1、概念
1.1 介绍
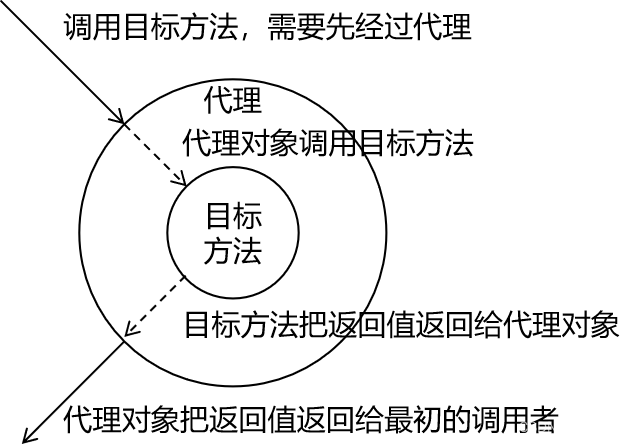
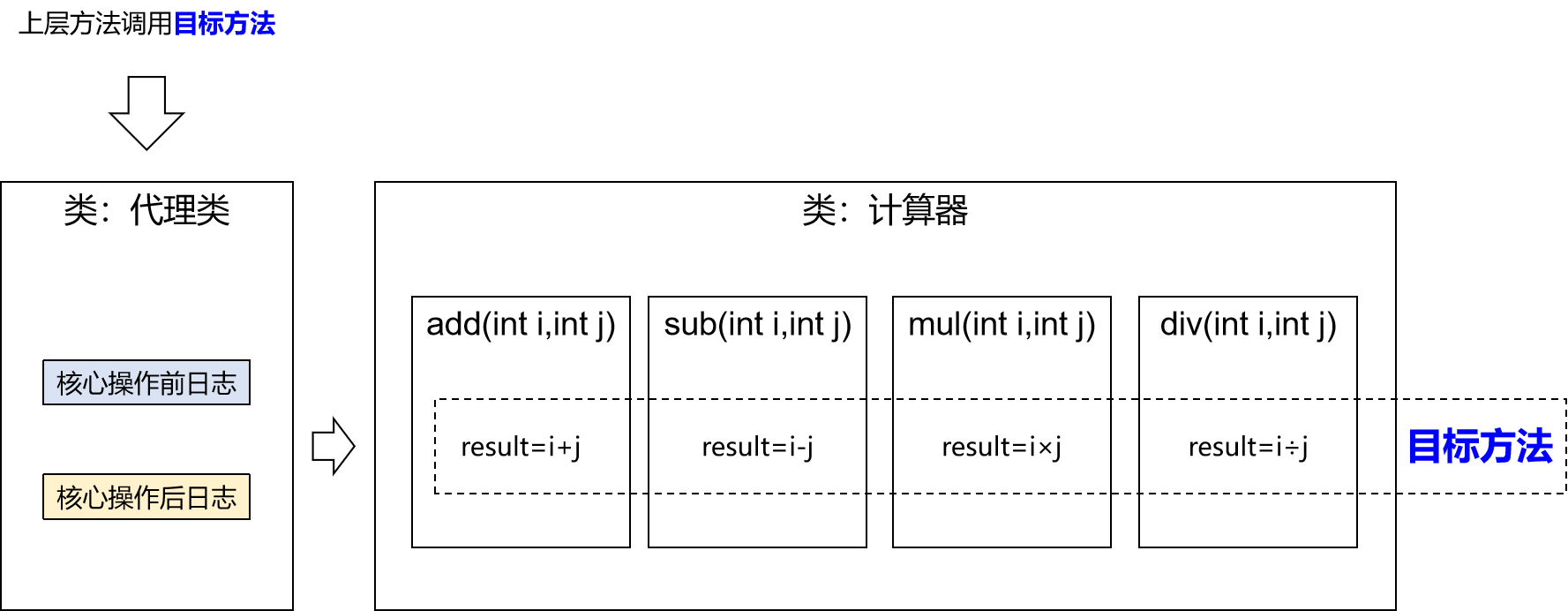
二十三种设计模式中的一种,属于结构型模式。它的作用就是通过提供一个代理类,让我们在调用目标方法的时候,不再是直接对目标方法进行调用,而是通过代理类间接调用。让不属于目标方法核心逻辑的代码从目标方法中剥离出来——解耦。调用目标方法时先调用代理对象的方法,减少对目标方法的调用和打扰,同时让附加功能能够集中在一起也有利于统一维护。
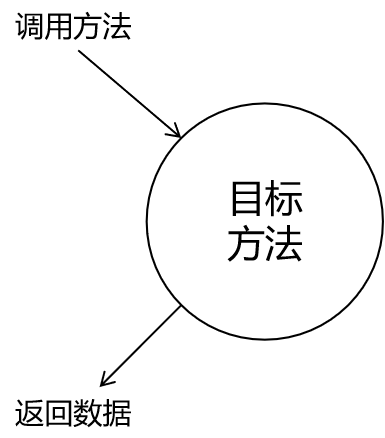
使用代理后:

②生活中的代理
- 广告商找大明星拍广告需要经过经纪人
- 合作伙伴找大老板谈合作要约见面时间需要经过秘书
- 房产中介是买卖双方的代理
1.2 相关术语
- 代理:将非核心逻辑剥离出来以后,封装这些非核心逻辑的类、对象、方法。
- 目标:被代理“套用”了非核心逻辑代码的类、对象、方法。
2 静态代理
public interface Calculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
package com.giser.java.spring6.calcu.impl;
import com.giser.java.spring6.calcu.Calculator;
/**
* @author giserDev
* @description 基础实现
* @date 2024-01-06 23:41:55
*/
public class CalculatorImpl implements Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
return result;
}
}
创建静态代理类
package com.giser.java.spring6.calcu.impl;
import com.giser.java.spring6.calcu.Calculator;
/**
* @author giserDev
* @description
* 提出问题
*
* ①现有代码缺陷
*
* 针对带日志功能的实现类,我们发现有如下缺陷:
*
* - 对核心业务功能有干扰,导致程序员在开发核心业务功能时分散了精力
* - 附加功能分散在各个业务功能方法中,不利于统一维护
*
* ②解决思路
*
* 解决这两个问题,核心就是:解耦。我们需要把附加功能从业务功能代码中抽取出来。
*
* ③困难
*
* 解决问题的困难:要抽取的代码在方法内部,靠以前把子类中的重复代码抽取到父类的方式没法解决。所以需要引入新的技术。
* @date 2024-01-06 23:43:25
*/
public class CalculatorLogImpl implements Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("[日志] add 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j);
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
System.out.println("[日志] add 方法结束了,结果是:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("[日志] sub 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j);
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
System.out.println("[日志] sub 方法结束了,结果是:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("[日志] mul 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j);
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
System.out.println("[日志] mul 方法结束了,结果是:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("[日志] div 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j);
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);
System.out.println("[日志] div 方法结束了,结果是:" + result);
return result;
}
}
静态代理的问题:
静态代理确实实现了解耦,但是由于代码都写死了,完全不具备任何的灵活性。就拿日志功能来说,将来其他地方也需要附加日志,那还得再声明更多个静态代理类,那就产生了大量重复的代码,日志功能还是分散的,没有统一管理。
提出进一步的需求:将日志功能集中到一个代理类中,将来有任何日志需求,都通过这一个代理类来实现。这就需要使用动态代理技术了。
3 动态代理
package com.giser.spring6.calcu.impl.dynamicproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author giserDev
* @description 代理工厂类
* @date 2024-01-06 23:52:21
*/
public class DynamicProxyFactory {
/**
* 被持有的被代理对象
*/
private Object target;
public DynamicProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
/**
* 创建代理对象
* @return 代理对象
*/
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
// 代理对象的类加载器
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
// 代理对象实现的接口列表
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
// 处理器
new InvocationHandler() {
/**
*
* @param proxy the proxy instance that the method was invoked on
* 代理对象
*
* @param method the {@code Method} instance corresponding to
* the interface method invoked on the proxy instance. The declaring
* class of the {@code Method} object will be the interface that
* the method was declared in, which may be a superinterface of the
* proxy interface that the proxy class inherits the method through.
* 代理对象需要实现的方法
*
* @param args an array of objects containing the values of the
* arguments passed in the method invocation on the proxy instance,
* or {@code null} if interface method takes no arguments.
* Arguments of primitive types are wrapped in instances of the
* appropriate primitive wrapper class, such as
* {@code java.lang.Integer} or {@code java.lang.Boolean}.
* method对应的方法参数
*
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",参数:"+ Arrays.toString(args));
result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",结果:"+ result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",异常:"+e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",方法执行完毕");
}
return result;
}
}
);
}
}
测试
package com.giser.spring6;
import com.giser.spring6.calcu.Calculator;
import com.giser.spring6.calcu.impl.CalculatorImpl;
import com.giser.spring6.calcu.impl.dynamicproxy.DynamicProxyFactory;
/**
* @author giserDev
* @description 动态代理测试
* @date 2024-01-07 00:02:54
*/
public class DynamicProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DynamicProxyFactory dynamicProxyFactory = new DynamicProxyFactory(new CalculatorImpl());
Calculator proxy = (Calculator) dynamicProxyFactory.getProxy();
int add = proxy.add(1, 3);
}
}