主要是我自己刷题的一些记录过程。如果有错可以指出哦,大家一起进步。
转载代码随想录
原文链接:
代码随想录
leetcode链接:513.找树左下角的值
题目:
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例:
示例 1:
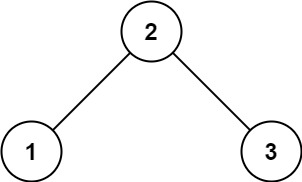
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
示例 2:
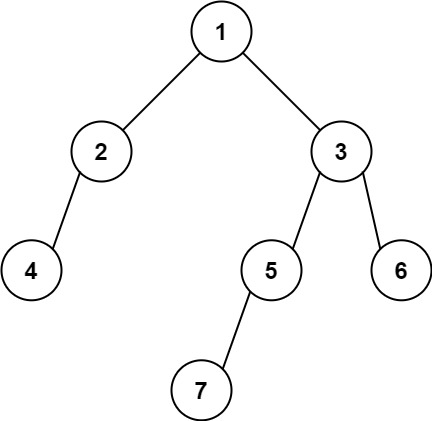
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7
提示:
二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [1,10^4]
-2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
思路:
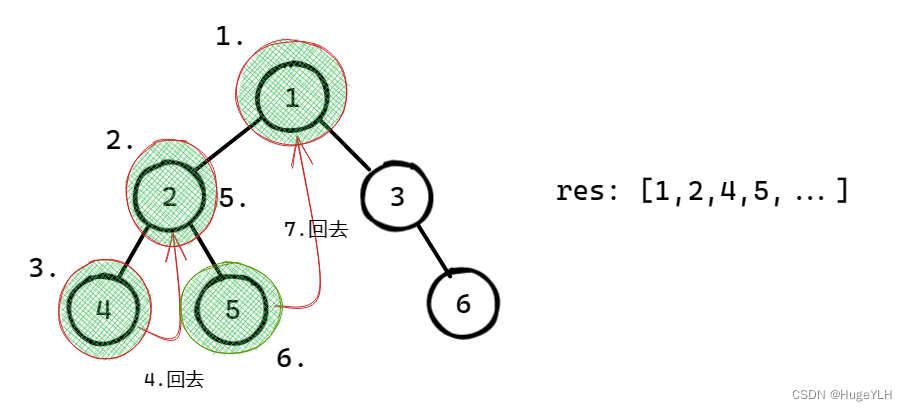
本题要找出树的最后一行的最左边的值。此时大家应该想起用层序遍历是非常简单的了,反而用递归的话会比较难一点。
我们依然还是先介绍递归法。
咋眼一看,这道题目用递归的话就就一直向左遍历,最后一个就是答案呗?
没有这么简单,一直向左遍历到最后一个,它未必是最后一行啊。
我们来分析一下题目:在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。首先要是最后一行,然后是最左边的值。
如果使用递归法,如何判断是最后一行呢,其实就是深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。
如果对二叉树深度和高度还有点疑惑的话,请看:110.平衡二叉树。
所以要找深度最大的叶子节点。
那么如何找最左边的呢?可以使用前序遍历(当然中序,后序都可以,因为本题没有 中间节点的处理逻辑,只要左优先就行),保证优先左边搜索,然后记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值。
递归三部曲:
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为void。
本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxLen用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
代码如下:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN; // 全局变量 记录最大深度
int result; // 全局变量 最大深度最左节点的数值
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth)
2.确定终止条件
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
代码如下:
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth; // 更新最大深度
result = root->val; // 最大深度最左面的数值
}
return;
}
3.确定单层递归的逻辑
在找最大深度的时候,递归的过程中依然要使用回溯,代码如下:
// 中
if (root->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度加一
traversal(root->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度减一
}
if (root->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度加一
traversal(root->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度减一
}
return;
完整代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN;
int result;
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth;
result = root->val;
}
return;
}
if (root->left) {
depth++;
traversal(root->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯
}
if (root->right) {
depth++;
traversal(root->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯
}
return;
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root, 0);
return result;
}
};
当然回溯的地方可以精简,精简代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN;
int result;
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth;
result = root->val;
}
return;
}
if (root->left) {
traversal(root->left, depth + 1); // 隐藏着回溯
}
if (root->right) {
traversal(root->right, depth + 1); // 隐藏着回溯
}
return;
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root, 0);
return result;
}
};
如果对回溯部分精简的代码 不理解的话,可以看这篇257. 二叉树的所有路径
迭代法
本题使用层序遍历再合适不过了,比递归要好理解得多!
只需要记录最后一行第一个节点的数值就可以了。
如果对层序遍历不了解,看这篇二叉树:层序遍历登场!,这篇里也给出了层序遍历的模板,稍作修改就一过刷了这道题了。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int result = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i == 0) result = node->val; // 记录最后一行第一个元素
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
总结
本题涉及如下几点:
- 递归求深度的写法,我们在110.平衡二叉树中详细的分析了深度应该怎么求,高度应该怎么求。
- 递归中其实隐藏了回溯,在257. 二叉树的所有路径中讲解了究竟哪里使用了回溯,哪里隐藏了回溯。
- 层次遍历,在二叉树:层序遍历登场!深度讲解了二叉树层次遍历。 所以本题涉及到的点,我们之前都讲解过,这些知识点需要同学们灵活运用,这样就举一反三了。
自己的代码
class Solution {//迭代法,这个基本和他的代码一样了
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return -1;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int result;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i == 0) result = que.front()->val;
auto temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if (temp->left) que.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right) que.push(temp->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
class Solution {//递归法,我这个主要是深度优先搜索,其实就是前序遍历来做处理,
public:
int result{-1};
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int curDepth, int& maxDepth) {
if (curDepth > maxDepth) {
result = node->val;
maxDepth = curDepth;
}
if(node->left) dfs(node->left, curDepth+1, maxDepth);
if (node->right) dfs(node->right, curDepth + 1, maxDepth);
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return -1;
int curDepth = 0;
int maxDepth = -1;
dfs(root, curDepth, maxDepth);
return result;
}
};


![Rabbit客户端操作不同交换机[包含延迟类型]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b61baf95e18a431a82cd1ae06c2d1751.png)

![[牛客复盘] 牛客2022跨年场 20221212](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/07c2880706ad4a5eb2363567714be2e9.png)