文章目录
- 第08章_面向对象编程(高级)拓展练习
- 01-关键字:static
- 1、银行账户类
- 2、图形类
- 3、数组工具类
- 4、二分查找
- 5、二分查找
- 6、素数
- 7、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 8、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 02-代码块
- 9、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 10、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 11、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 12、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 13、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 14、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 15、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 16、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 17、阅读代码,分析运行结果
- 03-关键字:final
- 18.代码阅读题
- 04-抽象类和抽象方法
- 19、numa、numb、numc输出
- 20、Woman类、Man类等
- 21、Chinese、American等
- 22、几何图形类
- 23、交通工具
- 05-接口
- 24、代码阅读题
- 25、代码阅读题
- 26、代码阅读题
- 27、FightAble接口
- 28、CompareAble接口
- 29、Filter接口
- 30、LiveAble接口
- 31、Runner、Swimming接口
- 32、A、B接口
- 33、Universe接口
- 34、Flyable、Swimming接口
- 35、Predicate接口
- 06-内部类
- 36、代码阅读题
- 37、代码阅读题
- 38、代码阅读题
- 39、继承Object匿名内部类
- 40、CompareAble接口匿名实现类
- 41、Filter接口匿名实现类
- 42、Thread、Runnable的匿名实现类
- 43、Selector、Touchable接口
- 44、Iterable接口实现类
- 07-枚举类
- 45、月份枚举类
- 46、颜色枚举类
- 47、拓展:颜色枚举类
- 48、月份枚举类
- 49、支付枚举类-1
- 50、支付枚举类-2
- 51、设备状态枚举类
- 08-注解
- 52、图形工具类
- 09-包装类
- 53、代码阅读题
- 54、代码阅读题
- 55、Employee、Programmer、Designer、Architect等类
第08章_面向对象编程(高级)拓展练习
01-关键字:static
1、银行账户类
(1)声明一个银行账户类Account
- 成员变量:利率、账号、余额,其中所有账户的利率是相同的,所有成员变量都私有化。
- 提供get/set
- 提供有参构造public Account(String id ,double balance)
- 提供计算年利息方法public double annualInterest(),余额*利率
- 重写toString方法,返回账号和余额、年利息
(2)在测试类的main中,创建账户类的两个对象,账号分别为“11111”和“22222”,余额分别为“1000和2000”元,利率初始值是0.035,调用方法测试。
public class Account {
private static double rate;
private String id;
private double balance;
public Account(String id, double balance) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
}
public static double getRate() {
return rate;
}
public static void setRate(double rate) {
Account.rate = rate;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double annualInterest(){
return balance * rate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
", 年利息 =" + annualInterest() +
'}';
}
}
public class Exercise1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account a1 = new Account("11111",1000);
Account a2 = new Account("22222",2000);
Account.setRate(0.035);
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
2、图形类
(1)声明一个图形父类Shape,包含
- public double area():返回0.0
- public double perimeter():返回0.0
- public String toString():返回“面积:xxx,周长:xxx”
(2)声明一个矩形Rectangle,继承Shape父类
- 属性:长和宽,私有化
- 提供get/set
- 提供无参构造和有参构造
- 重写area()和perimeter方法,
- 重写toString方法,返回“长:xx,宽:xx,面积:xxx,周长:xxx”
(3)声明一个三角形Triangle,继承Shape父类
- 属性:a,b,c分别代表三角形的三边,私有化
- 提供get/set
- 提供有参构造,public Triangle(double a, double b, double c),并验证a,b,c的值是否可以构成三角形,如果可以构成三角形再为a,b,c的属性赋值
- 重写area()和perimeter方法,
- 重写toString方法,返回“边长:xx,xx,xx,面积:xxx,周长:xxx”
(4)声明图形工具类ShapeTools
- 提供静态方法public static int compare(Shape s1, Shape s2)如果s1的面积大于、小于、等于s2的面积,分别返回正整数、符整数和0。
- 提供静态方法public static boolean equals(Shape s1, Shape s2)比较两个图形的面积和周长是否都相等
- 提供静态方法public static void sort(Shape[] arr)可以给所有图形按照面积从小到大排序,如果面积相同的按照周长从小到大排序
- 提供静态方法public static void print(Shape[] arr)可以遍历输出所有图形信息
(5)在测试类中:
- 创建两个矩形r1(2,3),r2(3,6),创建2个三角形t1(3,4,5),t2(6,6,6),
- 调用compare方法比较r1和t1,
- 调用equals方法比较r2和t2,
- 创建Shape数组中,把上面4个对象放到数组中,调用就sort方法排序,在排序前后调用print方法遍历显示信息
public class Shape {
public double area(){
return 0.0;
}
public double perimeter(){
return 0.0;
}
public String toString(){
return "面积:" + area() +",周长:" + perimeter();
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double length;
private double width;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double length, double width) {
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public double area() {
return length * width;
}
@Override
public double perimeter() {
return 2 * (length + width);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "长:" + length +
", 宽" + width +
"," + super.toString();
}
}
public class Triangle extends Shape {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public Triangle() {
}
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) {
if(a>0 && b> 0 && c>0 && a+b>c && b+c>a && a+c>b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(double a) {
this.a = a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(double b) {
this.b = b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(double c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public double area() {
double p = (a+b+c)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p * (p-a) * (p-b) *(p-c));
}
@Override
public double perimeter() {
return a+b+c;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "边长:" + a +
"," + b +
"," + c +
"," + super.toString();
}
}
public class ShapeTools {
public static int compare(Shape s1, Shape s2){
if(s1.area() > s2.area()){
return 1;
}else if(s1.area() < s2.area()){
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
public static boolean equals(Shape s1, Shape s2){
return s1.area() == s2.area() && s1.perimeter() == s2.perimeter();
}
public static void sort(Shape[] arr){
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-i; j++) {
boolean flag = false;
if(arr[j].area()>arr[j+1].area()){
flag = true;
}else if(arr[j].area() == arr[j+1].area()){
if(arr[j].perimeter() > arr[j+1].perimeter()) {
flag = true;
}
}
if(flag){
Shape temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void print(Shape[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
public class Exercise2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle(2,3);
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle(3,6);
Triangle t1 = new Triangle(3,4,5);
Triangle t2 = new Triangle(6,6,6);
int result = ShapeTools.compare(r1,t1);
if(result == 0){
System.out.println("r1和t1的面积相等");
}else if(result>0){
System.out.println("r1的面积大于t1的面积");
}else{
System.out.println("r1的面积小于t1的面积");
}
System.out.println("r2和t2的面积和周长是否都相等?" + ShapeTools.equals(r2,t2));
Shape[] arr = new Shape[4];
arr[0] = r1;
arr[1] = r2;
arr[2] = t1;
arr[3] = t2;
System.out.println("排序前:");
ShapeTools.print(arr);
ShapeTools.sort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:");
ShapeTools.print(arr);
}
}
3、数组工具类
声明一个数组工具类ArrayTools,包含如下方法:
- public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int value):使用二分查找法在arr数组中查找value的下标,如果value不存在,就返回-1,如果数组arr不是有序的,结果将不一定正确。
- public static int[] copyOf(int[] arr,int newLength):实现复制一个newLength长的数组,如果newLength<=arr.length,则新数组复制arr数组的[0, newLength-1]的元素,如果newLength>arr.length,则新数组前面[0, arr.length-1]的元素从arr数组复制,后面的元素保持默认值。
- public static void sort(int[] arr):可以给arr数组从小到大排序,用冒泡排序实现。
- public static String toString(int[] arr):将元素拼接为"{元素1,元素2,…}"的字符串返回。
在测试类的main方法中
- 随机产生10个[0,100)的元素然后遍历显示
- 从小到大排序后显示
- 从键盘输入一个整数,查找它是否在排序后的数组中,如果存在就显示下标,如果不存在就提示不存在
- 复制3个数组,新数组的长度分别为5,10,15,并遍历显示新数组
public class ArrayTools {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int value){
for(int left=0,right=arr.length-1; left<=right;){
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(value == arr[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(value < arr[mid]){
right = mid -1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static int[] copyOf(int[] arr, int newLength){
int[] newArr = new int[newLength];
for (int i = 0; i < newArr.length && i < arr.length; i++) {
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
return newArr;
}
public static void sort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-i; j++) {
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static String toString(int[] arr){
String result = "[";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i==0){
result += arr[i];
}else{
result += "," + arr[i];
}
}
result +="]";
return result;
}
}
public class Exercise3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
System.out.println(ArrayTools.toString(arr));
ArrayTools.sort(arr);
System.out.println(ArrayTools.toString(arr));
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个[0,100)范围的整数:");
int num = input.nextInt();
input.close();
int index = ArrayTools.binarySearch(arr, num);
if(index==-1){
System.out.println(num +"在arr中不存在");
}else{
System.out.println(num +"在arr的下标是:" + index);
}
int[] fiveElements = ArrayTools.copyOf(arr, 5);
System.out.println(ArrayTools.toString(fiveElements));
int[] tenElements = ArrayTools.copyOf(arr, 10);
System.out.println(ArrayTools.toString(tenElements));
int[] fifteenElements = ArrayTools.copyOf(arr, 15);
System.out.println(ArrayTools.toString(fifteenElements));
}
}
4、二分查找

public class Exercise4 {
public static int binarySearch(int[] intsArray, int des) {
int left = 0;
int right = intsArray.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (intsArray[mid] == des) {
return mid;
} else if (des > intsArray[mid]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
5、二分查找

public class Exercise5 {
public static int binarySearch(String[] intsArray, String des) {
int left = 0;
int right = intsArray.length-1;
while(left<=right) {
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
if(intsArray[mid].equals(des)) {
return mid;
}else if(des.compareTo(intsArray[mid])>0){//字符串比较大小的方法
left = mid+1;
}else {
right=mid-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
6、素数

public class Exercise6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(suShu(10)));
}
public static int[] suShu(int n){
int[] arr = new int[n];
int index=0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++) {
if(i%j==0) {
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
arr[index++] = i;
}
}
return Arrays.copyOf(arr, index);
}
}
7、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class Exercise7 {
static int x, y, z;
static {
int x = 5;
x--;
}
static {
x--;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("x=" + x);
z--;
method();
System.out.println("result:" + (z + y + ++z));
}
public static void method() {
y = z++ + ++z;
}
}
8、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class Exercise8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new SDText().x+","+new SDText().y+","+new SDText().x);
}
}
class SDText{
static SDText sd=new SDText();
static int x=3;
static int y;
public SDText(){
x++;
y++;
}
}
02-代码块
9、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class T {
public static int k = 0;
public static T t1 = new T("t1");
public static T t2 = new T("t2");
public static int i = print("i");
public static int n = 99;
public int j = print("j");
{
print("构造块");
}
static{
print("静态块");
}
public T(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++n;
++i;
}
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n);
++n;
return ++i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
/*
* 对于T来说,就完成类初始化
*
* 创建对象,调用类的实例初始化<init>()或<init>(String str)
*
* (1)静态变量的显式赋值
* k = 0;
t1 = new T("t1");
<init>(String str)
①j = print("j");
print方法代码如下:
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 1:j i=0 n=0
++n; n=1 k=1
return ++i; i=1
}
② {
print("构造块");
print方法代码如下:
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 2:构造块 i=1 n=1
++n; n=2 k=2
return ++i; i=2
}
}
③public T(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 3:t1 i=2 n=2
++n; n=3 k=3
++i; i=3
}
* t2 = new T("t2");
<init>(String str)
①j = print("j");
print方法代码如下:
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 4:j i=3 n=3
++n; n=4 k=4
return ++i; i=4
}
② {
print("构造块");
print方法代码如下:
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 5:构造块 i=4 n=4
++n; n=5 k=5
return ++i; i=5
}
}
③public T(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 6:t2 i=5 n=5
++n; n=6 k=6
++i; i=6
}
i = print("i");
print方法代码如下:
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 7:i i=6 n=6
++n; n=7 k=7
return ++i; i=7
}
n = 99;
* (2)静态代码块
* static{
print("静态块");
print方法代码如下:
public static int print(String str){
System.out.println((++k) + ":" + str + " i=" + i + " n=" + n); 8:静态块 i=7 n=99
++n; n=100 k=8
return ++i; i=8
}
}
*/
10、阅读代码,分析运行结果
考核点:类初始化,局部变量与类变量,自增自减
public class Exercise10 {
static int x, y, z;
static {
int x = 5;
x--;
}
static {
x--;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("x=" + x);
z--;
method();
System.out.println("result:" + (z + y + ++z));
}
public static void method() {
y = z++ + ++z;
}
}
11、阅读代码,分析运行结果
考核点:类初始化与实例初始化
class HelloA{
public HelloA(){
System.out.println("HelloA");
}
{
System.out.println("I'm A Class");
}
static{
System.out.println("static A");
}
}
public class HelloB extends HelloA{
public HelloB(){
System.out.println("HelloB");
}
{
System.out.println("I'm B Class");
}
static{
System.out.println("static B");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloB();
}
}
12、阅读代码,分析运行结果
知识点:实例初始化
class HelloA{
public HelloA(){
System.out.println("HelloA");
}
{
System.out.println("I'm A Class");
}
}
class HelloB extends HelloA{
public HelloB(){
System.out.println("HelloB");
}
{
System.out.println("I'm B Class");
}
}
public class Exercise12{
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloB();
}
}
/*
* 创建对象是通过执行实例初始化方法来完成的。
* 如果new后面跟无参构造,就说明调用无参的实例初始化方法<init>(),
* 如果new后面跟有参构造,就说明调用有参的实例初始化方法<init>(形参列表)。
* 编译器编译后类中没有构造器,而是编译为一个个的实例初始化方法。
* 实例初始化由:
* (1)非静态成员变量的显式赋值代码
* (2)非静态代码块代码
* (3)构造器代码
* 其中(1)(2)按编写顺序,(3)在最后
* 在子类实例初始化首行会有super()或super(实参列表)表示调用父类的实例初始化方法,
* 如果没写super()或super(实参列表),那么默认就是super(),因此:
* (1)先执行父类实例初始化
* <init>(){
* System.out.println("I'm A Class");
* System.out.println("HelloA");
* }
* (2)再执行子类实例初始化
* <init>(){
* System.out.println("I'm B Class");
* System.out.println("HelloB");
* }
*/
13、阅读代码,分析运行结果
知识点:实例初始化
public class Exercise13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sub s = new Sub();
}
}
class Base{
Base(){
method(100);
}
{
System.out.println("base");
}
public void method(int i){
System.out.println("base : " + i);
}
}
class Sub extends Base{
Sub(){
super.method(70);
}
{
System.out.println("sub");
}
public void method(int j){
System.out.println("sub : " + j);
}
}
/*
* 创建对象是通过执行实例初始化方法来完成的。
* 如果new后面跟无参构造,就说明调用无参的实例初始化方法<init>(),
* 如果new后面跟有参构造,就说明调用有参的实例初始化方法<init>(形参列表)。
* 编译器编译后类中没有构造器,而是编译为一个个的实例初始化方法。
* 实例初始化由:
* (1)非静态成员变量的显式赋值代码
* (2)非静态代码块代码
* (3)构造器代码
* 其中(1)(2)按编写顺序,(3)在最后
* 在子类实例初始化首行会有super()或super(实参列表)表示调用父类的实例初始化方法,
* 如果没写super()或super(实参列表),那么默认就是super(),因此:
* 1、执行父类的实例初始化方法
* <ini>(){
* System.out.println("base");
* method(100); //因为此时在创建子类的对象过程中,所以这个method(100)方法是
* 子类对象再调用,那么又因为子类重写了method(int)方法,
* 所以执行子类的method(int)
* 即System.out.println("sub : " + j);
* }
*
* 2、执行子类的实例初始化方法
* <init>(){
* System.out.println("sub");
* super.method(70);//因为这里用super.,那么一定是调用父类的method(int)
* 即System.out.println("base : " + i);
* }
*/
14、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class Exercise14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
}
}
class Father{
static{
System.out.println("(1)父类的静态代码块");
}
{
System.out.println("(2)父类的非静态代码块");
}
Father(){
System.out.println("(3)父类的无参构造");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
static{
System.out.println("(4)子类的静态代码块");
}
{
System.out.println("(5)子类的非静态代码块");
}
Son(){
System.out.println("(6)子类的无参构造");
}
}
/*
* (1)Father类的类初始化
* ①类变量显式赋值:这里没有
* ②静态代码块
* System.out.println("(1)父类的静态代码块");
* (2)Son类的类初始化
* ①类变量显式赋值:这里没有
* ②静态代码块
* System.out.println("(4)子类的静态代码块");
*
* (3)执行Father类的是实参初始化方法<init>()
* ①非静态成员变量的显式赋值:这里没有
* ②非静态代码块:
* System.out.println("(2)父类的非静态代码块");
* ③父类的无参构造
* System.out.println("(3)父类的无参构造");
*
* (4)执行Son类的实例初始化方法<init>()
* ①非静态成员变量的显式赋值:这里没有
* ②非静态代码块:
* System.out.println("(5)子类的非静态代码块");
* ③子类的无参构造
* System.out.println("(6)子类的无参构造");
*/
15、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class Exercise15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Zi zi = new Zi();
}
}
class Fu{
private static int i = getNum("(1)i");
private int j = getNum("(2)j");
static{
print("(3)父类静态代码块");
}
{
print("(4)父类非静态代码块,又称为构造代码块");
}
Fu(){
print("(5)父类构造器");
}
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + i);
}
public static int getNum(String str){
print(str);
return ++i;
}
}
class Zi extends Fu{
private static int k = getNum("(6)k");
private int h = getNum("(7)h");
static{
print("(8)子类静态代码块");
}
{
print("(9)子类非静态代码块,又称为构造代码块");
}
Zi(){
print("(10)子类构造器");
}
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + k);
}
public static int getNum(String str){
print(str);
return ++k;
}
}
/*
* (1)Fu类的类初始化
* ①类变量显式赋值:
* i = getNum("(1)i");
* public static int getNum(String str){
print(str);
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + i); (1)i -> 0(默认值)
}
return ++i; i=1
}
* ②静态代码块
* static{
print("(3)父类静态代码块");
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + i); (3)父类静态代码块 -> 1
}
}
* (2)Zi类的类初始化
* ①类变量显式赋值:
* k = getNum("(6)k");
*
public static int getNum(String str){
print(str);
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + k); (6)k -> 0(默认值)
}
return ++k; k=1
}
* ②静态代码块
* static{
print("(8)子类静态代码块");
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + k); (8)子类静态代码块 -> 1
}
}
*
* (3)执行Fu类的是实参初始化方法<init>()
* ①非静态成员变量的显式赋值:
* j = getNum("(2)j");
*
public static int getNum(String str){
print(str);
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + i); (2)j -> 1
}
return ++i; i=2
}
* ②非静态代码块:
* {
print("(4)父类非静态代码块,又称为构造代码块");
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + i); (4)父类非静态代码块,又称为构造代码块 -> 2
}
}
* ③父类的无参构造
* Fu(){
print("(5)父类构造器");
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + i); (5)父类构造器 -> 2
}
}
*
* (4)执行Zi类的实例初始化方法<init>()
* ①非静态成员变量的显式赋值:
* h = getNum("(7)h");
public static int getNum(String str){
print(str);
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + k); (7)h ->1
}
return ++k; k=2
}
*
* ②非静态代码块:
* {
print("(9)子类非静态代码块,又称为构造代码块");
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + k); (9)子类非静态代码块,又称为构造代码块 ->2
}
}
* ③子类的无参构造
* Zi(){
print("(10)子类构造器");
print方法代码如下:
public static void print(String str){
System.out.println(str + "->" + k); (10)子类构造器 ->2
}
}
*/
16、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class Exercise16{
public static void main(String[] args){
Son s1 = new Son();//找到就是Son类的<init>()
}
}
class Father{
private int a = getNumber();
{
System.out.println("Father非静态代码块 a = " + a);
}
Father(){
System.out.println("Father()无参构造");
}
public int getNumber(){
System.out.println("Father:getNumber()");
return 1;
}
}
class Son extends Father{
{
System.out.println("Son非静态代码");
}
public Son(){
System.out.println("Son():无参构造");
}
public int getNumber(){
System.out.println("Son:getNumber()");
return 2;
}
}
/*
class Father{
private int a;
<init>(){
//super();//这里可以忽略它,因为Father类的父类是Object,它没有输出语句,不用管它
a = getNumber();
System.out.println("Father非静态代码块 a = " + a);
System.out.println("Father()无参构造");
}
public int getNumber(){
System.out.println("Father:getNumber()");
return 1;
}
}
class Son extends Father{
<init>(){
super();//它代表Father类<init>()
System.out.println("Son非静态代码");
System.out.println("Son():无参构造");
}
public int getNumber(){
System.out.println("Son:getNumber()");
return 2;
}
}
代码最终执行:
a = getNumber(); //因为我们现在在newSon类的对象,所以对象的运行时是Son类,
//而getNumber是虚方法,所以要看子类重写后的getNumber
System.out.println("Son:getNumber()");
return 2;
System.out.println("Father非静态代码块 a = " + a);
System.out.println("Father()无参构造");
System.out.println("Son非静态代码");
System.out.println("Son():无参构造");
*/
17、阅读代码,分析运行结果
public class Exercise17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sub s = new Sub();
}
}
class Base{
Base(){
this.method(100);
}
{
System.out.println("base");
}
public void method(int i){
System.out.println("base : " + i);
}
}
class Sub extends Base{
Sub(){
super.method(70);
}
{
System.out.println("sub");
}
public void method(int j){//是重写,虽然参数名不一样,但是参数的类型和个数一样,方法名也一样是重写
System.out.println("sub : " + j);
}
}
/*
先对类进行组装分析:
class Base{
<init>() {
//super(); 本题中可以忽略
System.out.println("base");
this.method(100);
}
public void method(int i){
System.out.println("base : " + i);
}
}
class Sub extends Base{
<init>(){
super();//这句话,要时刻记得它
System.out.println("sub");
super.method(70);
}
public void method(int j){
System.out.println("sub : " + j);
}
}
执行的代码是:
System.out.println("base");
this.method(100);//method是虚方法,我们现在在newSub类对象,所以执行重写的method
System.out.println("sub : " + j);
System.out.println("sub");
super.method(70); //method虽然是虚方法,但是这里有明确说执行父类被重写的method,因为前面有super.
System.out.println("base : " + i);
*/
03-关键字:final
18.代码阅读题
public class Exercise18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Other o = new Other();
new TestOther().addOne(o);
/*
(1)new TestOther():匿名对象,作用是为了调用addOne方法。
(2)上面的实参o,把Other对象的地址值,传给了下面的addOne方法的形参o
(3)下面的addOne方法的形参o,前面有一个final修饰,
这个final在这里的意思是,形参o不能够指向新的对象,
这就意味着,形参和实参此时一定是指向同一个对象。
(4)如果形参和实参指向同一个对象,那么形参对象属性值的修改,其实就是实参对象属性值的修改
*/
System.out.println(o.i);//1
}
public void addOne(final Other o){
// o = new Other();//错误,o不能重新赋值
o.i++;
}
}
class Other{
public int i; //如果i前面有final,才是表示i的值不能被修改
}
04-抽象类和抽象方法
19、numa、numb、numc输出
编写代码,效果如图所示:
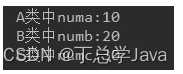
编写步骤:
- 定义抽象类A,抽象类B继承A,普通类C继承B
- A类中,定义成员变量numa,赋值为10,抽象showA方法。
- B类中,定义成员变量numb,赋值为20,抽象showB方法。
- C类中,定义成员变量numc,赋值为30,重写showA方法,打印numa,重写showB方法,打印numb,定义showC方法,打印numc。
- 测试类Exercise19中,创建C对象,调用showA方法,showB方法,showC方法。
public class Exercise19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
C c = new C();
c.showA();
c.showB();
c.showC();
}
}
abstract class A{
protected int numa = 10;
public abstract void showA();
}
abstract class B extends A{
protected int numb = 20;
public abstract void showB();
}
class C extends B{
private int numc = 30;
@Override
public void showB() {
System.out.println("B类中numb:" + numb);
}
@Override
public void showA() {
System.out.println("A类中numa:" + numa);
}
public void showC(){
System.out.println("C类中numc:" + numc);
}
}
20、Woman类、Man类等
案例:
1、声明抽象父类Person,包含抽象方法public abstract void coiffure();
2、声明子类Woman,重写抽象方法,打印留短发
3、声明子类Man,重写抽象方法,打印留长发
4、声明测试类Exercise20,创建Person数组,存放Woman和Man对象,并遍历数组,调用coiffure()方法
public abstract class Person {
public abstract void coiffure();
}
public class Man extends Person{
@Override
public void coiffure() {
System.out.println("男人留短发");
}
}
public class Woman extends Person{
@Override
public void coiffure() {
System.out.println("女人留长发");
}
}
public class Exercise20 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] all = new Person[2];
all[0] = new Woman();
all[1] = new Man();
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
all[i].coiffure();
}
}
}
21、Chinese、American等
案例:
1、声明抽象父类Person,包含抽象方法public abstract void eat();
2、声明子类中国人Chinese,重写抽象方法,打印用筷子吃饭
3、声明子类美国人American,重写抽象方法,打印用刀叉吃饭
4、声明子类印度人Indian,重写抽象方法,打印用手抓饭
5、声明测试类Test11,创建Person数组,存储各国人对象,并遍历数组,调用eat()方法
public class Exercise21 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] all = new Person[3];
all[0] = new Chinese();
all[1] = new American();
all[2] = new Indian();
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
all[i].eat();
}
}
}
abstract class Person{
public abstract void eat();
}
class Chinese extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("中国人用筷子吃饭");
}
}
class American extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("美国人用刀叉吃饭");
}
}
class Indian extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("印度人用手抓饭");
}
}
22、几何图形类
(1)声明一个抽象图形父类Shape,包含
- public abstract double area()
- public abstract double perimeter()
- public String toString():返回“面积:xxx,周长:xxx”
(2)声明一个矩形Rectangle,继承Shape父类
- 属性:长和宽,私有化
- 提供get/set
- 提供无参构造和有参构造
- 重写area()和perimeter方法,
- 重写toString方法,返回“长:xx,宽:xx,面积:xxx,周长:xxx”
(3)声明一个三角形Triangle,继承Shape父类
- 属性:a,b,c分别代表三角形的三边,私有化
- 提供get/set
- 提供有参构造,public Triangle(double a, double b, double c),并验证a,b,c的值是否可以构成三角形,如果可以构成三角形再为a,b,c的属性赋值
- 重写area()和perimeter方法,
- 重写toString方法,返回“边长:xx,xx,xx,面积:xxx,周长:xxx”
(4)在测试类中:
- 创建两个矩形(2,3)、(3,6),创建2个三角形(3,4,5)、(6,6,6)
- 创建Shape数组中,把上面4个对象放到数组中,遍历显示信息
public abstract class Shape {
public abstract double area();
public abstract double perimeter();
public String toString(){
return "面积:" + area() +",周长:" + perimeter();
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double length;
private double width;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double length, double width) {
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public double area() {
return length * width;
}
@Override
public double perimeter() {
return 2 * (length + width);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "长:" + length +
", 宽" + width +
"," + super.toString();
}
}
public class Triangle extends Shape {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public Triangle() {
}
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) {
if(a>0 && b> 0 && c>0 && a+b>c && b+c>a && a+c>b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(double a) {
this.a = a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(double b) {
this.b = b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(double c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public double area() {
double p = (a+b+c)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p * (p-a) * (p-b) *(p-c));
}
@Override
public double perimeter() {
return a+b+c;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "边长:" + a +
"," + b +
"," + c +
"," + super.toString();
}
}
public class Exercise22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape[] arr = new Shape[4];
arr[0] = new Rectangle(2,3);
arr[1] = new Rectangle(3,6);
arr[2] = new Triangle(3,4,5);
arr[3] = new Triangle(6,6,6);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
23、交通工具
(1)声明抽象类Vehicle交通工具
- 包含私有的int类型的属性wheels,代表轮子的数量
- 包含有参构造Vehicle(int wheels)
- 包含抽象方法public abstract void drive()
- 重写toString():返回轮子的数量
(2)声明子类Monocycle单轮车
- 重写抽象方法drive,输出“脚踏独轮车,摇摇摆摆往前走”
(3)声明子类Bicycle自行车
- 重写抽象方法drive,输出“脚踏双轮自行车,优哉游哉往前走”
(4)声明子类Tricycle三轮车
- 重写抽象方法drive,输出“脚踏三轮车,稳稳当当往前走“
(5)测试类
- 创建几个交通工具的对象,打印对象并调用drive方法
/*
(1)声明抽象类Vehicle交通工具
- 包含int类型的wheels代表轮子的数量
- 包含有参构造Vehicle(int wheels)
- 包含抽象方法public abstract void drive()
*/
public abstract class Vehicle {
private int wheels;
public Vehicle(int wheels) {
this.wheels = wheels;
}
public int getWheels() {
return wheels;
}
public void setWheels(int wheels) {
this.wheels = wheels;
}
public abstract void drive();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Vehicle{" +
"wheels=" + wheels +
'}';
}
}
public class Monocycle extends Vehicle {
public Monocycle(int wheels) {
super(wheels);
}
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("脚踏独轮车,摇摇摆摆往前走");
}
}
public class Bicycle extends Vehicle {
public Bicycle(int wheels) {
super(wheels);
}
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("脚踏双轮自行车,优哉游哉往前走");
}
}
public class Tricycle extends Vehicle {
public Tricycle(int wheels) {
super(wheels);
}
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("脚踏三轮车,稳稳当当往前走");
}
}
public class Exercise23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle[] arr = new Vehicle[3];
arr[0] = new Monocycle(1);
arr[1] = new Bicycle(2);
arr[2] = new Tricycle(3);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
arr[i].drive();
}
}
}
05-接口
24、代码阅读题
interface A{
int x = 0;
}
class B{
int x = 1;
}
class C extends B implements A{
public void printX(){
System.out.println(x);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().printX();
}
}
//编译不通过,因为在C类中x有歧义。
interface A{
int x = 0;
}
class B{
int x = 1;
}
class C extends B implements A{
public void printX(){
// System.out.println(x);//有歧义,要么写super.x,要么下A.x
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().printX();
}
}
25、代码阅读题
interface A {
int x = 0;
}
class B {
int x = 1;
}
class C extends B implements A {
public void pX() {
System.out.println(x);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().pX();
}
}
26、代码阅读题
interface Playable {
void play();
}
interface Bounceable {
void play();
}
interface Rollable extends Playable, Bounceable {
Ball ball = new Ball("PingPang");
}
class Ball implements Rollable {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Ball(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void play() {
ball = new Ball("Football");
System.out.println(ball.getName());
}
}
27、FightAble接口
- 模拟玩家选择角色。
- 定义接口FightAble:
- 抽象方法:specialFight。
- 默认方法:commonFight,方法中打印"普通打击"。
- 定义战士类:
- 实现FightAble接口,重写方法中打印"武器攻击"。
- 定义法师类Mage:
- 实现FightAble接口,重写方法中打印"法术攻击"。
- 定义玩家类Player:
- 静态方法:FightAble select(String str),根据指令选择角色。
- 法力角色,选择法师。
- 武力角色,选择战士。
- 静态方法:FightAble select(String str),根据指令选择角色。
- 代码实现,效果如图所示:

public class Exercise27 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("选择:");
String role1 = input.next();
FightAble f1 = Player.select(role1);
f1.specialFight();
f1.commonFight();
System.out.println("====================");
System.out.print("选择:");
String role2 = input.next();
FightAble f2 = Player.select(role2);
f2.specialFight();
f2.commonFight();
input.close();
}
}
interface FightAble{
void specialFight();
default void commonFight(){
System.out.println("普通攻击");
}
}
class Soldier implements FightAble{
@Override
public void specialFight() {
System.out.println("武器攻击");
}
}
class Mage implements FightAble{
@Override
public void specialFight() {
System.out.println("法术攻击");
}
}
class Player{
public static FightAble select(String str){
if("法力角色".equals(str)){
return new Mage();
}else if("武力角色".equals(str)){
return new Soldier();
}
return null;
}
}
28、CompareAble接口
- 模拟工人挑苹果。
- 定义苹果类:
- 属性:大小,颜色。
- 提供基本的构造方法和get方法,set方法
- 定义接口CompareAble:
- 定义默认方法compare,挑选较大苹果。
- 定义接口实现类CompareBig。
- 定义接口实现类CompareColor。挑选红色苹果。
- 定义工人类:
- 成员方法:挑选苹果public void pickApple(CompareAble c,Apple a1,Apple a2)。
- 测试类:
- 创建Worker对象。
- 创建两个Apple对象,一个Apple(5,“青色”),一个Apple(3,“红色”)
- 代码实现,效果如图所示:

public class Exercise28 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker w = new Worker();
Apple a1 = new Apple(5, "青色");
Apple a2 = new Apple(3, "红色");
w.pickApple(new CompareBig(), a1, a2);
w.pickApple(new CompareColor(), a1, a2);
}
}
class Apple{
private double size;
private String color;
public Apple(double size, String color) {
super();
this.size = size;
this.color = color;
}
public Apple() {
super();
}
public double getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(double size) {
this.size = size;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return size + "-" + color;
}
}
interface CompareAble{
default void compare(Apple a1,Apple a2){
System.out.println("默认挑大的:");
if(a1.getSize() > a2.getSize()){
System.out.println(a1);
}else{
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
}
class CompareBig implements CompareAble{
}
class CompareColor implements CompareAble{
@Override
public void compare(Apple a1, Apple a2) {
System.out.println("挑红的:");
if("红色".equals(a1.getColor())){
System.out.println(a1);
}
if("红色".equals(a2.getColor())){
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
}
class Worker{
public void pickApple(CompareAble c,Apple a1,Apple a2){
c.compare(a1, a2);
}
}
29、Filter接口
- 模拟接待员接待用户,根据用户id,给用户分组。
- 定义用户类:
- 属性:用户类型,用户id
- 提供基本的构造方法和get方法,set方法
- 定义接口Filter:
- 提供抽象方法filterUser(User u)
- 定义实现类V1Filter,实现抽象方法,将用户设置为v1
- 定义实现类V2Filter,实现抽象方法,将用户设置为v2
- 定义实现类AFilter,实现抽象方法,将用户设置为A
- 定义接待员类Receptionist:
- 属性:接口Filter
- 提供基本的构造方法和get方法,set方法
- 成员方法:接待用户方法,设置用户类型。
- 测试类:
- 初始化15个User对象,id为1-15。
- 创建三个接待员对象。
- 第一个接待员,设置接待规则,将1-5号用户类型设置为v1。
- 第二个接待员,设置接待规则,将6-10号用户类型设置为v2。
- 第三个接待员,设置接待规则,将11-15号用户类型设置为A。
- 遍历数组,给用户分区。
- 代码实现,效果如图所示:

class Exercise29 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User[] all = new User[15];
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
all[i] = new User(null,i+1);
}
V1Filter v1F = new V1Filter();
V2Filter v2F = new V2Filter();
AFilter aF = new AFilter();
Receptionist r1 = new Receptionist(v1F);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
r1.recept(all[i]);
}
Receptionist r2 = new Receptionist(v2F);
for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
r2.recept(all[i]);
}
Receptionist r3 = new Receptionist(aF);
for (int i = 10; i < 15; i++) {
r3.recept(all[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
System.out.println(all[i]);
}
}
}
class User{
private String type;
private int id;
public User(String type, int id) {
super();
this.type = type;
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + "-" + type;
}
}
interface Filter{
void filterUser(User u);
}
class V1Filter implements Filter{
@Override
public void filterUser(User u) {
u.setType("v1");
}
}
class V2Filter implements Filter{
@Override
public void filterUser(User u) {
u.setType("v2");
}
}
class AFilter implements Filter{
@Override
public void filterUser(User u) {
u.setType("A");
}
}
class Receptionist{
private Filter filter;
public Receptionist(Filter filter) {
super();
this.filter = filter;
}
public Filter getFilter() {
return filter;
}
public void setFilter(Filter filter) {
this.filter = filter;
}
public void recept(User u){
if(u.getType() != null){
return ;
}
filter.filterUser(u);
}
}
30、LiveAble接口
1、声明一个LiveAble接口
- 包含两个抽象方法:
- void eat();
- void breathe();
- 包含默认方法 default void sleep(),实现为打印“静止不动”
- 包含静态方法 static void drink(),实现为“喝水”
2、声明动物Animal类,实现LiveAble接口。
- void eat();实现为“吃东西”,
- void breathe();实现为"吸入氧气呼出二氧化碳"
- void sleep()重写为”躺下闭上眼睛睡觉"
3、声明植物Plant类,实现LiveAble接口。
- void eat();实现为“吸收营养”
- void breathe();实现为"吸入二氧化碳呼出氧气"
4、在测试类中,分别创建两个实现类的对象,调用对应的方法。通过接口名调用静态方法
public interface LiveAble {
// 定义抽象方法
void eat();
void breathe();
//定义默认方法
default void sleep(){
System.out.println("静止不动");
}
//定义静态方法
static void drink(){
System.out.println("喝水");
}
}
public class Animal implements LiveAble {
//重写/实现接口的抽象方法
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃东西");
}
//重写/实现接口的抽象方法
@Override
public void breathe(){
System.out.println("吸入氧气呼出二氧化碳");
}
//重写接口的默认方法
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("躺下闭上眼睛睡觉");
}
}
public class Plant implements LiveAble {
//重写/实现接口的抽象方法
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吸收营养");
}
//重写/实现接口的抽象方法
@Override
public void breathe(){
System.out.println("吸入二氧化碳呼出氧气");
}
}
public class Exercise30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建实现类(子类)对象
Animal a = new Animal();
// 调用实现后的方法
a.eat();
a.sleep();
a.breathe();
//创建实现类(子类)对象
Plant p = new Plant();
p.eat();
p.sleep();
p.breathe();
//通过接口调用静态方法
LiveAble.drink();
}
}
31、Runner、Swimming接口
(1)声明第一个接口Runner,包含抽象方法:void run()
(2)声明第二个接口Swimming,包含抽象方法:void swim()
(3)声明兔子类,实现Runner接口,
- 重写run(),实现为“兔子跑的快”
(4)声明乌龟类
-
实现Runner接口,重写run(),实现为“乌龟跑的快”
-
实现Swimming接口,重写swim()方法,实现为“乌龟游的快”
(5)测试类中创建兔子和乌龟类的对象,并调用相应方法
public interface Runner{
void run();
}
public interface Swimming {
void swim();
}
public class Rabbit implements Runner {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("兔子跑得快");
}
}
public class Tortoise implements Runner,Swimming{
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("乌龟游得快");
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("乌龟跑的慢");
}
}
public class Exercise31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rabbit r = new Rabbit();
r.run();
Tortoise t = new Tortoise();
t.run();
t.swim();
}
}
32、A、B接口
- 编写代码,效果如图所示:

- 编写步骤:
- 定义接口A,普通类B实现接口A
- A接口中,定义抽象方法showA。
- A接口中,定义默认方法showB。
- B类中,重写showA方法
- 测试类中,创建B类对象,调用showA方法,showB方法。
public class Exercise32 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
b.showA();
b.showB();
}
}
interface A{
void showA();
default void showB(){
System.out.println("BBB");
}
}
class B implements A{
@Override
public void showA() {
System.out.println("AAA");
}
}
33、Universe接口
- 编写代码,效果如图所示:

- 编写步骤
-
定义接口Universe,提供抽象方法doAnything。
-
定义普通类Star,提供成员发光shine方法,打印“star:星星一闪一闪亮晶晶"
-
定义普通类Sun,
继承Star类,重写shine方法,打印"sun:光照八分钟,到达地球"
实现Universe接口,实现doAnything,打印"sun:太阳吸引着9大行星旋转"
-
测试类中,创建Star对象,调用shine方法
-
测试类中,多态的方式创建Sun对象,调用doAnything方法,向下转型,调用shine方法。
public class Exercise33 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Star s = new Star();
s.shine();
System.out.println("======================");
Universe u = new Sun();
u.doAnything();
Star sun = (Star) u;
sun.shine();
}
}
interface Universe{
void doAnything();
}
class Star{
public void shine(){
System.out.println("star:星星一闪一闪亮晶晶");
}
}
class Sun extends Star implements Universe{
@Override
public void shine(){
System.out.println("sun:光照8分钟到达地球");
}
@Override
public void doAnything() {
System.out.println("sun:太阳吸引着9大行星旋转");
}
}
34、Flyable、Swimming接口
(1)声明Flyable接口
- 包含抽象方法void fly()方法
(2)声明Swimming接口
- 包含抽象方法void swim()方法
(3)声明类Bird
- 声明抽象方法:public abstract void eat()
(4)声明子类Penguin企鹅
- 继承Bird类,重写eat方法,输出"企鹅吃南极磷虾"
- 实现Swimming接口,重写swim()方法,输出“企鹅下海捉虾”
(5)声明子类Swan天鹅
- 继承Bird类,重写eat方法,输出“天鹅吃水生植物的根茎和种子、水生昆虫、螺类和小鱼”
- 实现Flyable接口,重写fly方法,输出“天鹅展翅高飞,天南海北任我游”
- 实现Swimming接口,重写swim()方法,输出“天鹅把羽毛洗的锃亮,顺便捉条鱼”
(6)声明子类Chicken鸡
- 继承Bird类,重写eat方法,输出“鸡吃谷子”
- 实现Flyable接口,重写fly方法,输出“鸡上房揭瓦,满院子乱扑腾"
(7)测试类
- 创建Bird数组,并且把Penguin企鹅、Swan天鹅、Chicken鸡的对象放到Bird数组中,遍历数组
- 调用各个元素的eat方法
- 如果会飞的调用fly方法(提示:可以使用instanceof判断)
- 如果会游的调用swim方法
public interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
public interface Swimming {
void swim();
}
public abstract class Bird {
public abstract void eat();
}
public class Penguin extends Bird implements Swimming {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("企鹅吃南极磷虾");
}
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("企鹅下海捉虾");
}
}
public class Swan extends Bird implements Flyable,Swimming {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("天鹅吃水生植物的根茎和种子、水生昆虫、螺类和小鱼");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("天鹅展翅高飞,天南海北任我游");
}
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("天鹅把羽毛洗的锃亮,顺便捉条鱼");
}
}
public class Chicken extends Bird implements Flyable{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("鸡吃谷子");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("鸡上房揭瓦,满院子乱扑腾");
}
}
public class Exercise34 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bird[] birds = new Bird[3];
birds[0] = new Penguin();
birds[1] = new Swan();
birds[2] = new Chicken();
for (int i = 0; i < birds.length; i++) {
birds[i].eat();
if(birds[i] instanceof Flyable){
Flyable f = (Flyable) birds[i];
f.fly();
}
if(birds[i] instanceof Swimming){
Swimming s = (Swimming)birds[i];
s.swim();
}
}
}
}
35、Predicate接口
(1)已知在java.util.function包下有一个Predicate接口(这个接口不用写)
- 包含抽象方法:boolean test(Object obj);
(2)声明一个数组工具类ArrayTools,包含
- 静态方法:public static void print(Object[] arr):使用for循环遍历输出数组元素
(3)声明一个员工类Emloyee
- 包含属性编号、姓名、年龄、薪资,私有化,
- 提供无参和有参构造
- 提供get/set方法
- 重写toString方法,返回员工对象的基本信息
(4)声明一个员工管理类:EmployeeService,
-
包含private Employee[] arr并创建长度为5的数组
-
包含private int total,记录arr中员工对象个数
-
包含public void add(Employee emp)方法,将emp对象添加到arr数组中,
-
包含public Employee[] get(Predicate p)方法,这个方法的作用就是在arr数组中筛选出满足某个条件的员工对象。
- 要求遍历arr数组,统计arr数组中有几个元素通过p的test方法判断返回true,假设count个
- 创建Emloyee[]数组result,长度为count,并把arr中满足p的test方法条件的元素就添加到返回值的result数组中。
(5)在测试类中,创建EmployeeService对象,
- 调用add方法添加如下员工对象
new Employee(4, "李四", 24, 24000);
new Employee(3, "张三", 23, 13000);
new Employee(5, "王五", 25, 15000);
new Employee(1, "赵六", 27, 17000);
new Employee(2, "钱七", 16, 6000);
- 调用get(Predicate p)方法,通过匿名内部类的对象给形参p赋值,分别实现获取:
- 所有员工对象
- 所有年龄超过25的员工
- 所有薪资高于15000的员工
- 所有年龄超过25且薪资高于15000的员工
- 分别遍历输出
public class ArrayTools {
public static void print(Object[] arr){
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", salary=" + salary +
'}';
}
}
public class EmployeeService {
private Employee[] arr = new Employee[5];
private int total;
public void add(Employee emp){
if(total >= arr.length){
System.out.println("数组已满,无法添加");
return;
}
arr[total++] = emp;
}
public Employee[] get(Predicate p){
int count = 0;
for (Employee employee : arr) {
if(p.test(employee)){
count++;
}
}
Employee[] result = new Employee[count];
count = 0;
for (Employee employee : arr) {
if(p.test(employee)){
result[count++] = employee;
}
}
return result;
}
}
public class Exercise35 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EmployeeService es = new EmployeeService();
es.add(new Employee(4, "李四", 24, 24000));
es.add(new Employee(3, "张三", 23, 13000));
es.add(new Employee(5, "王五", 25, 15000));
es.add(new Employee(1, "赵六", 27, 17000));
es.add(new Employee(2, "钱七", 16, 6000));
System.out.println("所有员工:");
Employee[] all = es.get(new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean test(Object o) {
return true;
}
});
ArrayTools.print(all);
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println("所有年龄超过25的员工:");
all = es.get(new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean test(Object o) {
return ((Employee)o).getAge()>25;
}
});
ArrayTools.print(all);
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println("所有薪资高于15000的员工:");
all = es.get(new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean test(Object o) {
Employee e = (Employee) o;
return e.getSalary()>15000;
}
});
ArrayTools.print(all);
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println("所有年龄超过25且薪资高于15000的员工:");
all = es.get(new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean test(Object o) {
Employee e = (Employee) o;
return e.getAge()>25 && e.getSalary()>15000;
}
});
ArrayTools.print(all);
}
}
06-内部类
36、代码阅读题
public class Exercise36 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Out out = new Out();
out.Print(3);
}
}
class Out {
private int age = 12;
public void Print(final int x) {
class In {
public void inPrint() {
System.out.println(x);//3
System.out.println(age);//12
}
}
new In().inPrint();
}
}
37、代码阅读题
public class Exercise37 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Out.In in = new Out().new In();
in.print();
}
}
class Out {
private int age = 12;
class In {
private int age = 13;
public void print() {
int age = 14;
System.out.println("局部变量:" + age);//14
System.out.println("内部类变量:" + this.age);//13
System.out.println("外部类变量:" + Out.this.age);//12
}
}
}
38、代码阅读题
public class Exercise38{
public Exercise38(){
Inner s1 = new Inner();
s1.a = 10;
Inner s2 = new Inner();
s2.a = 20;
Exercise38.Inner s3 = new Exercise38.Inner();
System.out.println(s3.a);
}
class Inner{
public int a = 5;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exercise38 t = new Exercise38();
Inner r = t.new Inner();
System.out.println(r.a);
}
}
39、继承Object匿名内部类
编写一个匿名内部类,它继承Object,并在匿名内部类中,声明一个方法public void print(),输出尚硅谷。
请编写代码调用这个方法。
public class Exercise39 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Object(){
public void print(){
System.out.println("尚硅谷");
}
}.print();
}
}
40、CompareAble接口匿名实现类
案例:将《05-接口第28题CompareAble接口》改用匿名内部类实现接口,来代替CompareBig和CompareColor
public class Exercise40 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker w = new Worker();
Apple a1 = new Apple(5, "青色");
Apple a2 = new Apple(3, "红色");
w.pickApple(new CompareAble(){}, a1, a2);
w.pickApple(new CompareAble(){
@Override
public void compare(Apple a1, Apple a2) {
System.out.println("挑红的:");
if("红色".equals(a1.getColor())){
System.out.println(a1);
}
if("红色".equals(a2.getColor())){
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
}, a1, a2);
}
}
class Apple{
private double size;
private String color;
public Apple(double size, String color) {
super();
this.size = size;
this.color = color;
}
public Apple() {
super();
}
public double getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(double size) {
this.size = size;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return size + "-" + color;
}
}
interface CompareAble{
default void compare(Apple a1,Apple a2){
System.out.println("默认挑大的:");
if(a1.getSize() > a2.getSize()){
System.out.println(a1);
}else{
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
}
class Worker{
public void pickApple(CompareAble c,Apple a1,Apple a2){
c.compare(a1, a2);
}
}
41、Filter接口匿名实现类
案例:将《05-接口第29题Filter接口》改用匿名内部类实现接口,来代替V1Filter、V2Filter、AFilter
public class Exercise41 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User[] all = new User[15];
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
all[i] = new User(null,i+1);
}
Receptionist r1 = new Receptionist(new Filter(){
@Override
public void filterUser(User u) {
u.setType("v1");
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
r1.recept(all[i]);
}
Receptionist r2 = new Receptionist(new Filter(){
@Override
public void filterUser(User u) {
u.setType("v2");
}
});
for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
r2.recept(all[i]);
}
Receptionist r3 = new Receptionist(new Filter(){
@Override
public void filterUser(User u) {
u.setType("A");
}
});
for (int i = 10; i < 15; i++) {
r3.recept(all[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
System.out.println(all[i]);
}
}
}
class User{
private String type;
private int id;
public User(String type, int id) {
super();
this.type = type;
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + "-" + type;
}
}
interface Filter{
void filterUser(User u);
}
class Receptionist{
private Filter filter;
public Receptionist(Filter filter) {
super();
this.filter = filter;
}
public Filter getFilter() {
return filter;
}
public void setFilter(Filter filter) {
this.filter = filter;
}
public void recept(User u){
if(u.getType() != null){
return ;
}
filter.filterUser(u);
}
}
42、Thread、Runnable的匿名实现类
(1)已知java.lang包下有一个Thread类(这个类不用写),该类有:
- ①public Thread(String name)构造器
- ②public Thread(Runnable target)构造器
- ③public void run()方法
- ④public void start()方法
- ⑤public String getName()方法
(2)已知java.lang包下还有一个Runnable接口(这个接口不用写),该接口有
- 抽象方法:public void run()
(3)测试类
- ①请用匿名内部类的方式继承Thread类,并显示使用Thread(String name)构造器,传入实参“自己的姓名”,在匿名内部类中重写run方法,输出“xx爱尚硅谷”,其中xx通过getName()方法获取。同时调用Thread类匿名子类对象的start()方法。
- ②请用Thread(Runnable target)构造器创建Thread类的对象,并且用匿名内部类的方式实现Runnable接口,重写run方法,输出“尚硅谷爱我”。调用Thread类对象的start方法
- ③运行测试类,查看运行效果
public class Exercise42 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread("康师傅"){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(getName() +"爱尚硅谷");
}
}.start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("尚硅谷爱我");
}
}).start();
}
}
43、Selector、Touchable接口
案例:
1、声明一个接口:Selector,包含抽象方法:
(1)boolean hasNext()
(2)Object next()
2、声明一个接口:Touchable,包含抽象方法:
(1)Selector select()
3、声明一个MyArrayList类,当做容器类使用,模拟动态数组数据结构的容器
(1)包含私有属性:
① Object[] all;用于保存对象,初始化长度为2
② int total;记录实际存储的对象个数
(2)包含方法:
① public void add(Object element):用于添加一个元素到当前容器中,如果数组all已满,就扩容为原来的2倍
② public void remove(int index):如果index<0或index>=total就打印“没有这个元素”并返回,否则删除index位置的元素
③ public void set(int index, Object value):如果index<0或index>=total就打印“没有这个元素”并返回,否则就替换index位置的元素为value
④ public Object get(int index):如果index<0或index>=total就打印“没有这个元素”并返回null,否则返回index位置的元素
⑤ 让类MyArrayList实现Touchable接口,并重写Selector select()方法,返回内部类MySelector的对象
⑥ 在类MyArrayList中声明private的内部类MySelector,实现Selector接口
A:在内部类MySelector声明一个属性:int cursor(游标)
B:MySelector实现Selector接口,并重写两个抽象方法,其中
> boolean hasNext()实现为:return cursor != total
> Object next()实现为:return all[cursor++]
4、在测试类Exercise43_1中,
(1)创建MyArrayList的对象list
(2)调用list的add方法,添加3个对象
(3)调用list的remove方法,删除[1]的对象
(4)调用list的set方法,替换[1]的对象
(5)调用list的get方法,获取[1]的对象
(6)调用list的select方法,获取Selector的对象,并调用hasNext()和next()遍历容器中所有的对象
5、在测试类Exercise43_2中,
(1)声明静态的MyArrayList类型的list类变量,
(2)声明public static void init()方法,
①在方法中创建MyArrayList类型对象,
②并调用list的add()方法,添加3个对象,
③并在init()方法上标记JUnit4的@BeforeClass注解
(3)声明public void before()方法,
①打印“该测试方法开始前list中的数据如下:"
②调用list的select方法,获取Selector的对象,并调用hasNext()和next()遍历容器中所有的对象
③并在before()方法上标记JUnit4的@Before的注解
(4)声明public void after()方法,
①打印“该测试方法结束后list中的数据如下:"
②调用list的select方法,获取Selector的对象,并调用hasNext()和next()遍历容器中所有的对象
③并在after()方法上标记JUnit4的@After的注解
(5)声明public void testAdd()方法,
①在方法中,打印“现在测试的是testAdd()方法"
②在方法中,再次调用list的add()方法往list容器对象中添加1个对象
③并在testAdd()方法上标记JUnit4的@Test的注解
(6)声明public void testRemove()方法,
①在方法中,打印“现在测试的是testRemove()方法"
②调用list的remove方法,删除[1]的对象
③并在testRemove()方法上标记JUnit4的@Test的注解
(7)声明public void testSet()方法
①在方法中,打印“现在测试的是testSet()方法"
②调用list的set方法,替换[1]的对象
③并在testSet()方法上标记JUnit4的@Test的注解
(8)声明public void testGet()方法
①在方法中,打印“现在测试的是testGet()方法"
②调用list的get方法,获取[1]的对象,并打印
③并在testGet()方法上标记JUnit4的@Test的注解
public interface Selector {
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
}
public interface Touchable {
Selector select();
}
public class MyArrayList implements Touchable{
private Object[] all = new Object[2];
private int total;
public void add(Object element){
if(total>=all.length){
all = Arrays.copyOf(all, all.length*2);
}
all[total++] = element;
}
public void remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= total){
System.out.println("没有这个元素");
return;
}
System.arraycopy(all, index+1, all, index, total-index-1);
all[--total]=null;
}
public void set(int index, Object value){
if(index < 0 || index >= total){
System.out.println("没有这个元素");
return;
}
all[index] = value;
}
public Object get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= total){
System.out.println("没有这个元素");
return null;
}
return all[index];
}
@Override
public Selector select() {
return new MySelector();
}
private class MySelector implements Selector{
private int cursor;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != total;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
return all[cursor++];
}
}
}
public class Exercise43_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList list = new MyArrayList();
//---add()---
list.add("张三");
list.add("李四");
list.add("王五");
//---remove()---
list.remove(1);
//---set()---
list.set(1,"赵六");
//---get()---
Object obj = list.get(1);
System.out.println("[1] = " + obj);
//---select()---
Selector select = list.select();
while(select.hasNext()){
Object next = select.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
public class Exercise43_2 {
private static MyArrayList list;
@BeforeClass
public static void init(){
list = new MyArrayList();
list.add("张三");
list.add("李四");
list.add("王五");
}
@Before
public void before(){
System.out.println("该测试方法开始前list中的数据如下:");
Selector select = list.select();
while(select.hasNext()){
Object next = select.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
@After
public void after(){
System.out.println("该测试方法结束后list中的数据如下:");
Selector select = list.select();
while(select.hasNext()){
Object next = select.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
@Test
public void testAdd(){
System.out.println("现在测试的是testAdd()方法");
list.add("康师傅");
}
@Test
public void testRemove(){
System.out.println("现在测试的是testRemove()方法");
list.remove(1);
}
@Test
public void testSet(){
System.out.println("现在测试的是testSet()方法");
list.set(1,"赵六");
}
@Test
public void testGet(){
System.out.println("现在测试的是testGet()方法");
Object object = list.get(1);
System.out.println(object);
}
}
44、Iterable接口实现类
(1)已知java.lang包有一个Iterable接口(这个接口不用写),实现该接口类型的对象,就支持foreach循环遍历。Iterable接口包含:
- 抽象方法:Iterator iterator();
(2)已知java.util包下有一个Iterator接口(这个接口不用写),Iterator接口包含抽象方法:
-
boolean hasNext()
-
Object next()
(3)声明一个动态数组类型MyArrayList,当做容器类使用,模拟动态数组数据结构的容器
-
包含私有属性:
①Object[] all;用于保存对象,初始化长度为10
②int total;记录实际存储的对象个数
-
包含方法:
①public void add(Object element):用于添加一个元素到当前容器中,如果数组all已满,不添加了
②public void remove(int index):如果index<0或index>=total就打印“没有这个元素”并返回,否则删除index位置的元素
③public void set(int index, Object value):如果index<0或index>=total就打印“没有这个元素”并返回,否则就替换index位置的元素为value
④public Object get(int index):如果index<0或index>=total就打印“没有这个元素”并返回null,否则返回index位置的元素
⑤让类MyArrayList实现Iterable接口,并重写Iterator iterator()方法,返回内部类Itr的对象
(4)在类MyArrayList内部中声明private的非静态内部类Itr,实现Iterator接口
- 声明一个属性:int cursor(游标)
- 实现抽象方法boolean hasNext()实现为:return cursor != total;
- 实现抽象方法Object next()实现为:return all[cursor++];
(5)在测试类中,
-
创建MyArrayList的对象list
-
调用list的add方法,连续添加5个对象,分别为"atguigu",“java”,“bigdata”,“h5”,“ui”,并用foreach遍历输出
-
调用list的set方法,替换[1]的对象为"javaee",并用foreach遍历输出
-
调用list的remove方法,删除[1]的对象,并用foreach遍历输出
-
调用list的get方法,获取[1]的对象
-
调用list的iterator方法,获取Iterator接口的实现类对象,结合while循环调用hasNext()和next()遍历容器中所有的对象
public class MyArrayList implements Iterable {
private Object[] all = new Object[10];
private int total;
public void add(Object element){
if(total>=all.length){
System.out.println("数组已满,无法添加");
return;
}
all[total++] = element;
}
public void remove(int index){
if(index<0 || index>=total){
System.out.println("没有这个元素");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < total; i++) {
all[i] = all[i+1];
}
all[--total] = null;
}
public void set(int index, Object value){
if(index<0 || index>=total){
System.out.println("没有这个元素");
return;
}
all[index] =value;
}
public Object get(int index){
if(index<0 || index>=total){
System.out.println("没有这个元素");
return null;
}
return all[index];
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator{
int cursor;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != total;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
return all[cursor++];
}
}
}
public class Exercise44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList list = new MyArrayList();
list.add("atguigu");
list.add("java");
list.add("bigdata");
list.add("h5");
list.add("ui");
System.out.println("添加完5个元素后:");
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("--------------------");
list.set(1,"javaee");
System.out.println("替换[1]位置的元素为javaee后");
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("--------------------");
list.remove(1);
System.out.println("删除[1]位置的元素后");
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("--------------------");
Object o = list.get(1);
System.out.println("[1]位置的元素现在是" + o);
System.out.println("--------------------");
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
07-枚举类
45、月份枚举类
(1)声明月份枚举类Month:
①声明一个属性,私有化,加final修饰
- description(描述,例如:JANUARY的description为一月,FEBRUARY的description为二月,依次类推)
②声明一个有参构造Month(String description),创建12个常量对象,常量对象的名称如下
JANUARY,FEBRUARY,MARCH,APRIL,MAY,JUNE,JULY,AUGUST,SEPTEMBER,OCTOBER,NOVEMBER,DECEMBER
③public static Month getByValue(int value):返回对应月份值的枚举对象,例如实参传入1,则返回JANUARY对象。
④public int length(boolean leapYear):返回这个月的总天数,如果当前对象是FEBRUARY,并且leapYear是true,则返回29,否则返回28。其他月份对象无论leapYear参数是true还是false,都正常返回月份总天数。
⑤重写toString():返回对象信息,例如:1->JANUARY->一月份。
2、在测试类中,从键盘输入年份和月份值,获取对应的月份对象,并打印月份对象,并获取月份总天数。
public enum Month {
JANUARY("一月"),
FEBRUARY("二月"),
MARCH("三月"),
APRIL("四月"),
MAY("五月"),
JUNE("六月"),
JULY("七月"),
AUGUST("八月"),
SEPTEMBER("九月"),
OCTOBER("十月"),
NOVEMBER("十一月"),
DECEMBER("十二月");
private final String description;
Month(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public static Month getByValue(int value){
if(value>=1 && value<=12){
return Month.values()[value-1];
}
return null;
}
public int length(boolean leapYear){
switch(this){
case FEBRUARY:
return leapYear ? 29 : 28;
case APRIL:
case JUNE:
case SEPTEMBER:
case NOVEMBER:
return 30;
default:
return 31;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (ordinal()+1) +"->" + name() +"->" + description;
}
}
public class Exercise45 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年份值:");
int year = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入月份值:");
int monthValue = input.nextInt();
Month month = Month.getByValue(monthValue);
System.out.println(month);
System.out.println("月份总天数:" + month.length(year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0));
input.close();
}
}
46、颜色枚举类
案例:
1、声明颜色枚举类:
- 7个常量对象:赤、橙、黄、绿、青、蓝、紫。
2、在测试类中,使用枚举类,获取绿色对象,并打印对象。
public class Exercise46 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color c = Color.GREEN;
System.out.println(c);
}
}
enum Color{
RED,ORANGE,YELLOW,GREEN,CYAN,BLUE,PURPLE
}
47、拓展:颜色枚举类
(1)声明颜色枚举类Color:
- 声明final修饰的int类型的属性red,green,blue
- 声明final修饰的String类型的属性description
- 声明有参构造Color(int red, int green, int blue,String description)
- 创建7个常量对象:赤、橙、黄、绿、青、蓝、紫,
- 重写toString方法,例如:RED(255,0,0)->红色
(2)在测试类中,使用枚举类,获取绿色对象,并打印对象。
提示:
- 7个常量对象的RGB值如下:
赤:(255,0,0)
橙:(255,128,0)
黄:(255,255,0)
绿:(0,255,0)
青:(0,255,255)
蓝:(0,0,255)
紫:(128,0,255)
- 7个常量对象名如下:
RED, ORANGE, YELLOW, GREEN, CYAN, BLUE,PURPLE
public enum Color {
RED(255,0,0,"赤"),
ORANGE(255,128,0,"橙"),
YELLOW(255,255,0,"黄"),
GREEN(0,255,0,"绿"),
CYAN(0,255,255,"青"),
BLUE(0,0,255,"蓝"),
PURPLE(128,0,255,"紫");
private final int red;
private final int green;
private final int blue;
private final String description;
Color(int red, int green, int blue,String description) {
this.red = red;
this.green = green;
this.blue = blue;
this.description = description;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name()+"("+red+","+green+","+green+")->" + description;
}
}
public class Exercise47 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color green = Color.GREEN;
System.out.println(green);
}
}
48、月份枚举类
案例:
1、声明月份枚举类Month:
(1)创建:1-12月常量对象
(2)声明两个属性:value(月份值,例如:JANUARY的value为1),
description(描述,例如:JANUARY的description为1月份是一年的开始)。
(3)声明一个有参构造,创建12个对象
(4) 声明一个方法:public static Month getByValue(int value)
(5)重写toString():返回对象信息,例如:1->JANUARY->1月份是一年的开始。
2、在测试类中,从键盘输入1个1-12的月份值,获取对应的月份对象,并打印对象
public class Exercise48 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入月份值(1-12):");
int m = input.nextInt();
Month month = Month.getByValue(m);
System.out.println(month);
input.close();
}
}
enum Month{
JANUARY(1,"1月份是一年的开始"),
FEBRUARY(2,"2月份是一年中最短的一个月"),
MARCH(3,"3月春暖花开"),
APRIL(4,"4月阳光明媚"),
MAY(5,"5月清凉初夏"),
JUNE(6,"6月骄阳似火"),
JULY(7,"7月下半年的第一个月"),
AUGUST(8,"8月人已晒干"),
SEPTEMBER(9,"秋风送爽"),
OCTOBER(10,"10月全国同欢"),
NOVEMBER(11,"11月寻找秋裤"),
DECMEBER(12,"12月冰天雪地");
private int value;
private String description;
private Month(int value,String description){
this.value = value;
this.description = description;
}
public static Month getByValue(int value){
return Month.values()[value-1];
}
public String toString(){
return value + "->" + name() + "->" + description;
}
}
49、支付枚举类-1
(1)声明可支付接口Payable:
- 包含抽象方法:void pay();
(2)声明支付枚举类Payment:
- 声明String类型的final属性description
- 声明有参构造Payment(String description)
- 重写toString方法,返回description
ALIPAY("支付宝"),WECHAT("微信"),CREDITCARD("信用卡"),DEPOSITCARD("储蓄卡")
- 枚举类Payment实现接口Payable
①支付宝/微信:对接口的实现是打印“扫码支付”
②信用卡/储蓄卡:对接口的实现是打印“输入卡号支付”
(3)在测试类中,获取所有支付对象,打印支付对象并调用它们的pay()方法
public interface Payable {
void pay();
}
public enum Payment implements Payable{
ALIPAY("支付宝"),WECHAT("微信"),CREDITCARD("信用卡"),DEPOSITCARD("储蓄卡");
private final String description;
Payment(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return description;
}
@Override
public void pay() {
switch (this){
case ALIPAY:
case WECHAT:
System.out.println("扫码支付");
break;
case CREDITCARD:
case DEPOSITCARD:
System.out.println("输入卡号支付");
break;
}
}
}
public class Exercise49 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Payment[] values = Payment.values();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
System.out.print(values[i]+":");
values[i].pay();
}
}
}
50、支付枚举类-2
案例:
1、声明可支付接口Payable:
包含抽象方法:void pay();
2、声明支付枚举类Payment:
(1)创建常量对象:支付宝(ALIPAY),微信(WECHAT),信用卡(CREDIT_CARD),储蓄卡(DEPOSIT_CARD)
(2)枚举类Payment实现接口Payable
①支付宝/微信:对接口的实现是打印“扫码支付”
②信用卡/储蓄卡:对接口的实现是打印“输入卡号支付”
3、在测试类中,获取所有支付对象,并调用它们的pay()
public class Exercise50 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Payment[] values = Payment.values();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
values[i].pay();
}
}
}
interface Payable{
void pay();
}
enum Payment implements Payable{
ALIPAY{
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("扫码支付");
}
},WECHAT{
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("扫码支付");
}
},CREDIT_CARD,DEPOSIT_CARD;
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("输入卡号支付");
}
}
51、设备状态枚举类
(1)声明设备状态枚举类Status
- 声明final修饰的String类型的属性description和int类型的属性value,value值初始化为ordinal()值
- 声明有参构造Status(String description)
- 重写toString方法,返回description值
- 提供静态方法public static Status getByValue(int value):根据value值获取Status状态对象
- 创建3个常量对象:
FREE("空闲"), USED("在用"), SCRAP("报废")
(2)声明设备类型Equipment
- 声明设备编号(int)、设备的品牌(String)、价格(double)、设备名称(String)、状态(Status)属性,私有化
- 提供无参和有参构造
- 重写toString方法,返回设备信息
(3)现有Data.java,代码如下:
public class Data {
public static final String[][] EQUIPMENTS = {
{"1", "联想", "6000", "拯救者","0"},
{"2", "宏碁 ","5000", "AT7-N52","0"},
{"3", "小米", "2000", "5V5Pro","1"},
{"4", "戴尔", "4000", "3800-R33","1"},
{"5", "苹果", "12000", "MBP15","1"},
{"6", "华硕", "8000", "K30BD-21寸","2"},
{"7", "联想", "7000", "YOGA","0"},
{"8", "惠普", "5800", "X500","2"},
{"9", "苹果", "4500","2021Pro","0"},
{"10", "惠普", "5800", "FZ5","1"}
};
}
(4)在测试类中,创建Equipment类型的数组,并使用Data类的二维数组EQUIPMENTS的信息初始化设备对象,遍历输出
public enum Status {
FREE("空闲"), USED("在用"), SCRAP("报废");
private final int value;
private final String description;
private Status(String description) {
this.value = ordinal();
this.description = description;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public static Status getByValue(int value){
return Status.values()[value];
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
public class Equipment {
private int id;
private String factory;
private double price;
private String name;
private Status status;
public Equipment() {}
public Equipment(int id, String factory, double price, String name, Status status) {
this.id = id;
this.factory = factory;
this.price = price;
this.name = name;
this.status = status;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFactory() {
return factory;
}
public void setFactory(String factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Status getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Status status) {
this.status = status;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Equipment{" +
"id=" + id +
", factory='" + factory + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", status=" + status +
'}';
}
}
public class Data {
public static final String[][] EQUIPMENTS = {
{"1", "联想", "6000", "拯救者","0"},
{"2", "宏碁 ","5000", "AT7-N52","0"},
{"3", "小米", "2000", "5V5Pro","1"},
{"4", "戴尔", "4000", "3800-R33","1"},
{"5", "苹果", "12000", "MBP15","1"},
{"6", "华硕", "8000", "K30BD-21寸","2"},
{"7", "联想", "7000", "YOGA","0"},
{"8", "惠普", "5800", "X500","2"},
{"9", "苹果", "4500","2021Pro","0"},
{"10", "惠普", "5800", "FZ5","1"}
};
}
public class Exercise51 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Equipment[] arr = new Equipment[EQUIPMENTS.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int id = Integer.parseInt(EQUIPMENTS[i][0]);
String factory = EQUIPMENTS[i][1];
double price = Double.parseDouble(EQUIPMENTS[i][2]);
String name = EQUIPMENTS[i][3];
int value = Integer.parseInt(EQUIPMENTS[i][4]);
Status status = Status.getByValue(value);
arr[i] = new Equipment(id,factory,price,name,status);
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
08-注解
52、图形工具类
案例:
1、编写图形工具类:ShapTools
(1)声明方法1:public static void printRectangle(),打印5行5列*组成的矩形图形
(2)声明方法2:public static void printRectangle(int line, int column, String sign),打印line行column列由sign组成的矩形图形
(3)给这个类加上文档注释:包含@author,@param等
(4)给方法1标记已过时注解
2、编写测试类Exercise52
在测试类中调用上面的两个方法测试,如果有警告,就在main方法上抑制警告
public class Exercise52 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapTools.printRectangle();
ShapTools.printRectangle(3, 10, "#");
}
}
class ShapTools{
@Deprecated
public static void printRectangle(){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void printRectangle(int line, int column, String sign){
for (int i = 0; i < line; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++) {
System.out.print(sign);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
09-包装类
53、代码阅读题
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = 128;
Integer i2 = 128;
int i3 = 128;
int i4 = 128;
System.out.println(i1 == i2);
System.out.println(i3 == i4);
System.out.println(i1 == i3);
}
package com.atguigu.test1;
public class Exercise53 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = 128;
Integer i2 = 128;
int i3 = 128;
int i4 = 128;
System.out.println(i1 == i2);//false,比较地址,128超过Integer缓存对象
System.out.println(i3 == i4);//true,比较数据值
System.out.println(i1 == i3);//true,i1自动拆箱按照基本数据类型比较
//包装类对象与基本数据类型进行比较时,就会把包装类对象自动拆箱,按照基本数据类型的规则进行比较
}
}
54、代码阅读题
public class Exercise54{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 2.0;
double b = 2.0;
Double c = 2.0;
Double d = 2.0;
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(c == d);
System.out.println(a == d);
}
}
public class Exercise54{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 2.0;
double b = 2.0;
Double c = 2.0;
Double d = 2.0;
System.out.println(a == b);//true,基本数据类型比较数据值
System.out.println(c == d);//false,对象比较地址值,Double没有缓存对象
System.out.println(a == d);//true,d自动拆箱,按照基本数据类型比较
}
}
55、Employee、Programmer、Designer、Architect等类
(1)现有Data.java文件
public class Data{
public static final int EMPLOYEE = 10;//表示普通员工
public static final int PROGRAMMER = 11;//表示程序员
public static final int DESIGNER = 12;//表示设计师
public static final int ARCHITECT = 13;//表示架构师
public static final String[][] EMPLOYEES = {
{"10", "1", "段誉", "22", "3000"},
{"13", "2", "令狐冲", "32", "18000", "15000", "2000"},
{"11", "3", "任我行", "23", "7000"},
{"11", "4", "张三丰", "24", "7300"},
{"12", "5", "周芷若", "28", "10000", "5000"},
{"11", "6", "赵敏", "22", "6800"},
{"12", "7", "张无忌", "29", "10800","5200"},
{"13", "8", "韦小宝", "30", "19800", "15000", "2500"},
{"12", "9", "杨过", "26", "9800", "5500"},
{"11", "10", "小龙女", "21", "6600"},
{"11", "11", "郭靖", "25", "7100"},
{"12", "12", "黄蓉", "27", "9600", "4800"}
};
}
(2)声明员工类、程序员类、设计师类、架构师类,关系如下:
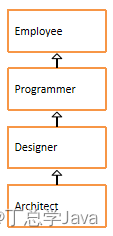
(2-1)普通员工Employee类
- 包含编号、姓名、年龄、工资,属性私有化
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary)
- 提供get/set方法
- 提供String getBasicInfo()方法:返回员工基本信息
- 重写toString():返回员工基本信息
(2-2)程序员Programmer类,继承普通员工类
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Programmer(int id, String name, int age, double salary)
- 重写toString(),增加职位“程序员”信息
(2-3)设计师Designer类,继承程序员类
- 增加奖金属性
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Designer(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus)
- 重写toString(),增加职位“设计师”和奖金信息
(2-4)架构师Architect类,继承设计师类
- 增加股票属性
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Architect(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus, int stock)
- 重写toString()方法,增加职位“架构师”和奖金、股票信息
(3)在测试类中创建员工数组,用Data类中的二维数组数据进行员工数组的初始化
提示:把字符串转为int和double类型的值,可以使用如下方式:
String idStr = "1";
int id = Integer.parseInt(idStr);
String salaryStr = "7300";
double salary = Double.parseDouble(salaryStr);
(4)遍历数组,使用如下格式
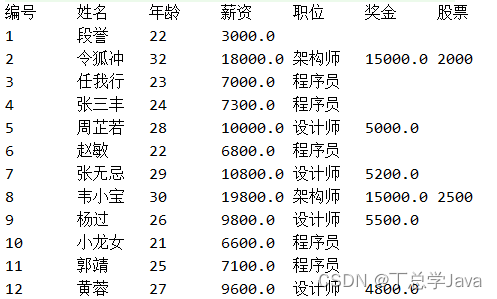
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;//姓名
private int age;//年龄
private double salary;//工资
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getBasicInfo(){
return id + "\t\t" + name + "\t" + age + "\t\t" + salary;
}
public String toString() {
return getBasicInfo();
}
}
public class Programmer extends Employee {
public Programmer() {
}
public Programmer(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
super(id, name, age, salary);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.getBasicInfo() + "\t\t程序员";
}
}
public class Designer extends Programmer {
private double bonus;// : 奖金
public Designer() {
}
public Designer(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus) {
super(id, name, age, salary);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.getBasicInfo() + "\t\t设计师" + "\t" + bonus;
}
}
public class Architect extends Designer {
private int stock;// : 股票
public Architect() {
}
public Architect(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus, int stock) {
super(id, name, age, salary, bonus);
this.stock = stock;
}
public int getStock() {
return stock;
}
public void setStock(int stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.getBasicInfo() + "\t\t架构师" + "\t" + getBonus() + "\t" + stock;
}
}
public class Data{
public static final int EMPLOYEE = 10;//表示普通员工
public static final int PROGRAMMER = 11;//表示程序员
public static final int DESIGNER = 12;//表示设计师
public static final int ARCHITECT = 13;//表示架构师
public static final String[][] EMPLOYEES = {
{"10", "1", "段誉", "22", "3000"},
{"13", "2", "令狐冲", "32", "18000", "15000", "2000"},
{"11", "3", "任我行", "23", "7000"},
{"11", "4", "张三丰", "24", "7300"},
{"12", "5", "周芷若", "28", "10000", "5000"},
{"11", "6", "赵敏", "22", "6800"},
{"12", "7", "张无忌", "29", "10800","5200"},
{"13", "8", "韦小宝", "30", "19800", "15000", "2500"},
{"12", "9", "杨过", "26", "9800", "5500"},
{"11", "10", "小龙女", "21", "6600"},
{"11", "11", "郭靖", "25", "7100"},
{"12", "12", "黄蓉", "27", "9600", "4800"}
};
}
import static com.atguigu.wrapper.Data.*;
public class Exercise55 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee[] arr = new Employee[EMPLOYEES.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int type = Integer.parseInt(EMPLOYEES[i][0]);
int id = Integer.parseInt(EMPLOYEES[i][1]);
String name = EMPLOYEES[i][2];
int age = Integer.parseInt(EMPLOYEES[i][3]);
double salary = Double.parseDouble(EMPLOYEES[i][4]);
switch (type){
case EMPLOYEE:
arr[i] = new Employee(id,name,age,salary);break;
case PROGRAMMER:
arr[i] = new Programmer(id,name,age,salary);break;
case DESIGNER:
double bonus = Double.parseDouble(EMPLOYEES[i][5]);
arr[i] = new Designer(id,name,age,salary,bonus);break;
case ARCHITECT:
bonus = Double.parseDouble(EMPLOYEES[i][5]);
int stock = Integer.parseInt(EMPLOYEES[i][6]);
arr[i] = new Architect(id,name,age,salary,bonus,stock);break;
}
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}