《博主简介》
小伙伴们好,我是阿旭。专注于人工智能、AIGC、python、计算机视觉相关分享研究。
✌更多学习资源,可关注公-仲-hao:【阿旭算法与机器学习】,共同学习交流~
👍感谢小伙伴们点赞、关注!
《------往期经典推荐------》
一、AI应用软件开发实战专栏【链接】
| 项目名称 | 项目名称 |
|---|---|
| 1.【人脸识别与管理系统开发】 | 2.【车牌识别与自动收费管理系统开发】 |
| 3.【手势识别系统开发】 | 4.【人脸面部活体检测系统开发】 |
| 5.【图片风格快速迁移软件开发】 | 6.【人脸表表情识别系统】 |
| 7.【YOLOv8多目标识别与自动标注软件开发】 | 8.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的行人跌倒检测系统】 |
| 9.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的PCB板缺陷检测系统】 | 10.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的生活垃圾分类目标检测系统】 |
| 11.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的安全帽目标检测系统】 | 12.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的120种犬类检测与识别系统】 |
| 13.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的路面坑洞检测系统】 | 14.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的火焰烟雾检测系统】 |
| 15.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的钢材表面缺陷检测系统】 | 16.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的舰船目标分类检测系统】 |
| 17.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的西红柿成熟度检测系统】 | 18.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的血细胞检测与计数系统】 |
| 19.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的吸烟/抽烟行为检测系统】 | 20.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的水稻害虫检测与识别系统】 |
| 21.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的高精度车辆行人检测与计数系统】 | 22.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的路面标志线检测与识别系统】 |
| 22.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的智能小麦害虫检测识别系统】 | 23.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的智能玉米害虫检测识别系统】 |
| 24.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的200种鸟类智能检测与识别系统】 | 25.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的45种交通标志智能检测与识别系统】 |
| 26.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的人脸面部表情识别系统】 |
二、机器学习实战专栏【链接】,已更新31期,欢迎关注,持续更新中~~
三、深度学习【Pytorch】专栏【链接】
四、【Stable Diffusion绘画系列】专栏【链接】
《------正文------》
前言

EfficientViT是一种新的高分辨率视觉模型家族,具有新颖的多尺度线性注意机制。本文详细介绍了如何使用efficientViT网络替换YOLOV8的主干网络结构,并且使用修改后的yolov8进行目标检测训练与推理。本文提供了所有源码免费供小伙伴们学习参考,需要的可以通过文末方式自行下载。
本文使用的ultralytics版本为:ultralytics == 8.0.227。
目录
- 前言
- 1. efficientViT简介
- 1.1 efficientViT网络结构
- 1.2 性能对比
- 2.使用efficientViT替换YOLOV8主干网络结构
- 第1步--添加efficientVit.py文件,并导入
- 第2步--修改tasks.py中的相关内容
- parse_model函数修改
- parse_model修改的详细内容对比
- _predict_once函数修改
- 第3步:创建配置文件--yolov8-efficientViT.yaml
- `yolov8.yaml`与`yolov8-efficientViT.yaml`对比
- 第4步:加载配置文件训练模型
- 第5步:模型推理
- 【源码获取】
- 结束语
1. efficientViT简介

论文发表时间:2023.09.27
github地址:https://github.com/mit-han-lab/efficientvit
paper地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14756
摘要:高分辨率密集预测技术能够实现许多吸引人的实际应用,比如计算摄影、自动驾驶等。然而,巨大的计算成本使得在硬件设备上部署最先进的高分辨率密集预测模型变得困难。本研究提出了EfficientViT,一种新的高分辨率视觉模型家族,具有新颖的多尺度线性注意机制。与先前依赖于重型softmax注意力、硬件效率低下的大卷积核卷积或复杂的拓扑结构来获得良好性能的高分辨率密集预测模型不同,我们的多尺度线性注意力通过轻量级而且硬件高效的操作实现了全局感受野和多尺度学习(这对高分辨率密集预测是两个理想的特性)。因此,EfficientViT在各种硬件平台上实现了显著的性能提升,并且具有显著的加速能力,包括移动CPU、边缘GPU等。
论文亮点如下:
• 我们引入了一种新的多尺度线性注意力模块,用于高效的高分辨率密集预测。它在保持硬件效率的同时实现了全局感知域和多尺度学习。据我们所知,我们的工作是首次展示线性注意力对于高分辨率密集预测的有效性。
• 我们基于提出的多尺度线性注意力模块设计了一种新型的高分辨率视觉模型——EfficientViT。
• 我们的模型在语义分割、超分辨率、任意分割和ImageNet分类等各种硬件平台(移动CPU、边缘GPU和云GPU)上相对于先前的SOTA模型展现出了显著的加速效果。
1.1 efficientViT网络结构
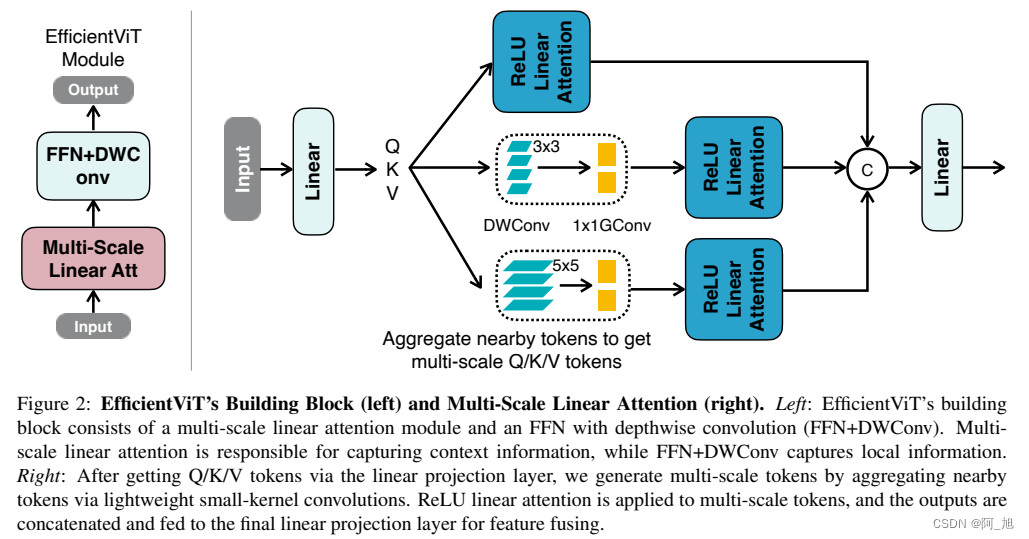
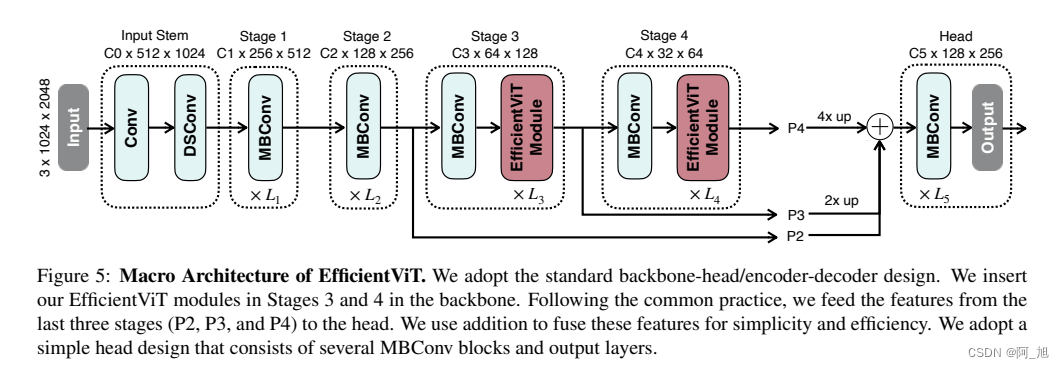
1.2 性能对比
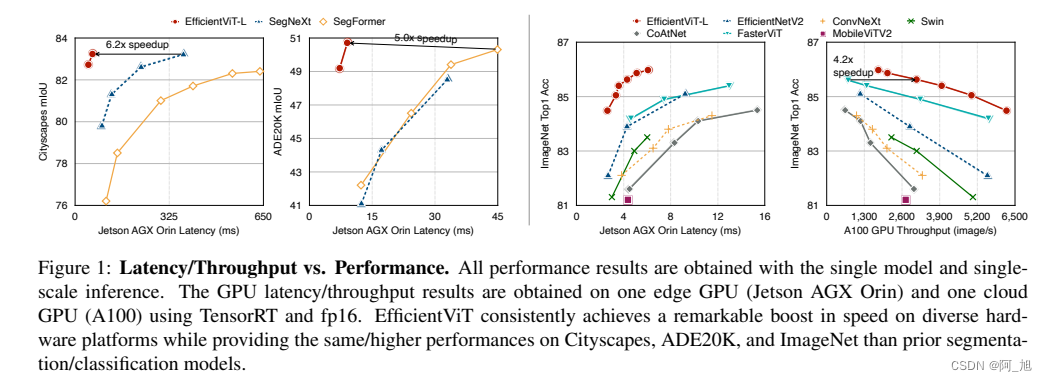
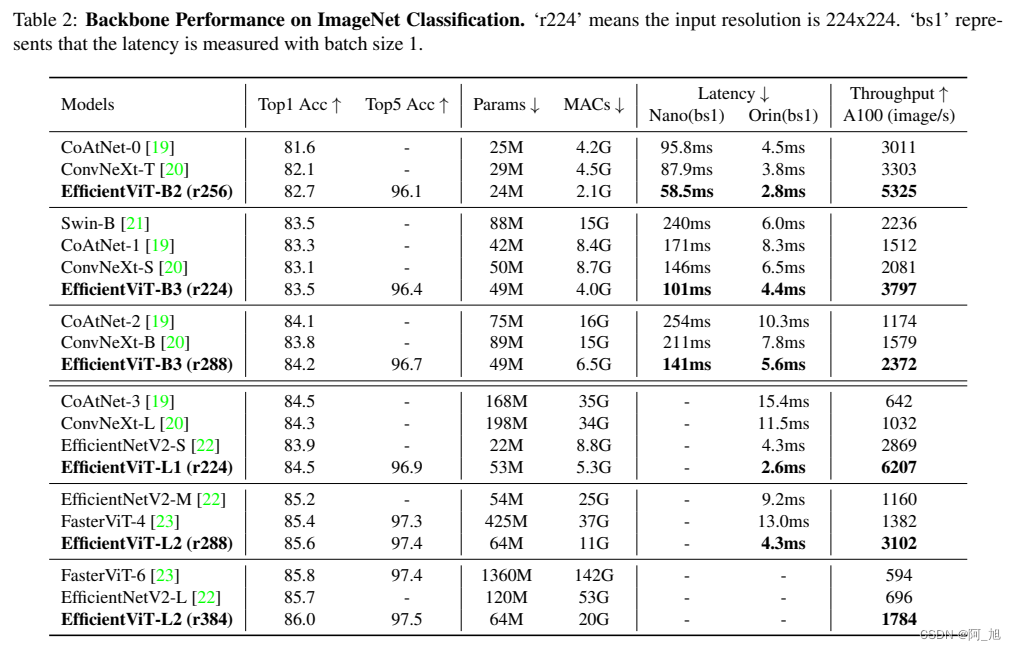
2.使用efficientViT替换YOLOV8主干网络结构
首先,在yolov8官网下载代码并解压,地址如下:
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
解压后,如下图所示:
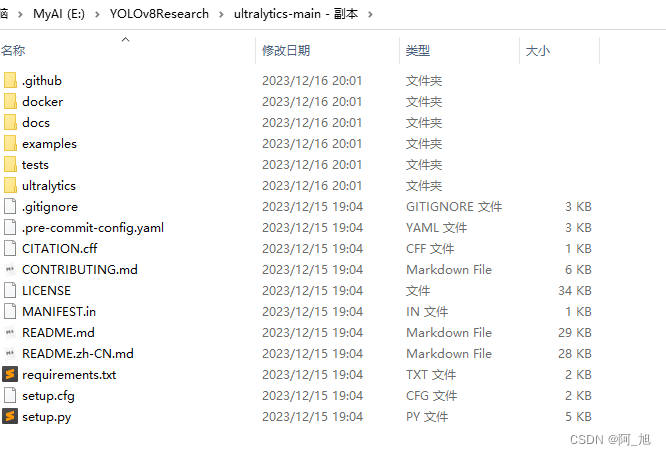
第1步–添加efficientVit.py文件,并导入
在ultralytics/nn/backbone目录下,新建backbone网络文件efficientVit.py,内容如下:
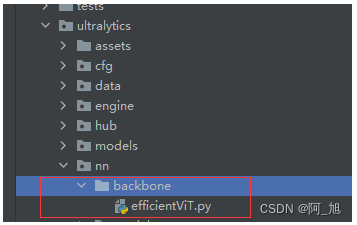
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.checkpoint as checkpoint
import itertools
from timm.models.layers import SqueezeExcite
import numpy as np
import itertools
__all__ = ['EfficientViT_M0', 'EfficientViT_M1', 'EfficientViT_M2', 'EfficientViT_M3', 'EfficientViT_M4', 'EfficientViT_M5']
class Conv2d_BN(torch.nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, a, b, ks=1, stride=1, pad=0, dilation=1,
groups=1, bn_weight_init=1, resolution=-10000):
super().__init__()
self.add_module('c', torch.nn.Conv2d(
a, b, ks, stride, pad, dilation, groups, bias=False))
self.add_module('bn', torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(b))
torch.nn.init.constant_(self.bn.weight, bn_weight_init)
torch.nn.init.constant_(self.bn.bias, 0)
@torch.no_grad()
def switch_to_deploy(self):
c, bn = self._modules.values()
w = bn.weight / (bn.running_var + bn.eps)**0.5
w = c.weight * w[:, None, None, None]
b = bn.bias - bn.running_mean * bn.weight / \
(bn.running_var + bn.eps)**0.5
m = torch.nn.Conv2d(w.size(1) * self.c.groups, w.size(
0), w.shape[2:], stride=self.c.stride, padding=self.c.padding, dilation=self.c.dilation, groups=self.c.groups)
m.weight.data.copy_(w)
m.bias.data.copy_(b)
return m
def replace_batchnorm(net):
for child_name, child in net.named_children():
if hasattr(child, 'fuse'):
setattr(net, child_name, child.fuse())
elif isinstance(child, torch.nn.BatchNorm2d):
setattr(net, child_name, torch.nn.Identity())
else:
replace_batchnorm(child)
class PatchMerging(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, out_dim, input_resolution):
super().__init__()
hid_dim = int(dim * 4)
self.conv1 = Conv2d_BN(dim, hid_dim, 1, 1, 0, resolution=input_resolution)
self.act = torch.nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = Conv2d_BN(hid_dim, hid_dim, 3, 2, 1, groups=hid_dim, resolution=input_resolution)
self.se = SqueezeExcite(hid_dim, .25)
self.conv3 = Conv2d_BN(hid_dim, out_dim, 1, 1, 0, resolution=input_resolution // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv3(self.se(self.act(self.conv2(self.act(self.conv1(x))))))
return x
class Residual(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, m, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.m = m
self.drop = drop
def forward(self, x):
if self.training and self.drop > 0:
return x + self.m(x) * torch.rand(x.size(0), 1, 1, 1,
device=x.device).ge_(self.drop).div(1 - self.drop).detach()
else:
return x + self.m(x)
class FFN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ed, h, resolution):
super().__init__()
self.pw1 = Conv2d_BN(ed, h, resolution=resolution)
self.act = torch.nn.ReLU()
self.pw2 = Conv2d_BN(h, ed, bn_weight_init=0, resolution=resolution)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pw2(self.act(self.pw1(x)))
return x
class CascadedGroupAttention(torch.nn.Module):
r""" Cascaded Group Attention.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
key_dim (int): The dimension for query and key.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
attn_ratio (int): Multiplier for the query dim for value dimension.
resolution (int): Input resolution, correspond to the window size.
kernels (List[int]): The kernel size of the dw conv on query.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, key_dim, num_heads=8,
attn_ratio=4,
resolution=14,
kernels=[5, 5, 5, 5],):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.scale = key_dim ** -0.5
self.key_dim = key_dim
self.d = int(attn_ratio * key_dim)
self.attn_ratio = attn_ratio
qkvs = []
dws = []
for i in range(num_heads):
qkvs.append(Conv2d_BN(dim // (num_heads), self.key_dim * 2 + self.d, resolution=resolution))
dws.append(Conv2d_BN(self.key_dim, self.key_dim, kernels[i], 1, kernels[i]//2, groups=self.key_dim, resolution=resolution))
self.qkvs = torch.nn.ModuleList(qkvs)
self.dws = torch.nn.ModuleList(dws)
self.proj = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.ReLU(), Conv2d_BN(
self.d * num_heads, dim, bn_weight_init=0, resolution=resolution))
points = list(itertools.product(range(resolution), range(resolution)))
N = len(points)
attention_offsets = {}
idxs = []
for p1 in points:
for p2 in points:
offset = (abs(p1[0] - p2[0]), abs(p1[1] - p2[1]))
if offset not in attention_offsets:
attention_offsets[offset] = len(attention_offsets)
idxs.append(attention_offsets[offset])
self.attention_biases = torch.nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros(num_heads, len(attention_offsets)))
self.register_buffer('attention_bias_idxs',
torch.LongTensor(idxs).view(N, N))
@torch.no_grad()
def train(self, mode=True):
super().train(mode)
if mode and hasattr(self, 'ab'):
del self.ab
else:
self.ab = self.attention_biases[:, self.attention_bias_idxs]
def forward(self, x): # x (B,C,H,W)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
trainingab = self.attention_biases[:, self.attention_bias_idxs]
feats_in = x.chunk(len(self.qkvs), dim=1)
feats_out = []
feat = feats_in[0]
for i, qkv in enumerate(self.qkvs):
if i > 0: # add the previous output to the input
feat = feat + feats_in[i]
feat = qkv(feat)
q, k, v = feat.view(B, -1, H, W).split([self.key_dim, self.key_dim, self.d], dim=1) # B, C/h, H, W
q = self.dws[i](q)
q, k, v = q.flatten(2), k.flatten(2), v.flatten(2) # B, C/h, N
attn = (
(q.transpose(-2, -1) @ k) * self.scale
+
(trainingab[i] if self.training else self.ab[i])
)
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1) # BNN
feat = (v @ attn.transpose(-2, -1)).view(B, self.d, H, W) # BCHW
feats_out.append(feat)
x = self.proj(torch.cat(feats_out, 1))
return x
class LocalWindowAttention(torch.nn.Module):
r""" Local Window Attention.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
key_dim (int): The dimension for query and key.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
attn_ratio (int): Multiplier for the query dim for value dimension.
resolution (int): Input resolution.
window_resolution (int): Local window resolution.
kernels (List[int]): The kernel size of the dw conv on query.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, key_dim, num_heads=8,
attn_ratio=4,
resolution=14,
window_resolution=7,
kernels=[5, 5, 5, 5],):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.resolution = resolution
assert window_resolution > 0, 'window_size must be greater than 0'
self.window_resolution = window_resolution
self.attn = CascadedGroupAttention(dim, key_dim, num_heads,
attn_ratio=attn_ratio,
resolution=window_resolution,
kernels=kernels,)
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
if H <= self.window_resolution and W <= self.window_resolution:
x = self.attn(x)
else:
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
pad_b = (self.window_resolution - H %
self.window_resolution) % self.window_resolution
pad_r = (self.window_resolution - W %
self.window_resolution) % self.window_resolution
padding = pad_b > 0 or pad_r > 0
if padding:
x = torch.nn.functional.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, pad_r, 0, pad_b))
pH, pW = H + pad_b, W + pad_r
nH = pH // self.window_resolution
nW = pW // self.window_resolution
# window partition, BHWC -> B(nHh)(nWw)C -> BnHnWhwC -> (BnHnW)hwC -> (BnHnW)Chw
x = x.view(B, nH, self.window_resolution, nW, self.window_resolution, C).transpose(2, 3).reshape(
B * nH * nW, self.window_resolution, self.window_resolution, C
).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
x = self.attn(x)
# window reverse, (BnHnW)Chw -> (BnHnW)hwC -> BnHnWhwC -> B(nHh)(nWw)C -> BHWC
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(B, nH, nW, self.window_resolution, self.window_resolution,
C).transpose(2, 3).reshape(B, pH, pW, C)
if padding:
x = x[:, :H, :W].contiguous()
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return x
class EfficientViTBlock(torch.nn.Module):
""" A basic EfficientViT building block.
Args:
type (str): Type for token mixer. Default: 's' for self-attention.
ed (int): Number of input channels.
kd (int): Dimension for query and key in the token mixer.
nh (int): Number of attention heads.
ar (int): Multiplier for the query dim for value dimension.
resolution (int): Input resolution.
window_resolution (int): Local window resolution.
kernels (List[int]): The kernel size of the dw conv on query.
"""
def __init__(self, type,
ed, kd, nh=8,
ar=4,
resolution=14,
window_resolution=7,
kernels=[5, 5, 5, 5],):
super().__init__()
self.dw0 = Residual(Conv2d_BN(ed, ed, 3, 1, 1, groups=ed, bn_weight_init=0., resolution=resolution))
self.ffn0 = Residual(FFN(ed, int(ed * 2), resolution))
if type == 's':
self.mixer = Residual(LocalWindowAttention(ed, kd, nh, attn_ratio=ar, \
resolution=resolution, window_resolution=window_resolution, kernels=kernels))
self.dw1 = Residual(Conv2d_BN(ed, ed, 3, 1, 1, groups=ed, bn_weight_init=0., resolution=resolution))
self.ffn1 = Residual(FFN(ed, int(ed * 2), resolution))
def forward(self, x):
return self.ffn1(self.dw1(self.mixer(self.ffn0(self.dw0(x)))))
class EfficientViT(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=400,
patch_size=16,
frozen_stages=0,
in_chans=3,
stages=['s', 's', 's'],
embed_dim=[64, 128, 192],
key_dim=[16, 16, 16],
depth=[1, 2, 3],
num_heads=[4, 4, 4],
window_size=[7, 7, 7],
kernels=[5, 5, 5, 5],
down_ops=[['subsample', 2], ['subsample', 2], ['']],
pretrained=None,
distillation=False,):
super().__init__()
resolution = img_size
self.patch_embed = torch.nn.Sequential(Conv2d_BN(in_chans, embed_dim[0] // 8, 3, 2, 1, resolution=resolution), torch.nn.ReLU(),
Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[0] // 8, embed_dim[0] // 4, 3, 2, 1, resolution=resolution // 2), torch.nn.ReLU(),
Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[0] // 4, embed_dim[0] // 2, 3, 2, 1, resolution=resolution // 4), torch.nn.ReLU(),
Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[0] // 2, embed_dim[0], 3, 1, 1, resolution=resolution // 8))
resolution = img_size // patch_size
attn_ratio = [embed_dim[i] / (key_dim[i] * num_heads[i]) for i in range(len(embed_dim))]
self.blocks1 = []
self.blocks2 = []
self.blocks3 = []
for i, (stg, ed, kd, dpth, nh, ar, wd, do) in enumerate(
zip(stages, embed_dim, key_dim, depth, num_heads, attn_ratio, window_size, down_ops)):
for d in range(dpth):
eval('self.blocks' + str(i+1)).append(EfficientViTBlock(stg, ed, kd, nh, ar, resolution, wd, kernels))
if do[0] == 'subsample':
#('Subsample' stride)
blk = eval('self.blocks' + str(i+2))
resolution_ = (resolution - 1) // do[1] + 1
blk.append(torch.nn.Sequential(Residual(Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[i], embed_dim[i], 3, 1, 1, groups=embed_dim[i], resolution=resolution)),
Residual(FFN(embed_dim[i], int(embed_dim[i] * 2), resolution)),))
blk.append(PatchMerging(*embed_dim[i:i + 2], resolution))
resolution = resolution_
blk.append(torch.nn.Sequential(Residual(Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[i + 1], embed_dim[i + 1], 3, 1, 1, groups=embed_dim[i + 1], resolution=resolution)),
Residual(FFN(embed_dim[i + 1], int(embed_dim[i + 1] * 2), resolution)),))
self.blocks1 = torch.nn.Sequential(*self.blocks1)
self.blocks2 = torch.nn.Sequential(*self.blocks2)
self.blocks3 = torch.nn.Sequential(*self.blocks3)
self.channel = [i.size(1) for i in self.forward(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))]
def forward(self, x):
outs = []
x = self.patch_embed(x)
x = self.blocks1(x)
outs.append(x)
x = self.blocks2(x)
outs.append(x)
x = self.blocks3(x)
outs.append(x)
return outs
EfficientViT_m0 = {
'img_size': 224,
'patch_size': 16,
'embed_dim': [64, 128, 192],
'depth': [1, 2, 3],
'num_heads': [4, 4, 4],
'window_size': [7, 7, 7],
'kernels': [7, 5, 3, 3],
}
EfficientViT_m1 = {
'img_size': 224,
'patch_size': 16,
'embed_dim': [128, 144, 192],
'depth': [1, 2, 3],
'num_heads': [2, 3, 3],
'window_size': [7, 7, 7],
'kernels': [7, 5, 3, 3],
}
EfficientViT_m2 = {
'img_size': 224,
'patch_size': 16,
'embed_dim': [128, 192, 224],
'depth': [1, 2, 3],
'num_heads': [4, 3, 2],
'window_size': [7, 7, 7],
'kernels': [7, 5, 3, 3],
}
EfficientViT_m3 = {
'img_size': 224,
'patch_size': 16,
'embed_dim': [128, 240, 320],
'depth': [1, 2, 3],
'num_heads': [4, 3, 4],
'window_size': [7, 7, 7],
'kernels': [5, 5, 5, 5],
}
EfficientViT_m4 = {
'img_size': 224,
'patch_size': 16,
'embed_dim': [128, 256, 384],
'depth': [1, 2, 3],
'num_heads': [4, 4, 4],
'window_size': [7, 7, 7],
'kernels': [7, 5, 3, 3],
}
EfficientViT_m5 = {
'img_size': 224,
'patch_size': 16,
'embed_dim': [192, 288, 384],
'depth': [1, 3, 4],
'num_heads': [3, 3, 4],
'window_size': [7, 7, 7],
'kernels': [7, 5, 3, 3],
}
def EfficientViT_M0(pretrained='', frozen_stages=0, distillation=False, fuse=False, pretrained_cfg=None, model_cfg=EfficientViT_m0):
model = EfficientViT(frozen_stages=frozen_stages, distillation=distillation, pretrained=pretrained, **model_cfg)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(update_weight(model.state_dict(), torch.load(pretrained)['model']))
if fuse:
replace_batchnorm(model)
return model
def EfficientViT_M1(pretrained='', frozen_stages=0, distillation=False, fuse=False, pretrained_cfg=None, model_cfg=EfficientViT_m1):
model = EfficientViT(frozen_stages=frozen_stages, distillation=distillation, pretrained=pretrained, **model_cfg)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(update_weight(model.state_dict(), torch.load(pretrained)['model']))
if fuse:
replace_batchnorm(model)
return model
def EfficientViT_M2(pretrained='', frozen_stages=0, distillation=False, fuse=False, pretrained_cfg=None, model_cfg=EfficientViT_m2):
model = EfficientViT(frozen_stages=frozen_stages, distillation=distillation, pretrained=pretrained, **model_cfg)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(update_weight(model.state_dict(), torch.load(pretrained)['model']))
if fuse:
replace_batchnorm(model)
return model
def EfficientViT_M3(pretrained='', frozen_stages=0, distillation=False, fuse=False, pretrained_cfg=None, model_cfg=EfficientViT_m3):
model = EfficientViT(frozen_stages=frozen_stages, distillation=distillation, pretrained=pretrained, **model_cfg)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(update_weight(model.state_dict(), torch.load(pretrained)['model']))
if fuse:
replace_batchnorm(model)
return model
def EfficientViT_M4(pretrained='', frozen_stages=0, distillation=False, fuse=False, pretrained_cfg=None, model_cfg=EfficientViT_m4):
model = EfficientViT(frozen_stages=frozen_stages, distillation=distillation, pretrained=pretrained, **model_cfg)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(update_weight(model.state_dict(), torch.load(pretrained)['model']))
if fuse:
replace_batchnorm(model)
return model
def EfficientViT_M5(pretrained='', frozen_stages=0, distillation=False, fuse=False, pretrained_cfg=None, model_cfg=EfficientViT_m5):
model = EfficientViT(frozen_stages=frozen_stages, distillation=distillation, pretrained=pretrained, **model_cfg)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(update_weight(model.state_dict(), torch.load(pretrained)['model']))
if fuse:
replace_batchnorm(model)
return model
def update_weight(model_dict, weight_dict):
idx, temp_dict = 0, {}
for k, v in weight_dict.items():
# k = k[9:]
if k in model_dict.keys() and np.shape(model_dict[k]) == np.shape(v):
temp_dict[k] = v
idx += 1
model_dict.update(temp_dict)
print(f'loading weights... {idx}/{len(model_dict)} items')
return model_dict
在ultralytics/nn/tasks.py中导入刚才的efficientVit模块:
# 主干网络
from ultralytics.nn.backbone.efficientViT import *
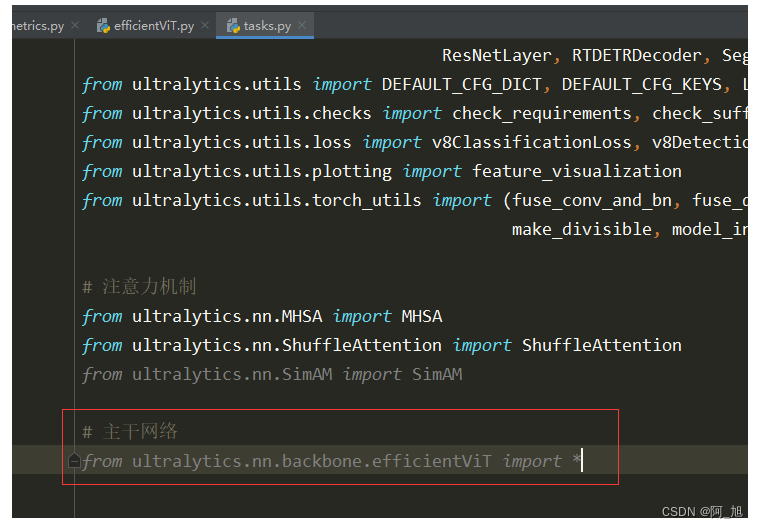
第2步–修改tasks.py中的相关内容
parse_model函数修改
修改ultralytics/nn/tasks.py中的parse_model函数,修改后完整代码如下:
def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
"""Parse a YOLO model.yaml dictionary into a PyTorch model."""
import ast
# Args
max_channels = float('inf')
nc, act, scales = (d.get(x) for x in ('nc', 'activation', 'scales'))
depth, width, kpt_shape = (d.get(x, 1.0) for x in ('depth_multiple', 'width_multiple', 'kpt_shape'))
if scales:
scale = d.get('scale')
if not scale:
scale = tuple(scales.keys())[0]
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ no model scale passed. Assuming scale='{scale}'.")
depth, width, max_channels = scales[scale]
if act:
Conv.default_act = eval(act) # redefine default activation, i.e. Conv.default_act = nn.SiLU()
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f"{colorstr('activation:')} {act}") # print
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>20}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<45}{'arguments':<30}")
ch = [ch]
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
is_backbone = False
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
try:
if m == 'node_mode':
m = d[m]
if len(args) > 0:
if args[0] == 'head_channel':
args[0] = int(d[args[0]])
t = m
m = getattr(torch.nn, m[3:]) if 'nn.' in m else globals()[m] # get module
except:
pass
for j, a in enumerate(args):
if isinstance(a, str):
with contextlib.suppress(ValueError):
try:
args[j] = locals()[a] if a in locals() else ast.literal_eval(a)
except:
args[j] = a
n = n_ = max(round(n * depth), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in (Classify, Conv, ConvTranspose, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, Focus,
BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x, RepC3):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in (BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, C3x, RepC3):
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is AIFI:
args = [ch[f], *args]
elif m in (HGStem, HGBlock):
c1, cm, c2 = ch[f], args[0], args[1]
args = [c1, cm, c2, *args[2:]]
if m is HGBlock:
args.insert(4, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is ResNetLayer:
c2 = args[1] if args[3] else args[1] * 4
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
elif m in (Detect, Segment, Pose):
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if m is Segment:
args[2] = make_divisible(min(args[2], max_channels) * width, 8)
elif m is RTDETRDecoder: # special case, channels arg must be passed in index 1
args.insert(1, [ch[x] for x in f])
elif m in {MHSA, ShuffleAttention}:
args = [ch[f], *args]
elif m in {EfficientViT_M0, EfficientViT_M1, EfficientViT_M2, EfficientViT_M3, EfficientViT_M4, EfficientViT_M5}:
m = m(*args)
c2 = m.channel
else:
c2 = ch[f]
if isinstance(c2, list):
is_backbone = True
m_ = m
m_.backbone = True
else:
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if is_backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(x % (i + 4 if is_backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if
x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
if isinstance(c2, list):
ch.extend(c2)
for _ in range(5 - len(ch)):
ch.insert(0, 0)
else:
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)
parse_model修改的详细内容对比
- 将
efficientVit.py中的all参数中的函数名,写入tasks.py的判断分支中。
新建if判断分支,添加如下内容:
elif m in {efficientvit_b0, efficientvit_b1, efficientvit_b2, efficientvit_b3}:
m = m(*args)
c2 = m.channel
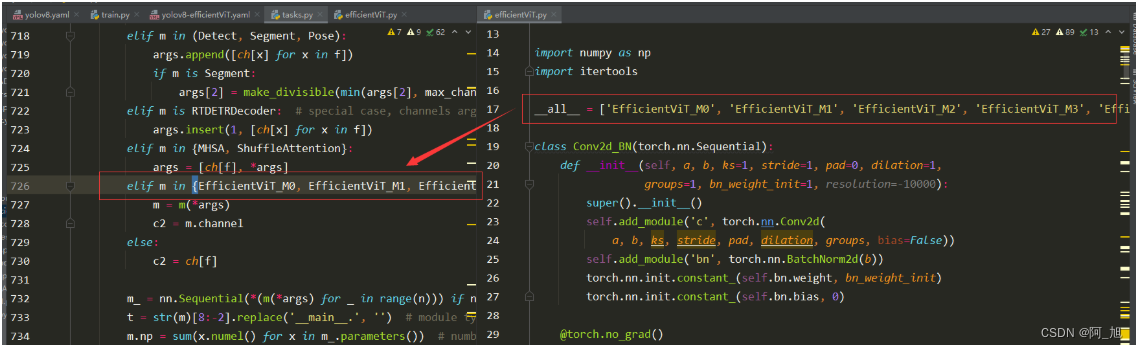
2.修改下图解析部分代码1,如下图:
修改前:
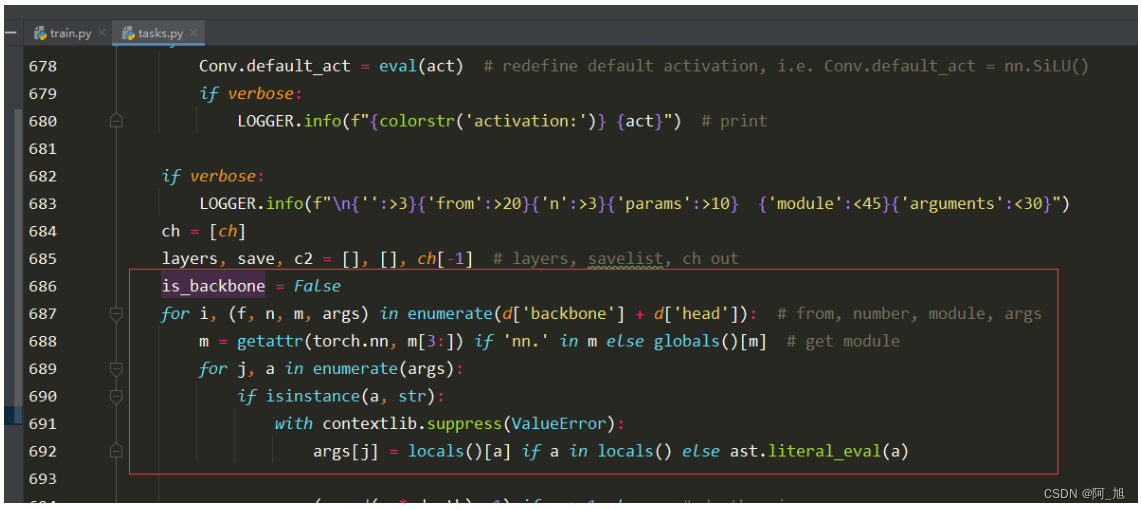
修改后:
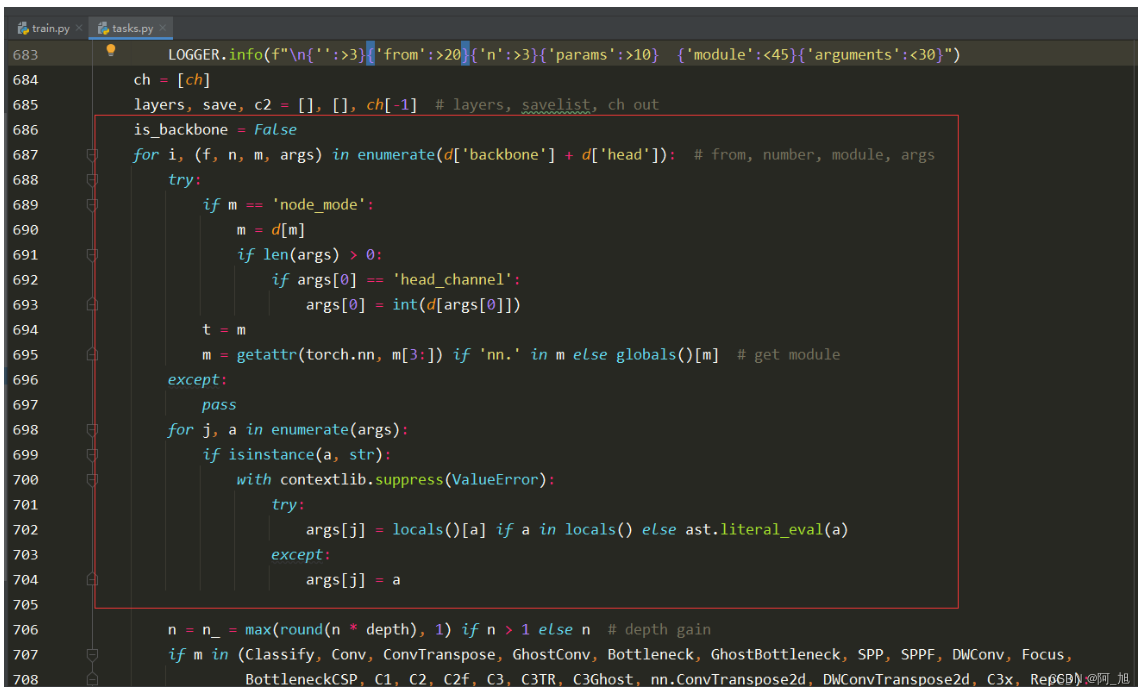
代码如下:
is_backbone = False
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
try:
if m == 'node_mode':
m = d[m]
if len(args) > 0:
if args[0] == 'head_channel':
args[0] = int(d[args[0]])
t = m
m = getattr(torch.nn, m[3:]) if 'nn.' in m else globals()[m] # get module
except:
pass
for j, a in enumerate(args):
if isinstance(a, str):
with contextlib.suppress(ValueError):
try:
args[j] = locals()[a] if a in locals() else ast.literal_eval(a)
except:
args[j] = a
3.修改下面截图中的部分代码2
修改前:
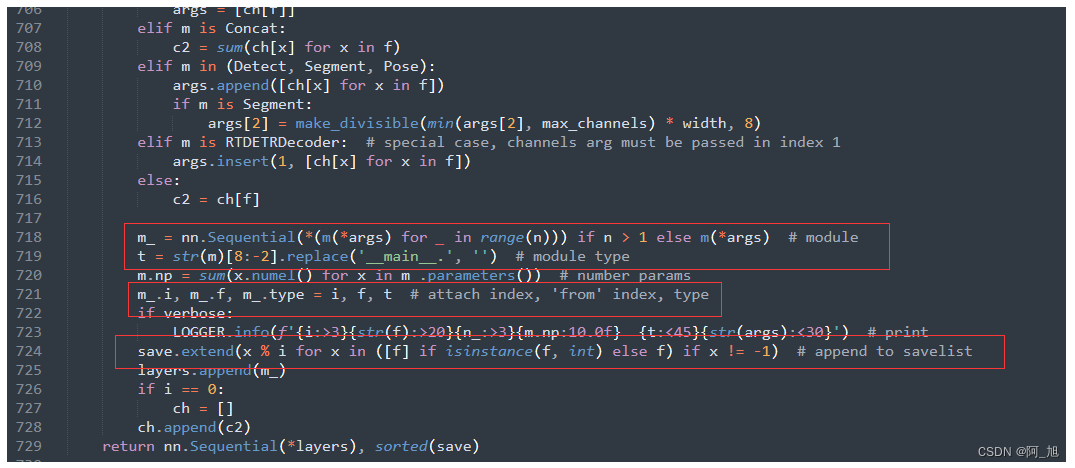
修改后:
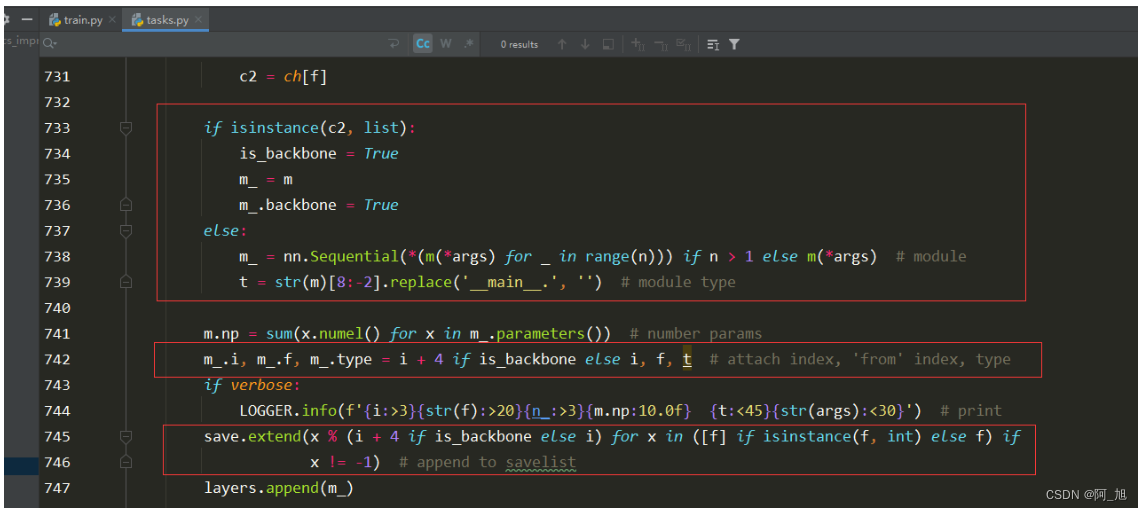
代码如下:
if isinstance(c2, list):
is_backbone = True
m_ = m
m_.backbone = True
else:
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if is_backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(x % (i + 4 if is_backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
4.修改下面截图部分代码
修改前:
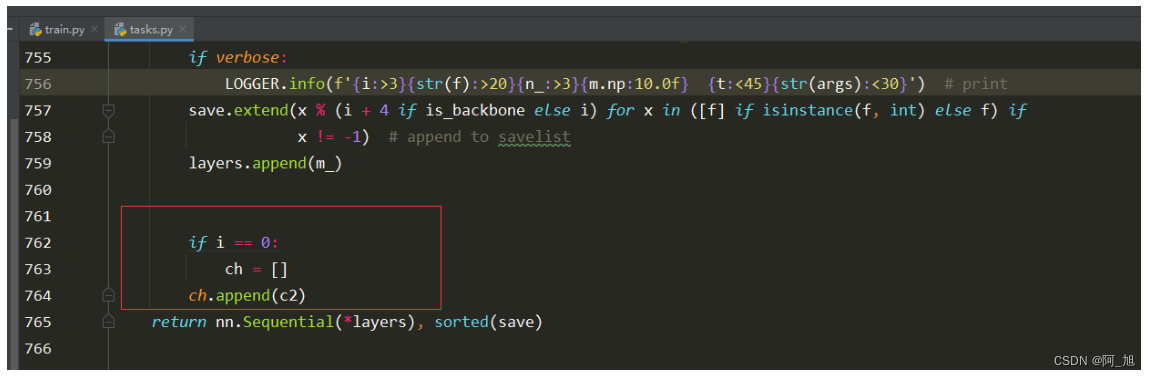
修改后:
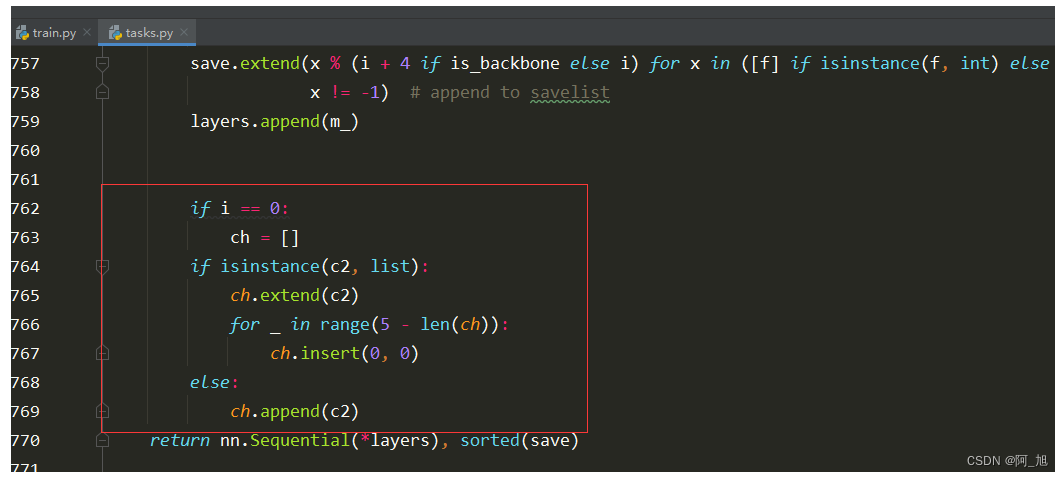
修改代码为:
if isinstance(c2, list):
ch.extend(c2)
for _ in range(5 - len(ch)):
ch.insert(0, 0)
else:
ch.append(c2)
_predict_once函数修改
替换ultralytics/nn/tasks.py中的BaseModel类的_predict_once函数,代码如下:
def _predict_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
if hasattr(m, 'backbone'):
x = m(x)
for _ in range(5 - len(x)):
x.insert(0, None)
for i_idx, i in enumerate(x):
if i_idx in self.save:
y.append(i)
else:
y.append(None)
# for i in x:
# if i is not None:
# print(i.size())
x = x[-1]
else:
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x
第3步:创建配置文件–yolov8-efficientViT.yaml
在ultralytics/cfg/models/v8目录下,创建新的配置文件yolov8-efficientViT.yaml,内容如下:
注:可以使用EfficientViT_M0, EfficientViT_M1, EfficientViT_M2, EfficientViT_M3, EfficientViT_M4, EfficientViT_M5中的任何一个,参数量不同。
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# 0-P1/2
# 1-P2/4
# 2-P3/8
# 3-P4/16
# 4-P5/32
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
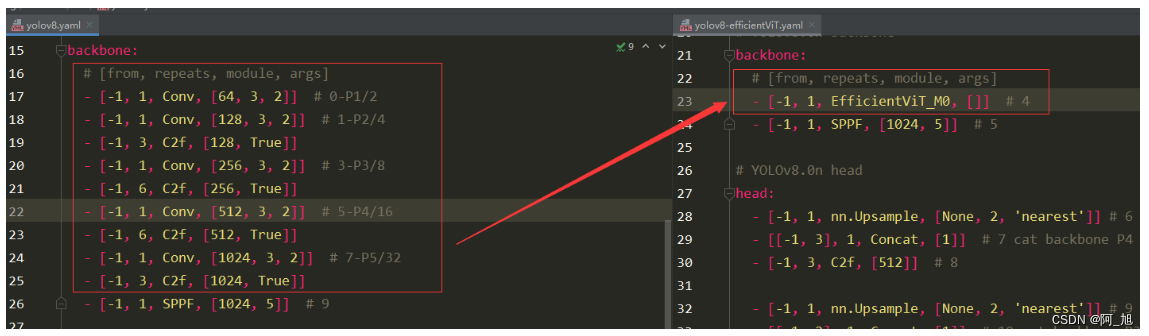
- [-1, 1, EfficientViT_M0, []] # 4
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 5
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] # 6
- [[-1, 3], 1, Concat, [1]] # 7 cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 8
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']] # 9
- [[-1, 2], 1, Concat, [1]] # 10 cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 11 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 12
- [[-1, 8], 1, Concat, [1]] # 13 cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 14 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 15
- [[-1, 5], 1, Concat, [1]] # 16 cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 17 (P5/32-large)
- [[11, 14, 17], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
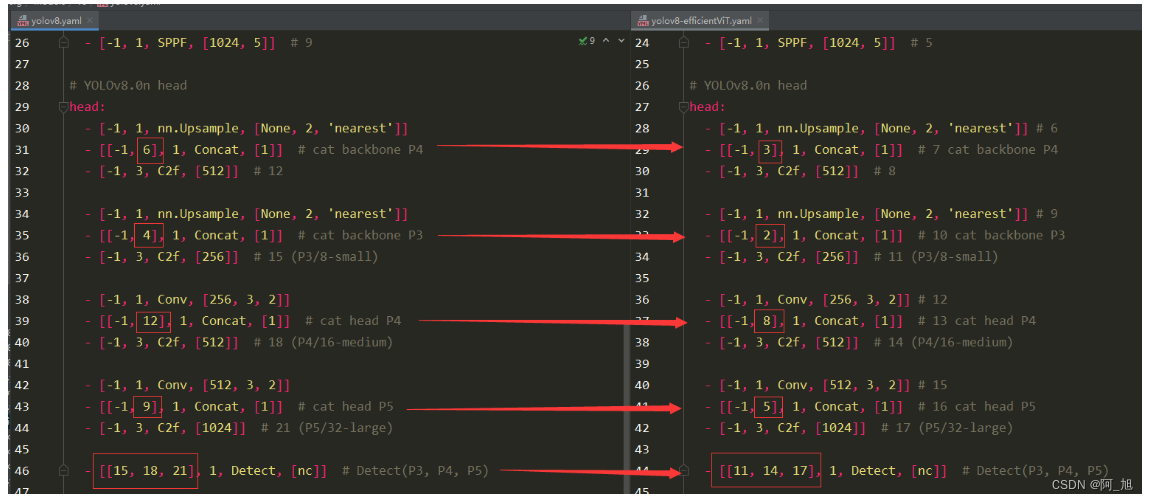
yolov8.yaml与yolov8-efficientViT.yaml对比
backbone部分:yolov8.yaml与yolov8-efficientViT.yaml对比:
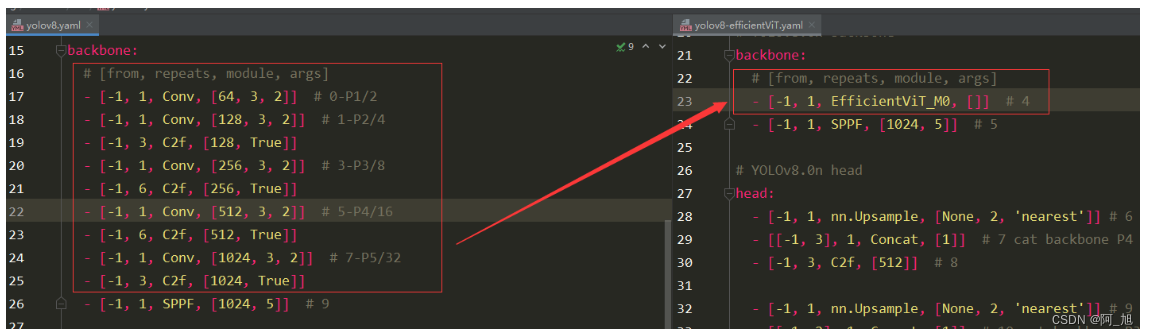
head部分:yolov8.yaml与yolov8-efficientViT.yaml对比:【注意层数的变化,所以要修改对应的层数数字部分】
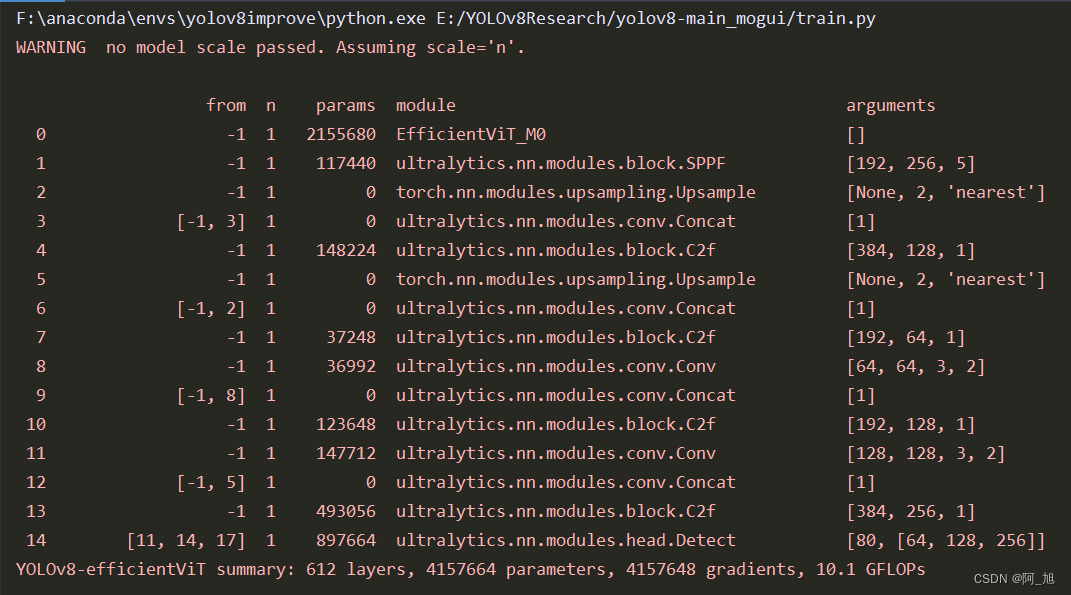
第4步:加载配置文件训练模型
运行训练代码train.py文件,内容如下:
#coding:utf-8
# 替换主干网络,训练
from ultralytics import YOLO
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLO('ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8-efficientViT.yaml')
model.load('yolov8n.pt') # loading pretrain weights
model.train(data='datasets/TomatoData/data.yaml', epochs=250, batch=4)
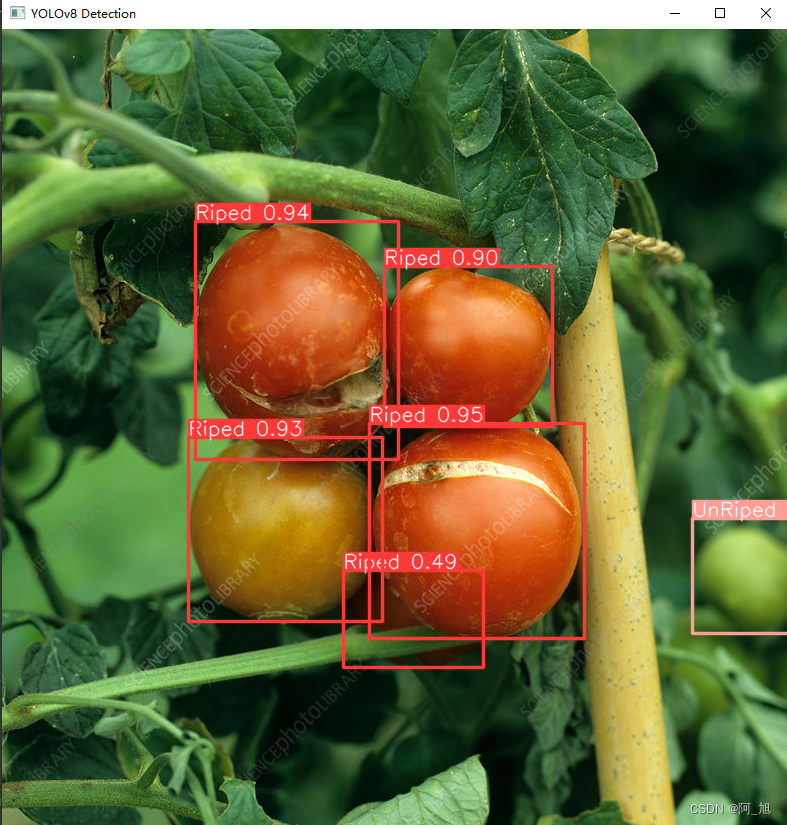
第5步:模型推理
模型训练完成后,我们使用训练好的模型对图片进行检测:
#coding:utf-8
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2
# 所需加载的模型目录
# path = 'models/best2.pt'
path = 'runs/detect/train9/weights/best.pt'
# 需要检测的图片地址
img_path = "TestFiles/Riped tomato_31.jpeg"
# 加载预训练模型
# conf 0.25 object confidence threshold for detection
# iou 0.7 intersection over union (IoU) threshold for NMS
model = YOLO(path, task='detect')
# 检测图片
results = model(img_path)
res = results[0].plot()
# res = cv2.resize(res,dsize=None,fx=2,fy=2,interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 Detection", res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
【源码获取】
为了小伙伴们能够,更好的学习实践,本文已将所有代码、数据集、论文等相关内容打包上传,供小伙伴们学习。获取方式如下:
关注下方名片G-Z-H:【阿旭算法与机器学习】,发送【yolov8改进】即可免费获取
结束语
关于本篇文章大家有任何建议或意见,欢迎在评论区留言交流!
觉得不错的小伙伴,感谢点赞、关注加收藏哦!




![[C#]利用paddleocr进行表格识别](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ddca10cd7ff844ceac57722395c9d97c.jpeg)