1221 Polish
1. Transfer the road coordinates from the UE coordinates system into the CAD coordinates system by using the functions in the file INDEX2UE.py
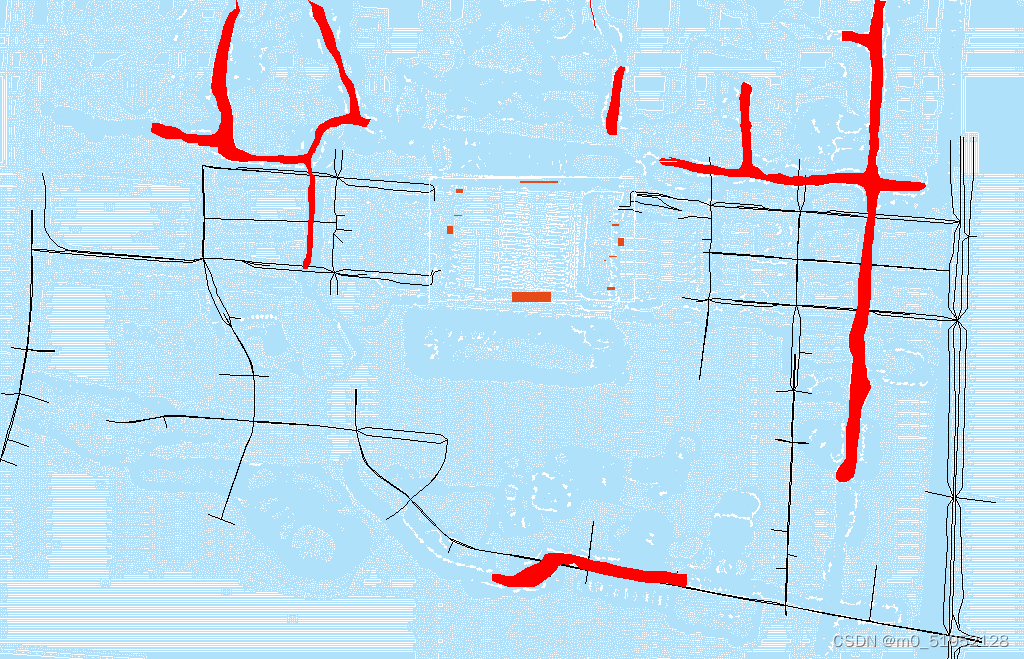
坐标转换的时候,插值,取特征点(交叉点)Transfer the road coordinates, which are in the CAD coordinate system into the UE coordinate system.
- 分散开来标注道路基准点,转换道路的坐标。也就是要让道路贴近河流,而不是河流贴近道路
- UE and CAD refer to two different coordinate systems.
- Key points of road from both CAD and UE coordinate systems are included in the file
高架点位对齐.xlsx
To senior Hu:
- 道路数据是否有从CAD数据转换为UE数据(目前在
model2.py文件中没有看到CAD2UE函数的调用)
To Prof Gao:
- How to transfer from the CAD coordinate system into the UE system?
What’ the meaning of the file
高架点位对齐.xlsxif I can use the functioncad2ue_plan2in the fileINDEX2UE.py
No means.
Report
Changes in the function initialMatrix
# 初始化标签
self.outdoor_label[self.wall_matrix == 1] = walls_label
self.outdoor_label[self.road_matrix == 1] = roads_label
# self.outdoor_label[self.river_matrix == 1] = river_label
self.outdoor_label[self.ditch_matrix == 1] = ditch_label
self.outdoor_label[soil_mask] = soil_label
# Realize this function.
self.initial_river()
df=pd.DataFrame(self.outdoor_label)
Changes in the function initial_position
def initial_position(self, file_name, x_shifting, y_shifting, x_scale, y_scale, pos_type):
"""
参数:file_name(文件路径名字), pos_type(坐标类型)
进行坐标转换,初始化墙、内门以及出口坐标
"""
# 读取文件
if pos_type == 'road':
df = pd.read_excel(file_name, header=None)
tuple_list = []
# 遍历每一行
for index, row in df.iterrows():
tuple_row = []
col_index = 1 # 初始列索引
# 在每行内部,每次读取两列数据,直到读完所有列
while col_index < len(row):
data1 = row.iloc[col_index] # 第一列的数据
data2 = row.iloc[col_index + 1] # 第二列的数据
if pd.notna(data1) and pd.notna(data2):
tuple_row.append((data1, data2))
col_index += 2 # 更新列索引,跳过已读取的两列
if tuple_row:
tuple_list.append(tuple_row)
for sublist in tuple_list:
# 遍历每一行
maxy = -100000
col_index = 0
while col_index + 1 < len(sublist):
# 获取两列数据
data1 = sublist[col_index]
data2 = sublist[col_index + 1]
start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y = data1[0], data1[1], data2[0], data2[1]
# end_x += x_shifting
# end_x /= x_scale
# # end_x *= self.grid.width
# end_x = round(end_x)
# end_y += y_shifting
# end_y /= y_scale
# # end_y *= self.grid.height
# end_y = round(end_y)
# start_x += x_shifting
# start_x /= x_scale
# start_x = round(start_x)
# start_y += y_shifting
# start_y /= y_scale
# start_y = round(start_y)
'''
Transfer the points from CAD coordinate system into UE coordinate system
'''
# apply the transfer function of cad2ue
x,y=start_x,start_y
x, y = self.outdoor_transer.cad2ue_plan2(x, y)
start_x, start_y = self.outdoor_transer.ue2index_model2(x, y, self.scaled_width, self.scaled_height)
x,y=end_x,end_y
x, y = self.outdoor_transer.cad2ue_plan2(x, y)
end_x, end_y = self.outdoor_transer.ue2index_model2(x, y, self.scaled_width, self.scaled_height)
self.roads.append({"start_x": start_x, "end_x": end_x, "start_y": start_y, "end_y": end_y})
'''
Applying 1 to self.road_matrix along the route
from the start point(star_x,star_y) to end point (end_x,end_x)
'''
self.apply_matrix_dots(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, 'road')
col_index += 1
elif pos_type == "river":
df = pd.read_excel(file_name)
num = df['x1'].notna().sum()
# print(pos_type, "数量:", num)
# 坐标变化
for i in range(num):
start_x, start_y = df['x1'][i], df['y1'][i]
start_x += x_shifting
start_x /= x_scale
start_x = round(start_x)
# align with roads
start_x = start_x - 38
start_y += y_shifting
start_y /= y_scale
start_y = round(start_y)
# align with roads
start_y = start_y + 28
self.stream_pos.append((start_x, start_y))
if i > 0:
'''
Applying 1 to self.river_matrix along the route
from the start point(start0_x,start0_y) to end point (start_x,start_y)
'''
self.apply_matrix_dots(start0_x, start0_y, start_x, start_y, 'river')
start0_x, start0_y = start_x, start_y
num2 = df['x2'].notna().sum()
# print(pos_type, "add 数量:", num2)
# 坐标变化
for i in range(num2):
start_x, start_y = df['x2'][i], df['y2'][i]
start_x += x_shifting
start_x /= x_scale
start_x = round(start_x)
# align with roads
start_x = start_x - 38
start_y += y_shifting
start_y /= y_scale
start_y = round(start_y)
# align with roads
start_y = start_y + 28
self.stream_pos2.append((start_x, start_y))
if i > 0:
'''
Applying 1 to self.river_matrix along the route
from the start point(start0_x,start0_y) to end point (start_x,start_y)
'''
self.apply_matrix_dots(start0_x, start0_y, start_x, start_y, 'river')
start0_x, start0_y = start_x, start_y
else:
df = pd.read_excel(file_name)
num = len(df['x1'])
# print(pos_type, "数量:", num)
# 坐标变化
for i in range(num):
if pos_type == 'wall':
start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y = df['x1'][i], df['y1'][i], df['x2'][i], df['y2'][i]
# end_x += x_shifting
# end_x /= x_scale
# end_x = round(end_x)
# end_y += y_shifting
# end_y /= y_scale
# end_y = round(end_y)
x,y=start_x,start_y
x, y = self.outdoor_transer.cad2ue_plan2(x, y)
start_x, start_y = self.outdoor_transer.ue2index_model2(x, y, self.scaled_width, self.scaled_height)
x,y=end_x,end_y
x, y = self.outdoor_transer.cad2ue_plan2(x, y)
end_x, end_y = self.outdoor_transer.ue2index_model2(x, y, self.scaled_width, self.scaled_height)
'''
Applying: 1 to self.wall_matrix along the route
from the start point(start_x,start_y) to end point (end_x,end_y)
'''
self.apply_matrix_dots(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, 'wall')
else:
start_x, start_y = df['x1'][i], df['y1'][i]
start_x += x_shifting
start_x /= x_scale
start_x = round(start_x)
start_y += y_shifting
start_y /= y_scale
start_y = round(start_y)
# if pos_type == 'wall':
# '''
# Applying: 1 to self.wall_matrix along the route
# from the start point(start_x,start_y) to end point (end_x,end_y)
# '''
# self.apply_matrix_dots(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, 'wall')
if pos_type == 'indoor':
self.indoors.append((start_x, start_y))
if i > 0:
'''
Applying 1 to self.indoor_matrix along the route
from the start point(start0_x,start0_y) to end point (start_x,start_y)
'''
self.apply_matrix_dots(start0_x, start0_y, start_x, start_y, 'indoor')
start0_x, start0_y = start_x, start_y
elif pos_type == 'exit':
if start_x == end_x:
for i in range(start_y, end_y + 1):
self.pos_exits.append((start_x, i))
# 920 apply coordinates to exits_matrix
self.exits_matrix[start_x][i] = 1
elif start_y == end_y:
for i in range(start_x, end_x + 1):
self.pos_exits.append((i, start_y))
# 920 apply coordinates to exits_matrix
self.exits_matrix[i][start_y] = 1
else:
continue
elif pos_type == "pillar":
pillar_positions = {"start_x": start_x, "end_x": end_x, "start_y": start_y, "end_y": end_y}
self.pillars.append(pillar_positions)
'''
Applying 1 to self.pillar_matrix along the route
from the start point(start_x,start_y) to end point (end_x,end_y)
'''
self.apply_matrix_dots(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, 'pillar')
else:
pass
# self.water_initial_pos.append((start_x, start_y))
New defined functions
- In the file
model2.py
def fill_area(self, array, target_value=3):
'''
fill the circled area
'''
# Create a binary mask where the target_value is True
mask = (array == target_value)
# Fill the holes in the binary mask
filled_mask = binary_fill_holes(mask)
# Set the filled area back to the target_value in the original array
array[filled_mask] = target_value
return array
def initial_river(self):
valid_time = 0
sum_time = 0
current_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
datadir = os.path.join(current_dir, './Model2_data/outdoor_data/outdoor_river')
filenames = os.listdir(rf'{datadir}')
# read each river points file
for file in filenames:
# 判断文件是否为空
if os.path.getsize(f'{datadir}/{file}') == 0:
continue
# 读取txt文件
with open(f'{datadir}/{file}', 'r') as f:
data = f.read()
# 将JSON格式的字符串解析为Python对象
data = json.loads(data)
temp_no=0
total_start_x,total_start_y=0,0
total_end_x,total_end_y=0,0
# 遍历每个坐标
for obj in data['selectedObjCoords']:
# 获取坐标值
x, y, z = obj['coords']['x'], obj['coords']['y'], obj['coords']['z']
# 将UE坐标转换为索引坐标
index_x, index_y = self.outdoor_transer.ue2index_model2(x, y, self.scaled_width, self.scaled_height)
# print(f'转换前{x}, {y}, 转换后{index_x}, {index_y}')
# 将z轴的值赋值给索引坐标
if 0 <= index_x < len(self.outdoor_topographic_matrix) and 0 <= index_y < len(
self.outdoor_topographic_matrix[0]):
# self.outdoor_topographic_matrix[int(index_x), int(index_y)] = z
# get all the points along the straight line
end_x,end_y=index_x,index_y
total_end_x,total_end_y=index_x,index_y
if temp_no!=0:
if calculate_distance(start_x,start_y,end_x,end_y)<=50:
points = bresenham_line(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y) # find all the points within the straight line
for x, y in points:
self.outdoor_label[int(x), int(y)] = 3 # Represent the river
valid_time += 1
else:
# find the dots that are too distant
print(f'({start_x},{start_y}),({end_x},{end_y})')
else:
total_start_x,total_start_y=index_x,index_y
start_x, start_y=index_x,index_y
temp_no=temp_no+1
sum_time += 1
# connect the last dot with the first dot. And the distance of the two dots should be within certain distance
if calculate_distance(total_start_x,total_start_y,total_end_x,total_end_y)<=5:
points = bresenham_line(total_start_x, total_start_y, total_end_x, total_end_y) # find all the points within the straight line
for x,y in points:
self.outdoor_label[int(x), int(y)] = 3 # Represent the river
# For the disconnect dots due to the reason of labeling sequence. (712,172),(716,267)
'''
Given the coordinate of a dot and find the closest dot coordinate with the same label,
which is 3, in a 2D numpy array, which is `self.outdoor_label` and it has different label numbers.
'''
start_x,start_y=712,172
clos_x,clos_y=self.find_closest_dot(start_x,start_y)
print(f'({clos_x},{clos_y})')
points = bresenham_line(start_x, start_y, clos_x, clos_y) # find all the points within the straight line
for x, y in points:
self.outdoor_label[int(x), int(y)] = 3 # Represent the river
start_x,start_y=716,267
clos_x,clos_y=self.find_closest_dot(start_x,start_y)
print(f'({clos_x},{clos_y})')
points = bresenham_line(start_x, start_y, clos_x, clos_y) # find all the points within the straight line
for x, y in points:
self.outdoor_label[int(x), int(y)] = 3 # Represent the river
# self.outdoor_label = linear_interpolation(self.outdoor_label) # 近邻插值,只需要做一次!!
# 对outdoor_label 补充河流的标签。 并且冲突的时候,河流的优先级最低.
self.outdoor_label = self.fill_area(self.outdoor_label, target_value=3) # fill the circled area
# Fill out the content of the river.
# self.outdoor_topographic_matrix = linear_interpolation(self.outdoor_topographic_matrix) # 近邻插值,只需要做一次!!
# self.outdoor_topographic_matrix = cv2.GaussianBlur(self.outdoor_topographic_matrix, (7, 7), 3)
print(f'all translate time is {sum_time}, valid translate time is {valid_time}')
def find_closest_dot(self, x, y):
min_dist = float('inf')
closest_dot = None
for i in range(self.outdoor_label.shape[0]):
for j in range(self.outdoor_label.shape[1]):
if self.outdoor_label[i, j] == 3:
dist = np.sqrt((x - i)**2 + (y - j)**2)
if dist < min_dist and dist>10:
min_dist = dist
closest_dot = (i, j)
return closest_dot
- In the file
model2_utils.py
def calculate_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2):
'''
The function calculates the distance between two dots
'''
return ((x2 - x1)**2 + (y2 - y1)**2)**0.5
- Import packages
import csv
import json
import math
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
import cv2
from skimage.util import img_as_float
from skimage.segmentation import slic
from INDEX2UE import INDEX2UE
from scipy.ndimage import zoom
from model2_utils import infiltrationRate, create_custom_colormap, get_neighborhood_vectorized, bresenham_line, \
get_coordinates_in_range, get_rectangle_coordinates, get_specific_neighbors_indices, linear_interpolation, \
get_UE_shift,calculate_distance
from parameters import Parameters
from scipy.ndimage import binary_fill_holes, binary_dilation, generate_binary_structure
Output