本文介绍基于STM32F103ZET6+MAX30102心率血氧测量+0.96寸OLED(7针)显示(完整程序代码见文末链接)
一、简介
MAX30102是一个集成的脉搏血氧仪和心率监测仪生物传感器的模块。它集成了一个红光LED和一个红外光LED、光电检测器、光器件,以及带环境光抑制的低噪声电子电路。
MAX30102采用一个1.8V电源和一个独立的5.0V用于内部LED的电源,应用于可穿戴设备进行心率和血氧采集检测,佩戴于手指点耳垂和手腕处。
标准的I2C兼容的通信接口可以将采集到的数值传输给Arduino、STM32、STC51等单片机进行心率和血氧计算。此外,该芯片还可以通过软件关断模块,待机电流接近为零,实现电源始终维持供电状态。
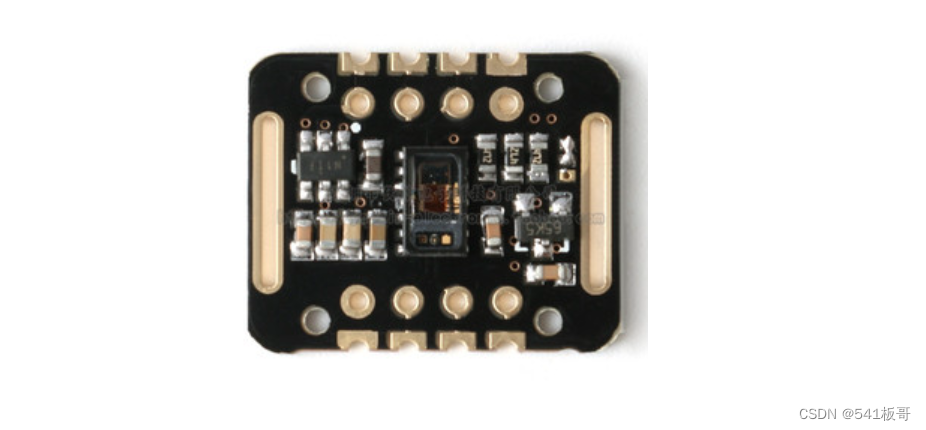
模块主要参数:
LED峰值波长器 :660nm/880nm
LED供电电压 : 3.3 ~ 5V
检测信号类型 : 光反射信号(PPG)
输出信号接口 : I2C接口
通信接口电压 : 1.8 ~ 3.3V ~ 5V(可选)
工作原理
光溶积法:利用人体组织在血管搏动时造成透光率不同来进行脉搏和血氧饱和度测量
光源:采用对动脉血中痒合血红蛋白(HbO2)和血红蛋白(Hb)有选择性的特定波长的发光二极管
透光率转化为电信号:动脉搏动充血容积变化导致这束光的透光率发送改变,此时由光电变换接收经人体组织反射光线,转变为电信号并将其放大输出。
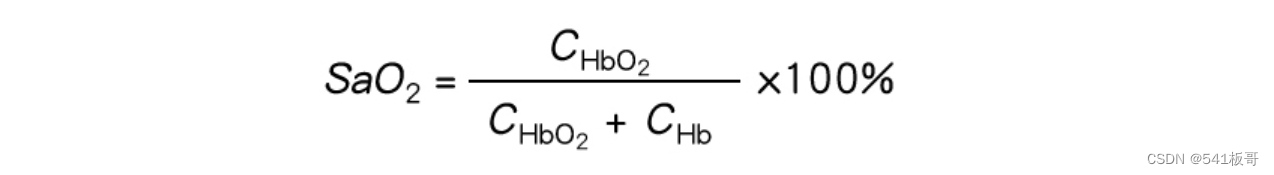
模块原理图
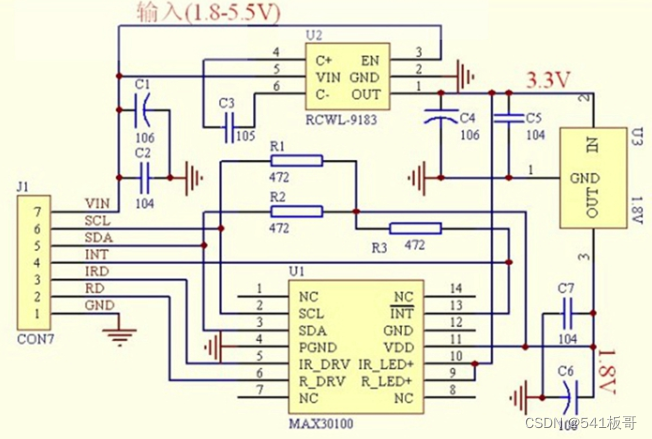
引脚说明
| 管脚定义 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| VIN | 电源输入 1.6V-5.5V,一般3.3V |
| SDA | IIC-SDA |
| SCL | IIC-SCL |
| GND | 地 |
| INT | INT 低电平有效中断(漏极开路)MAX30102 的中断引脚 |
| IRD | IR_DRV IR LED阴极和LED驱动器连接点,一般NC |
| RD | R_DRV 红色LED阴极和LED驱动器连接点,一般NC |
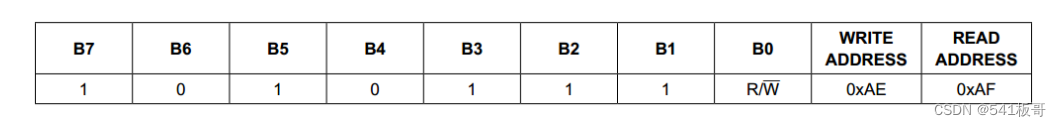
通讯协议
本模块采用I2C通讯方式,具有I2C/SMBus兼容的2线制由串行数据线(SDA)和串行时钟线(SCL),时钟速率高达400kHz。
设备地址:
本文主要介绍基于STM32F103ZET6和实现的MAX30102的心率和血氧测量,并显示在0.96寸的OLED(7针)屏幕上
二、接线图
设计中涉及STM32和MAX30102链接以及和OLED的管脚连接,具体连接脚说明如下:
STM32F103ZET6+MAX30102接线
| STM32F103ZET6 | MAX30102 |
|---|---|
| 3.3V | Vin |
| GND | GND |
| PC7 | SCL |
| PC8 | SDA |
| PC9 | INT |
STM32F103ZET6+0.96寸OLED接线,其中OLED选用的是7针OLED-4SPI通信
| STM32F103ZET6 | 0.96寸OLED(7针) |
|---|---|
| 3.3V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| PA5 | SCL/D0 |
| PA6 | SDA/D1 |
| PA3 | RST |
| PA4 | DC |
| PA2 | CS |
三、代码函数(完整工程文件见文末连接)
主函数,主要实现心率和血氧测量并显示在OLED屏幕,且当超过阈值后会蜂鸣器报警
int main(void)
{
//variables to calculate the on-board LED brightness that reflects the heartbeats
uint32_t un_min, un_max, un_prev_data;
int i;
int32_t n_brightness;
float f_temp;
// u8 temp_num=0;
u8 temp[6];
u8 str[100];
u8 dis_hr=0,dis_spo2=0;
NVIC_Configuration();
delay_init(); //延时函数初始化
uart_init(115200); //串口初始化为115200
LED_Init();
BEEP_Init();
//OLED
OLED_Init();
OLED_ShowString(0,0," initializing ",16);
OLED_Refresh_Gram();//更新显示到OLED
max30102_init();
printf("\r\n MAX30102 init \r\n");
un_min=0x3FFFF;
un_max=0;
n_ir_buffer_length=500; //buffer length of 100 stores 5 seconds of samples running at 100sps
//read the first 500 samples, and determine the signal range
for(i=0;i<n_ir_buffer_length;i++)
{
while(MAX30102_INT==1); //wait until the interrupt pin asserts
max30102_FIFO_ReadBytes(REG_FIFO_DATA,temp);
aun_red_buffer[i] = (long)((long)((long)temp[0]&0x03)<<16) | (long)temp[1]<<8 | (long)temp[2]; // Combine values to get the actual number
aun_ir_buffer[i] = (long)((long)((long)temp[3] & 0x03)<<16) |(long)temp[4]<<8 | (long)temp[5]; // Combine values to get the actual number
if(un_min>aun_red_buffer[i])
un_min=aun_red_buffer[i]; //update signal min
if(un_max<aun_red_buffer[i])
un_max=aun_red_buffer[i]; //update signal max
}
un_prev_data=aun_red_buffer[i];
//calculate heart rate and SpO2 after first 500 samples (first 5 seconds of samples)
maxim_heart_rate_and_oxygen_saturation(aun_ir_buffer, n_ir_buffer_length, aun_red_buffer, &n_sp02, &ch_spo2_valid, &n_heart_rate, &ch_hr_valid);
while(1)
{
i=0;
un_min=0x3FFFF;
un_max=0;
//dumping the first 100 sets of samples in the memory and shift the last 400 sets of samples to the top
for(i=100;i<500;i++)
{
aun_red_buffer[i-100]=aun_red_buffer[i];
aun_ir_buffer[i-100]=aun_ir_buffer[i];
//update the signal min and max
if(un_min>aun_red_buffer[i])
un_min=aun_red_buffer[i];
if(un_max<aun_red_buffer[i])
un_max=aun_red_buffer[i];
}
//take 100 sets of samples before calculating the heart rate.
for(i=400;i<500;i++)
{
un_prev_data=aun_red_buffer[i-1];
while(MAX30102_INT==1);
max30102_FIFO_ReadBytes(REG_FIFO_DATA,temp);
aun_red_buffer[i] = (long)((long)((long)temp[0]&0x03)<<16) | (long)temp[1]<<8 | (long)temp[2]; // Combine values to get the actual number
aun_ir_buffer[i] = (long)((long)((long)temp[3] & 0x03)<<16) |(long)temp[4]<<8 | (long)temp[5]; // Combine values to get the actual number
if(aun_red_buffer[i]>un_prev_data)
{
f_temp=aun_red_buffer[i]-un_prev_data;
f_temp/=(un_max-un_min);
f_temp*=MAX_BRIGHTNESS;
n_brightness-=(int)f_temp;
if(n_brightness<0)
n_brightness=0;
}
else
{
f_temp=un_prev_data-aun_red_buffer[i];
f_temp/=(un_max-un_min);
f_temp*=MAX_BRIGHTNESS;
n_brightness+=(int)f_temp;
if(n_brightness>MAX_BRIGHTNESS)
n_brightness=MAX_BRIGHTNESS;
}
//send samples and calculation result to terminal program through UART
if(ch_hr_valid == 1 && n_heart_rate<120)//**/ ch_hr_valid == 1 && ch_spo2_valid ==1 && n_heart_rate<120 && n_sp02<101
{
dis_hr = n_heart_rate;
dis_spo2 = n_sp02;
}
else
{
dis_hr = 0;
dis_spo2 = 0;
}
printf("HR=%i, ", n_heart_rate);
printf("HRvalid=%i, ", ch_hr_valid);
printf("SpO2=%i, ", n_sp02);
printf("SPO2Valid=%i\r\n", ch_spo2_valid);
}
maxim_heart_rate_and_oxygen_saturation(aun_ir_buffer, n_ir_buffer_length, aun_red_buffer, &n_sp02, &ch_spo2_valid, &n_heart_rate, &ch_hr_valid);
//显示刷新
LED0=0;
if(dis_hr == 0 && dis_spo2 == 0) //**dis_hr == 0 && dis_spo2 == 0
{
sprintf((char *)str,"HR:--- SpO2:--- ");//**HR:--- SpO2:---
}
else{
sprintf((char *)str,"HR:%3d SpO2:%3d ",dis_hr,dis_spo2);//**HR:%3d SpO2:%3d
}
OLED_ShowString(0,0,str,16);
OLED_Fill(0,23,127,63,0);
//红光在上,红外在下
dis_DrawCurve(aun_red_buffer,20);
dis_DrawCurve(aun_ir_buffer,0);
OLED_Refresh_Gram();//更新显示到OLED
}
}
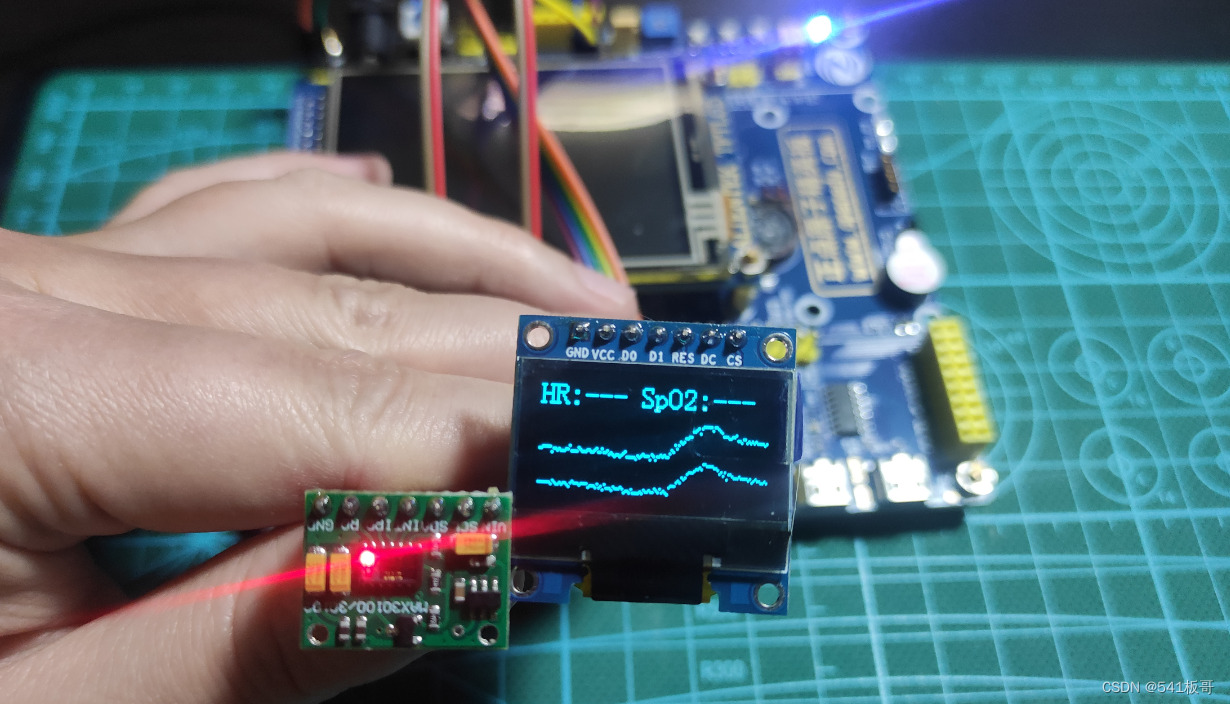
四、视频演示
MAX30102心率血氧测量
附完整代码程序资料
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1TaxlDzRbkNnz4guaJPrGnQ?pwd=6arw
提取码:6arw