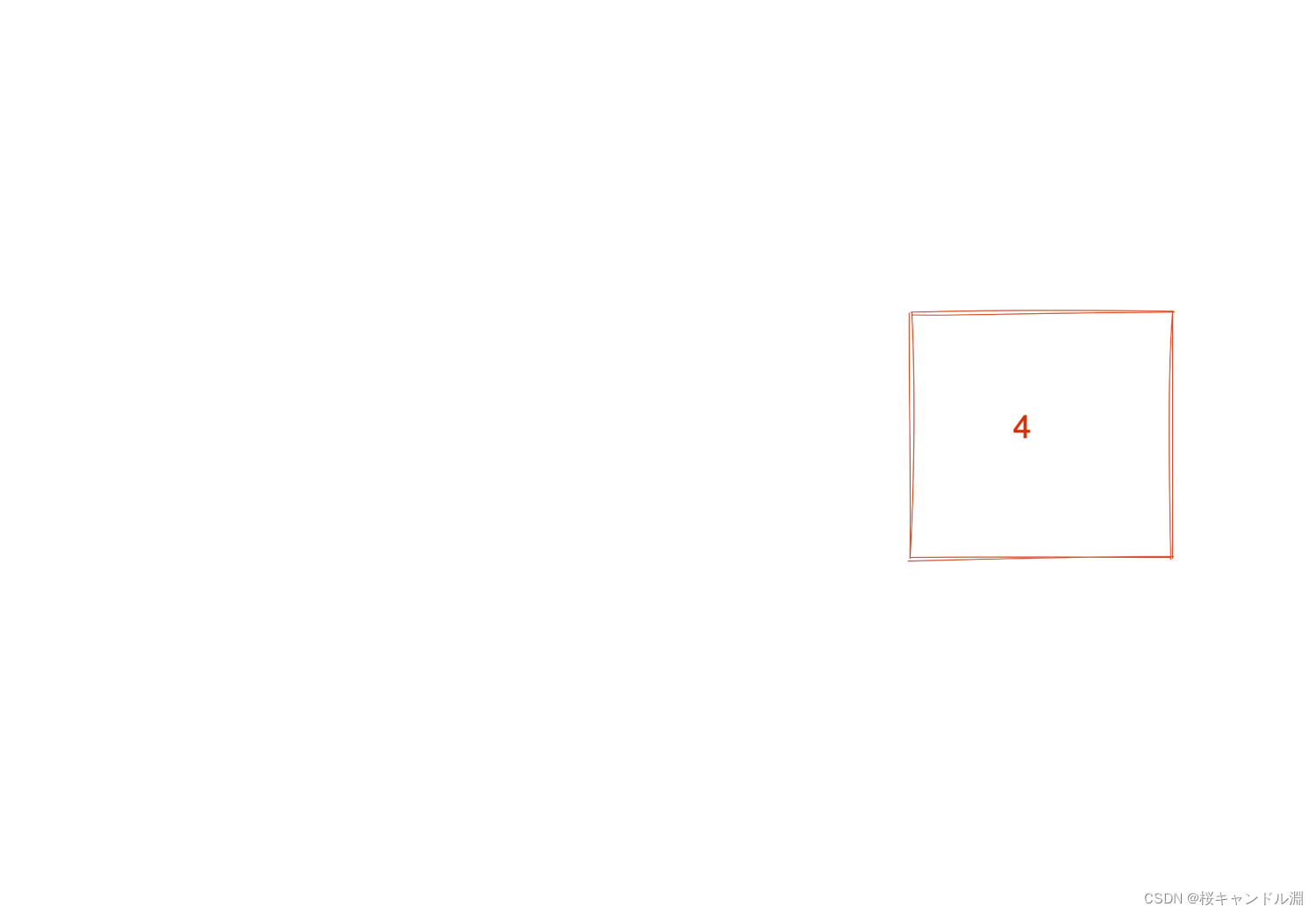
隐式转换概念
When an operator is used with operands of different types, type
conversion occurs to make the operands compatible. Some conversions
occur implicitly.
当运算符与不同类型的操作数一起使用时,将进行类型转换以使操作数兼容。某些转换是隐式发生的。
官方给的定义些许抽象,下面看例子。
有车辆表vehicle。
create table vehicle
(
id varchar(32) not null
primary key,
brand varchar(10) not null comment '车辆品牌',
plate_number varchar(10) not null comment '车牌号'
)
comment '车辆信息表';
INSERT INTO `daily_test`.`vehicle` (`id`, `brand`, `plate_number`) VALUES ('1', '比亚迪-汉DMI', '鲁B.11111');
INSERT INTO `daily_test`.`vehicle` (`id`, `brand`, `plate_number`) VALUES ('2', '比亚迪-秦DMI', '鲁B.22222');
INSERT INTO `daily_test`.`vehicle` (`id`, `brand`, `plate_number`) VALUES ('3', '比亚迪-宋DMI', '鲁B.33333');
查询语句:
select id, brand from vehicle where id = 1;
使用explain查询执行计划,扫描行数是3,即全表数据。

若将查询语句改为:
select id, brand from vehicle where id = '1';
使用explain查询执行计划,扫描行数是1,即使用了主键索引。
为什么两者逻辑一致执行存在差异
由于表数据量较少,共3行,所以两者在执行时间上相差无几,但是在数据量较大的表中,扫全表和使用主键索引的性能差距还是相距甚远的。
vehicle表中id字段被定义为varchar类型,但是在第一个查询语句中,where条件中1为int类型,那么,在执行SQL时便相当于:
select id, brand from vehicle where CAST(id AS signed int) = 1;
即在你不知道的情况下,MySQL “私自” 使用了CASE()函数,大家都知道,
对于索引字段做函数操作,可能会破坏索引值的有序性,因此优化器就决定放弃走树搜索功能。(无法通过树搜索功能快速定位)。
出现隐式转换的场景
翻译自MySQL
- 两个参数至少有一个是 NULL 时,比较的结果也是 NULL,例外是使用 <=> 对两个 NULL 做比较时会返回 1,这两种情况都不需要做类型转换
- 两个参数都是字符串,会按照字符串来比较,不做类型转换
- 两个参数都是整数,按照整数来比较,不做类型转换
- 十六进制的值和非数字做比较时,会被当做二进制串
- 有一个参数是 TIMESTAMP 或 DATETIME,并且另外一个参数是常量,常量会被转换为 timestamp
- 有一个参数是 decimal 类型,如果另外一个参数是 decimal 或者整数,会将整数转换为 decimal 后进行比较,如果另外一个参数是浮点数,则会把 decimal 转换为浮点数进行比较
- 所有其他情况下,两个参数都会被转换为浮点数再进行比较
隐式字符编码转换
当两个表的字符集不同时,关联查询时会导致被驱动表无法命中索引。
mysql> CREATE TABLE `tradelog` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`tradeid` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`operator` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
# 存储格式:yyyy-MM-dd
`t_modified` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `tradeid` (`tradeid`),
KEY `t_modified` (`t_modified`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
CREATE TABLE `trade_detail` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`tradeid` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`trade_step` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, /*操作步骤*/
`step_info` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL, /*步骤信息*/
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `tradeid` (`tradeid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into tradelog values(1, 'aaaaaaaa', 1000, now());
insert into tradelog values(2, 'aaaaaaab', 1000, now());
insert into tradelog values(3, 'aaaaaaac', 1000, now());
insert into trade_detail values(1, 'aaaaaaaa', 1, 'add');
insert into trade_detail values(2, 'aaaaaaaa', 2, 'update');
insert into trade_detail values(3, 'aaaaaaaa', 3, 'commit');
insert into trade_detail values(4, 'aaaaaaab', 1, 'add');
insert into trade_detail values(5, 'aaaaaaab', 2, 'update');
insert into trade_detail values(6, 'aaaaaaab', 3, 'update again');
insert into trade_detail values(7, 'aaaaaaab', 4, 'commit');
insert into trade_detail values(8, 'aaaaaaac', 1, 'add');
insert into trade_detail values(9, 'aaaaaaac', 2, 'update');
insert into trade_detail values(10, 'aaaaaaac', 3, 'update again');
insert into trade_detail values(11, 'aaaaaaac', 4, 'commit');
执行语句:
select d.* from tradelog l, trade_detail d where d.tradeid=l.tradeid and l.id=2;
编码格式不同时,上述查询语句就变成了:
select * from trade_detail where CONVERT(traideid USING utf8mb4)=$L2.tradeid.value;
CONVERT() 函数,在这里的意思是把输入的字符串转成 utf8mb4 字符集。
要在编写SQL语句时养成使用explain的习惯,及时发现SQL潜在问题,避免慢SQL导致的性能问题。
最后,祝大家2023新年快乐。