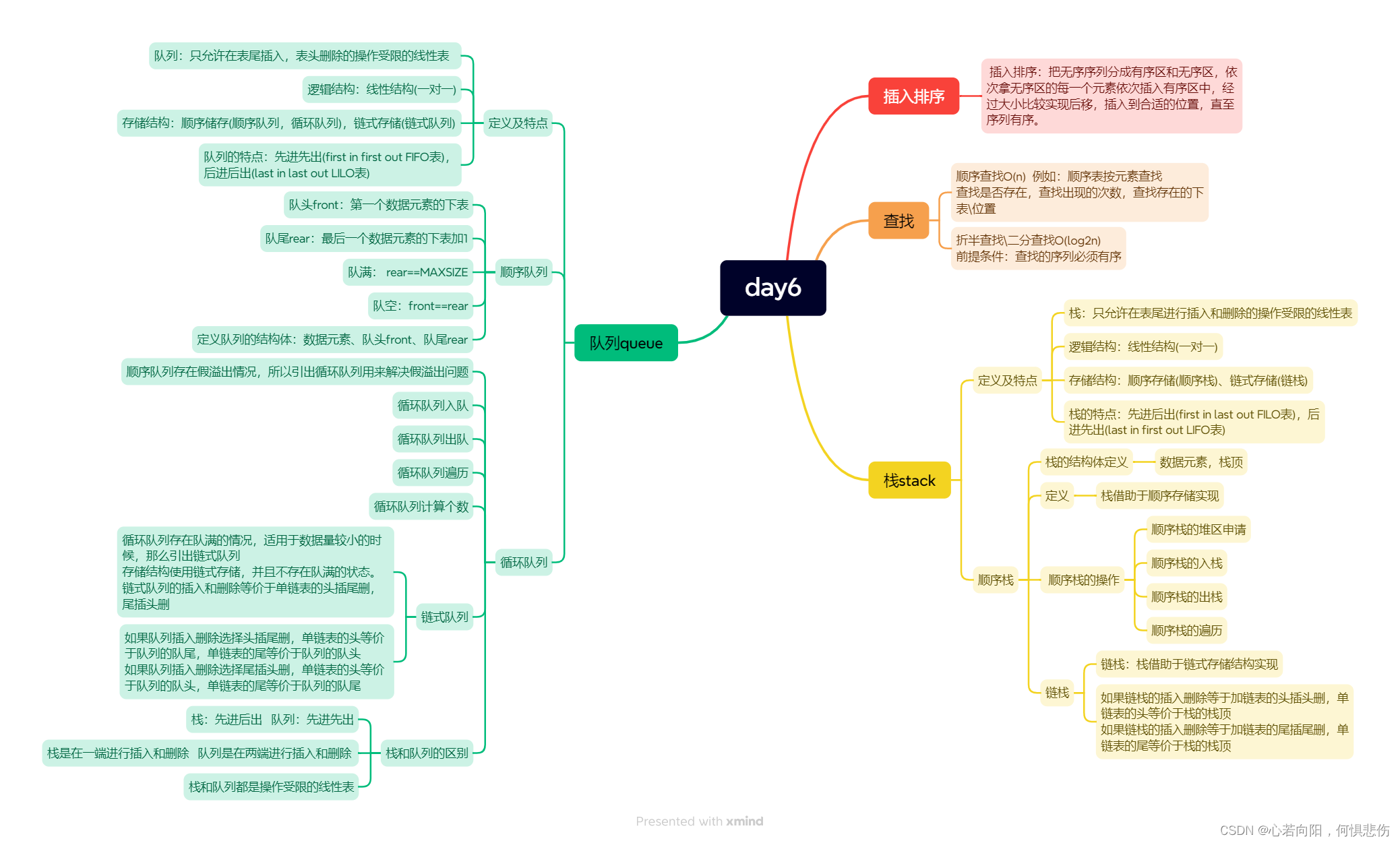
1. LinkedList简介
LinkedList是List接口的实现类,基于双向链表实现,继承自AbstractSequentialList类,同时也实现了Cloneable、Serializable接口。此外还实现了Queue和Deque接口,可以作为队列或双端队列使用。

LinkedList的插入删除时间复杂度:
- 在头部或尾部插入删除元素,只需要修改头节点或尾节点的指针即可完成,时间复杂度为
O(1); - 在其他位置插入删除元素,需要遍历到指定位置,再修改指定节点的指针,平均要移动
n/2个位置,时间复杂度为O(n)。
LinkedList没有像ArrayList有RandomAccess接口的标记,因为LinkedList基于链表实现,链表节点之间的内存地址不连续,只能通过指针来定位,因此无法实现快速随机访问。
1.1. 常用方法
public class LinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
//添加元素
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.addFirst(1);
linkedList.add(3);
linkedList.add(4);
linkedList.addLast(5);
//获取元素
System.out.println(linkedList.get(1));
System.out.println(linkedList.getFirst());
System.out.println(linkedList.getLast());
//创建双端队列
Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList<>();
//元素入队
deque.offer("a");
deque.offer("b");
deque.offer("c");
//获取队头元素,但不删除队头元素
System.out.println(deque.peek());
//元素出队
String a = deque.poll();
System.out.println(a);
}
}
2. LinkedList核心源码分析
下面以JDK17的LinkedList代码进行分析。
2.1. 类属性
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
//LinkedList大小
transient int size = 0;
//首节点
transient Node<E> first;
//尾节点
transient Node<E> last;
}
LinkedList中的节点由Node定义:
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //节点值
Node<E> next; //后继节点
Node<E> prev; //前驱节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
2.2. 构造方法
//创建一个空链表对象
public LinkedList() {
}
//传入一个集合,将集合中的元素存入链表
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
2.3. 添加元素
因为LinkedList基于双向链表实现,并且实现了List和Queue接口,所有有多种添加元素的方法。
add方法
//在链表尾部添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//尾插法
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//在指定下标出添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
//检查下标是否越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
//如果下标是最后位置则使用尾插法
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
//在指定节点之前插入元素
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//插入链表头部
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//头插法
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//插入链表尾部
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
2.4. 获取元素
LinkedList提供了三个get方法获取元素。
//获取链表第一个元素
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//获取链表最后一个元素
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
//根据下标获取链表中的元素
public E get(int index) {
//检查下标是否越界
checkElementIndex(index);
//遍历链表,返回查找到的节点值
return node(index).item;
}
node方法就是用来遍历链表的:
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//如果下标小于LinkedList的一半则从头节点开始遍历,否则从尾节点开始
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
2.5. 删除元素
removeFirst方法,删除链表头节点;
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
//保留待删除节点的信息
final E element = f.item;
//记录待删除节点的后继
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
removeLast方法,删除链表尾节点;
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
//记录待删除节点的前驱
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//实际执行删除节点的方法
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
//保留待删除节点的信息,记录前驱和后继
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
2.6. 队列操作
返回队头元素:
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
队头元素出队,调用了删除链表头节点的方法:
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
入队,调用了add方法:
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
此外还有一些双端队列的方法,如offerFirst、offerLast、peekFirst、peekLast、pollFirst、pollLast等。