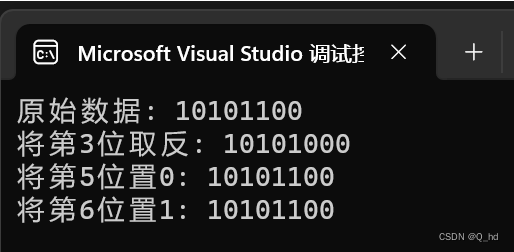
继续下一个阶段:
Train policy
python act/imitate_episodes.py \ --task_name [TASK] \ --ckpt_dir data/outputs/act_ckpt/[TASK]_waypoint \ --policy_class ACT --kl_weight 10 --chunk_size 50 --hidden_dim 512 --batch_size 8 --dim_feedforward 3200 \ --num_epochs 8000 --lr 1e-5 \ --seed 0 --temporal_agg --use_waypoint
For human datasets, set --kl_weight=80, as suggested by the ACT authors. To evaluate the policy, run the same command with --eval.
翻译:对于人类数据集,如ACT作者所建议的,设置--kl_weight=80。若要评估策略,请使用-eval运行相同的命令。
在完成了Bimanual Simulation Suite(Save waypoints)的这个博客内容之后,即
Save waypoints的操作完成后,下面便可以进行sim_transfer_cube_scripted这一任务的训练,即
Train policy:
首先进入awe的文件夹目录中,在linux的终端中输入以下的命令:
python act/imitate_episodes.py \ --task_name sim_transfer_cube_scripted \ --ckpt_dir data/outputs/act_ckpt/sim_transfer_cube_scripted_waypoint \ --policy_class ACT --kl_weight 10 --chunk_size 50 --hidden_dim 512 --batch_size 8 --dim_feedforward 3200 \ --num_epochs 8000 --lr 1e-5 \ --seed 0 --temporal_agg --use_waypoint
终端会进行训练进度的显示,截图如下:
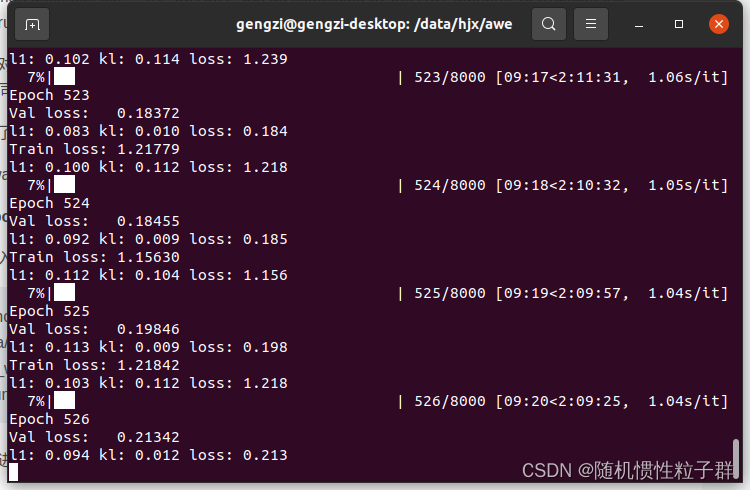
这时说明Train policy已经在进行了,等待训练结束即可。
在运行这个Train policy时,遇到了一些小bug(报错),记录如下:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'gym' 的解决方案:
pip install gym
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'gym' 错误表示你的Python环境中缺少了名为 gym 的Python模块。gym 是用于开发和测试强化学习算法的一个常用库,通常与OpenAI Gym一起使用。
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'dm_control' 的解决方案:
pip install dm_control
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'dm_control' 错误表示你的Python环境中缺少了名为 dm_control 的Python模块。dm_control 是DeepMind开发的一个用于机器人控制和物理仿真的库,通常与MuJoCo一起使用。
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] Unable to synchronously open file (unable to open file: name = 'data/act/sim_transfer_cube_scripted_copy/episode_0.hdf5', errno = 2, error message = 'No such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0) 的解决方案:
在awe/data/act/的文件路径中将sim_transfer_cube_scripted文件夹复制一份后更名为sim_transfer_cube_scripted_copy
FileNotFoundError 错误表示在指定的路径下找不到文件。具体来说,错误消息中提到了文件路径 'data/act/sim_transfer_cube_scripted_copy/episode_0.hdf5',但系统无法找到该文件,因为文件或路径不存在。
raise AssertionError("Torch not compiled with CUDA enabled") AssertionError: Torch not compiled with CUDA enabled 的的解决方案:
nvidia-smi # 查看显卡的CUDA Version: 12.2 我这里是 12.2,在去查找CUDA 12.2的PyTorch版本是1.10.0
pip install torch==1.10.0 # 安装CUDA 12.2的对应版本
请根据你的PyTorch版本和需求进行安装。
pip install torch==1.10.0安装完成后,接着进行Train policy时,又遇到了:
ERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts. torchvision 0.16.0 requires torch==2.1.0, but you have torch 1.10.0 which is incompatible.
其解决方案为:
pip install torchvision --upgrade
这将安装 torchvision 的最新版本,该版本可能与你的 PyTorch 版本兼容。
这个错误消息表明 torchvision 需要与特定版本的 PyTorch 兼容,但你当前的 PyTorch 版本与 torchvision 不兼容。为了解决这个问题,你需要升级 torchvision 或降级 PyTorch,以使它们兼容。
最后有必要解读一下 act/imitate_episodes.py 这个python文件,部分代码粘贴如下:
def main(args):
set_seed(1)
# command line parameters
is_eval = args["eval"]
ckpt_dir = args["ckpt_dir"]
policy_class = args["policy_class"]
onscreen_render = args["onscreen_render"]
task_name = args["task_name"]
batch_size_train = args["batch_size"]
batch_size_val = args["batch_size"]
num_epochs = args["num_epochs"]
use_waypoint = args["use_waypoint"]
constant_waypoint = args["constant_waypoint"]
if use_waypoint:
print("Using waypoint")
if constant_waypoint is not None:
print(f"Constant waypoint: {constant_waypoint}")
# get task parameters
# is_sim = task_name[:4] == 'sim_'
is_sim = True # hardcode to True to avoid finding constants from aloha
if is_sim:
from constants import SIM_TASK_CONFIGS
task_config = SIM_TASK_CONFIGS[task_name]
else:
from aloha_scripts.constants import TASK_CONFIGS
task_config = TASK_CONFIGS[task_name]
dataset_dir = task_config["dataset_dir"]
num_episodes = task_config["num_episodes"]
episode_len = task_config["episode_len"]
camera_names = task_config["camera_names"]
# fixed parameters
state_dim = 14
lr_backbone = 1e-5
backbone = "resnet18"
if policy_class == "ACT":
enc_layers = 4
dec_layers = 7
nheads = 8
policy_config = {
"lr": args["lr"],
"num_queries": args["chunk_size"],
"kl_weight": args["kl_weight"],
"hidden_dim": args["hidden_dim"],
"dim_feedforward": args["dim_feedforward"],
"lr_backbone": lr_backbone,
"backbone": backbone,
"enc_layers": enc_layers,
"dec_layers": dec_layers,
"nheads": nheads,
"camera_names": camera_names,
}
elif policy_class == "CNNMLP":
policy_config = {
"lr": args["lr"],
"lr_backbone": lr_backbone,
"backbone": backbone,
"num_queries": 1,
"camera_names": camera_names,
}
else:
raise NotImplementedError
config = {
"num_epochs": num_epochs,
"ckpt_dir": ckpt_dir,
"episode_len": episode_len,
"state_dim": state_dim,
"lr": args["lr"],
"policy_class": policy_class,
"onscreen_render": onscreen_render,
"policy_config": policy_config,
"task_name": task_name,
"seed": args["seed"],
"temporal_agg": args["temporal_agg"],
"camera_names": camera_names,
"real_robot": not is_sim,
}
if is_eval:
ckpt_names = [f"policy_best.ckpt"]
results = []
for ckpt_name in ckpt_names:
success_rate, avg_return = eval_bc(config, ckpt_name, save_episode=True)
results.append([ckpt_name, success_rate, avg_return])
for ckpt_name, success_rate, avg_return in results:
print(f"{ckpt_name}: {success_rate=} {avg_return=}")
print()
exit()
train_dataloader, val_dataloader, stats, _ = load_data(
dataset_dir,
num_episodes,
camera_names,
batch_size_train,
batch_size_val,
use_waypoint,
constant_waypoint,
)
# save dataset stats
if not os.path.isdir(ckpt_dir):
os.makedirs(ckpt_dir)
stats_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"dataset_stats.pkl")
with open(stats_path, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(stats, f)
best_ckpt_info = train_bc(train_dataloader, val_dataloader, config)
best_epoch, min_val_loss, best_state_dict = best_ckpt_info
# save best checkpoint
ckpt_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"policy_best.ckpt")
torch.save(best_state_dict, ckpt_path)
print(f"Best ckpt, val loss {min_val_loss:.6f} @ epoch{best_epoch}")这段代码是一个主程序,用于训练或评估一个深度学习模型。以下是代码的主要功能:
-
从命令行参数中获取模型训练和评估的相关配置。
-
根据任务名称和配置获取任务参数,例如数据集目录、任务类型等。
-
定义模型的架构和超参数,包括学习率、网络结构、层数等。
-
创建数据加载器,加载训练和验证数据集。
-
训练模型并保存最佳模型的权重。如果模型已经在以前的训练中保存了最佳权重,可以选择加载这些权重并进行评估。
-
如果设置为评估模式,加载保存的模型权重并在验证集上评估模型性能,计算成功率和平均回报。
-
最后,将结果打印出来。
请注意,这段代码需要其他模块和库的支持,例如数据加载、模型定义、训练和评估函数等。要运行这段代码,你需要确保所有的依赖项都已安装,并提供正确的命令行参数以配置模型训练或评估的行为。
def make_policy(policy_class, policy_config):
if policy_class == "ACT":
policy = ACTPolicy(policy_config)
elif policy_class == "CNNMLP":
policy = CNNMLPPolicy(policy_config)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return policy这个函数根据指定的policy_class(策略类别)和policy_config(策略配置)创建一个策略模型对象。策略模型用于执行某种任务或动作,通常是在强化学习中使用的。
函数的工作流程如下:
-
接受两个参数:
policy_class表示要创建的策略模型的类别,policy_config表示策略模型的配置参数。 -
根据
policy_class的值,决定创建哪种类型的策略模型。目前支持两种类型:"ACT"和"CNNMLP"。 -
创建指定类型的策略模型,并使用传递的
policy_config来配置模型的超参数和设置。 -
返回创建的策略模型对象。
这个函数的主要作用是根据需要创建不同类型的策略模型,并提供一个统一的接口供其他部分的代码使用。根据具体的应用和任务,可以选择不同的策略模型类型,以满足任务的需求。如果需要了解更多关于不同策略模型类型的详细信息,可以查看对应的策略模型的定义(例如,ACTPolicy和CNNMLPPolicy)。
def make_optimizer(policy_class, policy):
if policy_class == "ACT":
optimizer = policy.configure_optimizers()
elif policy_class == "CNNMLP":
optimizer = policy.configure_optimizers()
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return optimizer这个函数用于创建策略模型的优化器(optimizer),并返回创建的优化器对象。优化器的作用是根据策略模型的损失函数来更新模型的参数,以使损失函数尽量减小。
函数的工作流程如下:
-
接受两个参数:
policy_class表示策略模型的类别,policy表示已经创建的策略模型对象。 -
根据
policy_class的值,决定使用哪种类型的优化器配置。目前支持两种类型:"ACT"和"CNNMLP"。 -
调用策略模型的
configure_optimizers方法,该方法通常会返回一个用于优化模型的优化器对象。 -
返回创建的优化器对象。
这个函数的主要作用是根据策略模型的类别和已经创建的策略模型对象来创建相应的优化器。不同的策略模型可能需要不同的优化器配置,因此通过调用策略模型的方法来创建优化器,以确保配置的一致性。优化器对象通常用于后续的训练过程中,用于更新模型的参数以最小化损失函数。
def get_image(ts, camera_names):
curr_images = []
for cam_name in camera_names:
curr_image = rearrange(ts.observation["images"][cam_name], "h w c -> c h w")
curr_images.append(curr_image)
curr_image = np.stack(curr_images, axis=0)
curr_image = torch.from_numpy(curr_image / 255.0).float().cuda().unsqueeze(0)
return curr_image这个函数的作用是获取一个时间步(ts)的图像数据。函数接受两个参数:ts和camera_names。
-
ts是一个时间步的数据,包含了多个相机(摄像头)拍摄的图像。ts.observation["images"]包含了各个相机拍摄的图像数据,而camera_names是一个列表,包含了要获取的相机的名称。 -
函数通过循环遍历
camera_names中的相机名称,从ts.observation["images"]中获取对应相机的图像数据。这些图像数据首先通过rearrange函数重新排列维度,将"height-width-channels"的顺序变为"channels-height-width",以适应PyTorch的数据格式。 -
获取的图像数据被放入
curr_images列表中。 -
接下来,函数将
curr_images列表中的所有图像数据堆叠成一个张量(tensor),np.stack(curr_images, axis=0)这一行代码实现了这个操作。 -
接着,图像数据被归一化到[0, 1]的范围,然后转换为PyTorch的
float类型,并移到GPU上(如果可用)。最后,图像数据被增加了一个额外的维度(unsqueeze(0)),以适应模型的输入要求。
最终,函数返回包含时间步图像数据的PyTorch张量。这个图像数据可以被用于输入到神经网络模型中进行处理。
def eval_bc(config, ckpt_name, save_episode=True):
set_seed(1000)
ckpt_dir = config["ckpt_dir"]
state_dim = config["state_dim"]
real_robot = config["real_robot"]
policy_class = config["policy_class"]
onscreen_render = config["onscreen_render"]
policy_config = config["policy_config"]
camera_names = config["camera_names"]
max_timesteps = config["episode_len"]
task_name = config["task_name"]
temporal_agg = config["temporal_agg"]
onscreen_cam = "angle"
# load policy and stats
ckpt_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, ckpt_name)
policy = make_policy(policy_class, policy_config)
loading_status = policy.load_state_dict(torch.load(ckpt_path))
print(loading_status)
policy.cuda()
policy.eval()
print(f"Loaded: {ckpt_path}")
stats_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"dataset_stats.pkl")
with open(stats_path, "rb") as f:
stats = pickle.load(f)
pre_process = lambda s_qpos: (s_qpos - stats["qpos_mean"]) / stats["qpos_std"]
post_process = lambda a: a * stats["action_std"] + stats["action_mean"]
# load environment
if real_robot:
from aloha_scripts.robot_utils import move_grippers # requires aloha
from aloha_scripts.real_env import make_real_env # requires aloha
env = make_real_env(init_node=True)
env_max_reward = 0
else:
from act.sim_env import make_sim_env
env = make_sim_env(task_name)
env_max_reward = env.task.max_reward
query_frequency = policy_config["num_queries"]
if temporal_agg:
query_frequency = 1
num_queries = policy_config["num_queries"]
max_timesteps = int(max_timesteps * 1) # may increase for real-world tasks
num_rollouts = 50
episode_returns = []
highest_rewards = []
for rollout_id in range(num_rollouts):
rollout_id += 0
### set task
if "sim_transfer_cube" in task_name:
BOX_POSE[0] = sample_box_pose() # used in sim reset
elif "sim_insertion" in task_name:
BOX_POSE[0] = np.concatenate(sample_insertion_pose()) # used in sim reset
ts = env.reset()
### onscreen render
if onscreen_render:
ax = plt.subplot()
plt_img = ax.imshow(
env._physics.render(height=480, width=640, camera_id=onscreen_cam)
)
plt.ion()
### evaluation loop
if temporal_agg:
all_time_actions = torch.zeros(
[max_timesteps, max_timesteps + num_queries, state_dim]
).cuda()
qpos_history = torch.zeros((1, max_timesteps, state_dim)).cuda()
image_list = [] # for visualization
qpos_list = []
target_qpos_list = []
rewards = []
with torch.inference_mode():
for t in range(max_timesteps):
### update onscreen render and wait for DT
if onscreen_render:
image = env._physics.render(
height=480, width=640, camera_id=onscreen_cam
)
plt_img.set_data(image)
plt.pause(DT)
### process previous timestep to get qpos and image_list
obs = ts.observation
if "images" in obs:
image_list.append(obs["images"])
else:
image_list.append({"main": obs["image"]})
qpos_numpy = np.array(obs["qpos"])
qpos = pre_process(qpos_numpy)
qpos = torch.from_numpy(qpos).float().cuda().unsqueeze(0)
qpos_history[:, t] = qpos
curr_image = get_image(ts, camera_names)
### query policy
if config["policy_class"] == "ACT":
if t % query_frequency == 0:
all_actions = policy(qpos, curr_image)
if temporal_agg:
all_time_actions[[t], t : t + num_queries] = all_actions
actions_for_curr_step = all_time_actions[:, t]
actions_populated = torch.all(
actions_for_curr_step != 0, axis=1
)
actions_for_curr_step = actions_for_curr_step[actions_populated]
k = 0.01
exp_weights = np.exp(-k * np.arange(len(actions_for_curr_step)))
exp_weights = exp_weights / exp_weights.sum()
exp_weights = (
torch.from_numpy(exp_weights).cuda().unsqueeze(dim=1)
)
raw_action = (actions_for_curr_step * exp_weights).sum(
dim=0, keepdim=True
)
else:
raw_action = all_actions[:, t % query_frequency]
elif config["policy_class"] == "CNNMLP":
raw_action = policy(qpos, curr_image)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
### post-process actions
raw_action = raw_action.squeeze(0).cpu().numpy()
action = post_process(raw_action)
target_qpos = action
### step the environment
ts = env.step(target_qpos)
### for visualization
qpos_list.append(qpos_numpy)
target_qpos_list.append(target_qpos)
rewards.append(ts.reward)
plt.close()
if real_robot:
move_grippers(
[env.puppet_bot_left, env.puppet_bot_right],
[PUPPET_GRIPPER_JOINT_OPEN] * 2,
move_time=0.5,
) # open
pass
rewards = np.array(rewards)
episode_return = np.sum(rewards[rewards != None])
episode_returns.append(episode_return)
episode_highest_reward = np.max(rewards)
highest_rewards.append(episode_highest_reward)
print(
f"Rollout {rollout_id}\n{episode_return=}, {episode_highest_reward=}, {env_max_reward=}, Success: {episode_highest_reward==env_max_reward}"
)
if save_episode:
save_videos(
image_list,
DT,
video_path=os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"video{rollout_id}.mp4"),
)
success_rate = np.mean(np.array(highest_rewards) == env_max_reward)
avg_return = np.mean(episode_returns)
summary_str = f"\nSuccess rate: {success_rate}\nAverage return: {avg_return}\n\n"
for r in range(env_max_reward + 1):
more_or_equal_r = (np.array(highest_rewards) >= r).sum()
more_or_equal_r_rate = more_or_equal_r / num_rollouts
summary_str += f"Reward >= {r}: {more_or_equal_r}/{num_rollouts} = {more_or_equal_r_rate*100}%\n"
print(summary_str)
# save success rate to txt
result_file_name = "result_" + ckpt_name.split(".")[0] + ".txt"
with open(os.path.join(ckpt_dir, result_file_name), "w") as f:
f.write(summary_str)
f.write(repr(episode_returns))
f.write("\n\n")
f.write(repr(highest_rewards))
return success_rate, avg_return这个函数用于评估一个行为克隆(behavior cloning)模型。它接受以下参数:
config:配置信息,包含了模型、训练参数等。ckpt_name:要加载的模型权重的文件名。save_episode:一个布尔值,表示是否要保存评估过程中的图像数据。
函数的主要步骤如下:
-
加载行为克隆模型的权重文件,根据配置信息初始化模型,并将模型移动到GPU上。
-
加载数据集统计信息,用于对观测数据进行归一化和反归一化。
-
根据配置信息创建模拟环境或真实机器人环境。
-
设置评估的循环次数(
num_rollouts),每次循环都会进行一次评估。 -
在每次循环中,初始化环境,执行模型生成的动作并观测环境的响应。
-
将每个时间步的观测数据(包括图像、关节位置等)存储在相应的列表中。
-
计算每次评估的总回报,以及每次评估的最高回报,并记录成功率。
-
如果指定了保存评估过程中的图像数据,将每次评估的图像数据保存为视频。
-
输出评估结果,包括成功率、平均回报以及回报分布。
-
将评估结果保存到文本文件中。
最终,函数返回成功率和平均回报。这些结果可以用于评估模型的性能。
def forward_pass(data, policy):
image_data, qpos_data, action_data, is_pad = data
image_data, qpos_data, action_data, is_pad = (
image_data.cuda(),
qpos_data.cuda(),
action_data.cuda(),
is_pad.cuda(),
)
return policy(qpos_data, image_data, action_data, is_pad) # TODO remove None这个函数用于执行前向传播(forward pass)操作,以生成模型的输出。它接受以下参数:
data:包含输入数据的元组,其中包括图像数据、关节位置数据、动作数据以及填充标志。policy:行为克隆模型。
函数的主要步骤如下:
-
将输入数据转移到GPU上,以便在GPU上进行计算。
-
调用行为克隆模型的前向传播方法(
policy),将关节位置数据、图像数据、动作数据和填充标志传递给模型。 -
返回模型的输出,这可能是模型对动作数据的预测结果。
在这里,需要注意的是,在调用模型的前向传播方法时,传递了四个参数:qpos_data、image_data、action_data 和 is_pad。
def train_bc(train_dataloader, val_dataloader, config):
num_epochs = config["num_epochs"]
ckpt_dir = config["ckpt_dir"]
seed = config["seed"]
policy_class = config["policy_class"]
policy_config = config["policy_config"]
set_seed(seed)
policy = make_policy(policy_class, policy_config)
# if ckpt_dir is not empty, prompt the user to load the checkpoint
if os.path.isdir(ckpt_dir) and len(os.listdir(ckpt_dir)) > 1:
print(f"Checkpoint directory {ckpt_dir} is not empty. Load checkpoint? (y/n)")
load_ckpt = input()
if load_ckpt == "y":
# load the latest checkpoint
latest_idx = max(
[
int(f.split("_")[2])
for f in os.listdir(ckpt_dir)
if f.startswith("policy_epoch_")
]
)
ckpt_path = os.path.join(
ckpt_dir, f"policy_epoch_{latest_idx}_seed_{seed}.ckpt"
)
print(f"Loading checkpoint from {ckpt_path}")
loading_status = policy.load_state_dict(torch.load(ckpt_path))
print(loading_status)
else:
print("Not loading checkpoint")
latest_idx = 0
else:
latest_idx = 0
policy.cuda()
optimizer = make_optimizer(policy_class, policy)
train_history = []
validation_history = []
min_val_loss = np.inf
best_ckpt_info = None
for epoch in tqdm(range(latest_idx, num_epochs)):
print(f"\nEpoch {epoch}")
# validation
with torch.inference_mode():
policy.eval()
epoch_dicts = []
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(val_dataloader):
forward_dict = forward_pass(data, policy)
epoch_dicts.append(forward_dict)
epoch_summary = compute_dict_mean(epoch_dicts)
validation_history.append(epoch_summary)
epoch_val_loss = epoch_summary["loss"]
if epoch_val_loss < min_val_loss:
min_val_loss = epoch_val_loss
best_ckpt_info = (epoch, min_val_loss, deepcopy(policy.state_dict()))
print(f"Val loss: {epoch_val_loss:.5f}")
summary_string = ""
for k, v in epoch_summary.items():
summary_string += f"{k}: {v.item():.3f} "
print(summary_string)
# training
policy.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_dataloader):
forward_dict = forward_pass(data, policy)
# backward
loss = forward_dict["loss"]
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
train_history.append(detach_dict(forward_dict))
e = epoch - latest_idx
epoch_summary = compute_dict_mean(
train_history[(batch_idx + 1) * e : (batch_idx + 1) * (epoch + 1)]
)
epoch_train_loss = epoch_summary["loss"]
print(f"Train loss: {epoch_train_loss:.5f}")
summary_string = ""
for k, v in epoch_summary.items():
summary_string += f"{k}: {v.item():.3f} "
print(summary_string)
if epoch % 100 == 0:
ckpt_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"policy_epoch_{epoch}_seed_{seed}.ckpt")
torch.save(policy.state_dict(), ckpt_path)
plot_history(train_history, validation_history, epoch, ckpt_dir, seed)
ckpt_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"policy_last.ckpt")
torch.save(policy.state_dict(), ckpt_path)
best_epoch, min_val_loss, best_state_dict = best_ckpt_info
ckpt_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"policy_epoch_{best_epoch}_seed_{seed}.ckpt")
torch.save(best_state_dict, ckpt_path)
print(
f"Training finished:\nSeed {seed}, val loss {min_val_loss:.6f} at epoch {best_epoch}"
)
# save training curves
plot_history(train_history, validation_history, num_epochs, ckpt_dir, seed)
return best_ckpt_info这个函数用于训练行为克隆(Behavior Cloning)模型。它接受以下参数:
train_dataloader:训练数据的数据加载器,用于从训练集中获取批次的数据。val_dataloader:验证数据的数据加载器,用于从验证集中获取批次的数据。config:包含训练配置信息的字典。
函数的主要步骤如下:
-
初始化训练过程所需的各种参数和配置。
-
创建行为克隆模型,并根据是否存在之前的训练检查点来加载模型权重。
-
定义优化器,用于更新模型的权重。
-
进行训练循环,每个循环迭代一个 epoch,包括以下步骤:
- 验证:在验证集上计算模型的性能,并记录验证结果。如果当前模型的验证性能优于历史最佳模型,则保存当前模型的权重。
- 训练:在训练集上进行模型的训练,计算损失并执行反向传播来更新模型的权重。
- 每隔一定周期,保存当前模型的权重和绘制训练曲线图。
-
训练完成后,保存最佳模型的权重和绘制训练曲线图。
总体来说,这个函数负责管理模型的训练过程,包括训练循环、验证和模型参数的保存。训练过程中的损失、性能指标等信息都会被记录下来以供后续分析和可视化。
def plot_history(train_history, validation_history, num_epochs, ckpt_dir, seed):
# save training curves
for key in train_history[0]:
plot_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, f"train_val_{key}_seed_{seed}.png")
plt.figure()
train_values = [summary[key].item() for summary in train_history]
val_values = [summary[key].item() for summary in validation_history]
plt.plot(
np.linspace(0, num_epochs - 1, len(train_history)),
train_values,
label="train",
)
plt.plot(
np.linspace(0, num_epochs - 1, len(validation_history)),
val_values,
label="validation",
)
# plt.ylim([-0.1, 1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.legend()
plt.title(key)
plt.savefig(plot_path)
print(f"Saved plots to {ckpt_dir}")这个函数用于绘制训练过程中的损失曲线以及其他指标的曲线。它接受以下参数:
train_history:包含训练过程中损失和其他指标的历史记录。validation_history:包含验证过程中损失和其他指标的历史记录。num_epochs:总的训练周期数。ckpt_dir:检查点文件的保存目录。seed:用于随机种子的值。
该函数的主要功能是遍历 train_history 和 validation_history 中的指标,并为每个指标创建一个绘图,其中包括训练集和验证集的曲线。具体步骤如下:
-
对于每个指标(如损失、准确率等),创建一个绘图并设置其标题。
-
从
train_history和validation_history中提取相应指标的值,并分别绘制训练集和验证集的曲线。 -
将绘图保存到指定的文件路径(使用随机种子和指标名称命名文件)。
-
最后,输出已保存绘图的信息。
这个函数的作用是帮助可视化训练过程中的指标变化,以便更好地理解模型的训练效果。
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--eval", action="store_true")
parser.add_argument("--onscreen_render", action="store_true")
parser.add_argument(
"--ckpt_dir", action="store", type=str, help="ckpt_dir", required=True
)
parser.add_argument(
"--policy_class",
action="store",
type=str,
help="policy_class, capitalize",
required=True,
)
parser.add_argument(
"--task_name", action="store", type=str, help="task_name", required=True
)
parser.add_argument(
"--batch_size", action="store", type=int, help="batch_size", required=True
)
parser.add_argument("--seed", action="store", type=int, help="seed", required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--num_epochs", action="store", type=int, help="num_epochs", required=True
)
parser.add_argument("--lr", action="store", type=float, help="lr", required=True)
# for ACT
parser.add_argument(
"--kl_weight", action="store", type=int, help="KL Weight", required=False
)
parser.add_argument(
"--chunk_size", action="store", type=int, help="chunk_size", required=False
)
parser.add_argument(
"--hidden_dim", action="store", type=int, help="hidden_dim", required=False
)
parser.add_argument(
"--dim_feedforward",
action="store",
type=int,
help="dim_feedforward",
required=False,
)
parser.add_argument("--temporal_agg", action="store_true")
# for waypoints
parser.add_argument("--use_waypoint", action="store_true")
parser.add_argument(
"--constant_waypoint",
action="store",
type=int,
help="constant_waypoint",
required=False,
)
main(vars(parser.parse_args()))这段代码是一个入口点,用于执行训练和评估操作。它首先解析命令行参数,然后根据这些参数执行不同的操作。以下是每个参数的简要说明:
--eval:是否执行评估操作(可选参数)。--onscreen_render:是否进行屏幕渲染(可选参数)。--ckpt_dir:检查点文件的保存目录(必需参数)。--policy_class:策略类别,首字母大写(必需参数)。--task_name:任务名称(必需参数)。--batch_size:批处理大小(必需参数)。--seed:随机种子(必需参数)。--num_epochs:训练周期数(必需参数)。--lr:学习率(必需参数)。
接下来是一些与特定策略(如ACT策略)和路点(waypoints)相关的可选参数,以及一些用于控制训练过程的参数。最后,它调用了 main 函数,并传递解析后的参数作为参数。根据参数的不同组合,代码将执行训练或评估操作,具体操作由 main 函数中的逻辑决定。




![Electron[4] Electron最简单的打包实践](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1af744d223624f0faac86a65b536ef9f.png)