📫作者简介:zhz小白
公众号:小白的Java进阶之路
专业技能:
1、Java基础,并精通多线程的开发,熟悉JVM原理
2、熟悉Java基础,并精通多线程的开发,熟悉JVM原理,具备⼀定的线上调优经验
3、熟悉MySQL数据库调优,索引原理等,⽇志原理等,并且有出过⼀篇专栏
4、了解计算机⽹络,对TCP协议,滑动窗⼝原理等有⼀定了解
5、熟悉Spring,Spring MVC,Mybatis,阅读过部分Spring源码
6、熟悉SpringCloud Alibaba体系,阅读过Nacos,Sentinel,Seata,Dubbo,Feign,Gateway核⼼源码与设计,⼆次开发能⼒
7、熟悉消息队列(Kafka,RocketMQ)的原理与设计
8、熟悉分库分表ShardingSphere,具有真实⽣产的数据迁移经验
9、熟悉分布式缓存中间件Redis,对其的核⼼数据结构,部署架构,⾼并发问题解决⽅案有⼀定的积累
10、熟悉常⽤设计模式,并运⽤于实践⼯作中
11、了解ElasticSearch,对其核⼼的原理有⼀定的了解
12、了解K8s,Jekins,GitLab
13、了解VUE,GO
14、⽬前有正在利⽤闲暇时间做互游游戏,开发、运维、运营、推销等
本人著作git项目:https://gitee.com/zhouzhz/star-jersey-platform,有兴趣的可以私聊博主一起编写,或者给颗star
领域:对支付(FMS,FUND,PAY),订单(OMS),出行行业等有相关的开发领域
🔥如果此文还不错的话,还请👍关注、点赞、收藏三连支持👍一下博主~
文章目录
- 使用XML文件配置包扫描
- BookDao
- BookService
- BookController
- 使用注解配置包扫描(常用)
- 关于@ComponentScan注解的源码解析
- 扫描时排除注解标注的类(excludeFilters)
- 扫描时只包含注解标注的类(includeFilters)
- 重复注解(@Repeatable)
- java8之后
- Java8之前
- 总结
在实际项目中,我们更多的是使用Spring的包扫描功能对项目中的包进行扫描,凡是在指定的包或其子包中的类上标注了**@Repository、@Service、@Controller、@Component**注解的类都会被扫描到,并将这个类注入到Spring容器中。
Spring包扫描功能可以使用XML配置文件进行配置,也可以直接使用**@ComponentScan**注解进行设置,使用@ComponentScan注解进行设置比使用XML配置文件来配置要简单的多。
使用XML文件配置包扫描
我们可以在Spring的XML配置文件中配置包的扫描,在配置包扫描时,需要在Spring的XML配置文件中的beans节点中引入context标签,如下所示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描:只要是标注了我们熟悉的@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component这四个注解中的任何一个的组件,它就会被自动扫描,并加进容器中 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhz"/>
<!-- 注册组件 -->
<bean id="person" class="com.zhz.bean.Person">
<property name="age" value="18"/>
<property name="name" value="zhz"/>
</bean>
</beans>
这样配置以后,只要在com.zhz包下,或者com.zhz的子包下标注了**@Repository、@Service、@Controller、@Component注解的类都会被扫描到,并自动注入到Spring容器中。
此时,我们分别创建BookDao、BookService以及BookController这三个类,并在这三个类中分别添加@Repository、@Service、@Controller**注解,如下所示。
BookDao
package com.zhz.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:56
* @since v1
*/
@Repository
public class BookDao {
}
BookService
package com.zhz.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:56
* @since v1
*/
@Service
public class BookService {
}
BookController
package com.zhz.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:57
* @since v1
*/
@Controller
public class BookController {
}
我们写一个测试类,在src/test/java/com/zhz/test下,建立一个IOCTest测试类
package com.zhz.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:58
* @since v1
*/
public class IOCTest {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
@Test
public void test() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-bean.xml");
// 我们现在就来看一下IOC容器中有哪些bean,即容器中所有bean定义的名字
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
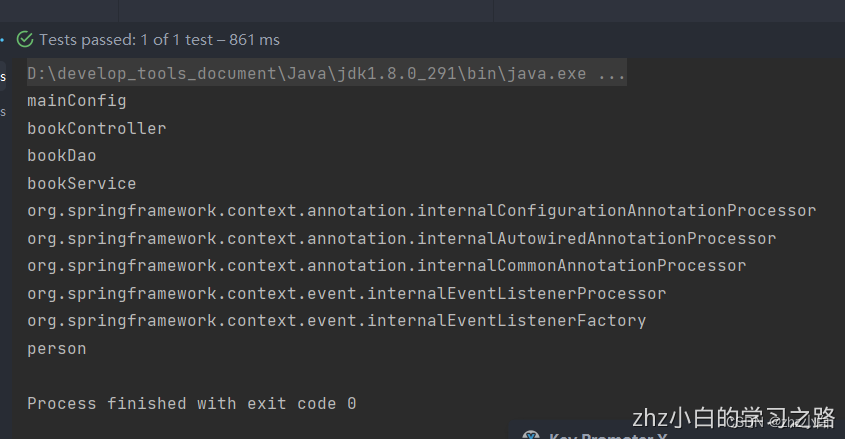
我们可以清晰的发现,扫到的包中包含我们写的bean
使用注解配置包扫描(常用)
我们只需要在MainConfig中添加
package com.zhz.config;
import com.zhz.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:27
* @since v1
*/
@ComponentScan("com.zhz")
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
/**
* @Bean注解是给IOC容器中注册一个bean,类型自然就是返回值的类型,id默认是用方法名作为id
*/
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("zhz", 20);
}
}
然后我们改造一下IOCTest
package com.zhz.test;
import com.zhz.config.MainConfig;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:58
* @since v1
*/
public class IOCTest {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
@Test
public void test() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
// 我们现在就来看一下IOC容器中有哪些bean,即容器中所有bean定义的名字
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
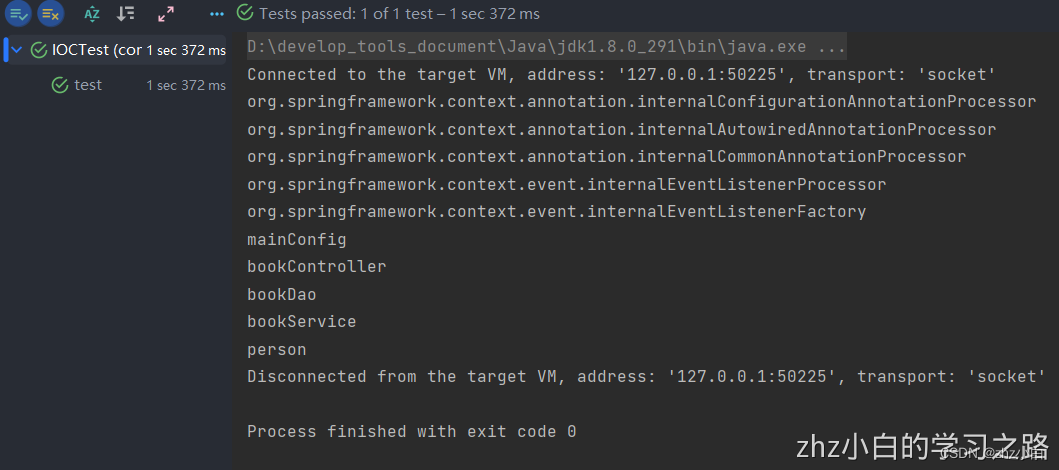
我们就会发现他跟XML文件配置方法的输出结果是一样的
关于@ComponentScan注解的源码解析
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class;
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT;
String resourcePattern() default "**/*.class";
boolean useDefaultFilters() default true;
Filter[] includeFilters() default {};
Filter[] excludeFilters() default {};
boolean lazyInit() default false;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Filter {
FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION;
@AliasFor("classes")
Class<?>[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
Class<?>[] classes() default {};
String[] pattern() default {};
}
}
我们可以发现他又两个比较核心的方法:
- Filter[] includeFilters() default {}:方法指定Spring扫描的时候按照什么规则只需要包含哪些组件
- Filter[] excludeFilters() default {}:指定Spring扫描的时候按照什么规则排除哪些组件
扫描时排除注解标注的类(excludeFilters)
假设我们要排除@Controller包下的Bean,那么我们要怎么实现呢?
我们只需要在MainConfig类中添加如下
package com.zhz.config;
import com.zhz.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:27
* @since v1
*/
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.zhz"},excludeFilters = {
/*
* type:指定你要排除的规则,是按照注解进行排除,还是按照给定的类型进行排除,还是按照正则表达式进行排除,等等
* classes:除了@Controller标注的组件之外,IOC容器中剩下的组件我都要,即相当于是我要排除@Controller这俩注解标注的组件。
*/
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
})
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
/**
* @Bean注解是给IOC容器中注册一个bean,类型自然就是返回值的类型,id默认是用方法名作为id
*/
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("zhz", 20);
}
}
我们可以观察到运行结果中并没有@Controller注释修饰的Bean
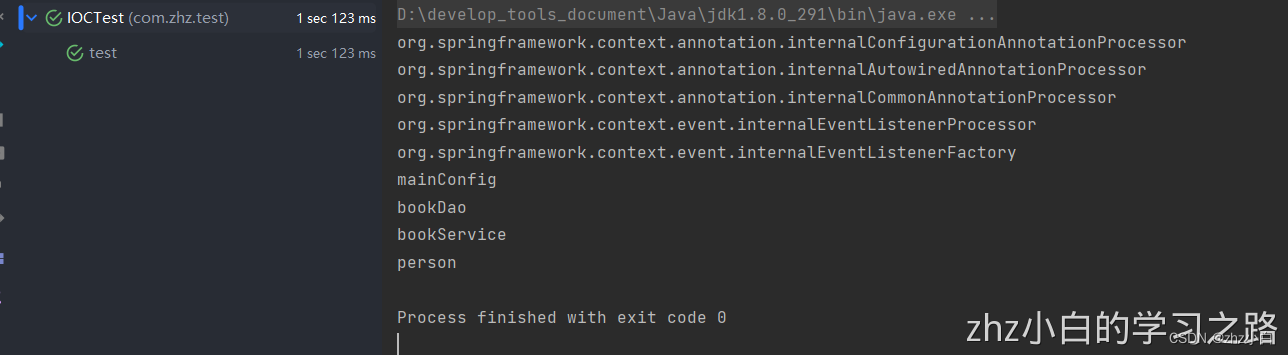
扫描时只包含注解标注的类(includeFilters)
跟上面哪个相反,代表只会扫描注解下的包,其他不会扫描,如下,我们只要@Controller修饰的包
package com.zhz.config;
import com.zhz.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:27
* @since v1
*/
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.zhz"},includeFilters = {
/*
* type:指定你要排除的规则,是按照注解进行排除,还是按照给定的类型进行排除,还是按照正则表达式进行排除,等等
* classes:除了@Controller标注的组件之外,IOC容器中剩下的组件我都不要,即相当于是我要排除@Controller注解以外的标注的组件。
*/
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
/**
* @Bean注解是给IOC容器中注册一个bean,类型自然就是返回值的类型,id默认是用方法名作为id
*/
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("zhz", 20);
}
}
我们可以发现运行结果中是没有**@Repository、@Service**注解修饰的Bean,具体演示效果如下:
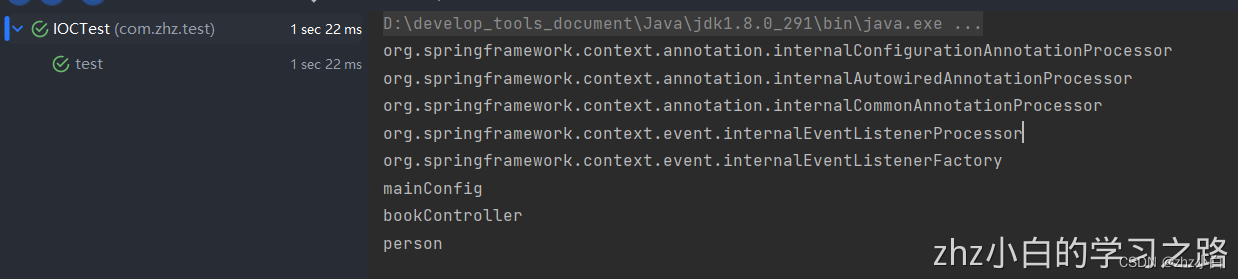
重复注解(@Repeatable)
java8之后
我们发现@ComponentScan注解下面是有这样的一个注解的:@Repeatable
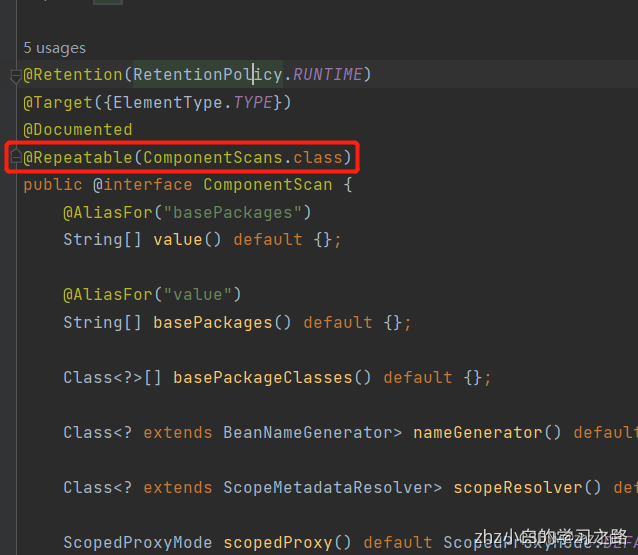
然后我们可以进入他括号里面的类ComponentScans,可以发现他是一个数组注解,因此我们可知@Repeatable代表重复注解,也就是说我们可以在一个类上重复使用这个注解
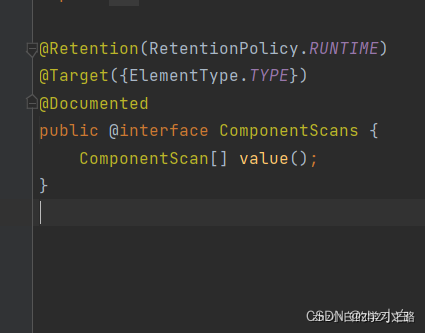
让我们来演示一下具体的demo
package com.zhz.config;
import com.zhz.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:27
* @since v1
*/
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.zhz"},includeFilters = {
/*
* type:指定你要排除的规则,是按照注解进行排除,还是按照给定的类型进行排除,还是按照正则表达式进行排除,等等
* classes:除了@Controller标注的组件之外,IOC容器中剩下的组件我都不要,即相当于是我要排除@Controller注解以外的标注的组件。
*/
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.zhz"},includeFilters = {
/*
* type:指定你要排除的规则,是按照注解进行排除,还是按照给定的类型进行排除,还是按照正则表达式进行排除,等等
* classes:除了@Service标注的组件之外,IOC容器中剩下的组件我都不要,即相当于是我要排除@Service注解以外的标注的组件。
*/
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Service.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
/**
* @Bean注解是给IOC容器中注册一个bean,类型自然就是返回值的类型,id默认是用方法名作为id
*/
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("zhz", 20);
}
}
从下图运行效果中,我们可以发现他是两个@ComponentScan注解都生效了。
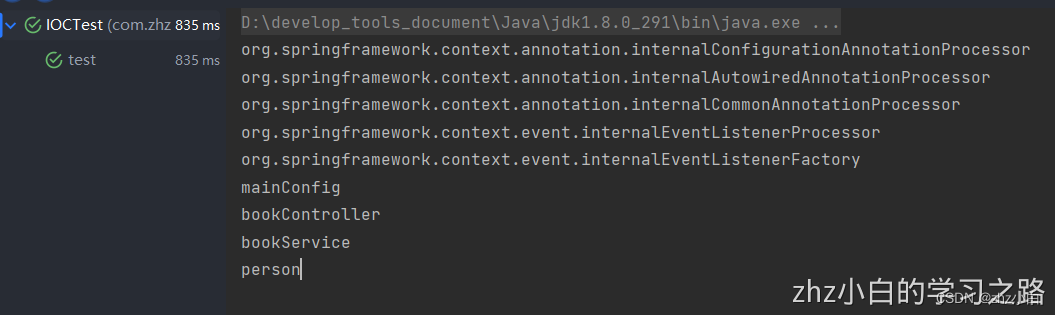
Java8之前
如果是Java8之前,我们要实现上面那种方式,需要改成如下
package com.zhz.config;
import com.zhz.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author zhouhengzhe
* @description: todo
* @date 2022/11/4 10:27
* @since v1
*/
@ComponentScans({
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.zhz"},includeFilters = {
/*
* type:指定你要排除的规则,是按照注解进行排除,还是按照给定的类型进行排除,还是按照正则表达式进行排除,等等
* classes:除了@Controller标注的组件之外,IOC容器中剩下的组件我都要,即相当于是我要排除@Controller和@Service这俩注解标注的组件。
*/
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false),
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.zhz"},includeFilters = {
/*
* type:指定你要排除的规则,是按照注解进行排除,还是按照给定的类型进行排除,还是按照正则表达式进行排除,等等
* classes:除了@Controller标注的组件之外,IOC容器中剩下的组件我都要,即相当于是我要排除@Controller和@Service这俩注解标注的组件。
*/
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Service.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
})
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
/**
* @Bean注解是给IOC容器中注册一个bean,类型自然就是返回值的类型,id默认是用方法名作为id
*/
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("zhz", 20);
}
}
从下面演示效果上可以发现是跟Java8之后实现上是一样的
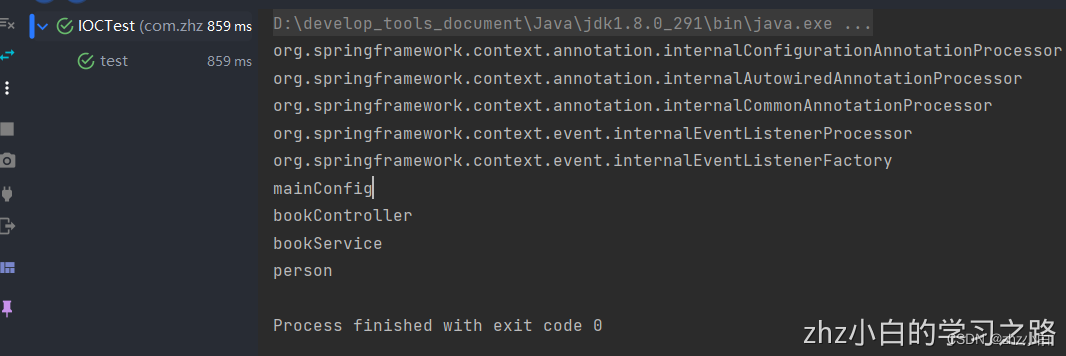
总结
我们可以使用@ComponentScan注解来指定Spring扫描哪些包,可以使用excludeFilters()方法来指定扫描时排除哪些组件,也可以使用includeFilters()方法来指定扫描时只包含哪些组件。当使用includeFilters()方法指定只包含哪些组件时,需要禁用掉默认的过滤规则。