文章目录
- 1 栈的表示与实践
- 1.1 栈的概念及结构
- 1.2 定义数据结构
- 1.3 初始化与销毁
- 1.4 入栈
- 1.5 出栈
- 1.6 栈顶的数据
- 1.7 栈的个数
- 1.8 栈是否是空
- 1.9 打印栈
- 2 队列的表示与实现
- 2.1 队列的概念与结构
- 2.2 队列的数据结构定义
- 2.3 队列的初始化与销毁
- 2.4 入队
- 2.5 出队
- 2.6 取队头数据
- 2.7 取队尾数据
- 2.8 队的个数
- 2.9 判断队是否是空
- 2.10 打印出队列
- 3 栈和队列完整代码
- 3.1 Stack.h
- 3.2 Stack.c
- 3.3 Queue.h
- 3.4 Queue.c
- 3.5 test.c
1 栈的表示与实践
1.1 栈的概念及结构
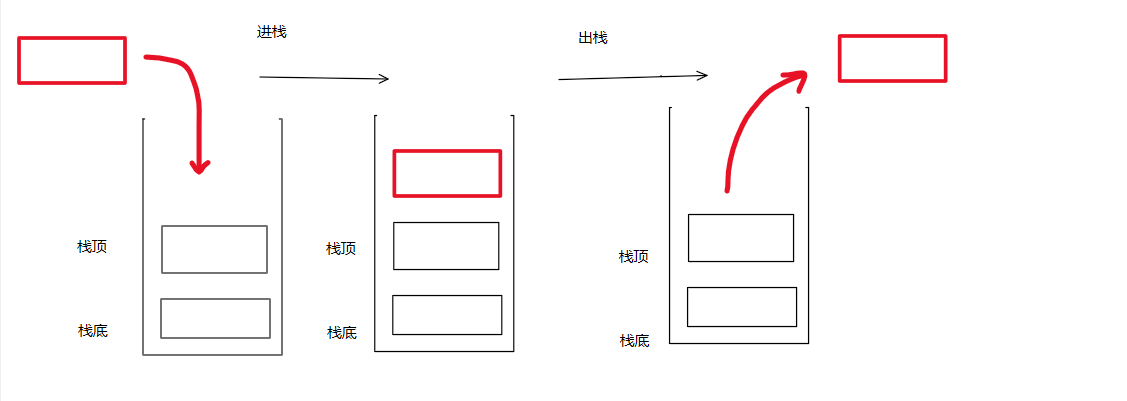
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定一段进行插入和删除元素操作。
进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
栈中的数据元素遵循后进先出LIFO(Last in First out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
1.2 定义数据结构
//1 定义栈的数据结构类型
typedef int StackDataType;
//动态增长的栈
typedef struct Stack
{
StackDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//静态栈一般不用,我们常常使用动态增长的栈
//typedef struct Stack
//{
// STDataType a[50];
// int top;
//}Stack;
1.3 初始化与销毁
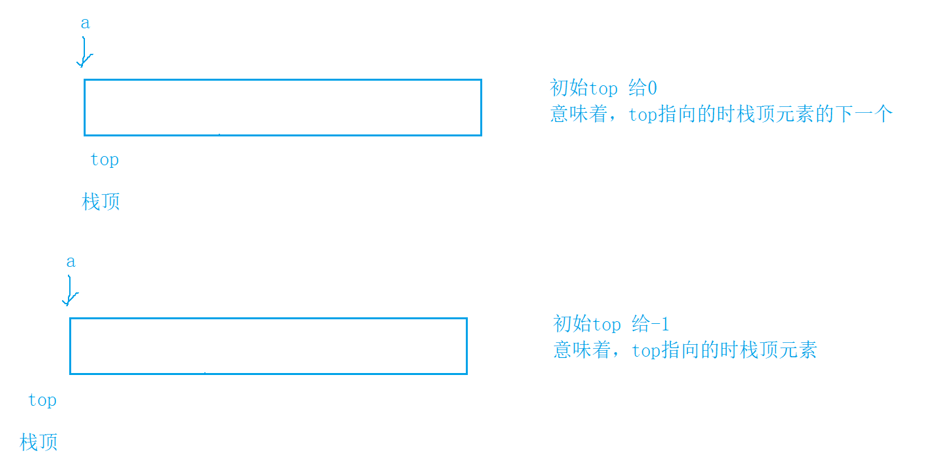
ps->top = 0; 和ps->top = -1;说实话我也说不清楚,要根据画图思考,根据调试得结果
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//刚刚开始给4个数据结构大小
ps->a = (StackDataType*)malloc(sizeof(StackDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0; //top指向栈顶元素的后一个
//ps->top = -1; //top指向栈顶元素
}
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
1.4 入栈
接下来跟我们前面学的顺序表,链表十分类似,也比较容易理解
//检查扩容
void StackCheckCapacity(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(StackDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2; //初始化函数中,capacity大小为4
}
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, StackDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//检查扩容
StackCheckCapacity(ps);
//ps->a[ps->top] = x;
//ps->top++;
//上面两个代码简写成一下一行
ps->a[ps->top++] = x;
}
1.5 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//当栈顶没有元素再删除就产生越界
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
//ps->a[ps->top - 1] = 0;
}
1.6 栈顶的数据
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
//取出栈顶元素
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
1.7 栈的个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//tope位于栈最后一个元素的下一个,同时是前面的数据个数
return ps->top;
}
1.8 栈是否是空
布尔类型检查空间是否是空挺合适的
bool StackIfEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//如果是top是0,真,栈空
return ps->top==0;
}
1.9 打印栈
简单封装一下
void StackPrint(Stack* ps)
{
while (!StackIfEmpty(ps))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(ps));
StackPop(ps);
}
printf("\n");
}
2 队列的表示与实现
2.1 队列的概念与结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先
进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 。 即队尾入,队头出。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
front 队头, rear队尾 在百度百科找的图
2.2 队列的数据结构定义
typedef int QueueDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QueueDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
2.3 队列的初始化与销毁
销毁队列记得存储 cur->next
销毁队列记得存储 cur->next
销毁队列记得存储 cur->next
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* NEXT = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NEXT;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
2.4 入队
常常忘记队列为空时的情况了
//队尾插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//插入的第一个节点
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
//已经有一个节点
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
//pq->tail = newnode;
pq->tail = pq->tail->next;
}
}
2.5 出队
//队头取出数据
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* NEXT = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = NEXT;
}
}
2.6 取队头数据
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
2.7 取队尾数据
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
2.8 队的个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur=cur->next;
}
return size;
}
2.9 判断队是否是空
bool QueueIfEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head==NULL;
}
2.10 打印出队列
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{
while (!QueueIfEmpty(pq))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(pq));
QueuePop(pq);
}
printf("\n");
}
3 栈和队列完整代码
3.1 Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//1 定义栈的数据结构类型
typedef int StackDataType;
//静态栈一般不用,我们常常使用动态增长的栈
//typedef struct Stack
//{
// STDataType a[50];
// int top;
//}Stack;
//动态增长的栈
typedef struct Stack
{
StackDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//2 初始化与销毁
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
void StackDestory(Stack* ps);
//3 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, StackDataType x);
//4 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
//5 返回栈顶的数据
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
//6 栈的个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
//7 栈是否是空
bool StackIfEmpty(Stack* ps);
//8 打印栈
void StackPrint(Stack* ps);
3.2 Stack.c
#include "Stack.h"
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//刚刚开始给4个数据结构大小
ps->a = (StackDataType*)malloc(sizeof(StackDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0; //top指向栈顶元素的后一个
//ps->top = -1; //top指向栈顶元素
}
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//检查扩容
void StackCheckCapacity(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(StackDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2; //初始化函数中,capacity大小为4
}
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, StackDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//检查扩容
StackCheckCapacity(ps);
//ps->a[ps->top] = x;
//ps->top++;
ps->a[ps->top++] = x;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//当栈顶没有元素再删除就产生越界
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
//ps->a[ps->top - 1] = 0;
}
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
//取出栈顶元素
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//tope位于栈最后一个元素的下一个,同时是前面的数据个数
return ps->top;
}
bool StackIfEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//如果是top是0,真,栈空
return ps->top==0;
}
void StackPrint(Stack* ps)
{
while (!StackIfEmpty(ps))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(ps));
StackPop(ps);
}
printf("\n");
}
3.3 Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//队尾入,队头出
//定义队列数据结构
typedef int QueueDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QueueDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
//队列的初始化与销毁
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
//插入与取出
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//取队头数据
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//取队尾数据
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//队的个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//判断队是否是空
bool QueueIfEmpty(Queue* pq);
//打印出队列
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq);
3.4 Queue.c
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* NEXT = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NEXT;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//队尾插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//插入的第一个节点
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
//已经有一个节点
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
//pq->tail = newnode;
pq->tail = pq->tail->next;
}
}
//队头取出数据
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* NEXT = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = NEXT;
}
}
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur=cur->next;
}
return size;
}
bool QueueIfEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head==NULL;
}
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{
while (!QueueIfEmpty(pq))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(pq));
QueuePop(pq);
}
printf("\n");
}
3.5 test.c
#include"Stack.h"
#include"Queue.h"
void test_stack()
{
Stack stack;
StackInit(&stack);
StackPush(&stack, 1);
StackPush(&stack, 2);
StackPush(&stack, 3);
StackPush(&stack, 4);
StackPush(&stack, 5);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&stack));
StackPop(&stack);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&stack));
StackPop(&stack);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&stack));
StackPush(&stack, 11);
StackPush(&stack, 12);
printf("\n");
StackPrint(&stack);
StackDestory(&stack);
}
void test_Queen()
{
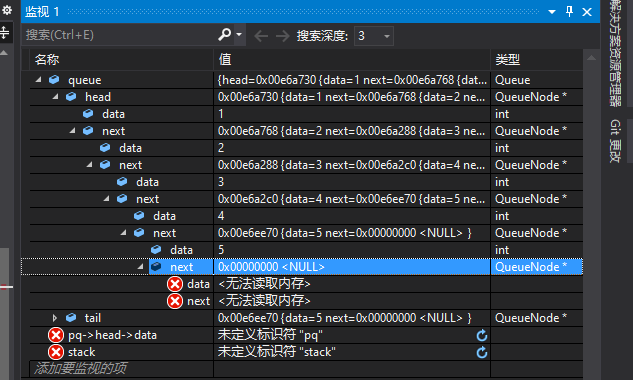
Queue queue;
QueueInit(&queue);
QueuePush(&queue,1);
QueuePush(&queue,2);
QueuePush(&queue,3);
QueuePush(&queue,4);
QueuePush(&queue,5);
printf("%d ", QueueSize(&queue));
//printf("\n");
//printf("%d ", QueueFront(&queue));
//printf("%d ", QueueBack(&queue));
//printf("\n");
//QueuePop(&queue);
//QueuePop(&queue);
//printf("%d ", QueueFront(&queue));
//printf("%d ", QueueBack(&queue));
printf("\n");
//QueuePrint(&queue);
while (!QueueIfEmpty(&queue))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&queue));
QueuePop(&queue);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestory(&queue);
}
int main()
{
//test_stack();
test_Queen();
return 0;
}