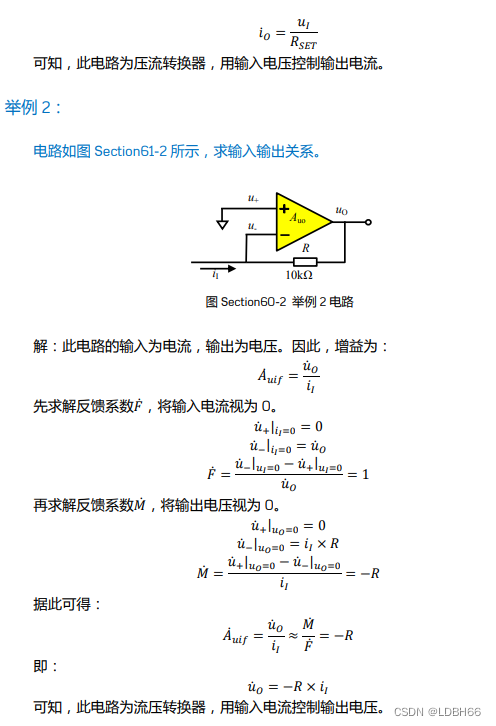
文章目录
- 前言
- 创建 User 结构体
- 添加辅助修饰符
- 使用新的修饰符
- 使用修饰符来替换和覆盖数据
- 可运行代码
- 总结
前言
SwiftUI 3 发布了许多新的辅助功能 API,我们可以利用这些 API 以轻松的方式显著提高用户体验。本篇文章来聊聊另一个新的 API,我们可以使用 SwiftUI 中的新 accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符提供自定义的辅助功能内容。
创建 User 结构体
让我们从一个简单的示例开始,定义 User 结构体以及呈现 User 结构体实例的视图。
import SwiftUI
struct User: Decodable {
let name: String
let email: String
let address: String
let age: Int
}
struct UserView: View {
let user: User
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(user.name)
.font(.headline)
Text(user.address)
.font(.subheadline)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text(user.email)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text("Age: \(user.age)")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
}
}
添加辅助修饰符
SwiftUI 在开箱即用时为我们提供了出色的辅助功能支持。不需要执行任何操作即可使你的 UserView 可访问。UserView 内的每个文本片段都对辅助技术(如VoiceOver和Switch Control)可访问。这听起来很好,但它可能会通过大量数据压倒VoiceOver用户。让我们通过向 UserView 添加一些辅助功能修饰符来稍微改进辅助功能支持。
struct UserView: View {
let user: User
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(user.name)
.font(.headline)
Text(user.address)
.font(.subheadline)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text(user.email)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text("Age: \(user.age)")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
.accessibilityElement(children: .ignore)
.accessibilityLabel(user.name)
}
}
如上例所示,我们使用辅助功能修饰符来忽略子元素的辅助功能内容,使堆栈本身成为辅助功能元素。我们还向堆栈添加了辅助功能标签,但仍然错过了其他部分。我们希望使所有数据都可访问。通常,我们使用不同的字体和颜色在视觉上为文本设置优先级,但是如何在辅助技术中实现相同的影响呢?
使用新的修饰符
SwiftUI 通过全新的 accessibilityCustomContent视图修饰符提供了一种使用不同重要性生成自定义辅助功能内容的方法。让我们看看如何使用它。
struct UserView: View {
let user: User
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(user.name)
.font(.headline)
Text(user.address)
.font(.subheadline)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text(user.email)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text("Age: \(user.age)")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
.accessibilityElement(children: .ignore)
.accessibilityLabel(user.name)
.accessibilityCustomContent("Age", "\(user.age)")
.accessibilityCustomContent("Email", user.email, importance: .high)
.accessibilityCustomContent("Address", user.address, importance: .default)
}
}
在这里,我们添加了一堆 accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符,以不同的优先级定义自定义辅助功能内容。accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符有三个参数:
- 用于你的自定义内容的本地化标签,VoiceOver 用于宣布。
- 用于呈现自定义内容的本地化标签或字符串值。
- 你的自定义内容的重要性级别。它可以是默认或高。VoiceOver 会立即读取具有高重要性的内容,而具有默认重要性的内容仅在用户使用垂直滑动访问更多数据时以冗长模式朗读。
accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符允许我们为辅助技术优先考虑数据。例如,VoiceOver会立即读取具有高重要性的数据,并允许用户使用垂直滑动根据需要访问具有默认重要性的数据。
使用修饰符来替换和覆盖数据
你可以使用尽可能多的 accessibilityCustomContent视图修饰符来呈现大量的数据子集。还可以通过使用相同的标签引入具有相同标签的 accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符来替换和覆盖数据或重要性。
在整个大型代码库中保持自定义辅助功能内容标签的一种绝佳方式是使用 AccessibilityCustomContentKey 类型。你可以将其实例用作 accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符的第一个参数。
extension AccessibilityCustomContentKey {
static let age = AccessibilityCustomContentKey("Age")
static let email = AccessibilityCustomContentKey("Email")
static let address = AccessibilityCustomContentKey("Address")
}
struct UserView: View {
let user: User
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(user.name)
.font(.headline)
Text(user.address)
.font(.subheadline)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text(user.email)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text("Age: \(user.age)")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
.accessibilityElement(children: .ignore)
.accessibilityLabel(user.name)
.accessibilityCustomContent(.age, "\(user.age)")
.accessibilityCustomContent(.email, user.email, importance: .high)
.accessibilityCustomContent(.address, user.address, importance: .default)
}
}
在上面的示例中,我们为自定义的辅助功能内容键定义了一些快捷方式,并与 accessibilityCustomContent 视图修饰符结合使用。
可运行代码
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个 ContentView,在其中创建了一个 User 实例,并将其传递给 UserView。这个示例使用了文章中第三个代码段,其中包括了一些辅助功能的设置。
import SwiftUI
struct User: Decodable {
let name: String
let email: String
let address: String
let age: Int
}
struct UserView: View {
let user: User
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(user.name)
.font(.headline)
Text(user.address)
.font(.subheadline)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text(user.email)
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
Text("Age: \(user.age)")
.foregroundColor(.secondary)
}
.accessibilityElement(children: .ignore)
.accessibilityLabel(user.name)
.accessibilityCustomContent("Age", "\(user.age)")
.accessibilityCustomContent("Email", user.email, importance: .high)
.accessibilityCustomContent("Address", user.address, importance: .default)
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
let exampleUser = User(name: "Swift Com", email: "swift.com@example.com", address: "123 Main St", age: 25)
UserView(user: exampleUser)
.padding()
}
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
ContentView()
}
}
运行截图:

总结
今天,我们学习了如何使用accessibilityCustomContent视图修饰符,通过为辅助技术优先处理我们的数据,以及根据需要允许用户访问更多详细信息,从而使我们的应用程序更具可访问性。




![[ACM学习] 动态规划基础之一二三维dp](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/23331bcd72ae4d4a9574ada0a8f88cc4.png)