----------------------- 🎈API 相关直达 🎈--------------------------
🚀Gradio: 实用篇 | 关于Gradio快速构建人工智能模型实现界面,你想知道的都在这里-CSDN博客
🚀Streamlit :实用篇 | 一文快速构建人工智能前端展示streamlit应用-CSDN博客
🚀Flask: 实用篇 | 一文学会人工智能中API的Flask编写(内含模板)-CSDN博客

Streamlit是一个用于机器学习、数据可视化的 Python 框架,它能几行代码就构建出一个精美的在线 app 应用。相比于Gradio,能展示更多的功能~
目录
1.Streamlit的安装
2.Streamlit的语法
2.1.基本语法
2.2.进阶语法
2.2.1.图片,语音,视频
2.2.2.进程提示
2.3.高级语法
2.3.1.@st.cache_data
2.3.2.st.cache_resource
3.创建一个简单的app
实时读取数据并作图
4.人工智能深度学习项目Streamlit实例
4.1.实例1:文本生成
4.1.1ChatGLM的交互
4.1.2.OpenAI的交互
4.2.图像类
4.2.1.图像分类
4.2.2.图片生成
4.3.语音类
4.3.1.语音合成
4.3.2.语音转文本
参考文献
官网:Get started - Streamlit Docs
1.Streamlit的安装
# 安装
pip install streamlit
pip install streamlit-chat
# 测试
streamlit hello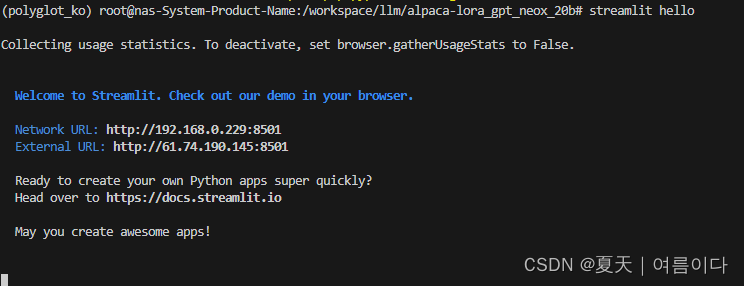
会出现一些案例
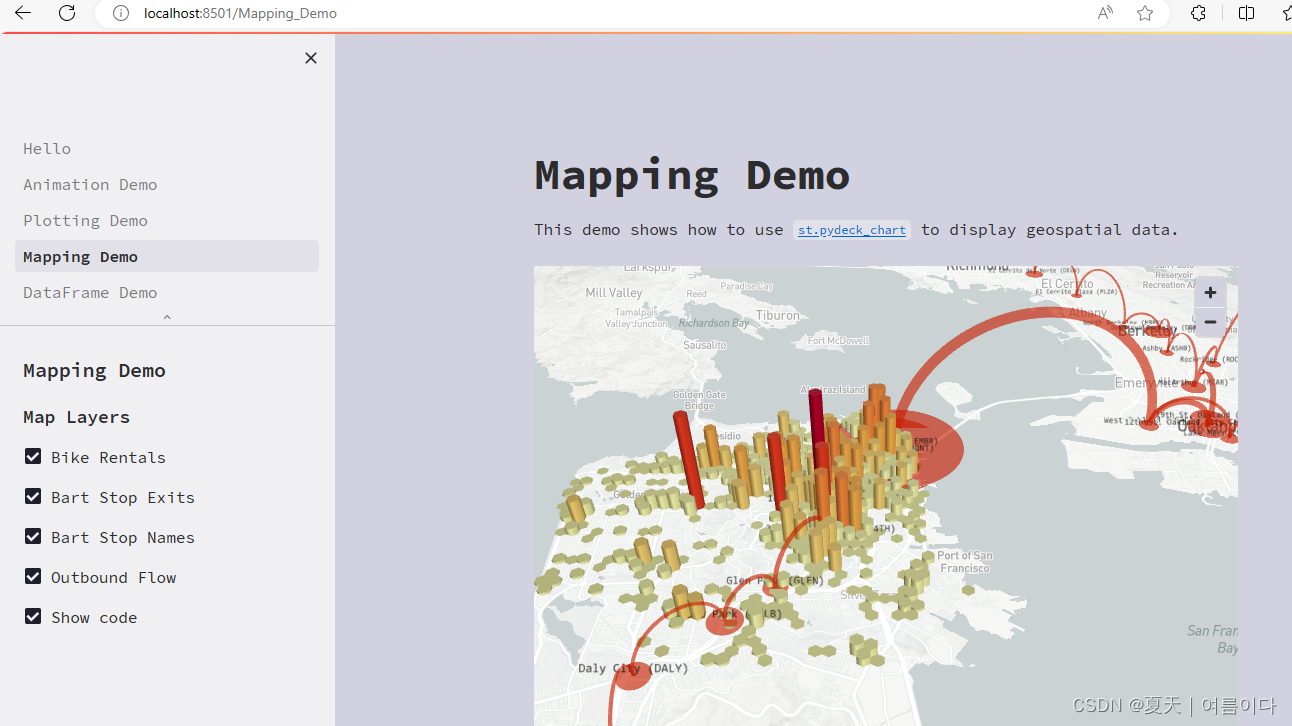
2.Streamlit的语法
2.1.基本语法
import streamlit as st
最常用的几种
- 标题st.title() : st.title("标题")
- 写入st.write(): st.write("Hello world ")
- 文本st.text():单行文本
- 多行文本框st.text_area():st.text_area("文本框",value=''key=None)
- 滑动条st.slider():st.slider(““)
- 按钮st.button():st.button(“按钮“)
- 输入文本st.text_input():st.text_input(“请求用户输入“)
- 单选框组件st.radio()
2.2.进阶语法
2.2.1.图片,语音,视频
都可以输入向量值,比特值,加载文件,文件路径
- st.image()
- st.audio()
- st.video()
2.2.2.进程提示
- st.progress() 显示进度
- st.spinner()显示执行状态
- st.error()显示错误信息
- st.warning - 显示警告信息
2.3.高级语法
2.3.1.@st.cache_data
当使用 Streamlit 的缓存注释标记函数时,它会告诉 Streamlit 每当调用函数时,它应该检查两件事:
- 用于函数调用的输入参数
- 函数内部的代码
2.3.2.st.cache_resource
用于缓存返回全局资源(例如数据库连接、ML 模型)的函数的装饰器。
缓存的对象在所有用户、会话和重新运行之间共享。他们 必须是线程安全的,因为它们可以从多个线程访问 同时。如果线程安全是一个问题,请考虑改用 st.session_state 来存储每个会话的资源。
默认情况下,cache_resource函数的所有参数都必须是可哈希的。 名称以 _ 开头的任何参数都不会进行哈希处理。
3.创建一个简单的app
实时读取数据并作图
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
st.title('Uber pickups in NYC')
DATA_COLUMN = 'data/time'
DATA_URL = ('https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/'
'streamlit-demo-data/uber-raw-data-sep14.csv.gz')
# 增加缓存
@st.cache_data
# 下载数据函数
def load_data(nrows):
# 读取csv文件
data = pd.rea_csv(data_url,nrows=nrows)
# 转换小写字母
lowercase = lambda x:tr(x).lower()
# 将数据重命名
data.rename(lowercase,axis='columns',inplace=True)
# 将数据以panda的数据列的形式展示出来
data[DATA_COLUMN] = pd.to_datatime(data[DATA_COLUMN])
# 返回最终数据
return data
# 直接打印文本信息
data_load_state = st.text('正在下载')
# 下载一万条数据中的数据
data = load_data(10000)
# 最后输出文本显示
data_load_state.text("完成!(using st.cache_data)")
# 检查原始数据
if st.checkbox('Show raw data'):
st.subheader('Raw data')
st.write(data)
# 绘制直方图
# 添加一个子标题
st.subheader('Number of pickups by hour')
# 使用numpy生成一个直方图,按小时排列
hist_values = np.histogram(data[DATE_COLUMN].dt.hour, bins=24, range=(0,24))[0]
# 使用Streamlit 的 st.bar_chart() 方法来绘制直方图
st.bar_chart(hist_values)
# 使用滑动块筛选结果
hour_to_filter = st.slider('hour', 0, 23, 17)
# 实时更新
filtered_data = data[data[DATE_COLUMN].dt.hour == hour_to_filter]
# 为地图添加一个副标题
st.subheader('Map of all pickups at %s:00' % hour_to_filter)
# 使用st.map()函数绘制数据
st.map(filtered_data)
运行
streamlit run demo.py
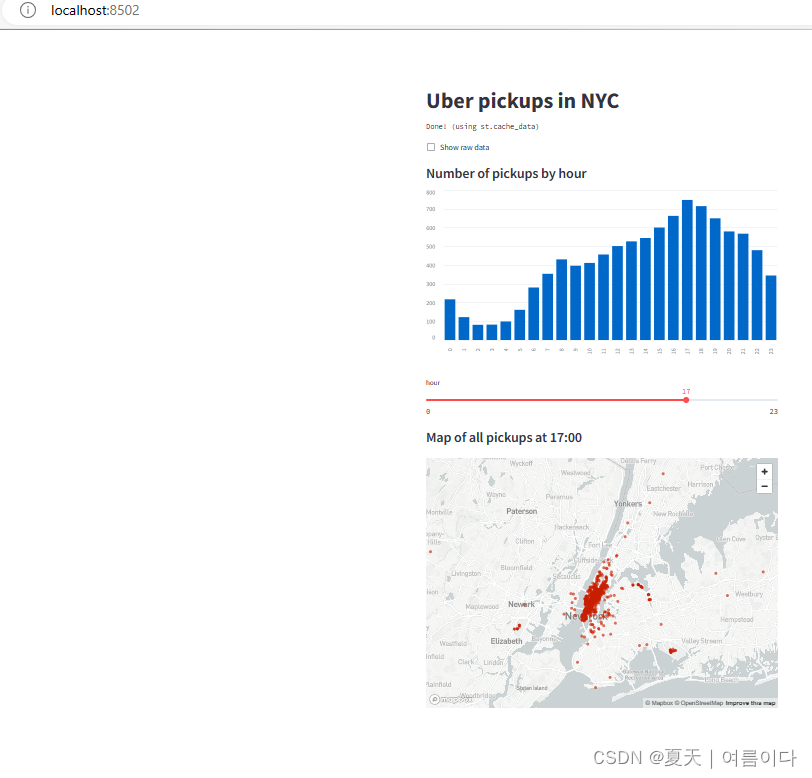
4.人工智能深度学习项目Streamlit实例
4.1.实例1:文本生成
4.1.1ChatGLM的交互
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
import streamlit as st
from streamlit_chat import message
st.set_page_config(
page_title="ChatGLM-6b 演示",
page_icon=":robot:"
)
@st.cache_resource
def get_model():
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm-6b", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("THUDM/chatglm-6b", trust_remote_code=True).half().cuda()
model = model.eval()
return tokenizer, model
MAX_TURNS = 20
MAX_BOXES = MAX_TURNS * 2
def predict(input, max_length, top_p, temperature, history=None):
tokenizer, model = get_model()
if history is None:
history = []
with container:
if len(history) > 0:
if len(history)>MAX_BOXES:
history = history[-MAX_TURNS:]
for i, (query, response) in enumerate(history):
message(query, avatar_style="big-smile", key=str(i) + "_user")
message(response, avatar_style="bottts", key=str(i))
message(input, avatar_style="big-smile", key=str(len(history)) + "_user")
st.write("AI正在回复:")
with st.empty():
for response, history in model.stream_chat(tokenizer, input, history, max_length=max_length, top_p=top_p,
temperature=temperature):
query, response = history[-1]
st.write(response)
return history
container = st.container()
# create a prompt text for the text generation
prompt_text = st.text_area(label="用户命令输入",
height = 100,
placeholder="请在这儿输入您的命令")
max_length = st.sidebar.slider(
'max_length', 0, 4096, 2048, step=1
)
top_p = st.sidebar.slider(
'top_p', 0.0, 1.0, 0.6, step=0.01
)
temperature = st.sidebar.slider(
'temperature', 0.0, 1.0, 0.95, step=0.01
)
if 'state' not in st.session_state:
st.session_state['state'] = []
if st.button("发送", key="predict"):
with st.spinner("AI正在思考,请稍等........"):
# text generation
st.session_state["state"] = predict(prompt_text, max_length, top_p, temperature, st.session_state["state"])4.1.2.OpenAI的交互
from openai import OpenAI
import streamlit as st
with st.sidebar:
openai_api_key = st.text_input("OpenAI API Key", key="chatbot_api_key", type="password")
"[Get an OpenAI API key](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys)"
"[View the source code](https://github.com/streamlit/llm-examples/blob/main/Chatbot.py)"
"[](https://codespaces.new/streamlit/llm-examples?quickstart=1)"
st.title("💬 Chatbot")
st.caption("🚀 A streamlit chatbot powered by OpenAI LLM")
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state["messages"] = [{"role": "assistant", "content": "How can I help you?"}]
for msg in st.session_state.messages:
st.chat_message(msg["role"]).write(msg["content"])
if prompt := st.chat_input():
if not openai_api_key:
st.info("Please add your OpenAI API key to continue.")
st.stop()
client = OpenAI(api_key=openai_api_key)
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
st.chat_message("user").write(prompt)
response = client.chat.completions.create(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=st.session_state.messages)
msg = response.choices[0].message.content
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": msg})
st.chat_message("assistant").write(msg)4.2.图像类
4.2.1.图像分类
import streamlit as st
st.markdown('<h1 style="color:black;">Vgg 19 Image classification model</h1>', unsafe_allow_html=True)
st.markdown('<h2 style="color:gray;">The image classification model classifies image into following categories:</h2>', unsafe_allow_html=True)
st.markdown('<h3 style="color:gray;"> street, buildings, forest, sea, mountain, glacier</h3>', unsafe_allow_html=True)
# 背景图片background image to streamlit
@st.cache(allow_output_mutation=True)
# 以base64的方式传输文件
def get_base64_of_bin_file(bin_file):
with open(bin_file, 'rb') as f:
data = f.read()
return base64.b64encode(data).decode()
#设置背景图片,颜色等
def set_png_as_page_bg(png_file):
bin_str = get_base64_of_bin_file(png_file)
page_bg_img = '''
<style>
.stApp {
background-image: url("data:image/png;base64,%s");
background-size: cover;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: scroll; # doesn't work
}
</style>
''' % bin_str
st.markdown(page_bg_img, unsafe_allow_html=True)
return
set_png_as_page_bg('/content/background.webp')
# 上传png/jpg的照片
upload= st.file_uploader('Insert image for classification', type=['png','jpg'])
c1, c2= st.columns(2)
if upload is not None:
im= Image.open(upload)
img= np.asarray(im)
image= cv2.resize(img,(224, 224))
img= preprocess_input(image)
img= np.expand_dims(img, 0)
c1.header('Input Image')
c1.image(im)
c1.write(img.shape)
# 下载预训练模型
# 输入尺寸
input_shape = (224, 224, 3)
# 定义优化器
optim_1 = Adam(learning_rate=0.0001)
# 分类数
n_classes=6
# 定义模型
vgg_model = model(input_shape, n_classes, optim_1, fine_tune=2)
# 下载权重
vgg_model.load_weights('/content/drive/MyDrive/vgg/tune_model19.weights.best.hdf5')
#预测
vgg_preds = vgg_model.predict(img)
vgg_pred_classes = np.argmax(vgg_preds, axis=1)
c2.header('Output')
c2.subheader('Predicted class :')
c2.write(classes[vgg_pred_classes[0]] )
4.2.2.图片生成
import streamlit as st
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
import openai
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
import torch
load_dotenv()
openai.api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
#function to generate AI based images using OpenAI Dall-E
def generate_images_using_openai(text):
response = openai.Image.create(prompt= text, n=1, size="512x512")
image_url = response['data'][0]['url']
return image_url
#function to generate AI based images using Huggingface Diffusers
def generate_images_using_huggingface_diffusers(text):
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
prompt = text
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
return image
#Streamlit Code
choice = st.sidebar.selectbox("Select your choice", ["Home", "DALL-E", "Huggingface Diffusers"])
if choice == "Home":
st.title("AI Image Generation App")
with st.expander("About the App"):
st.write("This is a simple image generation app that uses AI to generates images from text prompt.")
elif choice == "DALL-E":
st.subheader("Image generation using Open AI's DALL-E")
input_prompt = st.text_input("Enter your text prompt")
if input_prompt is not None:
if st.button("Generate Image"):
image_url = generate_images_using_openai(input_prompt)
st.image(image_url, caption="Generated by DALL-E")
elif choice == "Huggingface Diffusers":
st.subheader("Image generation using Huggingface Diffusers")
input_prompt = st.text_input("Enter your text prompt")
if input_prompt is not None:
if st.button("Generate Image"):
image_output = generate_images_using_huggingface_diffusers(input_prompt)
st.info("Generating image.....")
st.success("Image Generated Successfully")
st.image(image_output, caption="Generated by Huggingface Diffusers")4.3.语音类
4.3.1.语音合成
import torch
import streamlit as st
# 这里使用coqui-tts,直接pip install tts就可以
from TTS.api import TTS
import tempfile
import os
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# 模型选择
model_name = 'tts_models/en/jenny/jenny'
tts = TTS(model_name).to(device)
st.title('Coqui TTS')
# 输入文本
text_to_speak = st.text_area('Entire article text here:', '')
# 点击按钮监听
if st.button('Listen'):
if text_to_speak:
# temp path needed for audio to listen to
# 定义合成语音文件名称
temp_audio_path = './temp_audio.wav'
# 使用tts库中的tts_to_file函数
tts.tts_to_file(text=text_to_speak, file_path=temp_audio_path)
#输出语音
st.audio(temp_audio_path, format='audio/wav')
os.unlink(temp_audio_path)
4.3.2.语音转文本
import logging
import logging.handlers
import queue
import threading
import time
import urllib.request
import os
from collections import deque
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List
import av
import numpy as np
import pydub
import streamlit as st
from twilio.rest import Client
from streamlit_webrtc import WebRtcMode, webrtc_streamer
HERE = Path(__file__).parent
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# This code is based on https://github.com/streamlit/demo-self-driving/blob/230245391f2dda0cb464008195a470751c01770b/streamlit_app.py#L48 # noqa: E501
def download_file(url, download_to: Path, expected_size=None):
# Don't download the file twice.
# (If possible, verify the download using the file length.)
if download_to.exists():
if expected_size:
if download_to.stat().st_size == expected_size:
return
else:
st.info(f"{url} is already downloaded.")
if not st.button("Download again?"):
return
download_to.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# These are handles to two visual elements to animate.
weights_warning, progress_bar = None, None
try:
weights_warning = st.warning("Downloading %s..." % url)
progress_bar = st.progress(0)
with open(download_to, "wb") as output_file:
with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response:
length = int(response.info()["Content-Length"])
counter = 0.0
MEGABYTES = 2.0 ** 20.0
while True:
data = response.read(8192)
if not data:
break
counter += len(data)
output_file.write(data)
# We perform animation by overwriting the elements.
weights_warning.warning(
"Downloading %s... (%6.2f/%6.2f MB)"
% (url, counter / MEGABYTES, length / MEGABYTES)
)
progress_bar.progress(min(counter / length, 1.0))
# Finally, we remove these visual elements by calling .empty().
finally:
if weights_warning is not None:
weights_warning.empty()
if progress_bar is not None:
progress_bar.empty()
# This code is based on https://github.com/whitphx/streamlit-webrtc/blob/c1fe3c783c9e8042ce0c95d789e833233fd82e74/sample_utils/turn.py
@st.cache_data # type: ignore
def get_ice_servers():
"""Use Twilio's TURN server because Streamlit Community Cloud has changed
its infrastructure and WebRTC connection cannot be established without TURN server now. # noqa: E501
We considered Open Relay Project (https://www.metered.ca/tools/openrelay/) too,
but it is not stable and hardly works as some people reported like https://github.com/aiortc/aiortc/issues/832#issuecomment-1482420656 # noqa: E501
See https://github.com/whitphx/streamlit-webrtc/issues/1213
"""
# Ref: https://www.twilio.com/docs/stun-turn/api
try:
account_sid = os.environ["TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID"]
auth_token = os.environ["TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN"]
except KeyError:
logger.warning(
"Twilio credentials are not set. Fallback to a free STUN server from Google." # noqa: E501
)
return [{"urls": ["stun:stun.l.google.com:19302"]}]
client = Client(account_sid, auth_token)
token = client.tokens.create()
return token.ice_servers
def main():
st.header("Real Time Speech-to-Text")
st.markdown(
"""
This demo app is using [DeepSpeech](https://github.com/mozilla/DeepSpeech),
an open speech-to-text engine.
A pre-trained model released with
[v0.9.3](https://github.com/mozilla/DeepSpeech/releases/tag/v0.9.3),
trained on American English is being served.
"""
)
# https://github.com/mozilla/DeepSpeech/releases/tag/v0.9.3
MODEL_URL = "https://github.com/mozilla/DeepSpeech/releases/download/v0.9.3/deepspeech-0.9.3-models.pbmm" # noqa
LANG_MODEL_URL = "https://github.com/mozilla/DeepSpeech/releases/download/v0.9.3/deepspeech-0.9.3-models.scorer" # noqa
MODEL_LOCAL_PATH = HERE / "models/deepspeech-0.9.3-models.pbmm"
LANG_MODEL_LOCAL_PATH = HERE / "models/deepspeech-0.9.3-models.scorer"
download_file(MODEL_URL, MODEL_LOCAL_PATH, expected_size=188915987)
download_file(LANG_MODEL_URL, LANG_MODEL_LOCAL_PATH, expected_size=953363776)
lm_alpha = 0.931289039105002
lm_beta = 1.1834137581510284
beam = 100
sound_only_page = "Sound only (sendonly)"
with_video_page = "With video (sendrecv)"
app_mode = st.selectbox("Choose the app mode", [sound_only_page, with_video_page])
if app_mode == sound_only_page:
app_sst(
str(MODEL_LOCAL_PATH), str(LANG_MODEL_LOCAL_PATH), lm_alpha, lm_beta, beam
)
elif app_mode == with_video_page:
app_sst_with_video(
str(MODEL_LOCAL_PATH), str(LANG_MODEL_LOCAL_PATH), lm_alpha, lm_beta, beam
)
def app_sst(model_path: str, lm_path: str, lm_alpha: float, lm_beta: float, beam: int):
webrtc_ctx = webrtc_streamer(
key="speech-to-text",
mode=WebRtcMode.SENDONLY,
audio_receiver_size=1024,
rtc_configuration={"iceServers": get_ice_servers()},
media_stream_constraints={"video": False, "audio": True},
)
status_indicator = st.empty()
if not webrtc_ctx.state.playing:
return
status_indicator.write("Loading...")
text_output = st.empty()
stream = None
while True:
if webrtc_ctx.audio_receiver:
if stream is None:
from deepspeech import Model
model = Model(model_path)
model.enableExternalScorer(lm_path)
model.setScorerAlphaBeta(lm_alpha, lm_beta)
model.setBeamWidth(beam)
stream = model.createStream()
status_indicator.write("Model loaded.")
sound_chunk = pydub.AudioSegment.empty()
try:
audio_frames = webrtc_ctx.audio_receiver.get_frames(timeout=1)
except queue.Empty:
time.sleep(0.1)
status_indicator.write("No frame arrived.")
continue
status_indicator.write("Running. Say something!")
for audio_frame in audio_frames:
sound = pydub.AudioSegment(
data=audio_frame.to_ndarray().tobytes(),
sample_width=audio_frame.format.bytes,
frame_rate=audio_frame.sample_rate,
channels=len(audio_frame.layout.channels),
)
sound_chunk += sound
if len(sound_chunk) > 0:
sound_chunk = sound_chunk.set_channels(1).set_frame_rate(
model.sampleRate()
)
buffer = np.array(sound_chunk.get_array_of_samples())
stream.feedAudioContent(buffer)
text = stream.intermediateDecode()
text_output.markdown(f"**Text:** {text}")
else:
status_indicator.write("AudioReciver is not set. Abort.")
break
def app_sst_with_video(
model_path: str, lm_path: str, lm_alpha: float, lm_beta: float, beam: int
):
frames_deque_lock = threading.Lock()
frames_deque: deque = deque([])
async def queued_audio_frames_callback(
frames: List[av.AudioFrame],
) -> av.AudioFrame:
with frames_deque_lock:
frames_deque.extend(frames)
# Return empty frames to be silent.
new_frames = []
for frame in frames:
input_array = frame.to_ndarray()
new_frame = av.AudioFrame.from_ndarray(
np.zeros(input_array.shape, dtype=input_array.dtype),
layout=frame.layout.name,
)
new_frame.sample_rate = frame.sample_rate
new_frames.append(new_frame)
return new_frames
webrtc_ctx = webrtc_streamer(
key="speech-to-text-w-video",
mode=WebRtcMode.SENDRECV,
queued_audio_frames_callback=queued_audio_frames_callback,
rtc_configuration={"iceServers": get_ice_servers()},
media_stream_constraints={"video": True, "audio": True},
)
status_indicator = st.empty()
if not webrtc_ctx.state.playing:
return
status_indicator.write("Loading...")
text_output = st.empty()
stream = None
while True:
if webrtc_ctx.state.playing:
if stream is None:
from deepspeech import Model
model = Model(model_path)
model.enableExternalScorer(lm_path)
model.setScorerAlphaBeta(lm_alpha, lm_beta)
model.setBeamWidth(beam)
stream = model.createStream()
status_indicator.write("Model loaded.")
sound_chunk = pydub.AudioSegment.empty()
audio_frames = []
with frames_deque_lock:
while len(frames_deque) > 0:
frame = frames_deque.popleft()
audio_frames.append(frame)
if len(audio_frames) == 0:
time.sleep(0.1)
status_indicator.write("No frame arrived.")
continue
status_indicator.write("Running. Say something!")
for audio_frame in audio_frames:
sound = pydub.AudioSegment(
data=audio_frame.to_ndarray().tobytes(),
sample_width=audio_frame.format.bytes,
frame_rate=audio_frame.sample_rate,
channels=len(audio_frame.layout.channels),
)
sound_chunk += sound
if len(sound_chunk) > 0:
sound_chunk = sound_chunk.set_channels(1).set_frame_rate(
model.sampleRate()
)
buffer = np.array(sound_chunk.get_array_of_samples())
stream.feedAudioContent(buffer)
text = stream.intermediateDecode()
text_output.markdown(f"**Text:** {text}")
else:
status_indicator.write("Stopped.")
break
if __name__ == "__main__":
import os
DEBUG = os.environ.get("DEBUG", "false").lower() not in ["false", "no", "0"]
logging.basicConfig(
format="[%(asctime)s] %(levelname)7s from %(name)s in %(pathname)s:%(lineno)d: "
"%(message)s",
force=True,
)
logger.setLevel(level=logging.DEBUG if DEBUG else logging.INFO)
st_webrtc_logger = logging.getLogger("streamlit_webrtc")
st_webrtc_logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
fsevents_logger = logging.getLogger("fsevents")
fsevents_logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
main()参考文献
【1】API Reference - Streamlit Docs
【2】andfanilo/streamlit-lottie: Streamlit component to render Lottie animations (github.com)turner-anderson/streamlit-cropper: A simple image cropper for Streamlit (github.com)andfanilo/streamlit-lottie: Streamlit component to render Lottie animations (github.com)
【3】awetomate/text-to-speech-streamlit: Text-to-Speech solution using Google's Cloud TTS API and a Streamlit front end (github.com) 【4】Using streamlit for an STT / TTS model demo? - 🧩 Streamlit Components - Streamlit
【5】AI-App/Streamlit-TTS (github.com)
【6】Building a Voice Assistant using ChatGPT API | Vahid's ML-Blog (vahidmirjalili.com)
【7】streamlit/llm-examples: Streamlit LLM app examples for getting started (github.com)
【8】whitphx/streamlit-stt-app: Real time web based Speech-to-Text app with Streamlit (github.com)


![[Linux] nginx防盗链与优化](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3d4a001b765a4079a6f88bfaa39c9db4.png)