参考资料:
参考视频
拦截器自定义注解
AOP自定义注解
通过AOP获取属性
拦截器、过滤器、AOP的区别和联系
个人学习笔记及源码
注:这里仅讲怎么使用,具体原理请参考个人学习笔记
自定义注解源码介绍:

- 其中视频例子2为上述参考视频的例子
- 视频例子1为原先反射视频的例子
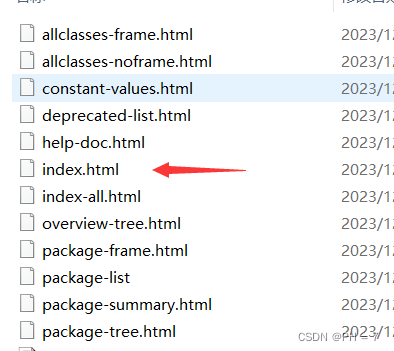
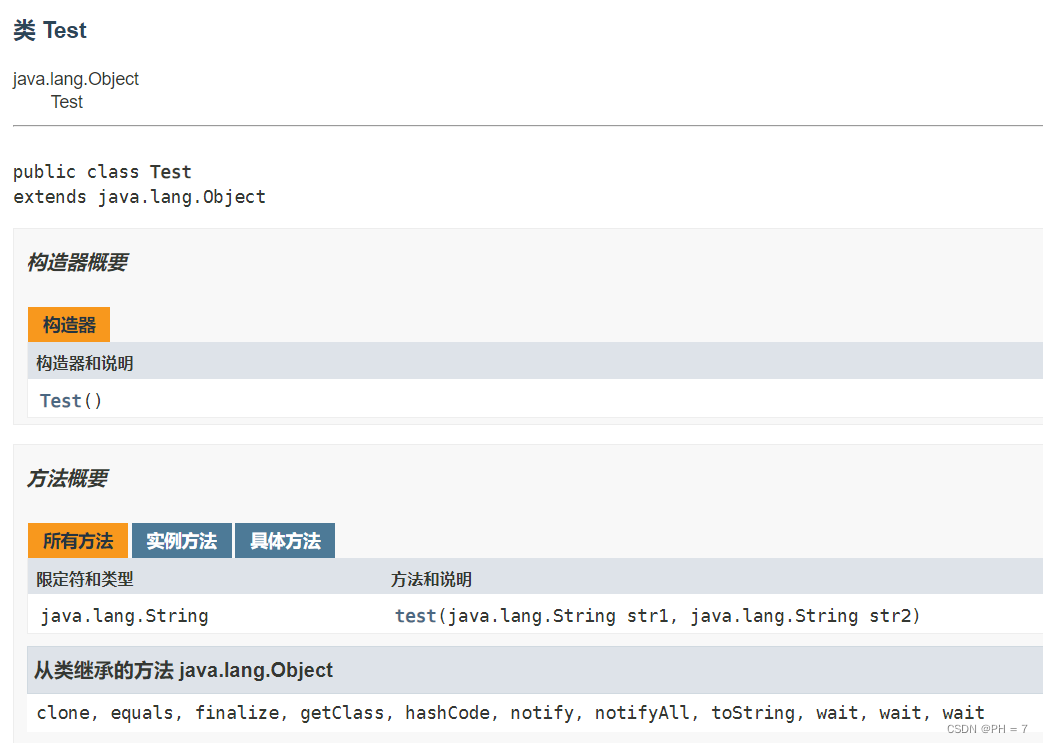
生成JAVA文档:
可以通过javadoc命令生成API文档
- 首先将要转为文档的类,去掉包名,放在磁盘中


- 用记事本,notepad++,或者其他工具将编码转化为ANSI编码

- 在磁盘目录 打开CMD,输入以下命令,回车即可生成API文旦
javadoc XXX.java

- 打开生成的inde.html即可看到API文档
注解的基本结构
- 注解的基本结构为:
#{元注解}
public @interface #{注解名称} {
#{属性列表}
}
注解名称:自定义的注解名称
元注解:用于定义注解的注解,常用的元注解有如下四个:
@Target : 描述该注解作用范围,即应该标注在java文件的什么上面,常用的值为:
- ElementType.Type : 作用于类
- ElementType.METHOD: 作用于方法
- ElementType.FIELD:作用于字段
当然还有其他值可以进行查阅
@Retention:描述注解被保留的阶段,常用的值为:
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:当前描述的注解,会保留到class字节码文件中,并被jvm读取到
当然还有其他值可以进行查阅
@Documented:描述注解是否被抽取到api文档中,选填,填上就表示参与到API文档中
@Inherited:描述注解是否可以被继承,选填,填上就表示可以被继承
属性列表:注解的属性,需要抽象方法来定义,且必须要有返回值,关于原理下面会讲,这里仅仅讲使用规则
- 抽象方法必须有返回结果,且返回结果必须是如下类型:
① 基本数据类型
② String类型
③ 枚举类型
④ 注解
⑤ 以上类型的数组
属性赋值注意点:
下面将结合例子进行说明
- 如果定义的属性时,使用default关键字给属性默认初始值,可以在使用注解时不赋值;
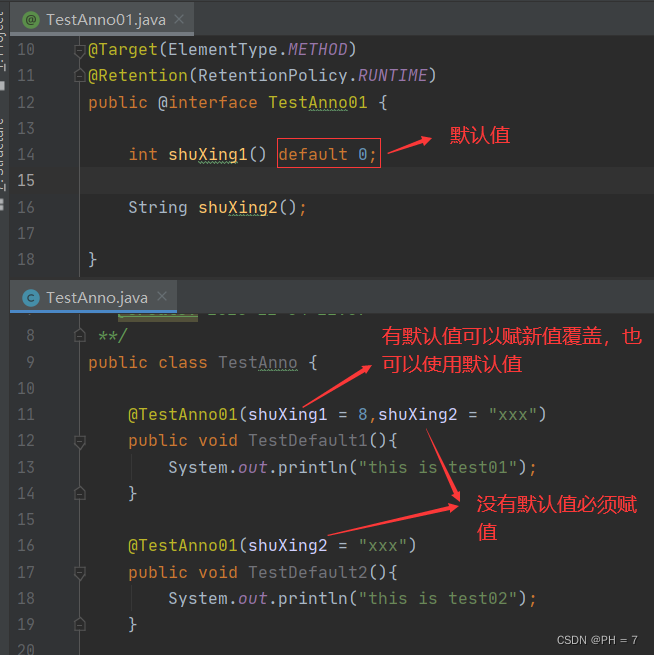
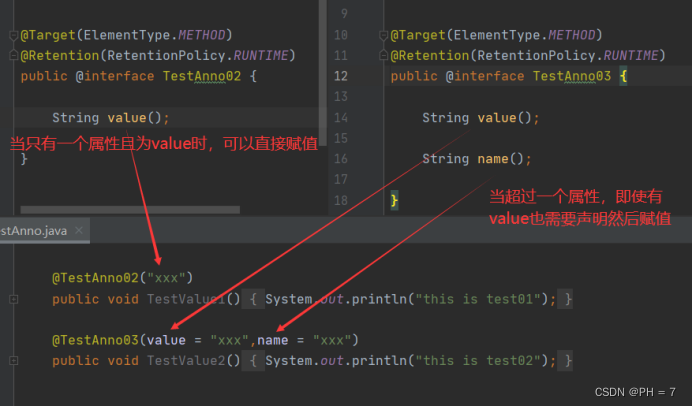
- 注解只有一个抽象方法,且抽象方法名为value,那么在使用时可以直接赋值而不去声明value = XXX;
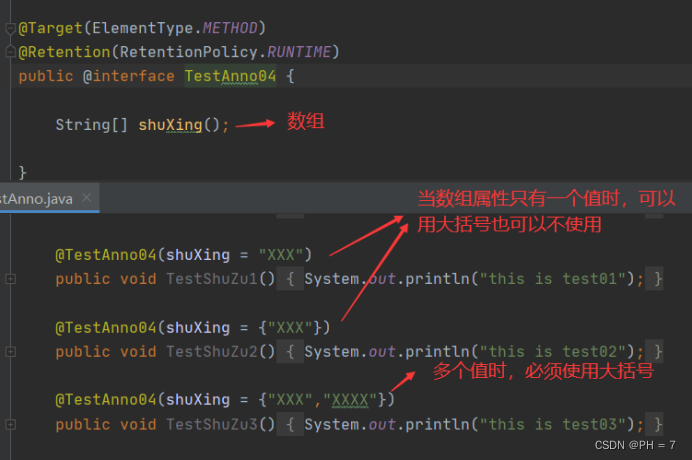
- 数组赋值的时,使用大括号{}进行包裹,但是如果只有一个值,那么大括号{}可以省略
注解的基本使用方式
下面演示在不结合SpringBoot的情况下,使用自定义注解进行简单的测试
- 首先自定义一个注解
package com.example.demo.localAnnotation.selfDemo.annoUse;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TestAnno {
String shuXing1() default "zhangsan";
int shuXing2();
}
- 然后加在测试的方法上
package com.example.demo.localAnnotation.selfDemo.annoUse;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-04 23:48
**/
@TestAnno(shuXing2 = 12315)
public class AnnoMethods {
@TestAnno(shuXing1 = "XXX",shuXing2 = 66)
private String str = "testShuXing";
@TestAnno(shuXing2 = 10086)
public int method01(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
@TestAnno(shuXing1 = "lisi",shuXing2 = 10010)
public String method02(String str1,String str2,String str3){
return str1+"======"+str2+"======"+str3;
}
@TestAnno(shuXing1 = "wanglong",shuXing2 = 123456)
public void method03(){
}
}
- 然后使用反射进行解析
package com.example.demo.localAnnotation.selfDemo.annoUse;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-05 00:14
**/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class TestAnnoMethods {
@Test
public void test01() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
String mathodName = "method01";
// 一定要创建一个实例
AnnoMethods methods = new AnnoMethods();
// 确定执行方法
Class<?> methodsClass = methods.getClass();
Class<?>[] classArr = new Class[]{int.class,int.class};
Method method = methodsClass.getDeclaredMethod(mathodName, classArr);
// 设置私有方法可达
method.setAccessible(true);
// 确定方法的参数
Object[] valueArr = new Object[]{1,100};
// 执行方法 和返回值
Object result = method.invoke(methods, valueArr);
// 获取 该方法上面的注解 以及相关值
TestAnno anno = method.getAnnotation(TestAnno.class);
String shuXing1 = anno.shuXing1();
int shuXing2 = anno.shuXing2();
// 遍历进行输出
System.out.println("下面是获取到的相关值,以及通过反射获取到的结果");
System.out.println("执行方法为:"+mathodName);
System.out.println("方法参数为:"+valueArr[0]+"******"+valueArr[1]);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+result);
System.out.println("注解属性1的值为:"+shuXing1);
System.out.println("注解属性2的值为:"+shuXing2);
}
@Test
public void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
String mathodName = "method02";
// 一定要创建一个实例
AnnoMethods methods = new AnnoMethods();
// 确定执行方法
Class<?> methodsClass = methods.getClass();
Class<?>[] classArr = new Class[]{String.class,String.class,String.class};
Method method = methodsClass.getDeclaredMethod(mathodName, classArr);
// 设置私有方法可达
method.setAccessible(true);
// 确定方法的参数
Object[] valueArr = new Object[]{"peter","wanglili","xuanfeng"};
// 执行方法 和返回值
Object result = method.invoke(methods, valueArr);
// 获取 该方法上面的注解 以及相关值
TestAnno anno = method.getAnnotation(TestAnno.class);
String shuXing1 = anno.shuXing1();
int shuXing2 = anno.shuXing2();
// 遍历进行输出
System.out.println("下面是获取到的相关值,以及通过反射获取到的结果");
System.out.println("执行方法为:"+mathodName);
System.out.println("方法参数为:"+valueArr[0]+"******"+valueArr[1]+"******"+valueArr[2]);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+result);
System.out.println("注解属性1的值为:"+shuXing1);
System.out.println("注解属性2的值为:"+shuXing2);
}
@Test
public void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
String mathodName = "method03";
// 一定要创建一个实例
AnnoMethods methods = new AnnoMethods();
// 确定执行方法
Class<?> methodsClass = methods.getClass();
Class<?>[] classArr = new Class[]{};
Method method = methodsClass.getDeclaredMethod(mathodName, classArr);
// 设置私有方法可达
method.setAccessible(true);
// 确定方法的参数
Object[] valueArr = new Object[]{};
// 执行方法 和返回值
Object result = method.invoke(methods, valueArr);
// 获取 该方法上面的注解 以及相关值
TestAnno anno = method.getAnnotation(TestAnno.class);
String shuXing1 = anno.shuXing1();
int shuXing2 = anno.shuXing2();
// 遍历进行输出
System.out.println("下面是获取到的相关值,以及通过反射获取到的结果");
System.out.println("执行方法为:"+mathodName);
System.out.println("方法参数为:");
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+result);
System.out.println("注解属性1的值为:"+shuXing1);
System.out.println("注解属性2的值为:"+shuXing2);
}
@Test
public void test04(){
Class<AnnoMethods> methodsClass = AnnoMethods.class;
TestAnno annotation = methodsClass.getAnnotation(TestAnno.class);
String shuXing1 = annotation.shuXing1();
int shuXing2 = annotation.shuXing2();
System.out.println("类上注解属性1的值为:"+shuXing1);
System.out.println("类上注解属性2的值为:"+shuXing2);
}
@Test
public void test05() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
AnnoMethods methods = new AnnoMethods();
// 确定执行方法
Class<?> methodsClass = methods.getClass();
Field field = methodsClass.getDeclaredField("str");
field.setAccessible(Boolean.TRUE);
String fieldName = field.getName();
Object o = field.get(methods);
TestAnno annotation = field.getAnnotation(TestAnno.class);
String shuXing1 = annotation.shuXing1();
int shuXing2 = annotation.shuXing2();
System.out.println(fieldName);
System.out.println(o);
System.out.println(shuXing1);
System.out.println(shuXing2);
}
}
AOP+自定义注解:
AOP+自定义注解,是以自定义注解作为切面,进入动态代理,获取到被加注解的类、方法、变量的信息,结合注解的值,进行相关操作,比如:记录日志等;

参考文章
配置流程如下(具体见本人demo):
- 搭建SpringBoot项目,参考
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>- 添加自定义注解
package com.example.demo.springAnnotation.AOP;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyLog {
String upDbName();
}- 添加自定义注解的解析类
package com.example.demo.springAnnotation.AOP;
import com.example.demo.utils.IPAddressUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class MyLogAspect {
/**
* IP 地址 解析工具类
*/
@Autowired
private IPAddressUtils ipAddressUtils;
/**
* 只要用到了com.javaxl.p2.annotation.springAop.MyLog这个注解的,就是目标类
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(MyLog)")
private void MyValid() {
}
/* @Before("MyValid()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("----------Before开始-----------");
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
String classType = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
MyLog myLog = method.getAnnotation(MyLog.class);
String desc = myLog.upDbName();
//获取当前请求request对象
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
log.info("方法名:"+ signature.getName());
log.info("参数值集合:"+ Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
log.info("参数值类型:"+ joinPoint.getArgs()[0].getClass().getTypeName());
log.info("获取目标方法所在类:"+ classType);
log.info("指定注解MyLog的属性值为:"+desc);
log.info("获取URI地址:"+request.getRequestURI());
log.info("获取URL地址:"+request.getRequestURL());
log.info("获取请求方式:"+request.getMethod());
log.info("获取请求的ip地址:"+IPAddressUtils.getIpAdrress(request));
log.info("----------Before结束-----------");
}*/
/* @After("MyValid()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("后置通知");
}*/
@Around("MyValid()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint)throws Throwable {
log.info("----------Around开始-----------");
log.info("=========================================================");
log.info("==========================================================");
log.info("===你可以根据获取到的信息进行任何操作,比如:进行日志的记录等!!!===");
log.info("==========================================================");
log.info("==========================================================");
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
String classType = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
MyLog myLog = method.getAnnotation(MyLog.class);
String desc = myLog.upDbName();
//获取当前请求request对象
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
log.info("方法名:"+ signature.getName());
log.info("参数值集合:"+ Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
log.info("参数值类型:"+ joinPoint.getArgs()[0].getClass().getTypeName());
log.info("获取目标方法所在类:"+ classType);
log.info("指定注解MyLog的属性值为:"+desc);
log.info("获取URI地址:"+request.getRequestURI());
log.info("获取URL地址:"+request.getRequestURL());
log.info("获取请求方式:"+request.getMethod());
log.info("获取请求的ip地址:"+IPAddressUtils.getIpAdrress(request));
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
log.info("方法的执行结果:"+result);
log.info("----------Around结束-----------");
}
}
- 工具类:IP解析类
package com.example.demo.utils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.net.InetAddress;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class IPAddressUtils {
/**
* 获取IP地址
*/
public static String getIpAdrress(HttpServletRequest request) {
String ipAddress = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
if (ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getRemoteAddr();
if ("127.0.0.1".equals(ipAddress) || "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ipAddress)) {
// 根据网卡取本机配置的IP
InetAddress inet = null;
try {
inet = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("根据网卡获取本机配置的IP异常=>", e.getMessage());
}
if (inet.getHostAddress() != null) {
ipAddress = inet.getHostAddress();
}
}
}
// 对于通过多个代理的情况,第一个IP为客户端真实IP,多个IP按照','分割
if (ipAddress != null && ipAddress.length() > 15) {
if (ipAddress.indexOf(",") > 0) {
ipAddress = ipAddress.substring(0, ipAddress.indexOf(","));
}
}
return ipAddress;
}
}
- 添加Service及其实现
package com.example.demo.service;
public interface LogService {
String test01(String str1,String str2);
Integer test02(Integer num1,Integer num2);
}
package com.example.demo.service.impl;
import com.example.demo.service.LogService;
import com.example.demo.springAnnotation.AOP.MyLog;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-13 00:49
**/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class LogServiceImpl implements LogService {
@Override
@MyLog(upDbName = "redis")
public String test01(String str1, String str2) {
log.info("进入方法,参数方法分别为: {} ,{}",str1,str2);
String str = str1+"==="+str2;
return str;
}
@Override
@MyLog(upDbName = "mysql")
public Integer test02(Integer num1,Integer num2) {
log.info("进入方法,参数方法分别为: {} ,{}",num1,num2);
Integer num = num1+num2;
return num;
}
}
- 添加Controller
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.service.LogService;
import com.example.demo.springAnnotation.AOP.MyLog;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-01 00:02
**/
@RestController
public class AopController {
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
@RequestMapping("test_01")
public String testLogAspect01(@RequestParam("str1")String str1,@RequestParam("str2")String str2){
String str = logService.test01(str1, str2);
return str;
}
@RequestMapping("test_02")
public Integer testLogAspect02(@RequestParam("num1")Integer num1,@RequestParam("num2")Integer num2){
Integer num = logService.test02(num1, num2);
return num;
}
}
拦截器+自定义注解:
拦截器+自定义注解:拦截器通常是获取链接的入口方法(一半以controller方法为主),然后通过反射获取到方法信息以及相关注解的信息进行相关操作,比如登录验证等
参考文章
配置流程如下(具体见本人demo):
-
搭建SpringBoot项目,参考
- 自定义注解
package com.example.demo.springAnnotation.INTERCEPT;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LoginRequired {
String userName();
}
- 配置允许通过的请求和需要拦截的请求
package com.example.demo.springAnnotation.INTERCEPT;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-01 10:24
**/
@Configuration
public class InterceptorTrainConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new SourceAccessInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**") //需要拦截 验证的的
.excludePathPatterns("/test_01","/test_02"); //需要放过的
}
}
- 配置拦截的请求,需要进行的操作
package com.example.demo.springAnnotation.INTERCEPT;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-01 10:21
**/
public class SourceAccessInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("进入拦截器了");
// 反射获取方法上的LoginRequred注解
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
LoginRequired loginRequired = method.getAnnotation(LoginRequired.class);
if (loginRequired == null) {
return true;
}
// 有LoginRequired注解说明需要登录,提示用户登录
String userName = loginRequired.userName();
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().println("你访问的资源需要登录");
response.getWriter().println("注解的属性名为:"+userName);
response.getWriter().println("访问的方法名为:"+method.getName());
response.getWriter().println("返回的类型为:"+method.getReturnType().getName());
response.getWriter().println("=========================================================");
response.getWriter().println("=========================================================");
response.getWriter().println("=====拦截器同样可以获取到各种属性,根据自身需要进行调用=============");
response.getWriter().println("=========================================================");
response.getWriter().println("=========================================================");
return false;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
- 配置Controller请求
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.springAnnotation.INTERCEPT.LoginRequired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @program: AnnotationDemo
* @description:
* @author: wjl
* @create: 2023-12-01 10:15
**/
@RestController
public class InterceptController {
@GetMapping("/sourceA")
public String sourceA(){
return "你正在访问sourceA资源";
}
@GetMapping("/sourceB")
@LoginRequired(userName = "peter")
public String sourceB(){
return "你正在访问sourceB资源";
}
}

![[C/C++]数据结构 希尔排序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/78cd6c968f3e4f21af9b09874b8bb830.png)