我们在使用机器人的时候,总是习惯使用俯仰角来描述机器人末端姿态的变换。这样更直观,但是机器人为了插值方便计算,总是采用旋转矢量来来描述机器人的姿态。该旋转矢量及不直观,单一轴角度旋转时还可以理解,当两个轴或三个轴一起旋转,值的偏离很大。
1.找到机器人中如何描述旋转矢量和俯仰角

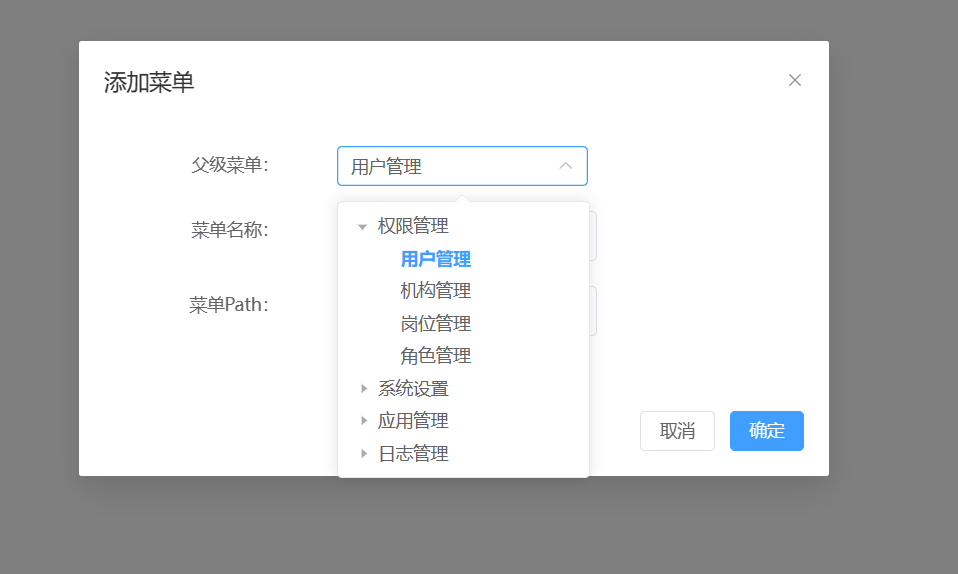
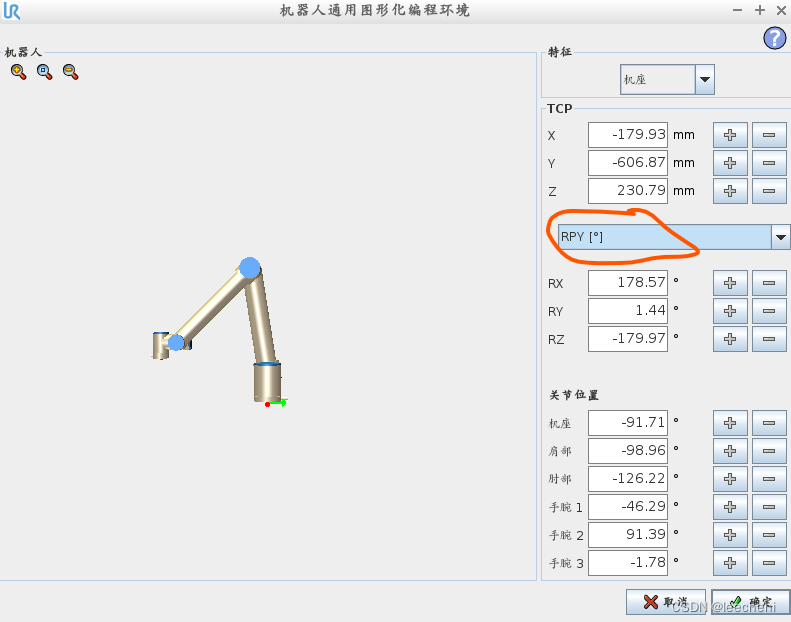
在此页面中,TCP中的RX,RY,RZ就是旋转矢量,而非俯仰角,点击此处任何输入框,可以跳转到点编辑界面。
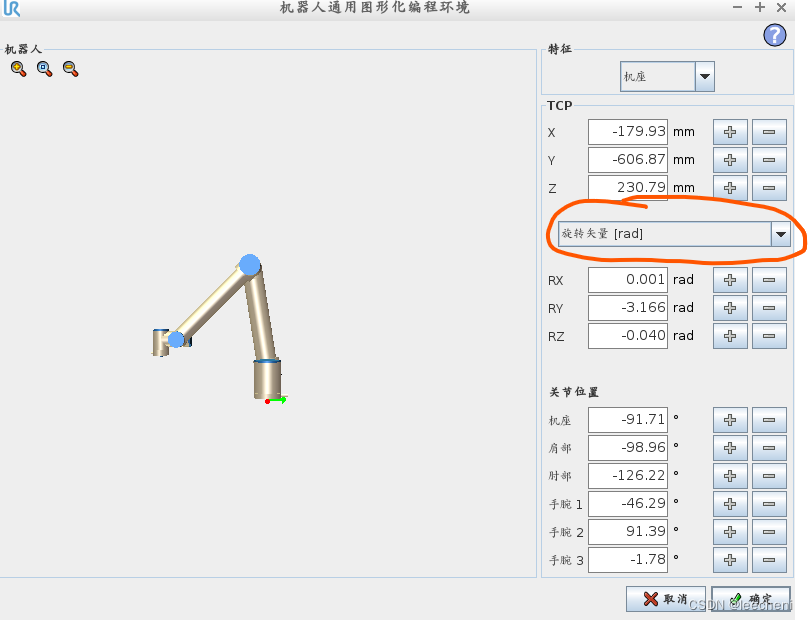
此处,明确显示了该值为旋转矢量,下拉选择俯仰角,即可以通过编辑俯仰角,改变旋转矢量。
 2.如何在UR-script,对应的指令是哪一个呢?
2.如何在UR-script,对应的指令是哪一个呢?
在e系列中对应的是如下截图,CB系列中也是类似的,可以自己查询。通过这两个指令,我们就可以在工控机中自己的代码中嵌入,计算完机器人的姿态后,进行最后的旋转。

3.这些概念的深层解释,官网描述如下
EXPLANATION ON ROBOT ORIENTATION
This is an explanation on robot orientation
A robot has position and orientation. In particular, one of advantages in 6-axis robotic arm is to pose diverse orientation. This article is written for better understanding of robot orientation.
机器人具有位置和方向。特别是,六轴机械臂的一个优点是能够呈现不同的方向。本文旨在更好地理解机器人的方向。
Rotation Matrix
旋转矩阵
A rotation is represented in a matrix. In Cartesian space, a robot orientation is decided by a combination of rotations in X, Y, and Z direction, and we can have a 3-by-3 rotation matrix for each orientation.
旋转以矩阵表示。在笛卡尔空间中,机器人的方向由X、Y和Z方向的旋转组合决定,我们可以为每个方向设置一个3乘3的旋转矩阵。

(Refer to Rotation matrix, wikipedia)
ROTATION VECTOR
旋转矢量 (轴角/四元数)
In Universal Robots, the axis-angle representation is used for robot orientation. As a brief explanation, let me assume that there is a direction vector. Around the vector, an orientation can be rotated by a certain angle, theta. As a result of rotation, we can have a different orientation. The axis-angle representation is useful for robotics calculation such as kinematics and dynamics.
在Universal Robots中,轴角表示用于机器人方向。简单来说,假设有一个方向向量。围绕该向量,方向可以旋转一定的角度θ。作为旋转的结果,我们可以得到不同的方向。轴角表示对于机器人运动学和动力学等计算很有用。

Rotation vector is a representation of the unit direction vector multiplied by the angle in the axis-angle representation.
旋转向量是单位方向向量乘以轴角表示中的角度的表示。
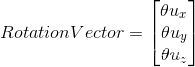
In order to define an orientation with the axis-angle representation, we need 4 values in total; three elements of unit direction vector and rotation angle. That is the reason why the values of rotation vector are not intuitive.
为了用轴角表示法定义方向,我们总共需要4个值;单位方向向量和旋转角度的3个元素。这就是为什么旋转向量的值不直观的原因。
(Refer to Axis-angle representation, wikipedia)
RPY
You may be more familiar with roll, pitch, and yaw to represent the robot orientation. In RPY, the order of rotation should be critical. For instance, despite the same amount of angles, the result of rotation roll->pitch would be different from that of pitch->roll.
你可能更熟悉用roll、pitch和yaw来表示机器人的方向。在RPY中,旋转顺序至关重要。例如,尽管角度相同,但旋转roll->pitch的结果与pitch->roll的结果不同。
Although the rotation vector is used in Universal Robots by default, you should be able to see the RPY values in Move tab of Polyscope. In addition, you can use the URScript functions to convert the representation between RPY and rotation vector.
虽然Universal Robots默认使用旋转矢量,但您应该能够在Polyscope的Move选项卡中看到RPY值。此外,您可以使用URScript函数在RPY和旋转矢量之间进行转换。
rotvec2rpy(rotation vector)
rpy2rotvec(rpy vector)
TRANSFORMATION MATRIX
变换矩阵
For calculation of kinematics, a transformation matrix can be defined as a 4-by-4 matrix, consisting of rotation matrix and position vector. The rotation vector and/or RPY will be converted to the rotation matrix. We can calculate the robot position and orientation based on the transformation matrix multiplication.
为了计算运动学,可以将变换矩阵定义为4乘4矩阵,由旋转矩阵和位置向量组成。旋转向量和/或RPY将被转换为旋转矩阵。我们可以根据变换矩阵的乘法计算机器人的位置和方向。
![]()
pose_trans() is using the principle of the transformation matrix. The calculated position and orientation is referred to the tool frame. With respect to pose_add(), the calculated position is ths sum of two position inputs, but the resulted orientation is the matrix multiplication of two rotation matrix. In other words, in pose_add(), the position is corresponding to the base frame but the orientation is referred to the tool frame.
pose_trans()使用的是变换矩阵的原理。计算出的位置和方向是指向工具坐标系的。相对于pose_add(),计算出的位置是两个位置输入的总和,但产生的方向是两个旋转矩阵的矩阵乘积。换句话说,在pose_add()中,位置对应于基座标系,但方向是指向工具坐标系的。