1 概述
ThreadPoolExecutor类可以非常方便的创建线程池对象,而不需要程序员设计大量的new实例化Thread相关的代码。
2 队列LinkedBlockingQueue的使用
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue();
queue.add("线程1");
queue.add("线程2");
queue.add("线程3");
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
}
}
LinkedBlockingQueue队列最简单的使用就像ArrayList一样,使用add()保存数据,使用poll()获取数据。从上面的运行结果可以发现,LinkedBlockingQueue队列的容量好像是可以扩充的,其实并不是这样,因为在构造方法时传入了Integer的最大值,源代码如下:
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}所以从本质上讲, LinkedBlockingQueue队列是有界的,下面验证其有界的实现:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue(2);
queue.add("线程1");
queue.add("线程2");
queue.add("线程3");
}
}

最大容量不能超过2。
3 ArrayBlockingQueue队列的使用
ArrayBlockingQueue队列在实例化时必须传入初始容量,并且容量不可以扩充,超出初始容量就出现异常。验证异常情况
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3);
queue.add("线程1");
queue.add("线程2");
queue.add("线程3");
queue.add("线程4");
}
}
正常使用
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayBlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);
queue.add("线程1");
queue.add("线程2");
queue.add("线程3");
queue.add("线程4");
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.poll()+" " + queue.size());
}
} 4 SynchronousQueue队列的使用
4 SynchronousQueue队列的使用
SynchronousQueue队列并不存储任何数据,通过该队列可以在2个线程之间直接传送数据。
public class Test5 {
private static SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread put = new Thread(){
public void run(){
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String putString = "线程"+Math.random();
queue.put(putString);
System.out.println("putstring = " + putString);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
};
put.start();
Thread get = new Thread(){
public void run(){
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String takeString = "" + queue.take();
System.out.println("takeString = " + takeString );
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
};
get.start();
}
}
通过上面3个队列进行实验,可以分析以下特点:
1、LinkedBlockingQueue和ArrayBlockingQueue可以存储多个数据,容量是有界限的。
2、SynchronousQueue不可以存储多个数据,没有容量的概念。
4 构造方法参数详解
ThreadPoolExecutor类最常使用的构造方法如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}解释如下:
1、corePoolSize:池中至少要保留的线程数,该属性就是定义corePool核心池的大小。
2、maximumPoolSize:池中允许的最大线程数,maximumPoolSize包含corePoolSize。
3、keepAliveTime:当线程数量大于corePoolSize值时,在没有超过执行的时间内是不能从线程池中将空闲线程删除的,如果超过这个时间单位,则删除空闲线程。“能删除的空闲线程”范围是corePoolSize~maximumPoolSize之间,也就是corePool之外的线程。
4、unit:keepAliveTime参数的时间单位。
5、workQueue:执行前用于保持任务的队列。此队列仅保持由execute方法提交的Runnable任务。
注意:所谓的空闲线程就是没有执行任务的线程,不管这个线程在哪里,只要不执行任务,就是空闲的。下面对这些参数进行分析:
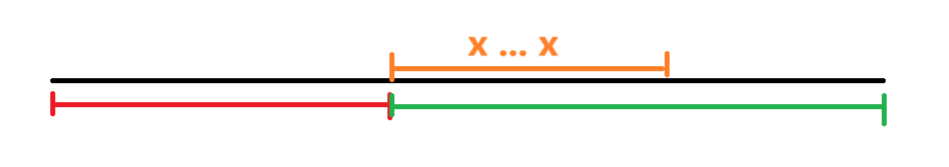
A 代表execute(runnable)要执行的task任务的数量,如下图

B 代表corePoolSize数量,如下图
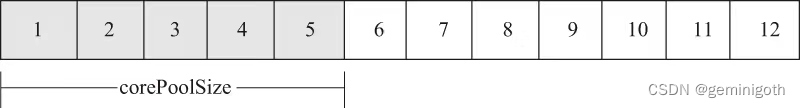
C 代表maximumPoolSize数量,如下图

D 代表A-B(假设A>B)的值
构造方法中5个参数之间都有关联关系,但从使用效果来讲,不同类型的队列能影响ThreadPool线程池执行的行为,所以后面的分析过程就以LinkedBlockingQueue和SynchronousQueue为主线,总结如下。
4.1 使用无参LinkedBlockingQueue队列的情况
注意,使用无参new LinkedBlockingQueue队列的特点就是只使用核心池中的线程执行任务。
(1)如果A<=B,立即在corePool核心池中创建线程并运行任务,这些任务并不会放入LinkedBlockingQueue中,构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit将会被忽略。
(2)如果A > B&& A <= C,构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit将会被忽略,并把D放入LinkedBlockingQueue中等待被核心池中的线程执行。
(3)如果A > C ,构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit将会被忽略,并把D放入LinkedBlockingQueue中等待被核心池中的线程执行。
4.2 使用SynchronousQueue队列的情况
(1)如果A<=B,立即在corePool核心池中创建线程并运行任务,这些任务并不会放入SynchronousQueue中,构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit将会被忽略。
(2)如果A > B&& A <= C,则构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit有效,并且拿上创建最多C个线程运行这些任务,而不把D放入SynchronousQueue队列中,D执行完任务后在指定的keepAliveTime时间发生超时时,将D进行清除,如果D在keepAliveTime时间之后未完成任务,则在D完成任务后进行清除。
4.3 使用new LinkedBlockingQueue(xxx)队列有参的情况下。其中,参数xxx代表队列的最大存储长度。
注意,使用有参new LinkBlockingQueue(xxx)队列的执行特点时核心池中的线程和maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 现成有可能一起执行任务,也就是最多执行任务的线程数量就是maximumPoolSize。另外在使用有参new LinkedBlockingQueue(xxx)队列时,执行的流程是先判断corePoolSize大小够不够,如果不够则向new LinkedBlockingQueue(xxx)队列中存储,如果new LinkedBlockingQueue(xxx)队列中放不下,则将剩余的任务尝试向C - B 中存放,如果C - B放不下,就报异常。
(1)如果 A <= B,立即在corePool核心池中创建线程并运行任务,这些任务并不会放入LinkedBlockingQueue中,构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit将会被忽略。
(2)如果 A > B && (A - B) <=xxx,立即在corePoolSize核心池中创建线程并运行任务,构造方法参数maximumPoolSize、keepAliveTime和unit将会被忽略,并把(A - B)方法LinkedBlockingQueue队列中等待被核心池中的线程执行。
5 shutdown()和shutdownNow()
public void shutdown()方法的作用是使当前未执行完的任务继续执行,而队列中未执行的任务也会继续执行,不删除队列中的任务,不再允许添加新的任务,同时shutdown()方法不会阻塞。
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow()方法的作用是使当前未执行完的任务继续执行,而队列中未执行的任务不再执行,删除队列中的任务,不再允许添加新的酿热物,同时shutdownNow()方法不会阻塞。
public class MyRunnable1 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("开始 "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("结束 "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable1 myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable1();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,10,0L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
System.out.println("main end");
}
} 
线程池中没有任何的任务执行,继续实验。
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable1 myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable1();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,10,0L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
System.out.println("main end");
}
} 
任务执行完成后,线程池继续等待新的任务。
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable1 myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable1();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(7,10,0L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
pool.shutdown();
System.out.println("main end");
}
} 
程序运行的效果是main线程输出“mian end”后,main线程立即销毁,线程池在4秒后销毁,进进程结束。
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable1 myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable1();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,9999,9999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
Thread.sleep(1000);
pool.shutdown();
pool.execute(myRunnable1);
System.out.println("main end");
}
} 
从运行结果可知,程序执行了4个任务,最后一个任务抛出异常,因为执行了shutdown()方法不能添加新的任务,这个实验也证明执行shutdown方法后未将队列中的任务删除,直到全部任务运行结束。
下面验证shutdownNow()方法。
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("开始 "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE / 50; i++) {
String newString = new String();
Math.random();
Math.random();
Math.random();
Math.random();
Math.random();
Math.random();
}
System.out.println("结束 "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}
}public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,9999,9999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myRunnable);
pool.execute(myRunnable);
pool.execute(myRunnable);
pool.execute(myRunnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
pool.shutdownNow();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}

从控制台可以看出,2个任务被成功执行,其余两个任务被取消运行,并且进程销毁。
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,9999,9999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(myRunnable);
pool.execute(myRunnable);
pool.execute(myRunnable);
pool.execute(myRunnable);
Thread.sleep(1000);
pool.shutdownNow();
pool.execute(myRunnable);
System.out.println("main end");
}
} 
控制台信息代表2个任务被成功执行,其余2个任务被取消运行,而最后一个任务则拒绝执行,抛出异常,进程最后会被销毁。
6 List<Runnable> shutdownNow()方法的返回值
在调用List<Runnable> shutdownNow()方法后,队列中的任务被取消运行,shutdownNow()方法的返回值是List<Runnable>,List对象存储的是还未运行的任务,也就是被取消掉的任务,下面进行验证。
public class MyRunnableA implements Runnable{
private String username;
public MyRunnableA(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE / 500; i++) {
String newString1 = new String();
String newString5 = new String();
String newString6 = new String();
String newString7 = new String();
Math.random();
Math.random();
Math.random();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "任务完成");
}
}
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyRunnableA a1 = new MyRunnableA("A1");
MyRunnableA a2 = new MyRunnableA("A2");
MyRunnableA a3 = new MyRunnableA("A3");
MyRunnableA a4 = new MyRunnableA("A4");
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,10,30, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(a1);
pool.execute(a2);
pool.execute(a3);
pool.execute(a4);
Thread.sleep(1000);
List<Runnable> list = pool.shutdownNow();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
MyRunnableA a = (MyRunnableA) list.get(i);
System.out.println(a.getUsername() + "任务取消");
}
System.out.println("main end");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 
有两个任务被取消。
7 shutdown()和shutdownNow()与中断
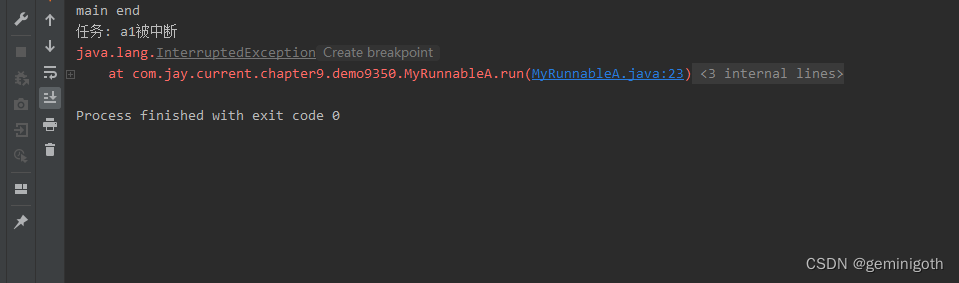
如果正在执行的任务使用if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() == true)和throw new InterruptedException()判断任务是否中断,那么在嗲用shutdown()后任务并不会被中断而是继续运行,当调用shutdownNow()方法后会将任务立即中断。
public class MyRunnableA implements Runnable{
private String username;
public MyRunnableA(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true){
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() == true){
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("任务: " + username + "被中断");
}
}
}public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnableA a1 = new MyRunnableA("a1");
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,10,30, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(a1);
Thread.sleep(2000);
pool.shutdown();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
程序运行后,线程池的任务并未中断,而是会继续运行。
public class Run2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnableA a1 = new MyRunnableA("a1");
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,10,30, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
pool.execute(a1);
Thread.sleep(2000);
pool.shutdownNow();
System.out.println("main end");
}
}







![[MySQL]视图索引以及连接查询案列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ddfc2e01211c4935934e7daaf4cd67de.png)