品总览
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/overviewDishes")
@ApiOperation("查询菜品总览")
public Result<DishOverViewVO> dishOverView(){
return Result.success(workspaceService.getDishOverView());
}
/**
* 查询套餐总览
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/overviewSetmeals")
@ApiOperation("查询套餐总览")
public Result<SetmealOverViewVO> setmealOverView(){
return Result.success(workspaceService.getSetmealOverView());
}
}
Service层实现类
WorkspaceServiceImpl.java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class WorkspaceServiceImpl implements WorkspaceService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private DishMapper dishMapper;
@Autowired
private SetmealMapper setmealMapper;
/**
* 根据时间段统计营业数据
* @param begin
* @param end
* @return
*/
public BusinessDataVO getBusinessData(LocalDateTime begin, LocalDateTime end) {
/**
* 营业额:当日已完成订单的总金额
* 有效订单:当日已完成订单的数量
* 订单完成率:有效订单数 / 总订单数
* 平均客单价:营业额 / 有效订单数
* 新增用户:当日新增用户的数量
*/
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("begin",begin);
map.put("end",end);
//查询总订单数
Integer totalOrderCount = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
map.put("status", Orders.COMPLETED);
//营业额
Double turnover = orderMapper.sumByMap(map);
turnover = turnover == null? 0.0 : turnover;
//有效订单数
Integer validOrderCount = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
Double unitPrice = 0.0;
Double orderCompletionRate = 0.0;
if(totalOrderCount != 0 && validOrderCount != 0){
//订单完成率
orderCompletionRate = validOrderCount.doubleValue() / totalOrderCount;
//平均客单价
unitPrice = turnover / validOrderCount;
}
//新增用户数
Integer newUsers = userMapper.countByMap(map);
return BusinessDataVO.builder()
.turnover(turnover)
.validOrderCount(validOrderCount)
.orderCompletionRate(orderCompletionRate)
.unitPrice(unitPrice)
.newUsers(newUsers)
.build();
}
/**
* 查询订单管理数据
*
* @return
*/
public OrderOverViewVO getOrderOverView() {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("begin", LocalDateTime.now().with(LocalTime.MIN));//获得当天的开始时间
map.put("status", Orders.TO_BE_CONFIRMED);
//待接单
Integer waitingOrders = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
//待派送
map.put("status", Orders.CONFIRMED);
Integer deliveredOrders = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
//已完成
map.put("status", Orders.COMPLETED);
Integer completedOrders = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
//已取消
map.put("status", Orders.CANCELLED);
Integer cancelledOrders = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
//全部订单
map.put("status", null);
Integer allOrders = orderMapper.countByMap(map);
return OrderOverViewVO.builder()
.waitingOrders(waitingOrders)
.deliveredOrders(deliveredOrders)
.completedOrders(completedOrders)
.cancelledOrders(cancelledOrders)
.allOrders(allOrders)
.build();
}
/**
* 查询菜品总览
*
* @return
*/
public DishOverViewVO getDishOverView() {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("status", StatusConstant.ENABLE);
Integer sold = dishMapper.countByMap(map);
map.put("status", StatusConstant.DISABLE);
Integer discontinued = dishMapper.countByMap(map);
return DishOverViewVO.builder()
.sold(sold)
.discontinued(discontinued)
.build();
}
/**
* 查询套餐总览
*
* @return
*/
public SetmealOverViewVO getSetmealOverView() {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("status", StatusConstant.ENABLE);
Integer sold = setmealMapper.countByMap(map);
map.put("status", StatusConstant.DISABLE);
Integer discontinued = setmealMapper.countByMap(map);
return SetmealOverViewVO.builder()
.sold(sold)
.discontinued(discontinued)
.build();
}
}
Mapper层
在SetmealMapper中添加countByMap方法定义
/**
* 根据条件统计套餐数量
* @param map
* @return
*/
Integer countByMap(Map map);
在SetmealMapper.xml中添加对应SQL实现
<select id="countByMap" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(id) from setmeal
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="categoryId != null">
and category_id = #{categoryId}
</if>
</where>
</select>
在DishMapper中添加countByMap方法定义
/**
* 根据条件统计菜品数量
* @param map
* @return
*/
Integer countByMap(Map map);
在DishMapper.xml中添加对应SQL实现
<select id="countByMap" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(id) from dish
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="categoryId != null">
and category_id = #{categoryId}
</if>
</where>
</select>
测试
Apache POI
Apache POI 是一个处理Miscrosoft Office各种文件格式的开源项目。简单来说就是,我们可以使用 POI 在 Java 程序中对Miscrosoft Office各种文件进行读写操作。
一般情况下,POI 都是用于操作 Excel 文件。

Apache POI 的应用场景:银行网银系统导出交易明细、各种业务系统导出Excel报表、批量导入业务数据。
入门案例
Apache POI既可以将数据写入Excel文件,也可以读取Excel文件中的数据,接下来分别进行实现。
Apache POI的maven坐标:(项目中已导入)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.16</version>
</dependency>
将数据写入Excel文件
package com.sky.test;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class POITest {
/**
* 基于POI向Excel文件写入数据
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void write() throws Exception{
//在内存中创建一个Excel文件对象
XSSFWorkbook excel = new XSSFWorkbook();
//创建Sheet页
XSSFSheet sheet = excel.createSheet("itcast");
//在Sheet页中创建行,0表示第1行
XSSFRow row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建单元格并在单元格中设置值,单元格编号也是从0开始,1表示第2个单元格
row1.createCell(1).setCellValue("姓名");
row1.createCell(2).setCellValue("城市");
XSSFRow row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
row2.createCell(1).setCellValue("张三");
row2.createCell(2).setCellValue("北京");
XSSFRow row3 = sheet.createRow(2);
row3.createCell(1).setCellValue("李四");
row3.createCell(2).setCellValue("上海");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\itcast.xlsx"));
//通过输出流将内存中的Excel文件写入到磁盘上
excel.write(out);
//关闭资源
out.flush();
out.close();
excel.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
write();
}
}
在D盘中生成itcast.xlsx文件,创建名称为itcast的Sheet页,同时将内容成功写入。
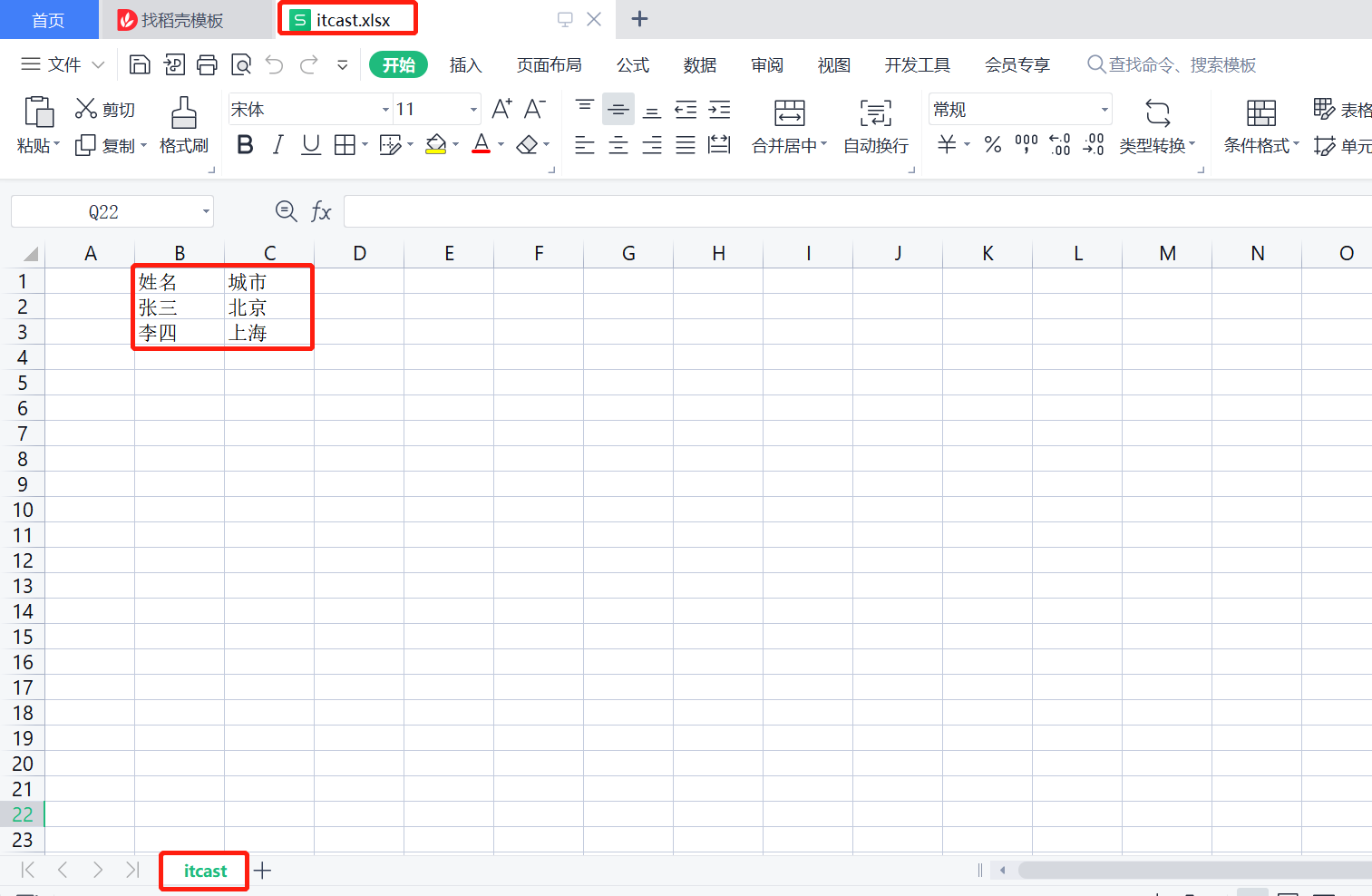
读取Excel文件中的数据
package com.sky.test;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class POITest {
/**
* 基于POI读取Excel文件
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void read() throws Exception{
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\itcast.xlsx"));
//通过输入流读取指定的Excel文件
XSSFWorkbook excel = new XSSFWorkbook(in);
//获取Excel文件的第1个Sheet页
XSSFSheet sheet = excel.getSheetAt(0);
//获取Sheet页中的最后一行的行号
int lastRowNum = sheet.getLastRowNum();
for (int i = 0; i <= lastRowNum; i++) {
//获取Sheet页中的行
XSSFRow titleRow = sheet.getRow(i);
//获取行的第2个单元格
XSSFCell cell1 = titleRow.getCell(1);
//获取单元格中的文本内容
String cellValue1 = cell1.getStringCellValue();
//获取行的第3个单元格
XSSFCell cell2 = titleRow.getCell(2);
//获取单元格中的文本内容
String cellValue2 = cell2.getStringCellValue();
System.out.println(cellValue1 + " " +cellValue2);
}
//关闭资源
in.close();
excel.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
read();
}
}
将itcast.xlsx文件中的数据进行读取
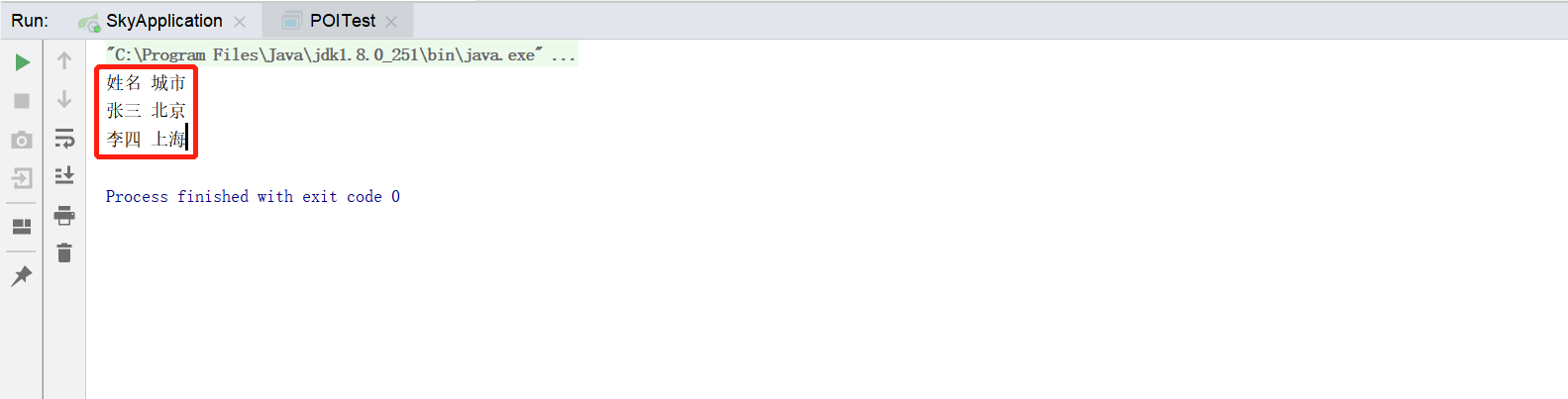
导出运营数据Excel报表
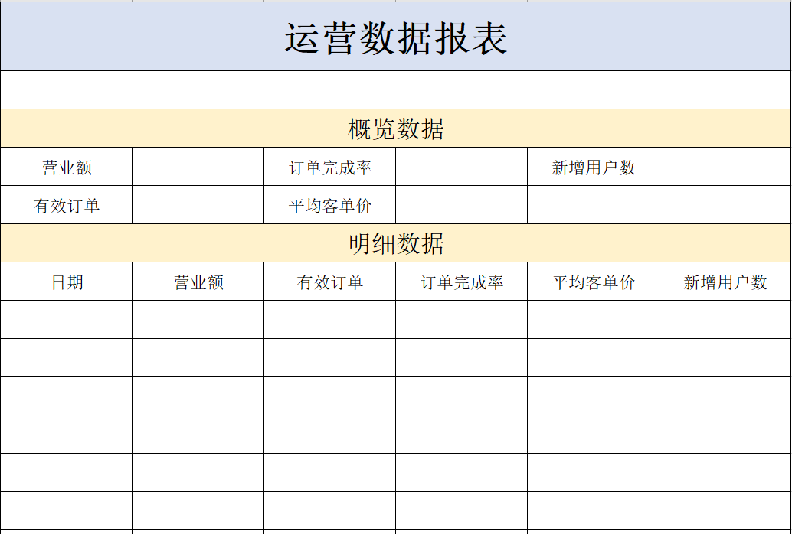
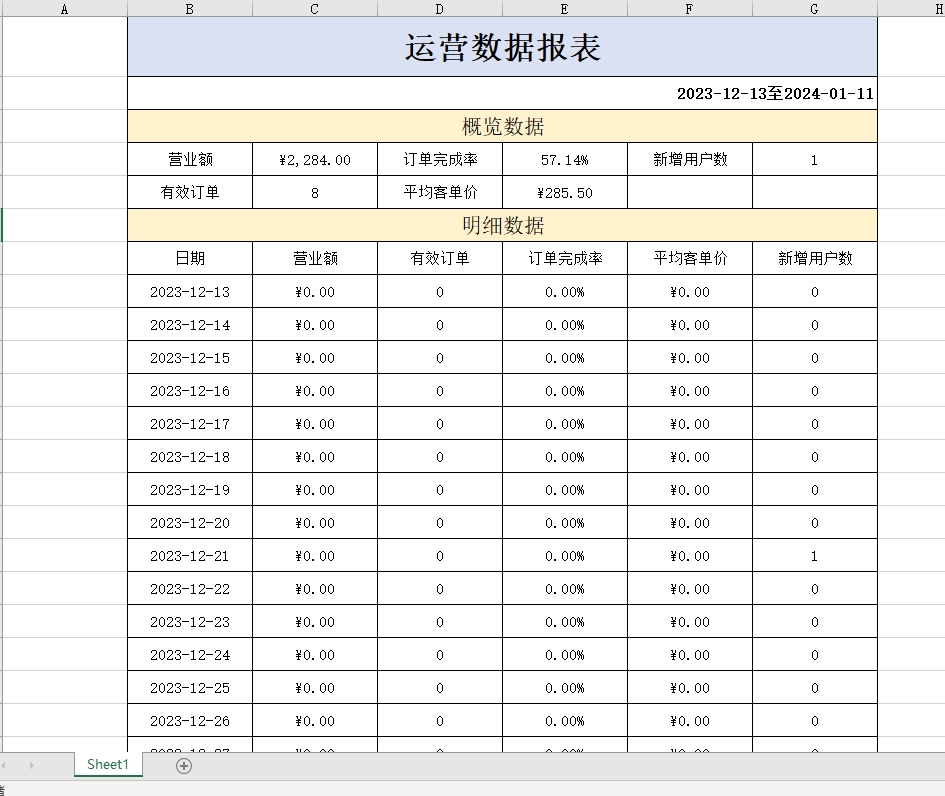
在数据统计页面,有一个数据导出的按钮,点击该按钮时就会下载一个文件。这是一个Excel形式的文件,主要包含最近30日运营相关的数据。表格的形式已经固定,主要由概览数据和明细数据两部分组成。导出这个报表之后,相对应的数字就会填充在表格中。
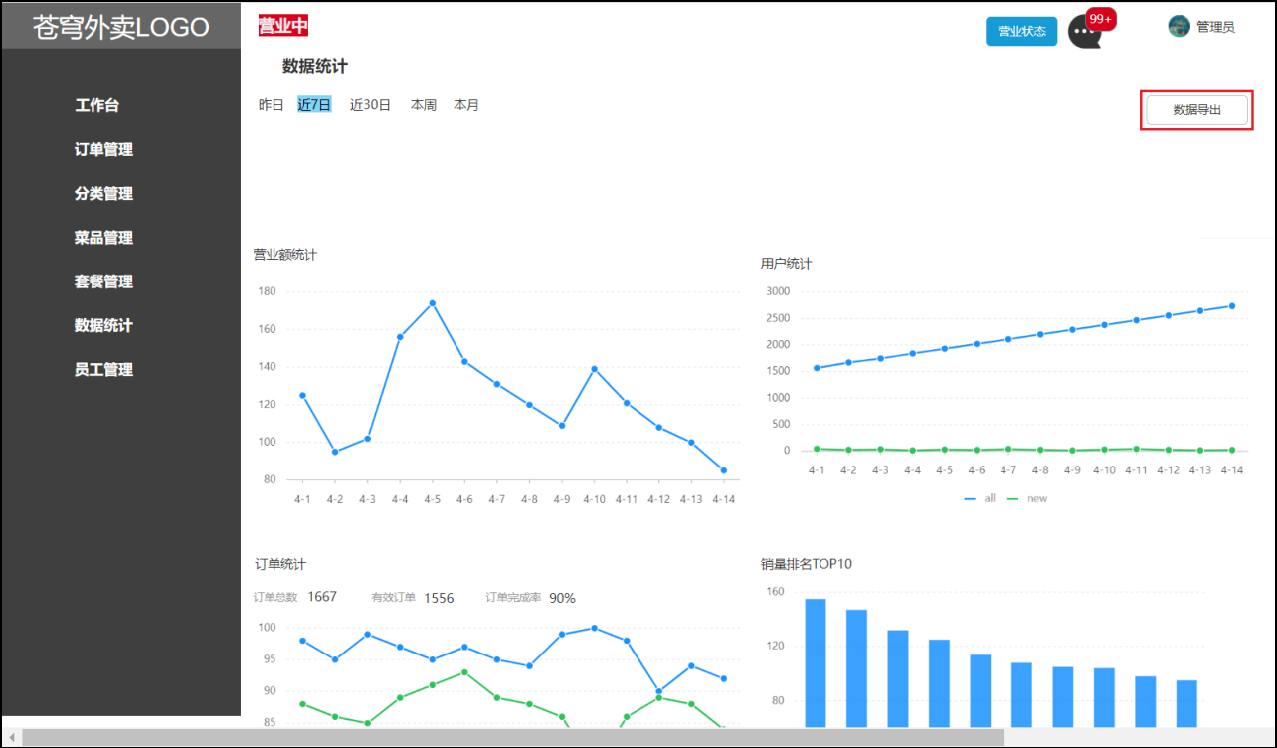
导出的Excel报表格式:

当前接口没有传递参数,因为导出的是最近30天的运营数据,后端计算即可,所以不需要任何参数
当前接口没有返回数据,因为报表导出功能本质上是文件下载,服务端会通过输出流将Excel文件下载到客户端浏览器
实现步骤:1). 设计Excel模板文件 2). 查询近30天的运营数据 3). 将查询到的运营数据写入模板文件 4). 通过输出流将Excel文件下载到客户端浏览器
Controller层
根据接口定义,在ReportController中创建export方法:
/**
* 导出运营数据报表
* @param response
*/
@GetMapping("/export")
@ApiOperation("导出运营数据报表")
public void export(HttpServletResponse response){ //直接在形参里获取到响应对象response
reportService.exportBusinessData(response);
}
Service层实现类
按照excel模版编写代码填充数据

在ReportServiceImpl实现类中实现导出运营数据报表的方法。注意要提前将资料中的运营数据报表模板.xlsx拷贝到项目的resources/template目录中
/**导出近30天的运营数据报表
* @param response
**/
public void exportBusinessData(HttpServletResponse response) { //直接在形参里获取到响应对象response
LocalDate begin = LocalDate.now().minusDays(30);
LocalDate end = LocalDate.now().minusDays(1); //查到截止昨天 不查今天 因为今天的数据可能还在变
//查询概览运营数据,提供给Excel模板文件
BusinessDataVO businessData = workspaceService.getBusinessData(LocalDateTime.of(begin,LocalTime.MIN), LocalDateTime.of(end, LocalTime.MAX));
InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("template/运营数据报表模板.xlsx");
try {
//基于提供好的模板文件创建一个新的Excel表格对象
XSSFWorkbook excel = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//获得Excel文件中的一个Sheet页
XSSFSheet sheet = excel.getSheet("Sheet1");
//填充数据-时间
sheet.getRow(1).getCell(1).setCellValue(begin + "至" + end);//填充数据至第2行第2个单元格
XSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(3);//获得第4行
//获取单元格
row.getCell(2).setCellValue(businessData.getTurnover());//第4行第3格填充营业额
row.getCell(4).setCellValue(businessData.getOrderCompletionRate());//第4行第5格填充订单完成率
row.getCell(6).setCellValue(businessData.getNewUsers());//第4行第7格填充新增用户数
row = sheet.getRow(4);//获得第5行
row.getCell(2).setCellValue(businessData.getValidOrderCount());//第5行第3格填充有效订单数
row.getCell(4).setCellValue(businessData.getUnitPrice());//第5行第5格填充平均客单价
//到此概览数据填充完毕 还剩明细数据没有填
//明细数据每行分别是日期、营业额、有效订单、订单完成率、平均客单价和新增用户数 跟上面的概览数据是一样的
//区别是概览数据是最近三十天的 明细数据是具体到每一天的
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
LocalDate date = begin.plusDays(i);//要获取每一天的数据
//准备明细数据
businessData = workspaceService.getBusinessData(LocalDateTime.of(date,LocalTime.MIN), LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MAX));
row = sheet.getRow(7 + i);
row.getCell(1).setCellValue(date.toString());
row.getCell(2).setCellValue(businessData.getTurnover());
row.getCell(3).setCellValue(businessData.getValidOrderCount());
row.getCell(4).setCellValue(businessData.getOrderCompletionRate());
row.getCell(5).setCellValue(businessData.getUnitPrice());
row.getCell(6).setCellValue(businessData.getNewUsers());
}
//通过输出流将文件下载到客户端浏览器中
ServletOutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
excel.write(out);
//关闭资源
out.flush();
out.close();
excel.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(“template/运营数据报表模板.xlsx”);
这个语句用到了类加载器(getClassLoader())来获取运营数据报表模板.xlsx的输入流,什么原理呢?
在Java的resources文件夹src/main/resources文件夹下的内容会被打包到生成的JAR(或者WAR)文件中,因此这些资源文件会被ClassLoader加载。
在我们的代码中,this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(“template/运营数据报表模板.xlsx”)这句代码的作用是通过类加载器获取运营数据报表模板.xlsx文件的输入流。
这里的getClassLoader()方法是java.lang.Class类的一个方法,用于获取类的ClassLoader。
getResourceAsStream(“template/运营数据报表模板.xlsx”)方法会在类路径下的template文件夹中查找名为运营数据报表模板.xlsx的文件,并返回该文件的输入流对象。
最后,getFile()方法获取该URL的文件表示形式,即文件的路径。
由于运营数据报表模板.xlsx位于resources文件夹的template文件夹下,它会被编译到类路径中。因此,通过类加载器就可以获取到这个文件的输入流。
这种方式通常用于获取类路径下的配置文件、模板文件等资源。
当应用程序打包成可执行的JAR文件时,这种方式仍然适用,因为resources文件夹中的内容会被包含在JAR文件中,ClassLoader可以正确地加载这些资源。更多的参考这篇博客 Java高级: 反射
进入数据统计,点击数据导出,Excel报表下载成功:
完结撒花。