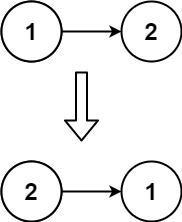
堆栈的定义、入栈、出栈、查询栈顶
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int DataType;
// 定义栈节点结构体
struct StackNode;
struct StackNode {
DataType data; // 节点数据
struct StackNode* next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
};
// 定义栈结构体
struct Stack {
struct StackNode* head; // 栈顶节点指针
int size; // 栈的大小(元素数量)
};
// 将元素压入栈中
void StackPushStack(struct Stack* stk, DataType dt) {
struct StackNode* vtx = (struct StackNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct StackNode)); // 创建新节点
vtx->next = stk->head; // 新节点的下一个节点指针指向栈顶节点
vtx->data = dt; // 设置新节点的数据为传入的数据
stk->head = vtx; // 更新栈顶节点为新节点
++stk->size; // 增加栈的大小
}
// 将栈顶元素弹出栈
void StackPopStack(struct Stack* stk) {
struct StackNode* temp = stk->head; // 临时存储栈顶节点指针
stk->head = temp->next; // 更新栈顶节点为下一个节点
free(temp); // 释放原栈顶节点的内存
--stk->size; // 减少栈的大小
}
// 获取栈顶元素的值
DataType StackGetTop(struct Stack* stk) {
return stk->head->data; // 返回栈顶节点的数据
}
int main() {
// 创建一个栈
struct Stack myStack;
myStack.head = NULL; // 初始化栈顶节点指针为空
myStack.size = 0; // 初始化栈的大小为0
// 将元素压入栈中
StackPushStack(&myStack, 10);
StackPushStack(&myStack, 20);
StackPushStack(&myStack, 30);
// 获取栈顶元素并打印
DataType top = StackGetTop(&myStack);
printf("Top element: %d\n", top);
// 从栈中弹出一个元素
StackPopStack(&myStack);
// 获取新的栈顶元素并打印
top = StackGetTop(&myStack);
printf("Top element after popping: %d\n", top);
return 0;
}例题1
括号的最大嵌套深度
提示
如果字符串满足以下条件之一,则可以称之为 有效括号字符串(valid parentheses string,可以简写为 VPS):
- 字符串是一个空字符串
"",或者是一个不为"("或")"的单字符。- 字符串可以写为
AB(A与B字符串连接),其中A和B都是 有效括号字符串 。- 字符串可以写为
(A),其中A是一个 有效括号字符串 。类似地,可以定义任何有效括号字符串
S的 嵌套深度depth(S):
depth("") = 0depth(C) = 0,其中C是单个字符的字符串,且该字符不是"("或者")"depth(A + B) = max(depth(A), depth(B)),其中A和B都是 有效括号字符串depth("(" + A + ")") = 1 + depth(A),其中A是一个 有效括号字符串例如:
""、"()()"、"()(()())"都是 有效括号字符串(嵌套深度分别为 0、1、2),而")("、"(()"都不是 有效括号字符串 。给你一个 有效括号字符串
s,返回该字符串的s嵌套深度 。示例 1:
输入:s = "(1+(2*3)+((8)/4))+1" 输出:3 解释:数字 8 在嵌套的 3 层括号中。示例 2:
输入:s = "(1)+((2))+(((3)))" 输出:3提示:
1 <= s.length <= 100s由数字0-9和字符'+'、'-'、'*'、'/'、'('、')'组成- 题目数据保证括号表达式
s是 有效的括号表达式
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct {
char* stack;
int top;
} Stack;
Stack* createStack(int capacity) {
Stack* stack = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
stack->stack = (char*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(char));
stack->top = -1;
return stack;
}
void push(Stack* stack, char element) {
stack->stack[++stack->top] = element;
}
char pop(Stack* stack) {
return stack->stack[stack->top--];
}
int isEmpty(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == -1;
}
int maxDepth(char* s) {
int maxDepth = 0;
int currentDepth = 0;
int i = 0;
Stack* stack = createStack(100);
while (s[i] != '\0') {
if (s[i] == '(') {
push(stack, s[i]);
currentDepth++;
if (currentDepth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = currentDepth;
}
} else if (s[i] == ')') {
pop(stack);
currentDepth--;
}
i++;
}
return maxDepth;
}
int main() {
char s[] = "(1+(2*3)+((8)/4))+1";
int depth = maxDepth(s);
printf("The maximum nesting depth is: %d\n", depth);
return 0;
}例题2
回文链表
给定一个链表的 头节点
head,请判断其是否为回文链表。如果一个链表是回文,那么链表节点序列从前往后看和从后往前看是相同的。
示例 1:
输入: head = [1,2,3,3,2,1] 输出: true示例 2:
输入: head = [1,2] 输出: false提示:
- 链表 L 的长度范围为
[1, 105]0 <= node.val <= 9
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
// 创建一个堆栈结构
struct Stack {
int* array;
int top;
int capacity;
};
// 初始化堆栈
struct Stack* createStack(int capacity) {
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
stack->array = (int*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(int));
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
return stack;
}
// 判断堆栈是否为空
bool isEmpty(struct Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == -1;
}
// 判断堆栈是否已满
bool isFull(struct Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == stack->capacity - 1;
}
// 将元素压入堆栈
void push(struct Stack* stack, int value) {
if (isFull(stack)) {
return;
}
stack->array[++stack->top] = value;
}
// 从堆栈中弹出元素
int pop(struct Stack* stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
return -1;
}
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
// 判断链表是否为回文链表
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return true;
}
// 统计链表的长度
int length = 0;
struct ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
length++;
curr = curr->next;
}
// 将链表前半部分的值压入堆栈
struct Stack* stack = createStack(length / 2);
curr = head;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < length / 2; i++) {
push(stack, curr->val);
curr = curr->next;
}
// 如果链表长度为奇数,跳过中间节点
if (length % 2 == 1) {
curr = curr->next;
}
// 比较链表后半部分的值与堆栈中弹出的值是否相等
while (curr) {
int value = pop(stack);
if (value != curr->val) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
// 创建链表 [1, 2, 3, 2, 1]
struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->val = 1;
head->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->val = 2;
head->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->next->val = 3;
head->next->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->next->next->val = 2;
head->next->next->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->next->next->next->val = 1;
head->next->next->next->next->next = NULL;
bool isPalin = isPalindrome(head);
if (isPalin) {
printf("The linked list is a palindrome.\n");
} else {
printf("The linked list is not a palindrome.\n");
}
// 释放链表的内存
struct ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
struct ListNode* temp = curr;
curr = curr->next;
free(temp);
}
return 0;
}例题3
反转链表
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000]-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
// 创建一个堆栈结构
struct Stack {
int* array;
int top;
int capacity;
};
// 初始化堆栈
struct Stack* createStack(int capacity) {
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
stack->array = (int*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(int));
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
return stack;
}
// 判断堆栈是否为空
bool isEmpty(struct Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == -1;
}
// 判断堆栈是否已满
bool isFull(struct Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == stack->capacity - 1;
}
// 将元素压入堆栈
void push(struct Stack* stack, int value) {
if (isFull(stack)) {
return;
}
stack->array[++stack->top] = value;
}
// 从堆栈中弹出元素
int pop(struct Stack* stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
return -1;
}
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
// 反转链表
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return head;
}
// 统计链表的长度
int length = 0;
struct ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
length++;
curr = curr->next;
}
// 将链表的值压入堆栈
struct Stack* stack = createStack(length);
curr = head;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < length; i++) {
push(stack, curr->val);
curr = curr->next;
}
// 将堆栈弹出的值给链表
curr = head;
while (curr) {
curr->val = pop(stack);
curr = curr->next;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
// 创建链表 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->val = 1;
head->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->val = 2;
head->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->next->val = 3;
head->next->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->next->next->val = 4;
head->next->next->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->next->next->next->next->val = 5;
head->next->next->next->next->next = NULL;
head=reverseList(head);
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%d ",head->val);
head=head->next;
}
// 释放链表的内存
struct ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
struct ListNode* temp = curr;
curr = curr->next;
free(temp);
}
return 0;
}