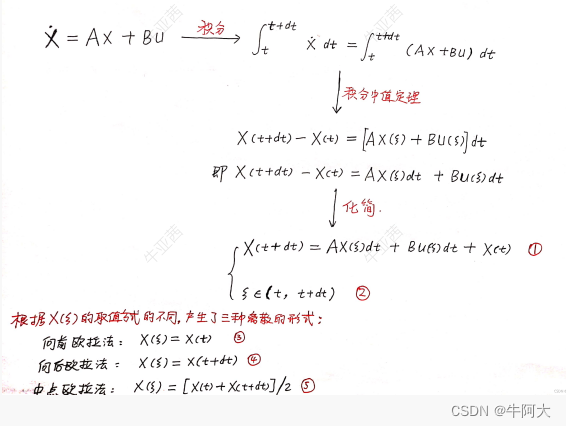
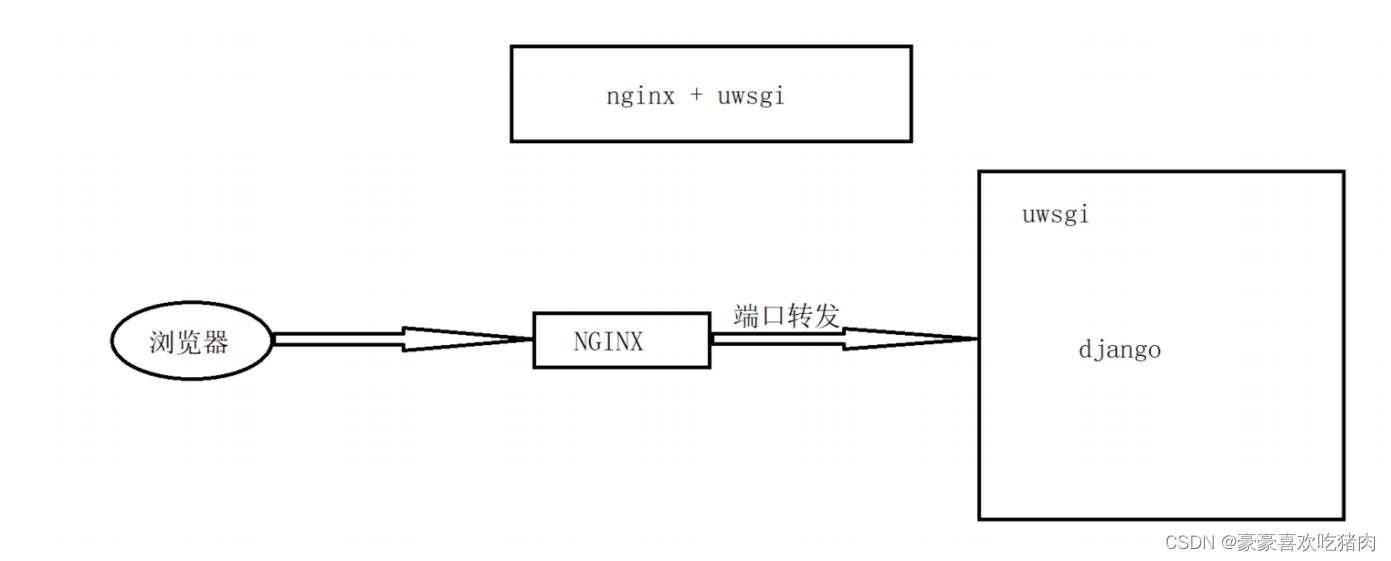
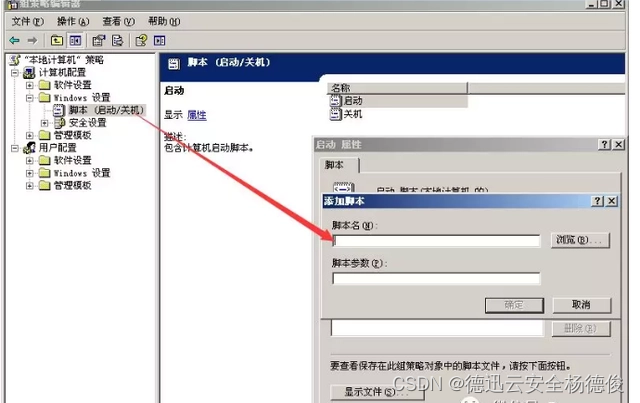
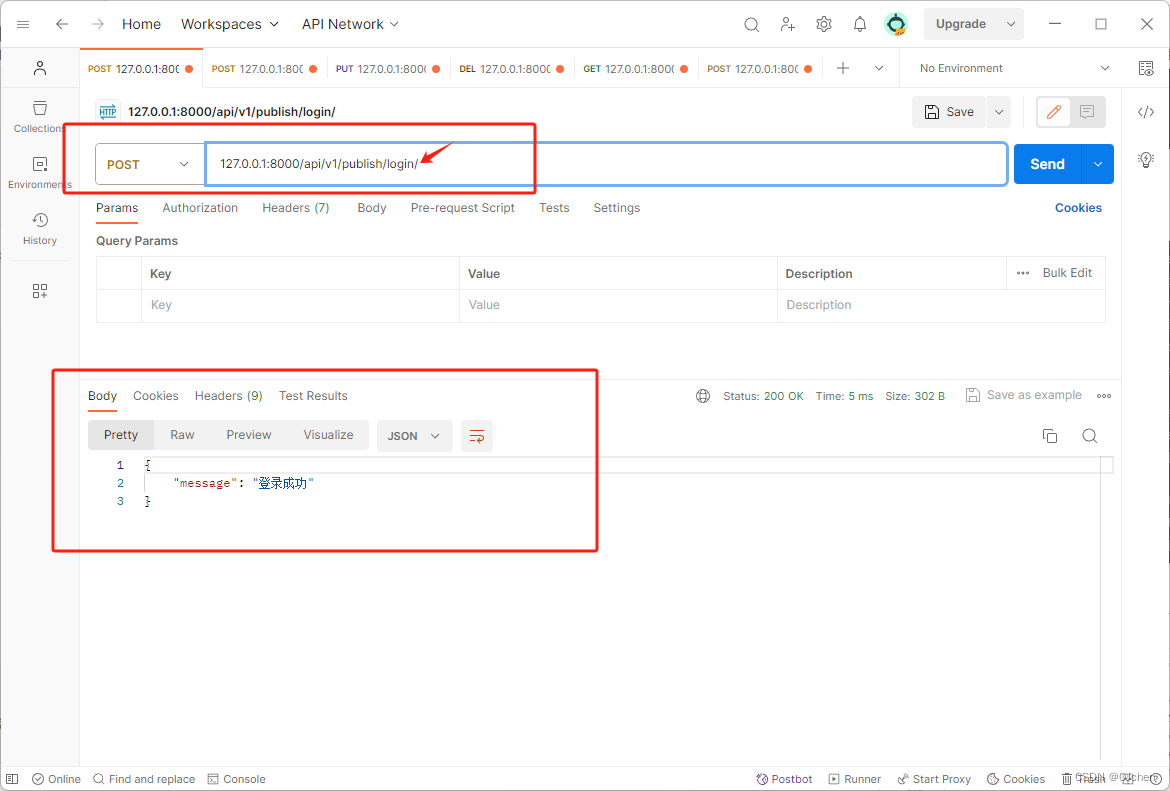
先来说说两个API 的作用
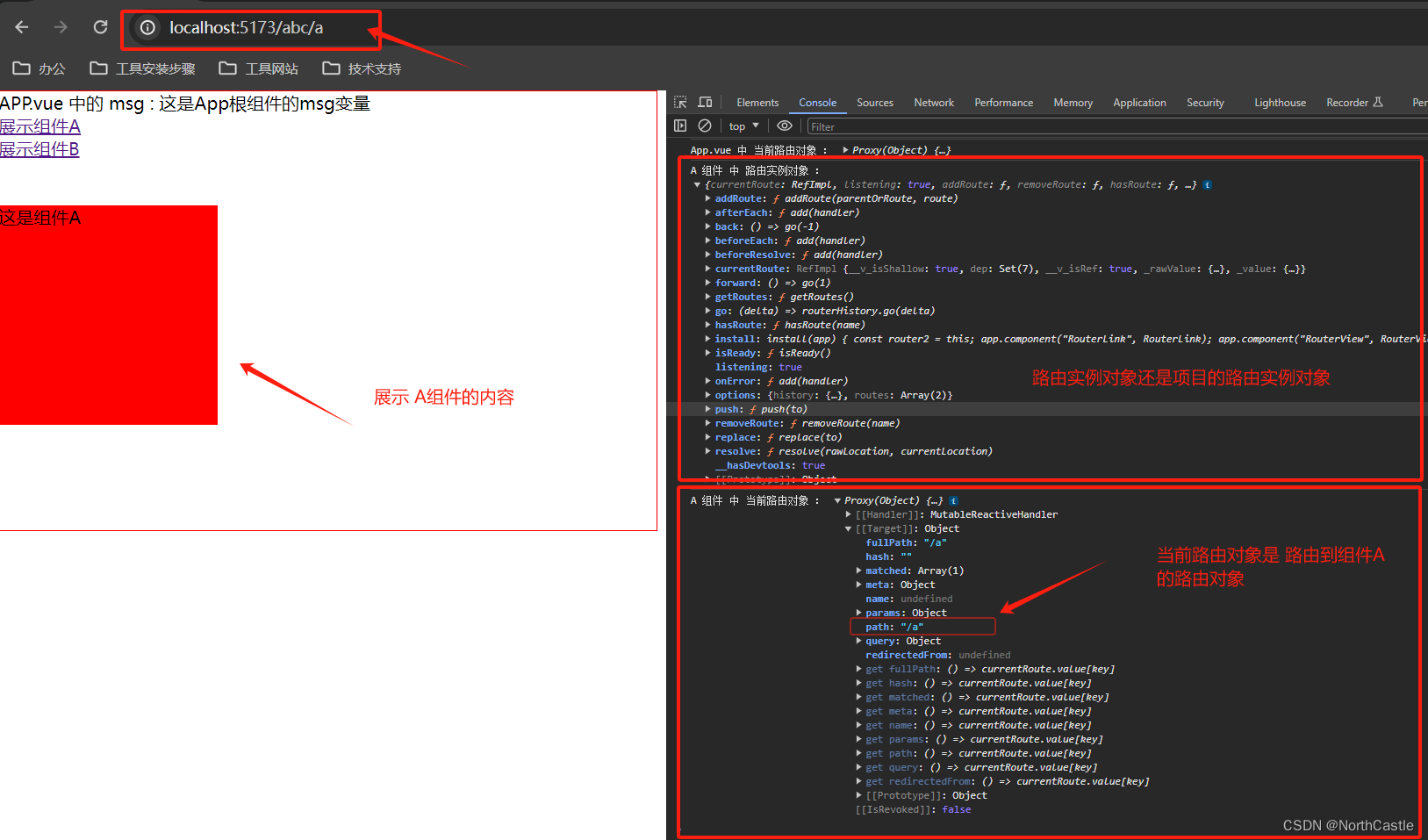
useRouter(): 返回的是项目中的路由实例的对象
可以通过这个实例对象进行路由的逻辑跳转
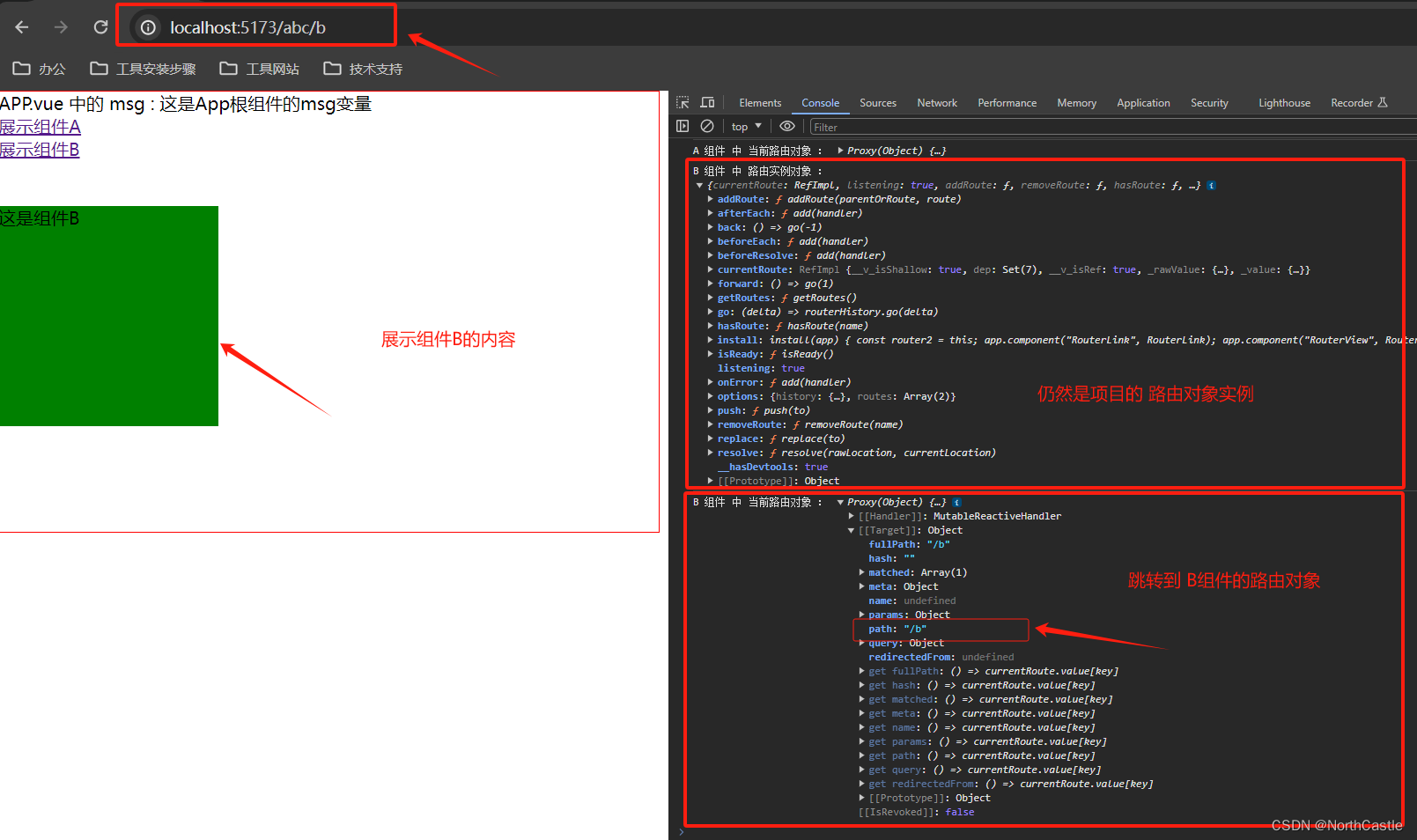
useRoute(): 返回的是当前的路由对象,
可以在当前路由对象中获取到路由名称、路由参数、路由路径等玩完整的路由信息。
写个案例看一下具体是什么
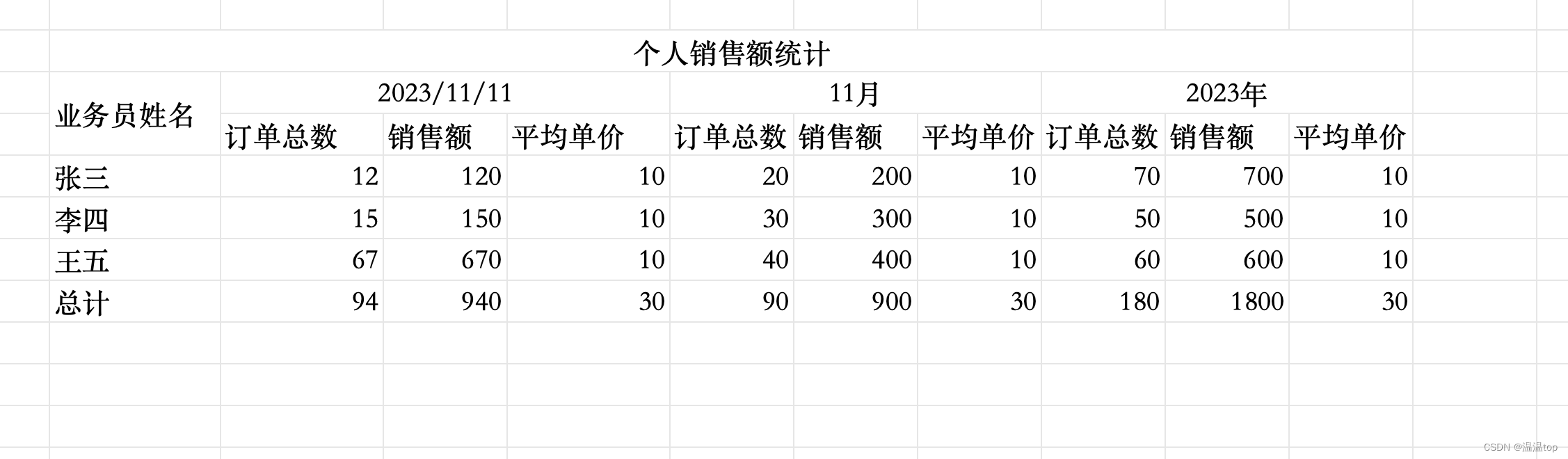
项目描述 :
1、router.ts 文件中配置并导出了 router路由实例的对象;
2、main.ts 文件中 使用了 router 路由实例,这样 整个项目中就可以进行路由跳转了;
3、App.vue 作为根组件,使用 <router-view> 标签 展示路由的目标组件;
4、componentA.vue 和 componentB.vue 是两个普通的组件;
5、通过 在组件中 引入两个API 来探究这两个API 到底是什么。
项目的目录解构如下 :
projectName
| -- index.html
| -- src
| -- App.vue
| -- main.ts
| -- router.ts
| -- componentA.vue
| -- componentB.vue
router.ts 文件
// 导入 定义路由的两个方法
import {createRouter,createWebHistory} from 'vue-router'
// 引入两个组件
import componentA from "./componentA.vue";
import componentB from "./componentB.vue";
// 声明路由跳转的路径与组件的对应关系
const routsList = [
{path:'/a',component:componentA},
{path:'/b',component:componentB},
]
// 创建路由的实例对象
const routerConfigObj = createRouter({
history:createWebHistory('abc'), // 带一个参数,表示是路由的一个前缀
routes:routsList // 指定路由的配置列表
})
// 导出路由的对象
export default routerConfigObj;
main.ts 文件
import { createApp } from 'vue'
// 导入 路由配置对象
import routerConfigObj from './router'
// 根组件
import App from './App.vue'
// 创建应用实例
const app = createApp(App)
// 挂载路由组件 - 核心操作
app.use(routerConfigObj)
// 挂在应用,渲染页面,这一步应该是在最后执行的
app.mount("#app")
App.vue文件
<template>
<div class="basediv">
APP.vue 中的 msg : {{ msg }}
<br>
<!-- router-link 进行路由的导航 -->
<router-link to="/a">展示组件A</router-link>
<br>
<router-link to="/b">展示组件B</router-link>
<br><br><br>
<!-- router-view 进行目标组件的展示 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
// 引入 provide 方法
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 引入路由配置实例 与 当前路由对象
import { useRouter,useRoute} from 'vue-router'
// 声明父组件的一个变量
const msg = ref('这是App根组件的msg变量')
// 接收一下路由实例对象 和 当前路由 对象
const routerObj = useRouter();
const currentRoute = useRoute();
console.log('App.vue 中 路由实例对象 :',routerObj)
console.log('App.vue 中 当前路由对象 :',currentRoute)
</script>
<style scoped>
.basediv{
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
componentA.vue 文件
<template>
<div class="diva">
这是组件A
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
// 引入两个路由相关的方法
import { useRouter,useRoute} from 'vue-router';
// 声明 路由实例对象 和 当前路由对象
const routerObj = useRouter()
const currentRoute = useRoute()
// 打印一下路由实例对象 和 当前路由对象
console.log('A 组件 中 路由实例对象 :',routerObj)
console.log('A 组件 中 当前路由对象 :',currentRoute)
</script>
<style scoped>
.diva{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: red;
}
</style>
componentB.vue文件
<template>
<div class="divb">
这是组件B
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
// 引入两个路由相关的方法
import { useRouter,useRoute} from 'vue-router';
// 声明 路由实例对象 和 当前路由对象
const routerObj = useRouter()
const currentRoute = useRoute()
// 打印一下路由实例对象 和 当前路由对象
console.log('B 组件 中 路由实例对象 :',routerObj)
console.log('B 组件 中 当前路由对象 :',currentRoute)
</script>
<style scoped>
.divb{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: green;
}
</style>
运行效果
初始状态 : 没有路由匹配的时候

路由到 A组件时
路由到 B组件时